Abstract
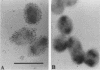
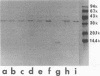
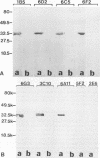
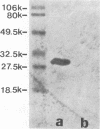
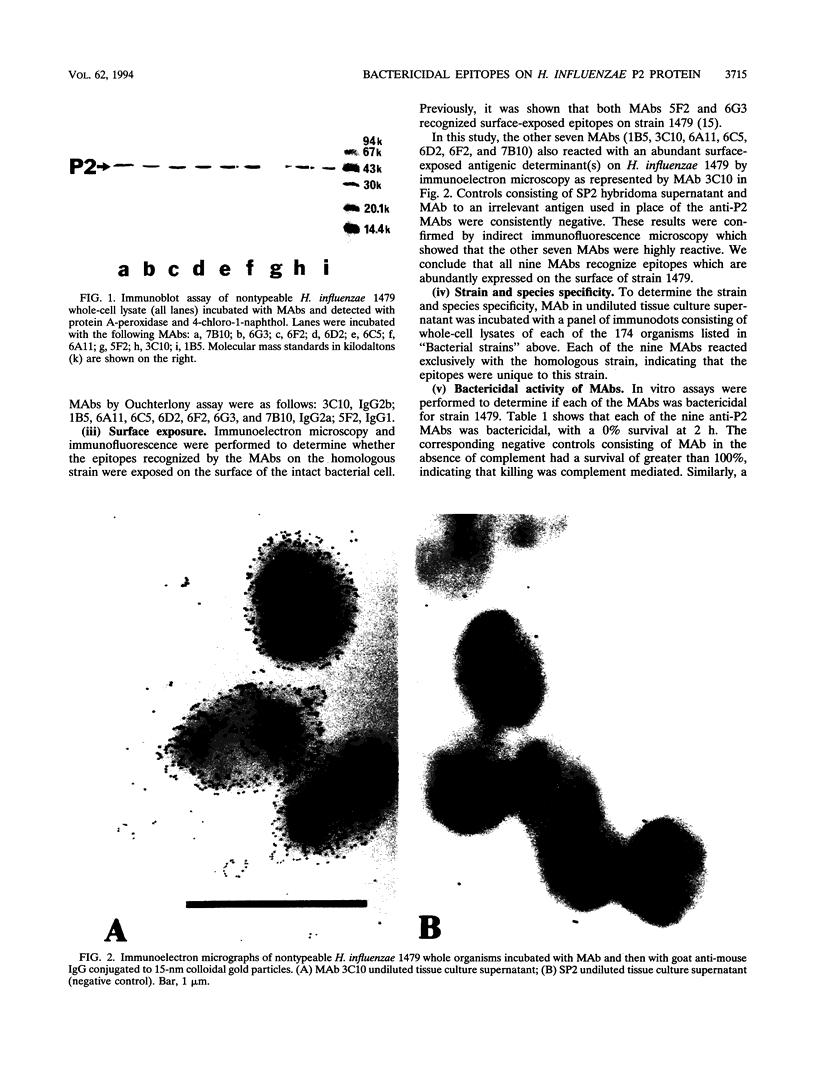
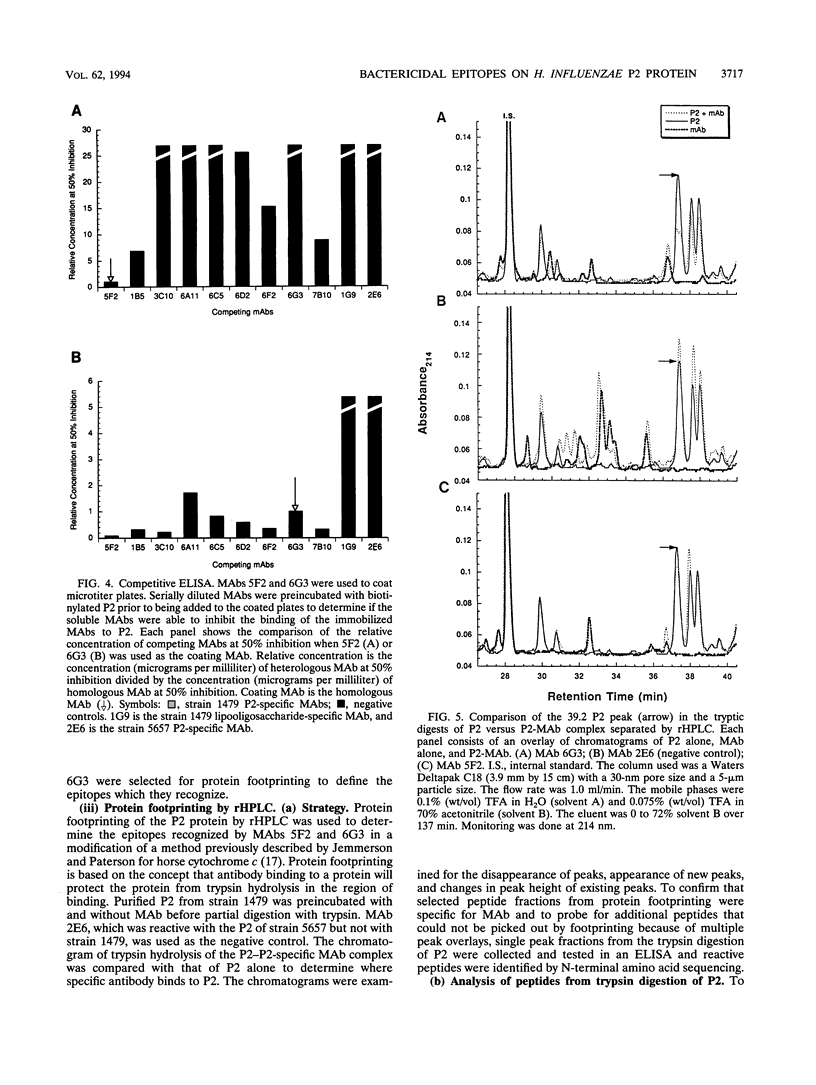
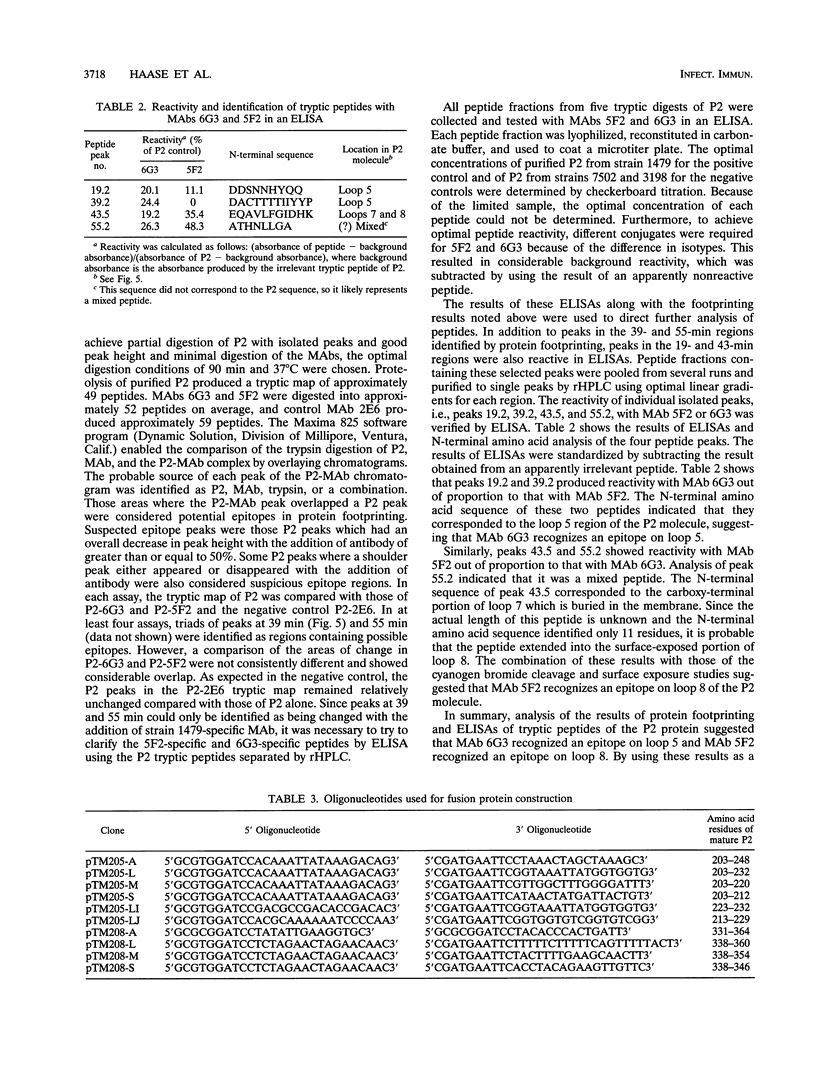
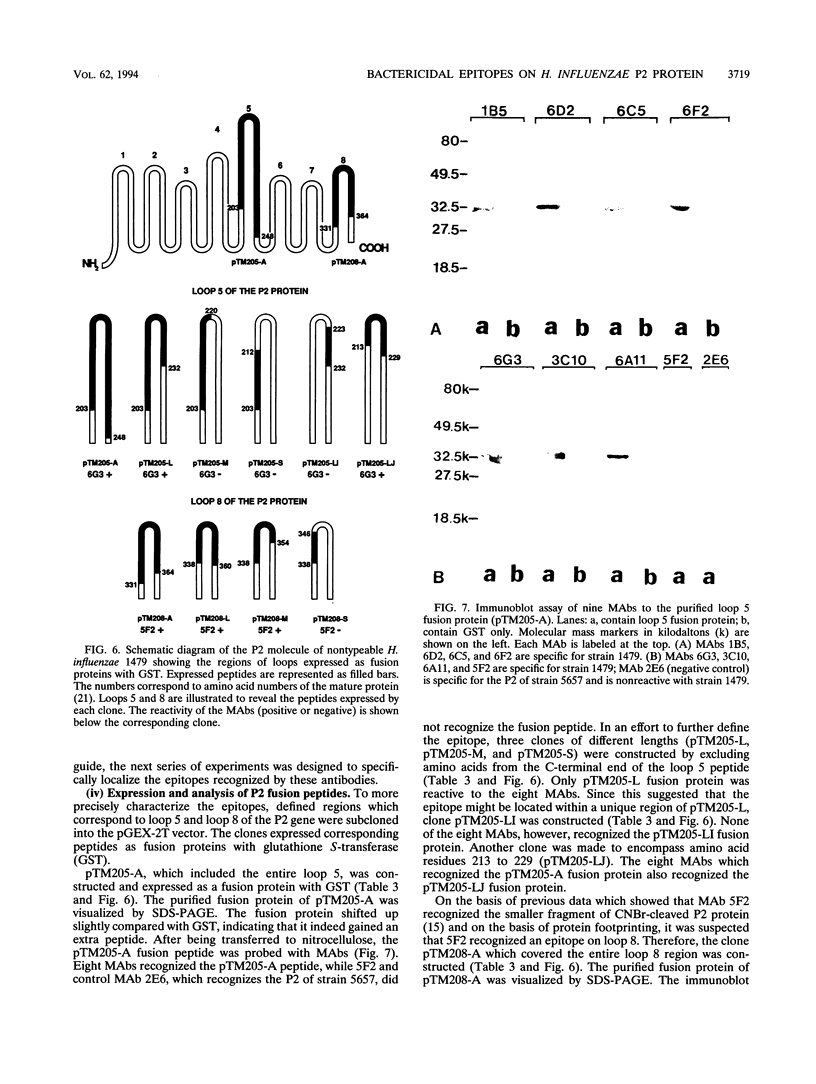
The P2 porin protein is the major outer membrane protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and is a potential target of a protective immune response. Nine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to P2 were developed by immunizing mice with nontypeable H. influenzae whole organisms. Each MAb reacted exclusively with the homologous strain in a whole-cell immunodot assay demonstrating exquisite strain specificity. All nine MAbs recognized abundantly expressed surface-exposed epitopes on the intact bacterium by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. Each MAb was bactericidal to the homologous strain in an in vitro complement-mediated killing assay. Immunoblot assay of cyanogen bromide cleavage products of purified P2 indicated that MAb 5F2 recognized the 10-kDa fragment, and the other eight MAbs recognized the 32-kDa fragment. Competitive ELISAs confirmed that 5F2 recognized an epitope that is different from the other eight MAbs. To further localize epitopes, MAbs 5F2 and 6G3 were studied in protein footprinting by using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Three potential epitope-containing peptides which were reactive in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with both 5F2 and 6G3 were isolated. These peptides were identified by N-terminal amino acid sequence and localized to loops 5 and 8 of the proposed model for P2. Fusion proteins consisting of glutathione S-transferase fused with variable-length peptides from loops 5 and 8 were expressed in the pGEX-2T vector. Immunoblot assay of fusion peptides of loops 5 and 8 confirmed that 5F2 recognized an epitope within residues 338 to 354 of loop 8; 6G3 and the remaining MAbs recognized an epitope within residues 213 to 229 of loop 5. These studies indicate that nontypeable H. influenzae contains bactericidal epitopes which have been mapped to two different surface-exposed loops of the P2 molecule. These potentially protective epitopes are strain specific and abundantly expressed on the surface of the intact bacterium.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Bodor F. F. Development of serum bactericidal activity following nontypable Haemophilus influenzae acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 May;9(5):333–339. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199005000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J. Protection by serum antibodies in experimental nontypable Haemophilus influenzae otitis media. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.572-578.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., Holtsclaw S. A., Wiener S. L., Smith J. K. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):537–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branefors P., Dahlberg T. Serum bactericidal effect on capsulated and non-capsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Feb;88(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Plummer F. A., Stephens R. S. Bacterial antigenic variation, host immune response, and pathogen-host coevolution. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2273–2276. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2273-2276.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Smith A. L. A major outer-membrane protein functions as a porin in Haemophilus influenzae. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 May;133(5):1273–1277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-5-1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duim B., Dankert J., Jansen H. M., van Alphen L. Genetic analysis of the diversity in outer membrane protein P2 of non-encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Microb Pathog. 1993 Jun;14(6):451–462. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1993.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Krystofik D., Shuff C., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. Otitis media in children. I. The systemic immune response to nontypable Hemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnehm H. E., Pelton S. I., Gulati S., Rice P. A. Characterization of antigens from nontypable Haemophilus influenzae recognized by human bactericidal antibodies. Role of Haemophilus outer membrane proteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1645–1658. doi: 10.1172/JCI111872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., Eijk P. P., Visschers G., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Endogenous and exogenous reinfections by Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the effect of antibiotic treatment on persistence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):512–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., Voorter C., Eijk P. P., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Antigenic drift of Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3038–3044. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3038-3044.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Hansen E. J. Coprecipitation of lipopolysaccharide and the 39,000-molecular-weight major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b by lipopolysaccharide-directed monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):819–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.819-827.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gump D. W., Tarr P., Phillips C. A., Forsyth B. R. Bactericidal antibodies to Hemophilus influenzae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):76–80. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase E. M., Campagnari A. A., Sarwar J., Shero M., Wirth M., Cumming C. U., Murphy T. F. Strain-specific and immunodominant surface epitopes of the P2 porin protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1278–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1278-1284.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T., Sakakura Y., Miyoshi Y. Serum bactericidal effect on capsulated and non-capsulated Haemophilus influenzae in chronic sinusitis. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1984;240(1):79–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00464349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemmerson R., Paterson Y. Mapping epitopes on a protein antigen by the proteolysis of antigen-antibody complexes. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1001–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.2422757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasic R. B., Trumpp C. E., Gnehm H. E., Rice P. A., Pelton S. I. Modification of otitis media in chinchillas rechallenged with nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and serological response to outer membrane antigens. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):273–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H. Cell fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:345–359. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebba P. E., Benson S. A., Bala S., Abdullah T., Reid J., Singh S. P., Nikaido H. Determinants of OmpF porin antigenicity and structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6800–6810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. O. Microbiology and antimicrobial treatment of otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1981 May-Jun;90(3 Pt 3):30–36. doi: 10.1177/00034894810903s209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingman K. L., Jansen E. M., Murphy T. F. Nearest neighbor analysis of outer membrane proteins of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3058–3063. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3058-3063.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Woodin K. A. Cross-reactivity of surface-exposed epitopes of outer membrane antigens of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2977–2983. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2977-2983.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D., Munson R., Jr, Grass S., Chong P., Hamel J., Zobrist G., Klein M., Brodeur B. R. Mapping of B-cell epitopes on the outer membrane P2 porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae by using recombinant proteins and synthetic peptides. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1457–1464. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1457-1464.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae is a basis for a serotyping system. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.15-21.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Human bactericidal antibody response to outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2673–2679. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2673-2679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bernstein J. M., Dryja D. M., Campagnari A. A., Apicella M. A. Outer membrane protein and lipooligosaccharide analysis of paired nasopharyngeal and middle ear isolates in otitis media due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenetic and epidemiological observations. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):723–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Hague-Park M., Baughn R. E., Wallace R. J., Jr, Cowley B. Opsonizing and bactericidal effects of normal human serum on nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):297–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.297-304.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Norden C. W., Demchak T. A. Significance of noncapsular antigens in protection against experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b disease: cross-reactivity. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):619–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.619-626.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel G. J., Katz S., Edelson P. J. Complement-mediated early clearance of Haemophilus influenzae type b from blood is independent of serum lytic activity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):85–90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheshberadaran H., Payne L. G. Protein footprinting method for studying antigen-antibody interactions and epitope mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1989;178:746–764. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)78049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Pelton S. I., Tager I. B., Kasper D. L. Bactericidal antibody and susceptibility to otitis media caused by nontypable strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):364–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema D. J., Murphy T. F. Molecular analysis of the P2 porin protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5204–5211. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5204-5211.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloyer J. L., Jr, Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H., Schiffman G., Johnston R. B., Jr Immune response to acute otitis media: association between middle ear fluid antibody and the clearing of clinical infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):306–308. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.306-308.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikumar R., Chin A. C., Vachon V., Richardson C. D., Ratcliffe M. J., Saarinen L., Käyhty H., Mäkelä P. H., Coulton J. W. Monoclonal antibodies specific to porin of Haemophilus influenzae type b: localization of their cognate epitopes and tests of their biological activities. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):665–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikumar R., Dahan D., Gras M. F., Ratcliffe M. J., van Alphen L., Coulton J. W. Antigenic sites on porin of Haemophilus influenzae type b: mapping with synthetic peptides and evaluation of structure predictions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4007–4016. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4007-4016.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Kristjanson D. N., Coulton J. W. Outer membrane porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b: pore size and subunit structure. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):134–140. doi: 10.1139/m88-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Lyew D. J., Coulton J. W. Transmembrane permeability channels across the outer membrane of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.918-924.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Milmoe G. J., Bowen A., Ledesma-Medina J., Salamon N., Bluestone C. D. Acute maxillary sinusitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):749–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Baker C. J., Quinones F. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Wiss K. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (biotype 4) as a neonatal, maternal, and genital pathogen. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Eijk P., Geelen-van den Broek L., Dankert J. Immunochemical characterization of variable epitopes of outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.247-252.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]