Abstract
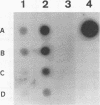
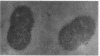
A gene from Streptococcus pneumoniae (nanA), with features entirely consistent with a neuraminidase gene, has been sequenced. High levels of neuraminidase activity were obtained after cloning of this gene, without flanking sequences, into a high-expression vector. RNA hybridization studies have shown that the gene is transcribed by a virulent pneumococcus strain. The predicted molecular weight of the protein and certain amino acid sequences are typical of other neuraminidases. NanA contains the four copies of the sequence SXDXGXTW that is present in all the bacterial neuraminidases previously described. Kyte and Doolittle analysis showed that NanA is a hydrophilic protein with hydrophobic domains at the N terminus and the C terminus. A putative signal peptide was found in the N terminus of this protein, indicating that the protein is exported from the pneumococcus. The C terminus has the features of the anchor motif found in other surface proteins from gram-positive bacteria. Electron microscopy studies showed the presence of neuraminidase associated with the cell surface of the pneumococcus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Dahmén J., Frejd T., Leffler H., Magnusson G., Noori G., Edén C. S. Identification of an active disaccharide unit of a glycoconjugate receptor for pneumococci attaching to human pharyngeal epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A. M., Paton J. C., Glare E. M., Hansman D., Catcheside D. E. Cloning and expression of the pneumococcal neuraminidase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camara M., Mitchell T. J., Andrew P. W., Boulnois G. J. Streptococcus pneumoniae produces at least two distinct enzymes with neuraminidase activity: cloning and expression of a second neuraminidase gene in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2856–2858. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2856-2858.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Morrison D. A. Cloning of Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA fragments in Escherichia coli requires vectors protected by strong transcriptional terminators. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crennell S. J., Garman E. F., Laver W. G., Vimr E. R., Taylor G. L. Crystal structure of a bacterial sialidase (from Salmonella typhimurium LT2) shows the same fold as an influenza virus neuraminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9852–9856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goward C. R., Scawen M. D., Murphy J. P., Atkinson T. Molecular evolution of bacterial cell-surface proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90021-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán C. A., Platé M., Pruzzo C. Role of neuraminidase-dependent adherence in Bacteroides fragilis attachment to human epithelial cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Sep 1;59(1-2):187–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henningsen M., Roggentin P., Schauer R. Cloning, sequencing and expression of the sialidase gene from Actinomyces viscosus DSM 43798. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Dec;372(12):1065–1072. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. L., Hamilton A. C., Steenbergen S. M., Vimr E. R. Cloning, sequencing and distribution of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 sialidase gene, nanH, provides evidence for interspecies gene transfer. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(7):873–884. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C., Evans P., Bergmeier L., Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Harris A. C., Aitken A., Bleiweis A. S., Lehner T. Sequence analysis of the cloned streptococcal cell surface antigen I/II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 20;258(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81632-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. T., Farmer S., Greiff D. Neuraminidase activities of clinical isolates of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):272–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.272-273.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Greiff D. Toxicity of pneumococcal neuraminidase. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):115–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.115-117.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock R. A., Paton J. C., Hansman D. Comparative efficacy of pneumococcal neuraminidase and pneumolysin as immunogens protective against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock R. A., Paton J. C., Hansman D. Purification and immunological characterization of neuraminidase produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jan;4(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B., Humbert O., Camara M., Guenzi E., Walker J., Mitchell T., Andrew P., Prudhomme M., Alloing G., Hakenbeck R. A highly conserved repeated DNA element located in the chromosome of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3479–3483. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole R. D., Goode L., Howe C. Neuraminidase activity in bacterial meningitis. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):979–985. doi: 10.1172/JCI106591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole R. D., Stahl W. L. Experimental pneumococcal meningitis. Effects of neuraminidase and other pneumococcal constituents on cerebrospinal fluid in the intact dog. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Oct;26(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson A., Eliasson M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Hellman U., Lindberg M., Uhlén M. Structure and evolution of the repetitive gene encoding streptococcal protein G. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Fischetti V. A. Identification of an endogenous membrane anchor-cleaving enzyme for group A streptococcal M protein. Its implication for the attachment of surface proteins in gram-positive bacteria. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2119–2133. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Mejia J. S., Ortega-Barria E., Matzilevich D., Prioli R. P. The Trypanosoma cruzi neuraminidase contains sequences similar to bacterial neuraminidases, YWTD repeats of the low density lipoprotein receptor, and type III modules of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):179–191. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggentin P., Rothe B., Kaper J. B., Galen J., Lawrisuk L., Vimr E. R., Schauer R. Conserved sequences in bacterial and viral sialidases. Glycoconj J. 1989;6(3):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01047853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggentin P., Schauer R., Hoyer L. L., Vimr E. R. The sialidase superfamily and its spread by horizontal gene transfer. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):915–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggentin T., Kleineidam R. G., Schauer R., Roggentin P. Effects of site-specific mutations on the enzymatic properties of a sialidase from Clostridium perfringens. Glycoconj J. 1992 Oct;9(5):235–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00731135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe B., Roggentin P., Frank R., Blöcker H., Schauer R. Cloning, sequencing and expression of a sialidase gene from Clostridium sordellii G12. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Nov;135(11):3087–3096. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-11-3087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe B., Rothe B., Roggentin P., Schauer R. The sialidase gene from Clostridium septicum: cloning, sequencing, expression in Escherichia coli and identification of conserved sequences in sialidases and other proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):190–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00273603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo T. A., Thompson J. S., Godoy V. G., Malamy M. H. Cloning and expression of the Bacteroides fragilis TAL2480 neuraminidase gene, nanH, in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2594–2600. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2594-2600.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon K. L., Diven W. F., Glew R. H. Purification and properties of Streptococcus pneumoniae neuraminidase. Enzyme. 1989;41(3):143–150. doi: 10.1159/000469069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneewind O., Mihaylova-Petkov D., Model P. Cell wall sorting signals in surface proteins of gram-positive bacteria. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4803–4811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneewind O., Model P., Fischetti V. A. Sorting of protein A to the staphylococcal cell wall. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90101-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl W. L., O'Toole R. D. Pneumococcal neuraminidase: purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 12;268(2):480–487. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanenbaum S. W., Gulbinsky J., Katz M., Sun S. C. Separation, purification and some properties of pneumococcal neuraminidase isoenzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):242–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanenbaum S. W., Sun S. C. Some molecular properties of pneumoccal neuraminidase isoenzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):824–828. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90301-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Lawrisuk L., Galen J., Kaper J. B. Cloning and expression of the Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase gene nanH in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1495–1504. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1495-1504.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. G., Harris R., McDowell R., Vimr E. R. Photolabelling of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 sialidase. Identification of a peptide with a predicted structural similarity to the active sites of influenza-virus sialidases. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 1;285(Pt 3):957–964. doi: 10.1042/bj2850957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Actinomyces viscosus T14V sialidase gene: presence of a conserved repeating sequence among strains of Actinomyces spp. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):109–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.109-116.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]