Abstract
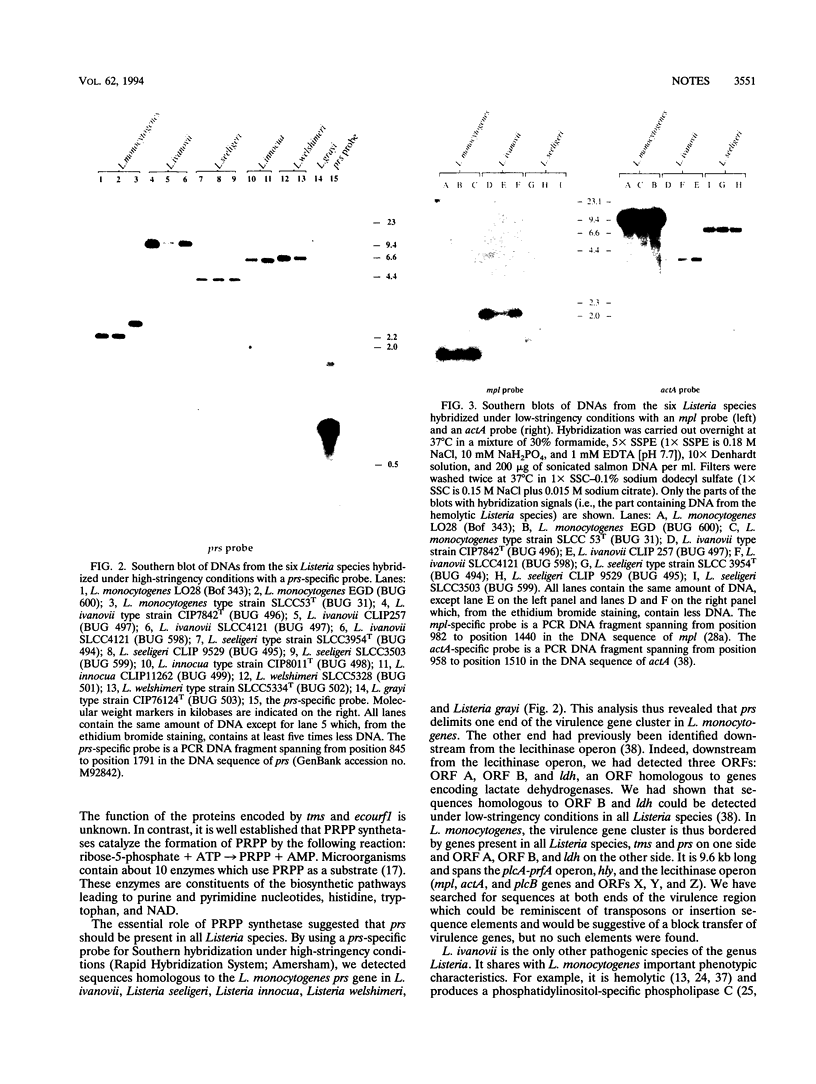
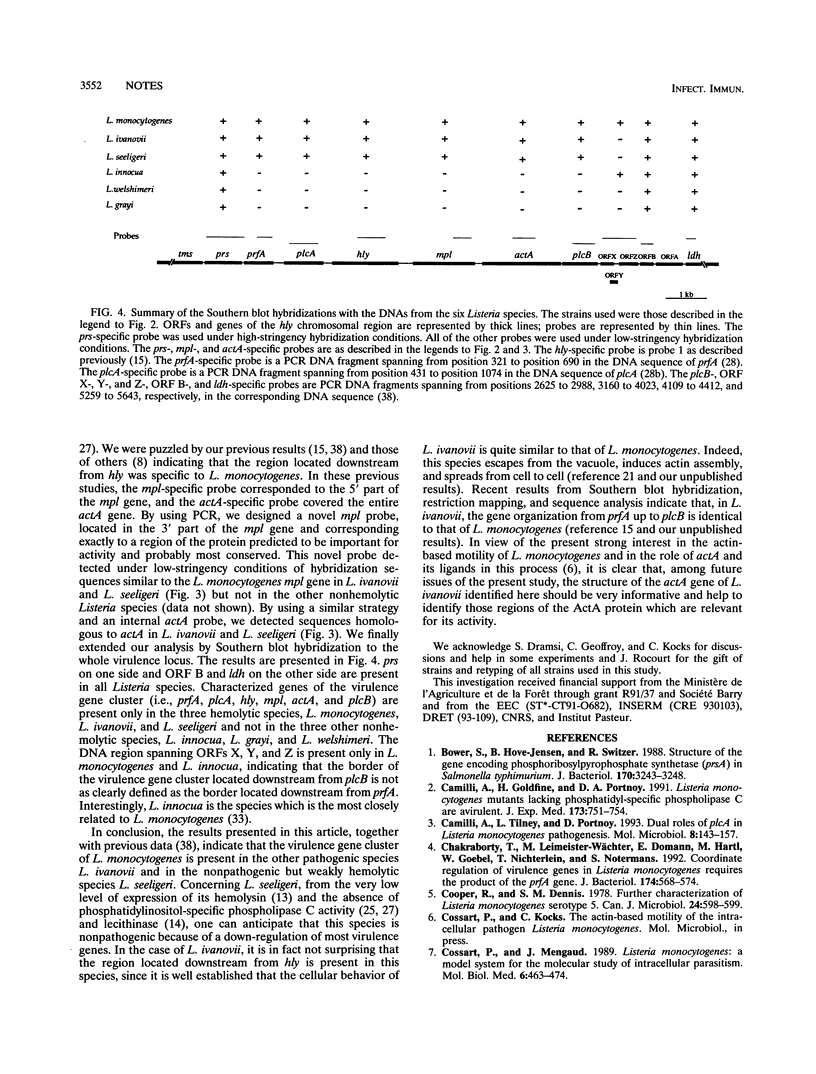
Most known Listeria monocytogenes virulence genes cluster within a 9.6-kb chromosomal region. This region is flanked on one end by two uncharacterized open reading frames (ORF A and ORF B) and ldh, an ORF presumably encoding the L. monocytogenes lactate dehydrogenase (J.-A. Vazquez-Boland, C. Kocks, S. Dramsi, H. Ohayon, C. Geoffroy, J. Mengaud, and P. Cossart, Infect. Immun. 60:219-230, 1992). We report here that the other end is flanked by prs, and ORF homologous to phosphoribosyl PPi synthetase genes. ORF B and prs were detected in all Listeria species and thus delimit the virulence region. This virulence gene cluster was detected exclusively in hemolytic Listeria species, Listeria ivanovii, an animal pathogen, and Listeria seeligeri, a nonpathogenic species.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bower S. G., Hove-Jensen B., Switzer R. L. Structure of the gene encoding phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase (prsA) in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3243–3248. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3243-3248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Goldfine H., Portnoy D. A. Listeria monocytogenes mutants lacking phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C are avirulent. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):751–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Dual roles of plcA in Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):143–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Hartl M., Goebel W., Nichterlein T., Notermans S. Coordinate regulation of virulence genes in Listeria monocytogenes requires the product of the prfA gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.568-574.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. F., Dennis S. M. Further characterization of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 5. Can J Microbiol. 1978 May;24(5):598–599. doi: 10.1139/m78-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Mengaud J. Listeria monocytogenes. A model system for the molecular study of intracellular parasitism. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):463–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coune A. Liposomes as drug delivery system in the treatment of infectious diseases. Potential applications and clinical experience. Infection. 1988 May-Jun;16(3):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01644088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Leimeister-Wächter M., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and identification of a metalloprotease gene from Listeria monocytogenes that is species specific and physically linked to the listeriolysin gene. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):65–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.65-72.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Wehland J., Rohde M., Pistor S., Hartl M., Goebel W., Leimeister-Wächter M., Wuenscher M., Chakraborty T. A novel bacterial virulence gene in Listeria monocytogenes required for host cell microfilament interaction with homology to the proline-rich region of vinculin. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1981–1990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dramsi S., Kocks C., Forestier C., Cossart P. Internalin-mediated invasion of epithelial cells by Listeria monocytogenes is regulated by the bacterial growth state, temperature and the pleiotropic activator prfA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):931–941. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Production of thiol-dependent haemolysins by Listeria monocytogenes and related species. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):481–487. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Raveneau J., Beretti J. L., Lecroisey A., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification and characterization of an extracellular 29-kilodalton phospholipase C from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2382–2388. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2382-2388.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gormley E., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Sequences homologous to the listeriolysin O gene region of Listeria monocytogenes are present in virulent and avirulent haemolytic species of the genus Listeria. Res Microbiol. 1989 Nov-Dec;140(9):631–643. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Jensen B., Harlow K. W., King C. J., Switzer R. L. Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase of Escherichia coli. Properties of the purified enzyme and primary structure of the prs gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6765–6771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Jensen B. Mutation in the phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase gene (prs) that results in simultaneous requirements for purine and pyrimidine nucleosides, nicotinamide nucleotide, histidine, and tryptophan in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1148–1152. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1148-1152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizasa T., Taira M., Shimada H., Ishijima S., Tatibana M. Molecular cloning and sequencing of human cDNA for phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase subunit II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karunasagar I., Krohne G., Goebel W. Listeria ivanovii is capable of cell-to-cell spread involving actin polymerization. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):162–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.162-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreft J., Funke D., Haas A., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. Production, purification and characterization of hemolysins from Listeria ivanovii and Listeria monocytogenes Sv4b. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. The gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes and its use as a specific probe for Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1943-1950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Haffner C., Domann E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Identification of a gene that positively regulates expression of listeriolysin, the major virulence factor of listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8336–8340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Dramsi S., Gouin E., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Milon G., Cossart P. Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2273–2283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Geoffroy C., Cossart P. Identification of a new operon involved in Listeria monocytogenes virulence: its first gene encodes a protein homologous to bacterial metalloproteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1043–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1043-1049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Cossart P. Transcriptional mapping and nucleotide sequence of the Listeria monocytogenes hlyA region reveal structural features that may be involved in regulation. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3695–3701. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3695-3701.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel E., Cossart P. Physical map of the Listeria monocytogenes chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7098–7103. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7098-7103.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson D., Hove-Jensen B., Arnvig K. Primary structure of the tms and prs genes of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):565–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00332425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S. H., Dufrenne J., Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity as a marker to distinguish between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Listeria species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2666–2670. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2666-2670.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Ishijima S., Kita K., Yamada K., Iizasa T., Tatibana M. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of two distinct cDNAs for rat phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14867–14870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Tilney M. S. The wily ways of a parasite: induction of actin assembly by Listeria. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Apr;1(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90021-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Dominguez L., Rodriguez-Ferri E. F., Suarez G. Purification and characterization of two Listeria ivanovii cytolysins, a sphingomyelinase C and a thiol-activated toxin (ivanolysin O). Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3928–3935. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3928-3935.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Gay N. J., Saraste M., Eberle A. N. DNA sequence around the Escherichia coli unc operon. Completion of the sequence of a 17 kilobase segment containing asnA, oriC, unc, glmS and phoS. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):799–815. doi: 10.1042/bj2240799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]