Abstract
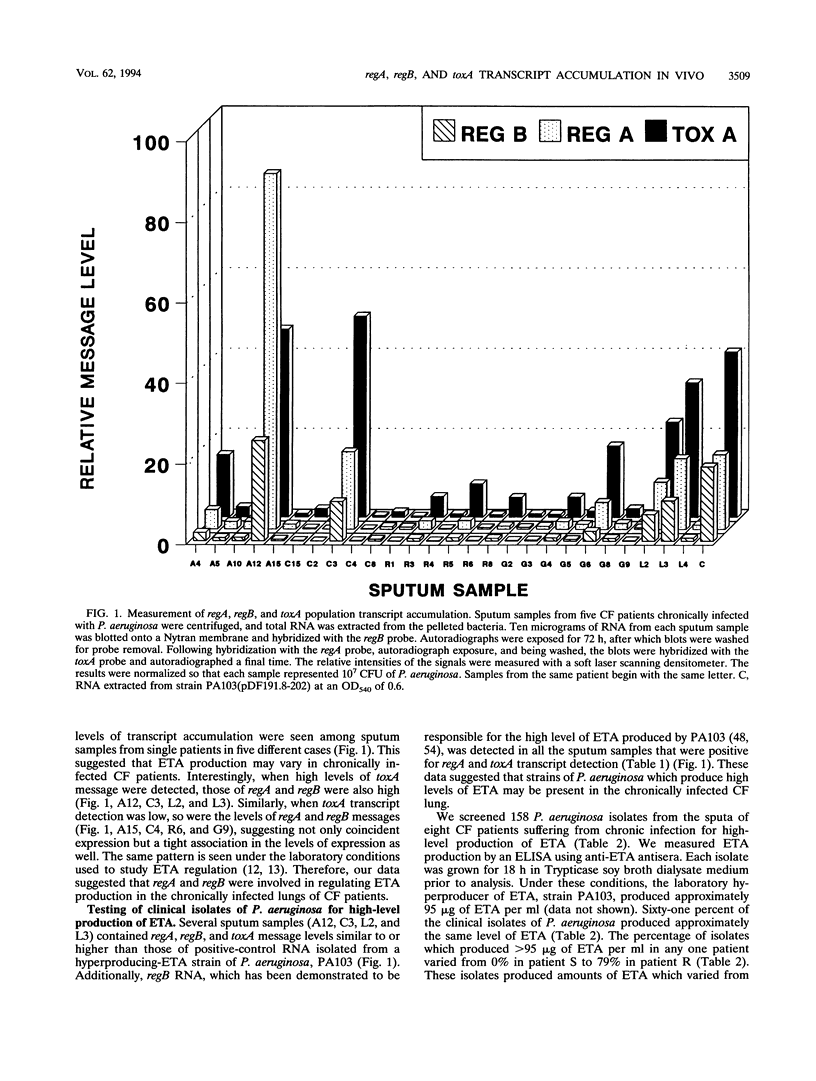
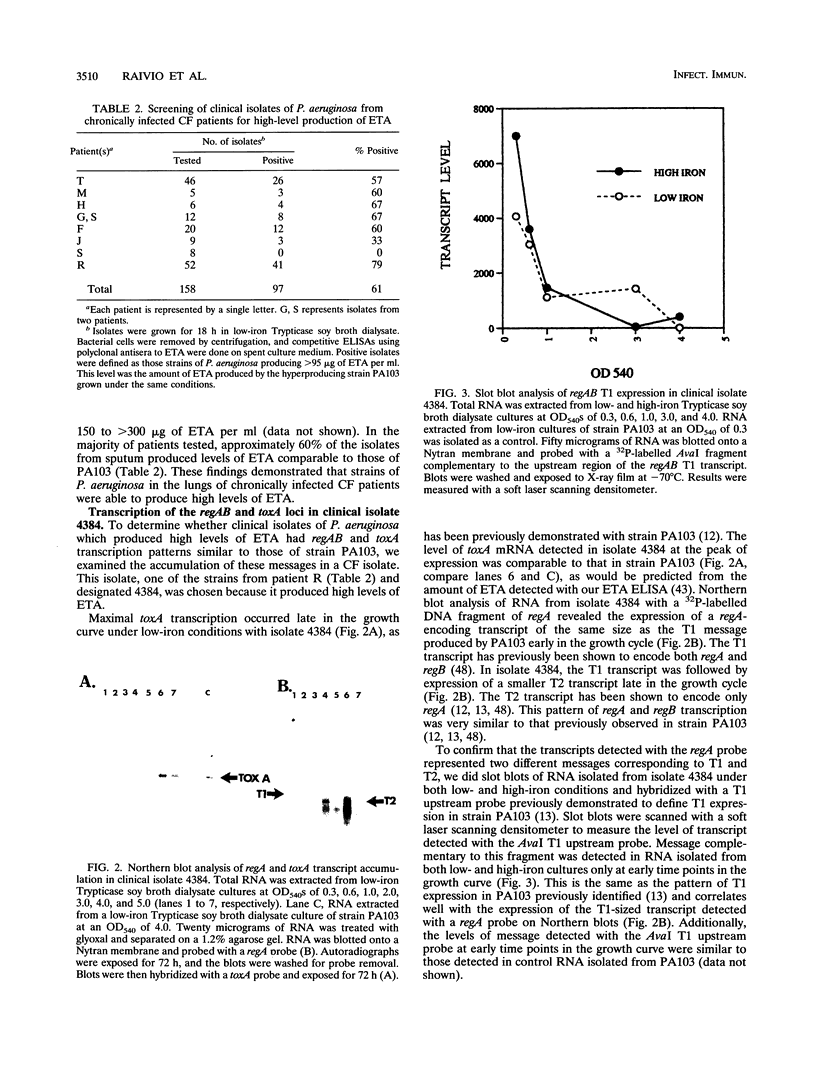
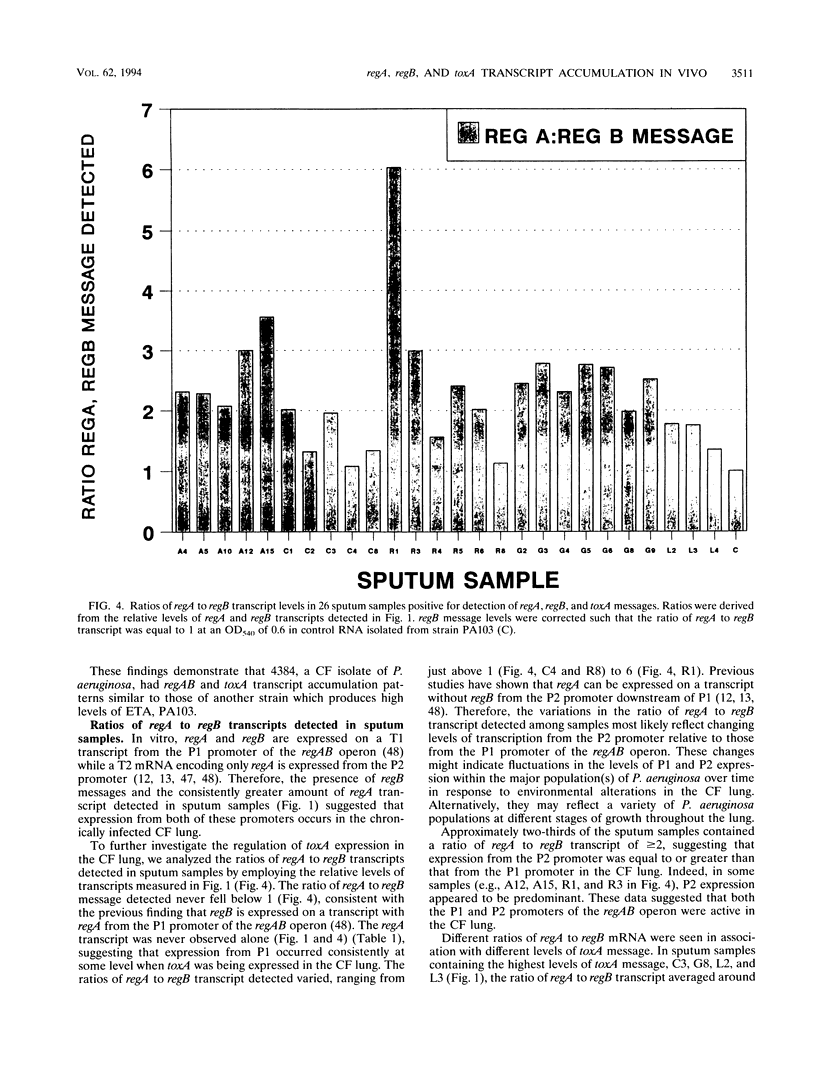
In this study, we examined the regulation of exotoxin A (ETA) production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa during chronic lung infections of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. We used a recently developed technique termed population transcript accumulation in hybridization studies with RNA extracted from sputa. With this technique, we demonstrated that the structural gene for ETA, toxA, as well as two genes encoding positive regulators of ETA synthesis, regA and regB, were expressed in the lungs of CF patients infected with P. aeruginosa. These genes were always expressed together, never alone or in pairs, suggesting coincident expression and a possible regulatory role for regA and regB in this environment. Fluctuations in the levels of the three gene products were observed among samples, consistent with a regulatory phenomenon. The level of regB RNA detected never exceeded that of regA, although the ratio of regA RNA to regB RNA detected did change between samples. These observations are in agreement with in vitro observations which have shown that regB is located 3' to regA in an operon which is expressed from two independently regulated promoters located upstream of regA. The presence of high levels of toxA, regA, and regB RNAs in some sputum samples prompted us to look for hyperproducing-toxin strains in the sputa of CF patients. In vitro, one such strain, 4384, had a transcript accumulation pattern for toxA, regA, and regB similar to that of a laboratory hyperproducer of ETA, strain PA103. These observations suggest that regA and regB are involved in the regulation of ETA production in strains of P. aeruginosa infecting the lungs of CF patients and that some of these strains may regulate ETA production in a manner similar to that of the hyperproducing-ETA strain PA103.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Vasil M. L., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Incidence of exotoxin production by Pseudomonas species. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.362-366.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI SANT'AGNESE P. A., DARLING R. C., PERERA G. A., SHEA E. Sweat electrolyte disturbances associated with childhood pancreatic disease. Am J Med. 1953 Dec;15(6):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOGGETT R. G., HARRISON G. M., WALLIS E. S. COMPARISON OF SOME PROPERTIES OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ISOLATED FROM INFECTIONS IN PERSONS WITH AND WITHOUT CYSTIC FIBROSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:427–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.427-431.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Buhl V., Høiby N., Schiøtz P. O., Botzenhart K. Detection of proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in immune complexes isolated from sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Oct;92(5):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Høiby N. Longitudinal study of immune response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):197–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.197-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterly J. R., Oppenheimer E. H. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas: structural changes in peripheral airways. Thorax. 1968 Nov;23(6):670–675. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.6.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fegan M., Francis P., Hayward A. C., Fuerst J. A. Heterogeneity, persistence, and distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa genotypes in cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2151–2157. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2151-2157.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr Pathogenesis of the pseudomonas lung lesion in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1989 Jul;96(1):158–164. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Kinetics of toxA and regA mRNA accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4477–4483. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4477-4483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Storey D. G., Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Differential regulation by iron of regA and toxA transcript accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5304–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5304-5313.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambello M. J., Kaye S., Iglewski B. H. LasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a transcriptional activator of the alkaline protease gene (apr) and an enhancer of exotoxin A expression. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1180-1184.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H. Microbiology of airway disease in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):35–51. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Funk C. R., Kaper J. B., Pavlovskis O. R., Galloway D. R. Cloning of a gene involved in regulation of exotoxin A expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.37-42.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Molecular studies of a positive regulator of toxin A synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:279–289. doi: 10.1159/000414353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollsing A. E., Granström M., Vasil M. L., Wretlind B., Strandvik B. Prospective study of serum antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1868-1874.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M., Gatzy J., Boucher R. Relative ion permeability of normal and cystic fibrosis nasal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1410–1417. doi: 10.1172/JCI110894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaard P. K., LeGrand R. D., Misfeldt M. L. Lymphoproliferative activity of Pseudomonas exotoxin A is dependent on intracellular processing and is associated with the carboxyl-terminal portion. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1273–1278. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1273-1278.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaard P. K., LeGrand R. D., Misfeldt M. L. The superantigen Pseudomonas exotoxin A requires additional functions from accessory cells for T lymphocyte proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jul;135(2):372–382. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90282-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Tai P. C. Biochemical and genetic aspects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:53–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Legaard P. K., Howell S. E., Fornella M. H., LeGrand R. D. Induction of interleukin-1 from murine peritoneal macrophages by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):978–982. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.978-982.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. B., Hsu Y. P., Lewiston N. J., Curd J. G., Milgrom H., Hart S., Dyer B., Larrick J. W. Association of systemic immune complexes, complement activation, and antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide and exotoxin A with mortality in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Apr;133(4):648–652. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pulmonary disease associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: current status of the host-bacterium interaction. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):575–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Taylor N. S., Callahan L. T., 3rd Exotoxin production by clinical isolates of pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):776–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.776-780.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. W., Storey D. G., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Regulation of toxA and regA by the Escherichia coli fur gene and identification of a Fur homologue in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103 and PA01. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2823–2831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G. Identification and molecular characterization of a transcriptional regulator from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 exhibiting structural and functional similarity to the FNR protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1469–1481. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. G., Frank D. W., Farinha M. A., Kropinski A. M., Iglewski B. H. Multiple promoters control the regulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa regA gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):499–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. G., Raivio T. L., Frank D. W., Wick M. J., Kaye S., Iglewski B. H. Effect of regB on expression from the P1 and P2 promoters of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa regAB operon. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6088–6094. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6088-6094.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. G., Ujack E. E., Rabin H. R. Population transcript accumulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and elastase in sputa from patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4687–4694. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4687-4694.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom M. S., Nunn D., Lory S. Multiple roles of the pilus biogenesis protein pilD: involvement of pilD in excretion of enzymes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1175–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1175-1180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman H. R., Marks M. I. Pulmonary infections in children with cystic fibrosis. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Sep;2(3):166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis: a review of pulmonary infections and interventions. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1987 Sep-Oct;3(5):334–351. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950030510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. J., Frank D. W., Storey D. G., Iglewski B. H. Identification of regB, a gene required for optimal exotoxin A yields in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmott R. W., Tyson S. L., Matthew D. J. Cystic fibrosis survival rates. The influences of allergy and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Jul;139(7):669–671. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140090031019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Schaffer M. S., Rabin H. R., Campbell G. D., Sokol P. A. Phenotypic comparison of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a variety of clinical sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.260-264.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




