Abstract
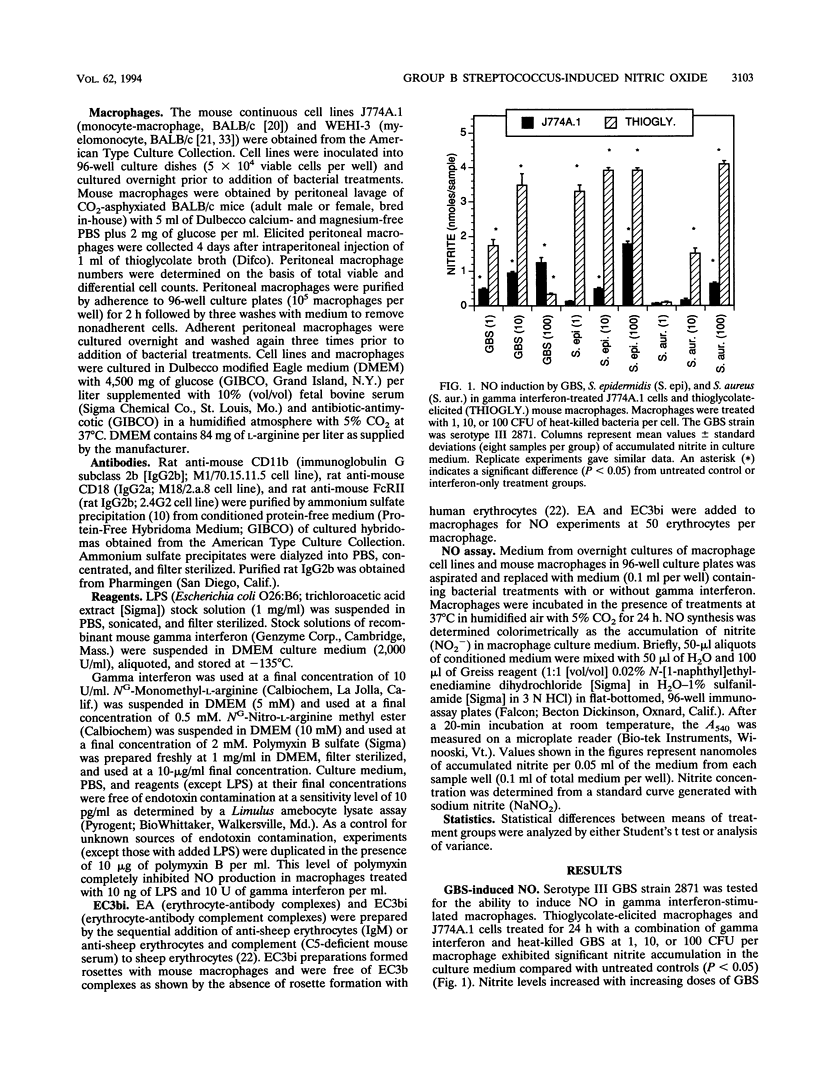
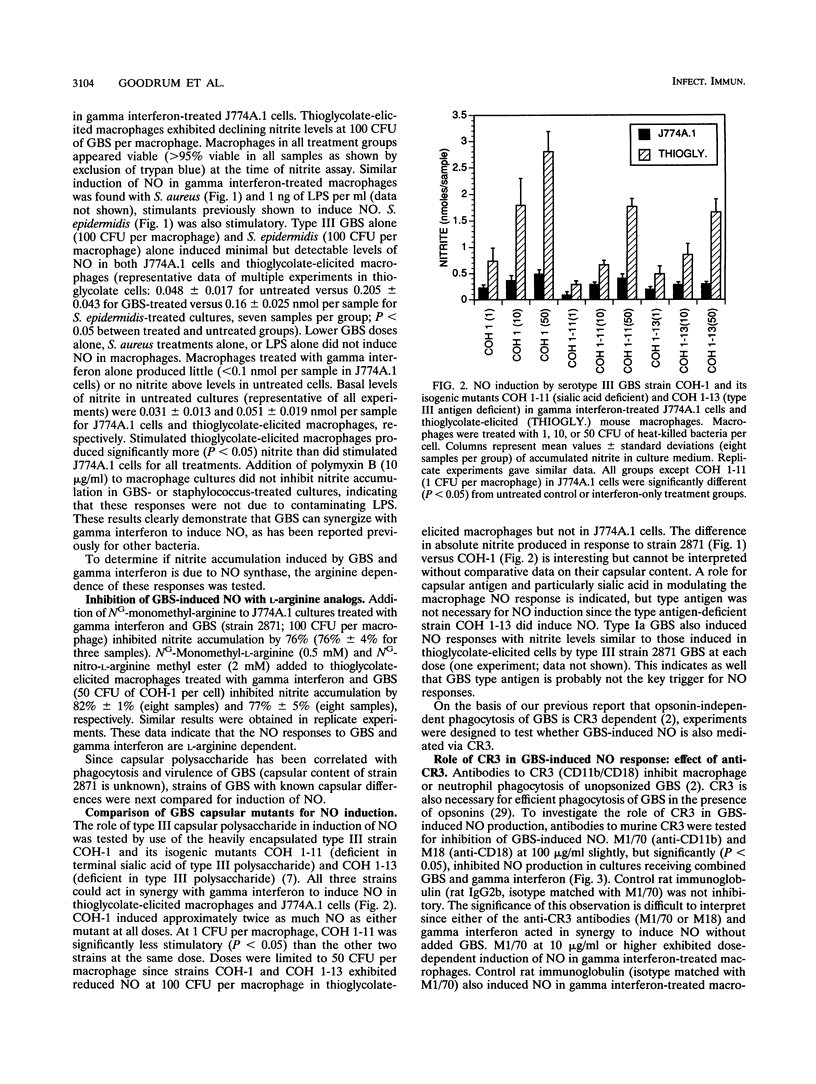
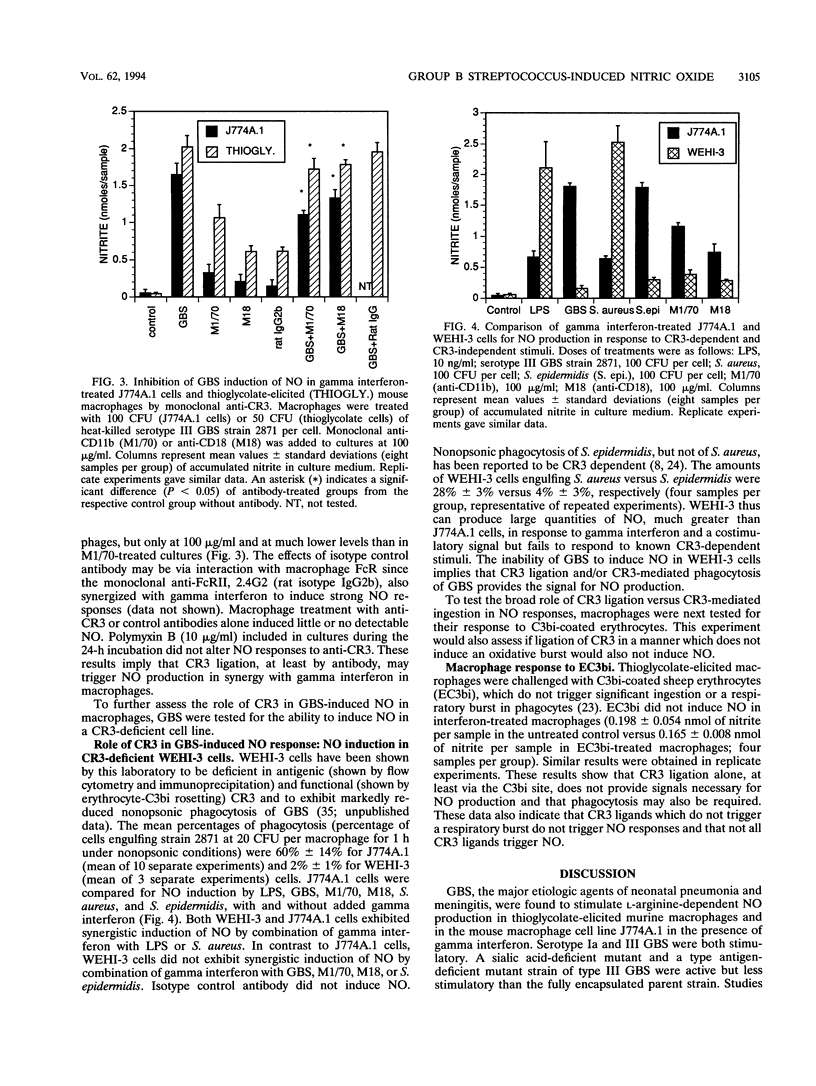
Nitric oxide (NO) is produced by murine macrophages in response to cytokines and/or gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide. NO induction by gram-positive bacteria such as group B streptococci (GBS), the major etiologic agents of neonatal pneumonia and meningitis, has received little study. GBS as well as two other gram-positive bacterial species, Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, were found to stimulate NO production in thioglycolate-elicited murine macrophages and in the mouse macrophage cell line J774A.1 in the presence of gamma interferon. Serotype Ia and III GBS were both stimulatory, as were asialo- and type antigen-deficient mutant strains of type III GBS. NO production was dose dependent, inhibitable by L-arginine analogs, and unaffected by polymyxin B. Since phagocytosis by murine and human phagocytes of GBS is dependent on complement receptor type 3 (CR3), the role of CR3 in the NO response to GBS was tested in the CR3-deficient myelomonocytic cell line WEHI-3. GBS did not induce NO, whereas S. aureus or lipopolysaccharide did induce NO in WEHI-3 cells. S. epidermidis, whose nonopsonic phagocytosis is also CR3 dependent, failed to induce NO in WEHI-3 cells. Monoclonal anti-CR3 (anti-CD11b or anti-CD18) in the presence of interferon also induced NO production in thioglycolate-elicited macrophages and in J774A.1 cells but not in WEHI-3 cells. This evidence suggests that ligated CR3 and gamma interferon act synergistically to induce NO production and that CR3 mediates the GBS-induced signal for NO production in interferon-treated macrophages.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Freeman K. L., Heerdt B., Hughes B. J., Jack R. M., Smith C. W. Abnormal stimulated adherence of neonatal granulocytes: impaired induction of surface Mac-1 by chemotactic factors or secretagogues. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):740–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antal J. M., Cunningham J. V., Goodrum K. J. Opsonin-independent phagocytosis of group B streptococci: role of complement receptor type three. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1114–1121. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1114-1121.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckerman K. P., Rogers H. W., Corbett J. A., Schreiber R. D., McDaniel M. L., Unanue E. R. Release of nitric oxide during the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation. Its role in resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):888–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Winter H. S., Gard S. E., Fischer T. J., Stiehm E. R. Deficiency of immune interferon production by leukocytes of normal newborns. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 15;55(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain J. A., Newman S. L., Ross G. D. Role of complement receptor type three and serum opsonins in the neutrophil response to yeast. Complement. 1987;4(2):75–86. doi: 10.1159/000463011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin S. B., Buchmüller-Rouiller Y., Mauël J. Phagocytosis enhances murine macrophage activation by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2553–2558. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. L., Lee M. K., Soderland C., Chi E. Y., Rubens C. E. Group B streptococci invade endothelial cells: type III capsular polysaccharide attenuates invasion. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):478–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.478-485.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. L., Rice J. L. Opsonin-dependent and independent surface phagocytosis of S. aureus proceeds independently of complement and complement receptors. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):709–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Specific amino acid (L-arginine) requirement for the microbiostatic activity of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1172/JCI113427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Augustine N. H., Jaffe H. S. Human recombinant interferon gamma enhances neonatal polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation and movement, and increases free intracellular calcium. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):767–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremsner P. G., Nüssler A., Neifer S., Chaves M. F., Bienzle U., Senaldi G., Grau G. E. Malaria antigen and cytokine-induced production of reactive nitrogen intermediates by murine macrophages: no relevance to the development of experimental cerebral malaria. Immunology. 1993 Feb;78(2):286–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langermans J. A., Van der Hulst M. E., Nibbering P. H., Hiemstra P. S., Fransen L., Van Furth R. IFN-gamma-induced L-arginine-dependent toxoplasmastatic activity in murine peritoneal macrophages is mediated by endogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):568–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Montgomery R. R., van Blaricom G. Evidence for reactive nitrogen intermediates in killing of staphylococci by human neutrophil cytoplasts. A new microbicidal pathway for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):631–636. doi: 10.1172/JCI115903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques M. B., Kasper D. L., Pangburn M. K., Wessels M. R. Prevention of C3 deposition by capsular polysaccharide is a virulence mechanism of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3986–3993. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3986-3993.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Ruzinski J. T., Rubens C. E., Chi E. Y., Wilson C. B. The effect of type-specific polysaccharide capsule on the clearance of group B streptococci from the lungs of infant and adult rats. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):306–314. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Srimal S., Farber C., Sanchez E., Kabbash L., Asch A., Gailit J., Wright S. D. Cytokine-induced respiratory burst of human neutrophils: dependence on extracellular matrix proteins and CD11/CD18 integrins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1341–1349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussler A. K., Billiar T. R. Inflammation, immunoregulation, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Aug;54(2):171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald I. P., Wynn T. A., Sher A., James S. L. Interleukin 10 inhibits macrophage microbicidal activity by blocking the endogenous production of tumor necrosis factor alpha required as a costimulatory factor for interferon gamma-induced activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8676–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Moore M. A., Nilsson K. Lysozyme synthesis by established human and murine histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1528–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Direct toxic effects of immunopotentiators on monocytic, myelomonocytic, and histiocytic or macrophage tumor cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):546–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Membrane complement receptor type three (CR3) has lectin-like properties analogous to bovine conglutinin as functions as a receptor for zymosan and rabbit erythrocytes as well as a receptor for iC3b. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3307–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Thompson R. A., Walport M. J., Springer T. A., Watson J. V., Ward R. H., Lida J., Newman S. L., Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. Characterization of patients with an increased susceptibility to bacterial infections and a genetic deficiency of leukocyte membrane complement receptor type 3 and the related membrane antigen LFA-1. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):882–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneemann M., Schoedon G., Hofer S., Blau N., Guerrero L., Schaffner A. Nitric oxide synthase is not a constituent of the antimicrobial armature of human mononuclear phagocytes. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1358–1363. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Li H. Q., Shen C. K., Wang J. H., Qin S. W., Liu R., Pan J. Plasma nitric oxide levels in newborn infants with sepsis. J Pediatr. 1993 Sep;123(3):435–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81753-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan A. R., Pistole T. G. Characterization of the murine macrophage receptor for group B streptococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Jun;278(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80825-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Baker C. J., Anderson D. C., Edwards M. S. Role of complement receptors in opsonophagocytosis of group B streptococci by adult and neonatal neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):489–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summersgill J. T., Powell L. A., Buster B. L., Miller R. D., Ramirez J. A. Killing of Legionella pneumophila by nitric oxide in gamma-interferon-activated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Dec;52(6):625–629. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.6.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti G., Mancuso G., Tomasello F. Cytokine appearance and effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibodies in a neonatal rat model of group B streptococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.227-235.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J. Recognition of bacterial endotoxins by receptor-dependent mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1993;53:267–289. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60502-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Bohnsack J. F., Augustine N. H., Drummond W. K., Rubens C. E., Hill H. R. Production of tumor necrosis factor by human cells in vitro and in vivo, induced by group B streptococci. J Pediatr. 1993 Aug;123(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81706-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide-induced selective priming effects on tumor necrosis factor alpha and nitric oxide production in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):511–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., van Schadewijk-Nieuwstad M., Elzenga-Claasen I., Cornelisse C., Nibbering P. Morphological, cytochemical, functional, and proliferative characteristics of four murine macrophage-like cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1985 Feb;90(2):339–357. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



