Abstract
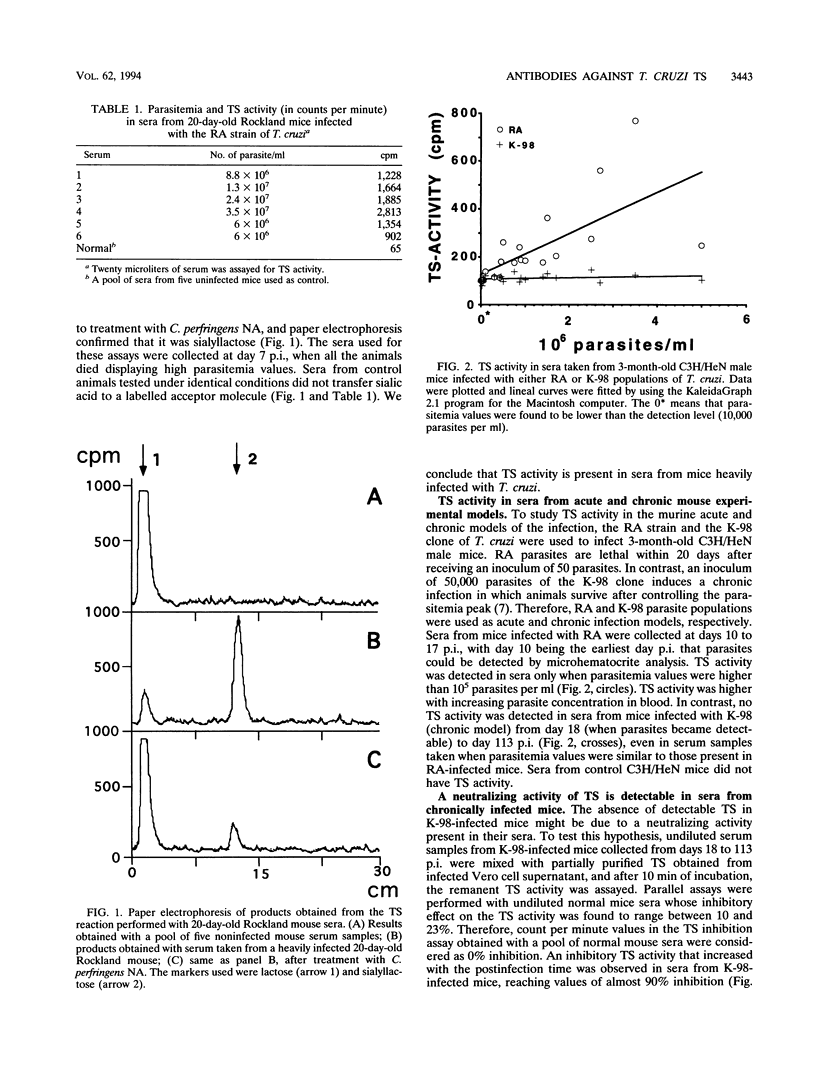
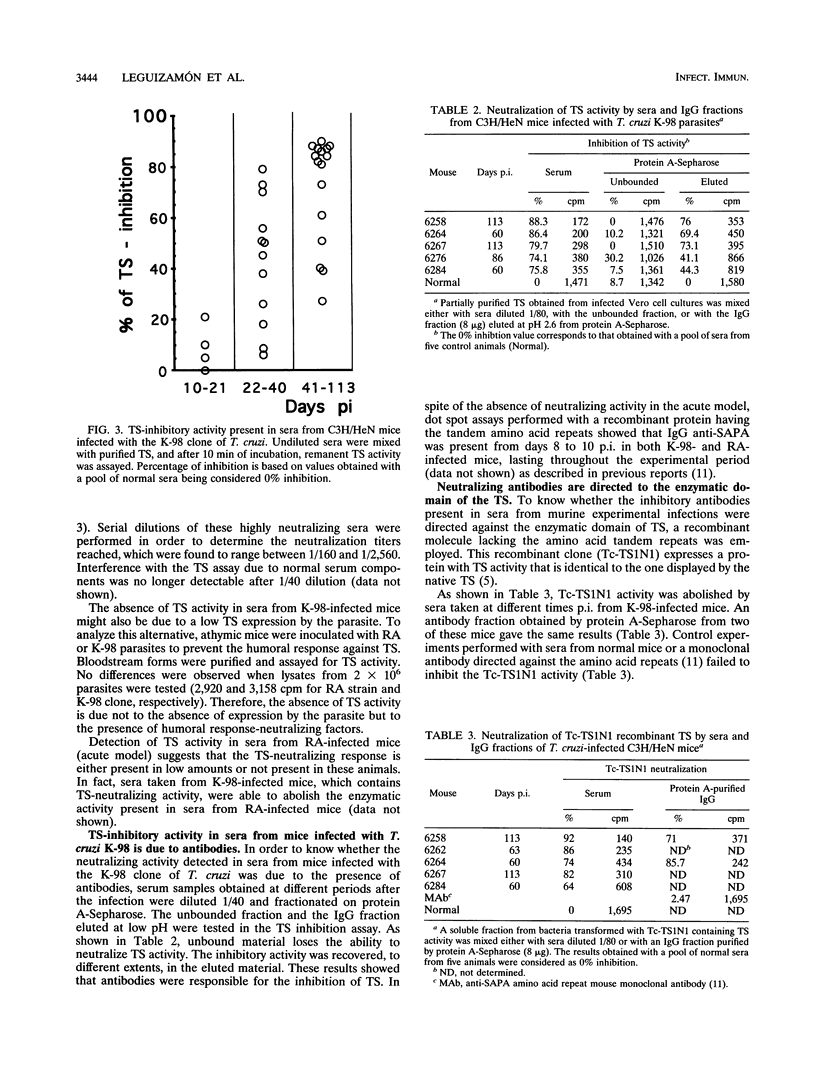
trans-Sialidase (TS) is an enzymatic activity described only for trypanosomes that is involved in the invasion of host cells by Trypanosoma cruzi. The enzyme that is shed by the parasite is made of two domains, the C-terminal region containing immunodominant amino acid repeats that define the SAPA antigen and the N-terminal domain that contains the putative region for enzymatic activity. The SAPA antigen induces a strong humoral response detected shortly after infection, both in humans and in mice. This response is directed to the immunodominant domain but is irrelevant in terms of neutralization of TS activity. We now show that TS activity can be detected in sera from acutely infected mice. However, mice infected with a T. cruzi strain whose growth can be controlled by the host did not have detectable levels of TS activity in sera. In fact, sera from these mice were able to abolish TS activity. This inhibition was due to the presence of specific antibodies directed against the enzymatic domain of the protein since they also abolish the activity of a recombinant molecule lacking the immunodominant amino acid repeats. The neutralizing antibodies were present from day 30 after the infection, while antibodies to the immunodominant repeats were detected by day 8 postinoculation, suggesting that the in vivo role of these repeats is to defect the humoral response to the repeat domain until the infection is established.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affranchino J. L., Ibañez C. F., Luquetti A. O., Rassi A., Reyes M. B., Macina R. A., Aslund L., Pettersson U., Frasch A. C. Identification of a Trypanosoma cruzi antigen that is shed during the acute phase of Chagas' disease. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 May 15;34(3):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Hong K. S., Robbins E. S., Nussenzweig V. Stage-specific surface antigens expressed during the morphogenesis of vertebrate forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Dec;64(3):474–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijovsky A. T., Elizari M. V., Muller L. A., Katzin V. J., González Cappa S. M. Chronic infection in mice with Trypanosoma cruzi. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1983 Sep-Oct;25(5):207–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campetella O. E., Uttaro A. D., Parodi A. J., Frasch A. C. A recombinant Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase lacking the amino acid repeats retains the enzymatic activity. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Apr;64(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)00036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campetella O., Sánchez D., Cazzulo J. J., Frasch A. C. A superfamily of Trypanosoma cruzi surface antigens. Parasitol Today. 1992 Nov;8(11):378–381. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Frasch A. C. SAPA/trans-sialidase and cruzipain: two antigens from Trypanosoma cruzi contain immunodominant but enzymatically inactive domains. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3259–3264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celentano A. M., González Cappa S. M. Induction of macrophage activation and opsonizing antibodies by Trypanosoma cruzi subpopulations. Parasite Immunol. 1992 Mar;14(2):155–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1992.tb00458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González Cappa S. M., Katzin A. M., Añasco N., Lajmanovich S. Comparative studies on infectivity and surface carbohydrates of several strains of Trypanosoma cruzi. Medicina (B Aires) 1981;41(5):549–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leguizamon M. S., Campetella O. E., Reyes M. B., Ibañez C. F., Basombrio M. A., Rincon J., Orn A., Frasch A. C. Bloodstream Trypanosoma cruzi parasites from mice simultaneously express antigens that are markers of acute and chronic human Chagas disease. Parasitology. 1991 Jun;102(Pt 3):379–385. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000064337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming M., Chuenkova M., Ortega-Barria E., Pereira M. E. Mediation of Trypanosoma cruzi invasion by sialic acid on the host cell and trans-sialidase on the trypanosome. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jun;59(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90222-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller L. A., Añasco N., González Cappa S. M. Trypanosoma cruzi: isolate dependence in the induction of lytic antibodies in the mouse and rabbit. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Jun;61(3):284–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller L. A., González Cappa S. M. Immunogenicity of Trypanosoma cruzi strains determined by neutralization test. Rev Argent Microbiol. 1987 Jul-Sep;19(3):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J., Pollevick G. D., Mautner M., Buschiazzo A., Sanchez D. O., Frasch A. C. Identification of the gene(s) coding for the trans-sialidase of Trypanosoma cruzi. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1705–1710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Mejia J. S., Ortega-Barria E., Matzilevich D., Prioli R. P. The Trypanosoma cruzi neuraminidase contains sequences similar to bacterial neuraminidases, YWTD repeats of the low density lipoprotein receptor, and type III modules of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):179–191. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras M. M., Henríquez D., Piras R. The effect of fetuin and other sialoglycoproteins on the in vitro penetration of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes into fibroblastic cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jan 15;22(2-3):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollevick G. D., Affranchino J. L., Frasch A. C., Sánchez D. O. The complete sequence of a shed acute-phase antigen of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Aug;47(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollevick G. D., Sanchez D. O., Campetella O., Trombetta S., Sousa M., Henriksson J., Hellman U., Pettersson U., Cazzulo J. J., Frasch A. C. Members of the SAPA/trans-sialidase protein family have identical N-terminal sequences and a putative signal peptide. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 May;59(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90018-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Andrade A. F., Pessolani M. C., Mendonça-Previato L. Incorporation of sialic acid into Trypanosoma cruzi macromolecules. A proposal for a new metabolic route. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jun;16(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prioli R. P., Ortega-Barria E., Mejia J. S., Pereira M. E. Mapping of a B-cell epitope present in the neuraminidase of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 May;52(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90038-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes M. B., Lorca M., Muñoz P., Frasch A. C. Fetal IgG specificities against Trypanosoma cruzi antigens in infected newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2846–2850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Diaz C., Nussenzweig V. Attachment of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes to receptors at restricted cell surface domains. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Jan;72(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90123-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Jiang M. S., Hart G. W., Nussenzweig V. A novel cell surface trans-sialidase of Trypanosoma cruzi generates a stage-specific epitope required for invasion of mammalian cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1117–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90008-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Kurosaki T., Ravetch J. V., Nussenzweig V. Evidence for the participation of the Ssp-3 antigen in the invasion of nonphagocytic mammalian cells by Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1635–1641. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souto-Padrón T., Reyes M. B., Leguizamon S., Campetella O. E., Frasch A. C., de Souza W. Trypanosoma cruzi proteins which are antigenic during human infections are located in defined regions of the parasite. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):272–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura H., Schenkman S., Nussenzweig V., Eichinger D. Only some members of a gene family in Trypanosoma cruzi encode proteins that express both trans-sialidase and neuraminidase activities. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3837–3844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingales B., Carniol C., de Lederkremer R. M., Colli W. Direct sialic acid transfer from a protein donor to glycolipids of trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Nov;26(1-2):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Titto E. H., Araujo F. G. Mechanism of cell invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi: importance of sialidase activity. Acta Trop. 1987 Sep;44(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Titto E. H., Araujo F. G. Serum neuraminidase activity and hematological alterations in acute human Chagas' disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jan;46(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



