Abstract
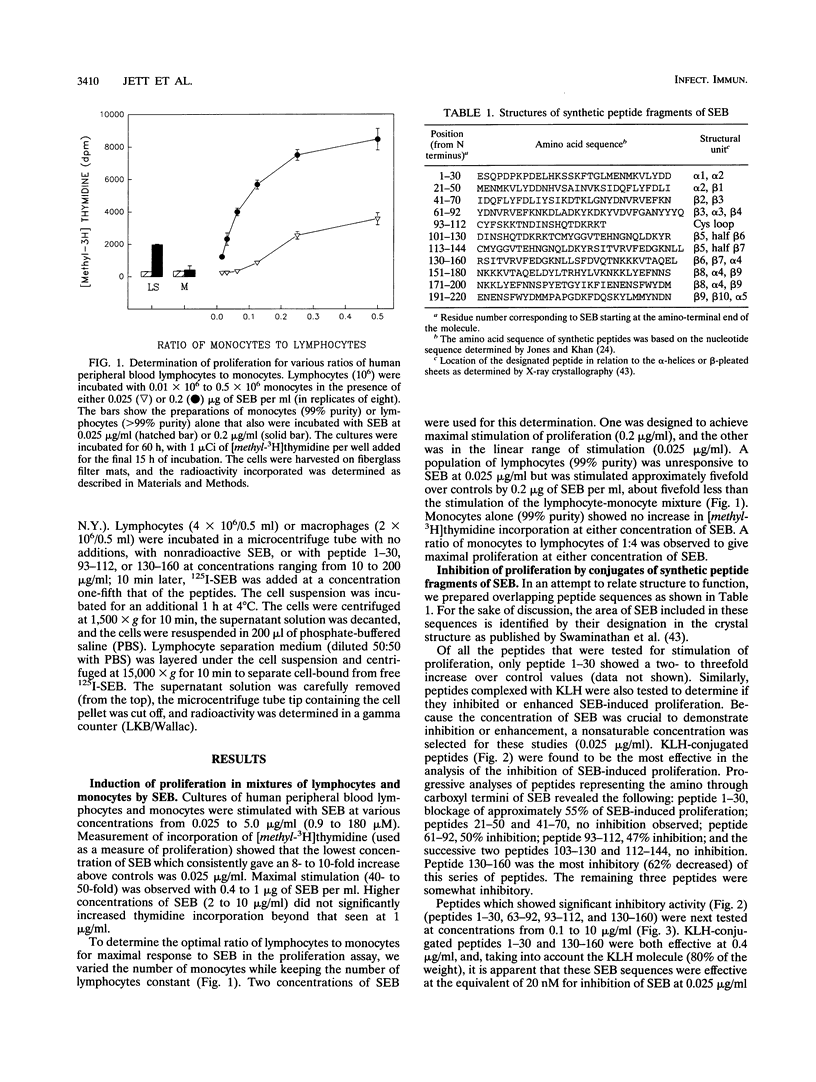
A series of 13 synthetic peptides, approximately 30 amino acids each, which spanned the entire sequence of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) were tested to evaluate their effects on T-cell proliferation in a culture system containing elutriated human peripheral blood lymphocytes incubated with a specific ratio of mononuclear cells. Four peptide regions were found to inhibit SEB-induced proliferation; they included sequences 1 to 30 (previously thought to be involved in major histocompatibility complex class II binding), 61 to 92 (sequences which relate to the T-cell receptor site), 93 to 112 (a linear sequence corresponding to the cysteine loop), and 130 to 160 (containing a highly conserved sequence, KKKVTAQEL). Antisera raised to this last peptide were capable of neutralizing SEB-induced proliferation. Antisera raised against the peptides which overlapped this sequence also were somewhat inhibitory. Neutralizing antisera were not produced from any other peptide sequence tested. To determine if any of these effects were nonspecific with regard to SEB-induced proliferation, the peptides were tested for inhibition of phorbol dibutyryl ester-induced proliferation, and only the sequence 93 to 112 (corresponding to the cysteinyl loop region) was consistently inhibitory (40%). Of the regions which displayed inhibition of SEB-induced proliferation, the peptide 130 to 160 inhibited binding of 125I-SEB to lymphocytes. These data suggest that the residues containing and surrounding the sequence KKKVTAQEL may be critical in the SEB-induced proliferation and may be useful for developing neutralizing antisera to SEB.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean A. G., Freiberg R. A., Andrade S., Menon S., Zlotnik A. Interleukin 10 protects mice against staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced lethal shock. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4937–4939. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4937-4939.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binek M., Newcomb J. R., Rogers C. M., Rogers T. J. Localisation of the mitogenic epitope of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Mar;36(3):156–163. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-3-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Handley J. P., Schlievert P. M. Biological and immunological properties of the carboxyl terminus of staphylococcal enterotoxin C1. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):23–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.23-28.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle T., Lancaster V., Hunt R., Gemski P., Jett M. Method for simultaneous isolation and quantitation of platelet activating factor and multiple arachidonate metabolites from small samples: analysis of effects of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B in mice. Anal Biochem. 1994 Feb 1;216(2):373–382. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunson K. W., Watson D. W. Pyrogenic specificity of streptococcal exotoxins, staphylococcal enterotoxin, and gram-negative endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.347-351.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buelow R., O'Hehir R. E., Schreifels R., Kummerehl T. J., Riley G., Lamb J. R. Localization of the immunologic activity in the superantigen Staphylococcal enterotoxin B using truncated recombinant fusion proteins. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. G., BORISON H. L. PYROGENIC EFFECT OF PURIFIED STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Nov;142:237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Jett M. Glycosphingolipids: the putative receptor for Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin-B in human kidney proximal tubular cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992 Jul 6;113(1):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00230882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Kotzin B., Herron L., Callahan J., Marrack P., Kappler J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs N. D., Pontzer C. H., Jarpe M. A., Johnson H. M. Mapping of multiple binding domains of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A for HLA. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2516–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman D., Cook R. G., Sparrow J. T., Mollick J. A., Rich R. R. Dissociation of the stimulatory activities of staphylococcal enterotoxins for T cells and monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman D., Lamphear J. G., Mollick J. A., Betley M. J., Rich R. R. Dual roles for class II major histocompatibility complex molecules in staphylococcal enterotoxin-induced cytokine production and in vivo toxicity. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5190–5196. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5190-5196.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. O., Grossman D., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Rich R. R., Betley M. J. Lack of complete correlation between emetic and T-cell-stimulatory activities of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3175–3183. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3175-3183.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. O., Hufnagle W. O., Betley M. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin type A internal deletion mutants: serological activity and induction of T-cell proliferation. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2059–2068. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2059-2068.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Herrmann T., Buell G., Lando P. A., Segrén S., Schrimsher J., MacDonald H. R., Sjögren H. O., Kalland T. A recombinant C-terminal fragment of staphylococcal enterotoxin A binds to human MHC class II products but does not activate T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4082–4085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. L., Jablonski L. M., Crum K. K., Hackett S. P., Chi Y. I., Stauffacher C. V., Stevens D. L., Bohach G. A. Predictions of T-cell receptor- and major histocompatibility complex-binding sites on staphylococcal enterotoxin C1. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3396–3407. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3396-3407.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson K. R., Robinson H., Fraser J. D. Two adjacent residues in staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E determine T cell receptor V beta specificity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):175–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagle W. O., Tremaine M. T., Betley M. J. The carboxyl-terminal region of staphylococcal enterotoxin type A is required for a fully active molecule. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2126-2134.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J. Genetic analysis of extracellular toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:375–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett M., Brinkley W., Neill R., Gemski P., Hunt R. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B challenge of monkeys: correlation of plasma levels of arachidonic acid cascade products with occurrence of illness. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3494–3499. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3494-3499.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Khan S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Herman A., Clements J., Marrack P. Mutations defining functional regions of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):387–396. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai N., Benedict S. H., Mills G. B., Gelfand E. W. Requirements for the simultaneous presence of phorbol esters and calcium ionophores in the expression of human T lymphocyte proliferation-related genes. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzroth B., Marx T., Linnig M., Fleischer B. Concomitant loss of conformation and superantigenic activity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B deletion mutant proteins. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2445–2452. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2445-2452.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollick J. A., McMasters R. L., Grossman D., Rich R. R. Localization of a site on bacterial superantigens that determines T cell receptor beta chain specificity. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):283–293. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J. Mediators in the pathogenesis of toxic shock syndrome: overview. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S263–S269. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontzer C. H., Russell J. K., Johnson H. M. Localization of an immune functional site on staphylococcal enterotoxin A using the synthetic peptide approach. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):280–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIYAMA H., MCKISSIC E. M., Jr, BERGDOLL M. S., HELLER B. ENHANCEMENT OF BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN LETHALITY BY STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN. J Infect Dis. 1964 Apr;114:111–118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.2.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Wagman J., Spero L., Dunnery D. A., Bergdoll M. S. Purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Role of superantigens in human disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):997–1002. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P. R., Trede N., Chatila T. A., Geha R. S. Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in monokine induction by the staphylococcal superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2237–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. G., Johnson H. M. The effect of staphylococcal enterotoxins on the primary in vitro immune response. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spero L., Morlock B. A. Biological activities of the peptides of staphylococcal enterotoxin C formed by limited tryptic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8787–8791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S., Furey W., Pletcher J., Sax M. Crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B, a superantigen. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):801–806. doi: 10.1038/359801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Leu 23 induction as an early marker of functional CD3/T cell antigen receptor triggering. Requirement for receptor cross-linking, prolonged elevation of intracellular [Ca++] and stimulation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1854–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. T cell activation via Leu-23 (CD69). J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1123–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Katona I. M., Wilder R. L., Winter C. C., Haraoui B., Scher I., Wahl S. M. Isolation of human mononuclear cell subsets by counterflow centrifugal elutriation (CCE). I. Characterization of B-lymphocyte-, T-lymphocyte-, and monocyte-enriched fractions by flow cytometric analysis. Cell Immunol. 1984 May;85(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90251-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Schlievert P. M., Gaber A. O., Kotb M. Localization of an immunologically functional region of the streptococcal superantigen pepsin-extracted fragment of type 5 M protein. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1419–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



