Abstract
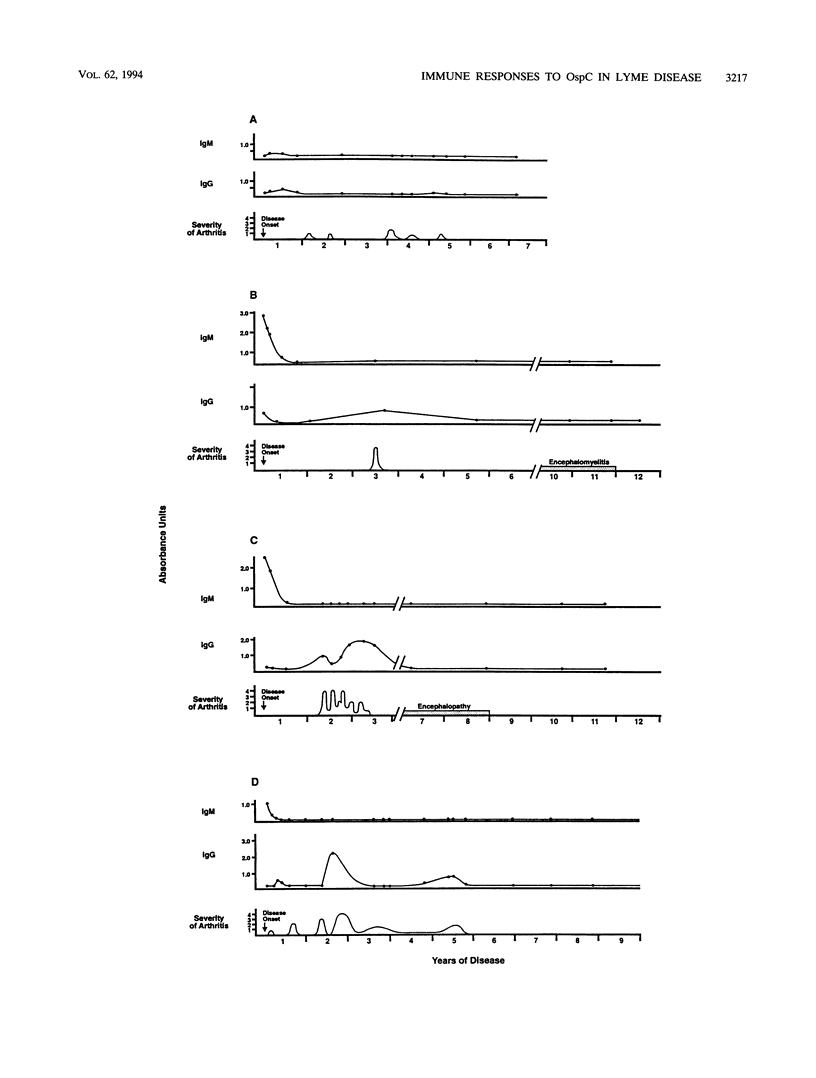
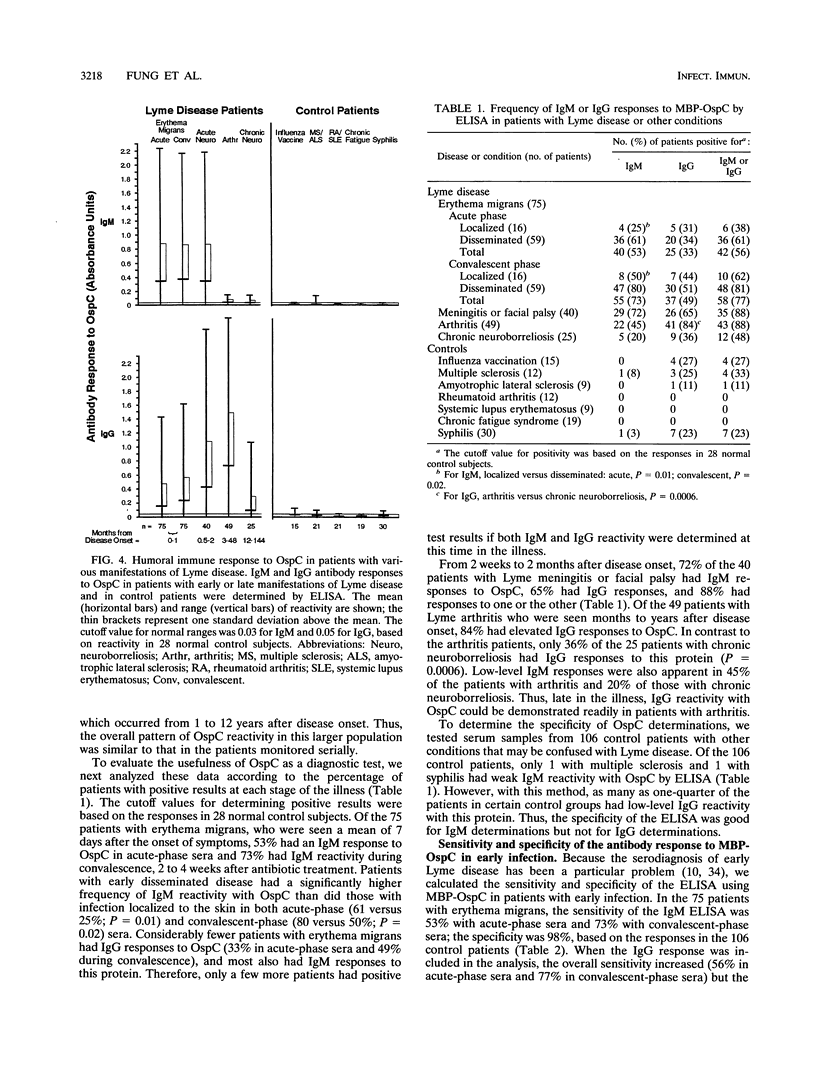
We determined the humoral immune response to outer surface protein C (OspC) of Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with early or late manifestations of Lyme disease and investigated the use of this antigen in the serodiagnosis of early infection. The ospC gene from the low-passage human isolate 297, a North American B. burgdorferi strain, was used to make a recombinant maltose-binding protein (MBP)-OspC fusion protein for serologic tests. This gene showed 84 to 85% nucleotide sequence identity and 76 to 79% amino acid identity with ospC of B. burgdorferi B31 and 2591. The antibody responses to MBP-OspC were determined in serial sera from 15 patients with Lyme disease who were monitored for 4 to 12 years of illness, in single-serum samples from 189 patients with early or late manifestations of the disorder, and in serum samples from 106 control patients. Early in the infection, patients with erythema migrans or meningitis commonly had weak to strong immunoglobulin M (IgM) responses to OspC and sometimes weak to moderate IgG responses. Months to years later, weak to strong IgG reactivity with this protein was often apparent in patients with arthritis, but this response was weak or absent in patients with chronic neuroborreliosis. When acute- and convalescent-phase serum samples from patients with erythema migrans were tested for reactivity against MBP-OspC, the sensitivity of the IgM test was 73% and the specificity was 98%, with either enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or Western blotting. We conclude that the majority of patients with Lyme disease have a prominent IgM response to OspC early in the illness, which is often followed by a prominent IgG response in patients with arthritis. For the serodiagnosis of early infection, the sensitivity and specificity of IgM ELISA and Western blotting were comparable or slightly improved when MBP-OspC was used as the antigen compared with tests in which spirochetal lysates were used.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken L. L., Case K. L., Callister S. M., Bourdeau N. J., Schell R. F. Performance of 45 laboratories participating in a proficiency testing program for Lyme disease serology. JAMA. 1992 Aug 19;268(7):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranton G., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C., Assous M., Grimont P. A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Fish D. The biological and social phenomenon of Lyme disease. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1610–1616. doi: 10.1126/science.8503006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canica M. M., Nato F., du Merle L., Mazie J. C., Baranton G., Postic D. Monoclonal antibodies for identification of Borrelia afzelii sp. nov. associated with late cutaneous manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1993;25(4):441–448. doi: 10.3109/00365549309008525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler F., Ackermann R., Steere A. C. Antibody responses to the three genomic groups of Borrelia burgdorferi in European Lyme borreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1994 Feb;169(2):313–318. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler F., Whalen J. A., Reinhardt B. N., Steere A. C. Western blotting in the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):392–400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Jauris S., Lottspeich F., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Soutschek E. Molecular analysis and expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi gene encoding a 22 kDa protein (pC) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg C. W., Osterholm M. T., MacDonald K. L., White K. E. An interlaboratory study of antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1325–1327. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauris-Heipke S., Fuchs R., Motz M., Preac-Mursic V., Schwab E., Soutschek E., Will G., Wilske B. Genetic heterogenity of the genes coding for the outer surface protein C (OspC) and the flagellin of Borrelia burgdorferi. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1993 Mar;182(1):37–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00195949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M., Noppa L., Barbour A. G., Bergström S. Heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins in Borrelia burgdorferi: comparison of osp operons of three isolates of different geographic origins. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1845–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1845-1853.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalish R. A., Leong J. M., Steere A. C. Association of treatment-resistant chronic Lyme arthritis with HLA-DR4 and antibody reactivity to OspA and OspB of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2774–2779. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2774-2779.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Fournier R. S., Isberg R. R. Mapping and topographic localization of epitopes of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3424–3433. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3424-3433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logigian E. L., Kaplan R. F., Steere A. C. Chronic neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 22;323(21):1438–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011223232102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Miller J. N., Anderson J. F., Riviere G. R. Cross-reactivity of nonspecific treponemal antibody in serologic tests for Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1276–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1276-1279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maina C. V., Riggs P. D., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Slatko B. E., Moran L. S., Tagliamonte J. A., McReynolds L. A., Guan C. D. An Escherichia coli vector to express and purify foreign proteins by fusion to and separation from maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Development of polymerase chain reaction primer sets for diagnosis of Lyme disease and for species-specific identification of Lyme disease isolates by 16S rRNA signature nucleotide analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2830–2834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2830-2834.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Samuels D. S., Garon C. F. Transcriptional analyses and mapping of the ospC gene in Lyme disease spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):926–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.926-932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Samuels D. S., Schwan T. G., Garon C. F. Identification of a protein in several Borrelia species which is related to OspC of the Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2577–2583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2577-2583.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massarotti E. M., Luger S. W., Rahn D. W., Messner R. P., Wong J. B., Johnson R. C., Steere A. C. Treatment of early Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1992 Apr;92(4):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90270-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachner A. R., Steere A. C. The triad of neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease: meningitis, cranial neuritis, and radiculoneuritis. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):47–53. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padula S. J., Sampieri A., Dias F., Szczepanski A., Ryan R. W. Molecular characterization and expression of p23 (OspC) from a North American strain of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5097–5105. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5097-5105.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Patsouris E., Jauris S., Will G., Soutschek E., Rainhardt S., Lehnert G., Klockmann U., Mehraein P. Active immunization with pC protein of Borrelia burgdorferi protects gerbils against B. burgdorferi infection. Infection. 1992 Nov-Dec;20(6):342–349. doi: 10.1007/BF01710681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Wilske B., Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. The cryptic ospC gene of Borrelia burgdorferi B31 is located on a circular plasmid. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2192–2195. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2192-2195.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Kime K. K., Schrumpf M. E., Coe J. E., Simpson W. J. Antibody response in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) experimentally infected with the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3445–3451. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3445-3451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H., Clover J. R., Wong J., Daugherty M., Struthers M., Rosa P. A. Distribution and molecular analysis of Lyme disease spirochetes, Borrelia burgdorferi, isolated from ticks throughout California. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Dec;31(12):3096–3108. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.12.3096-3108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha M., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Diagnosing early Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1985 Feb;78(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90432-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Schwan T. G. Reactivity of human Lyme borreliosis sera with a 39-kilodalton antigen specific to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1329–1337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1329-1337.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Levin R. E., Molloy P. J., Kalish R. A., Abraham J. H., 3rd, Liu N. Y., Schmid C. H. Treatment of Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jun;37(6):878–888. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Schoen R. T., Taylor E. The clinical evolution of Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):725–731. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Jauris S., Hofmann A., Pradel I., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Will G., Wanner G. Immunological and molecular polymorphisms of OspC, an immunodominant major outer surface protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2182–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2182-2191.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Busch K. V. Immunochemical and immunological analysis of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):92–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




