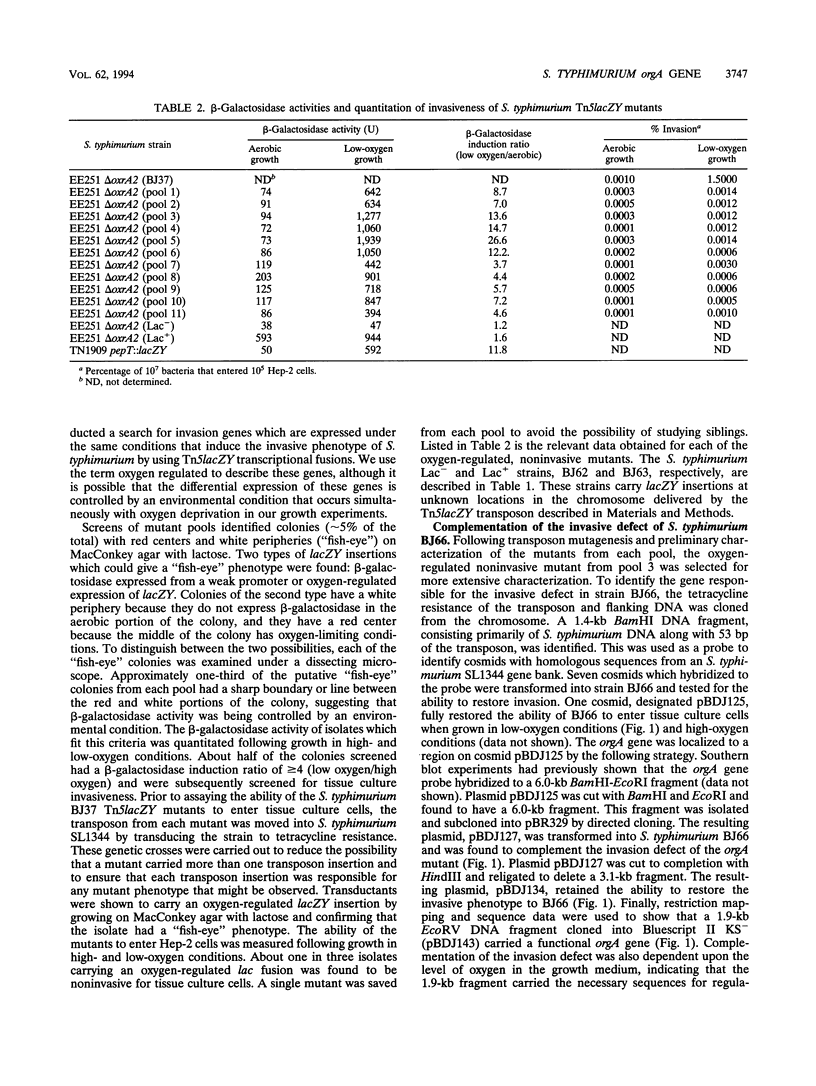
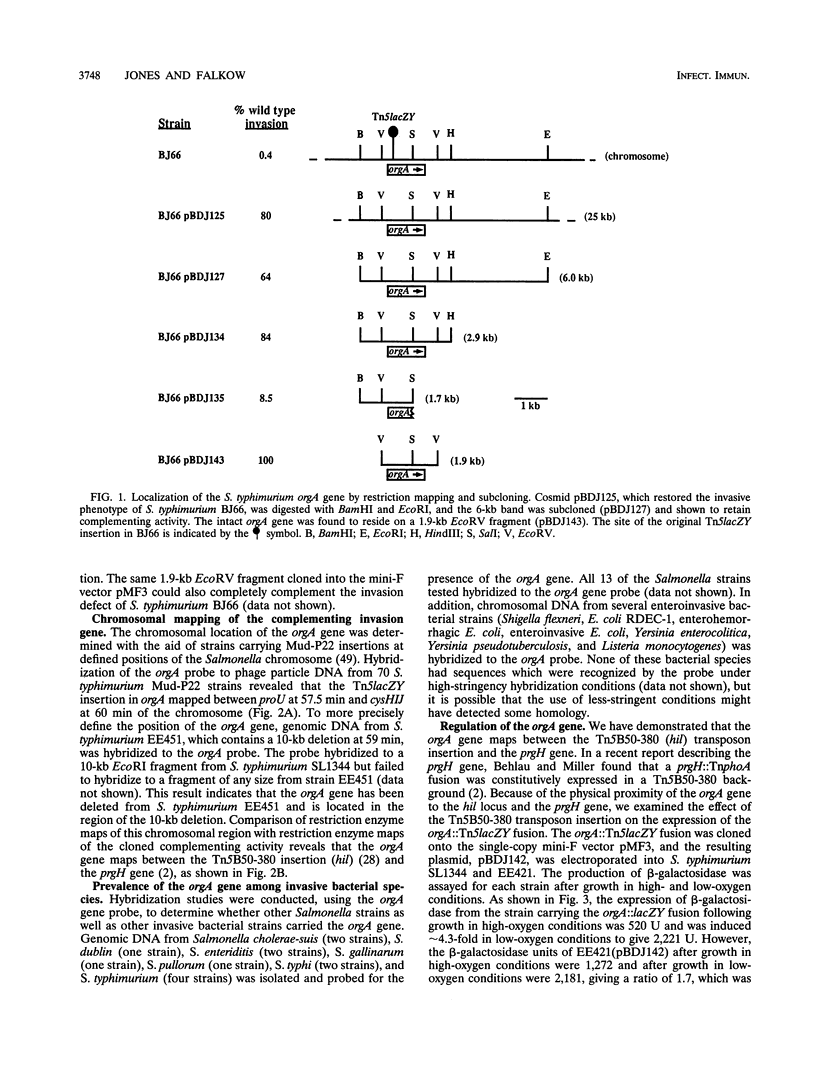
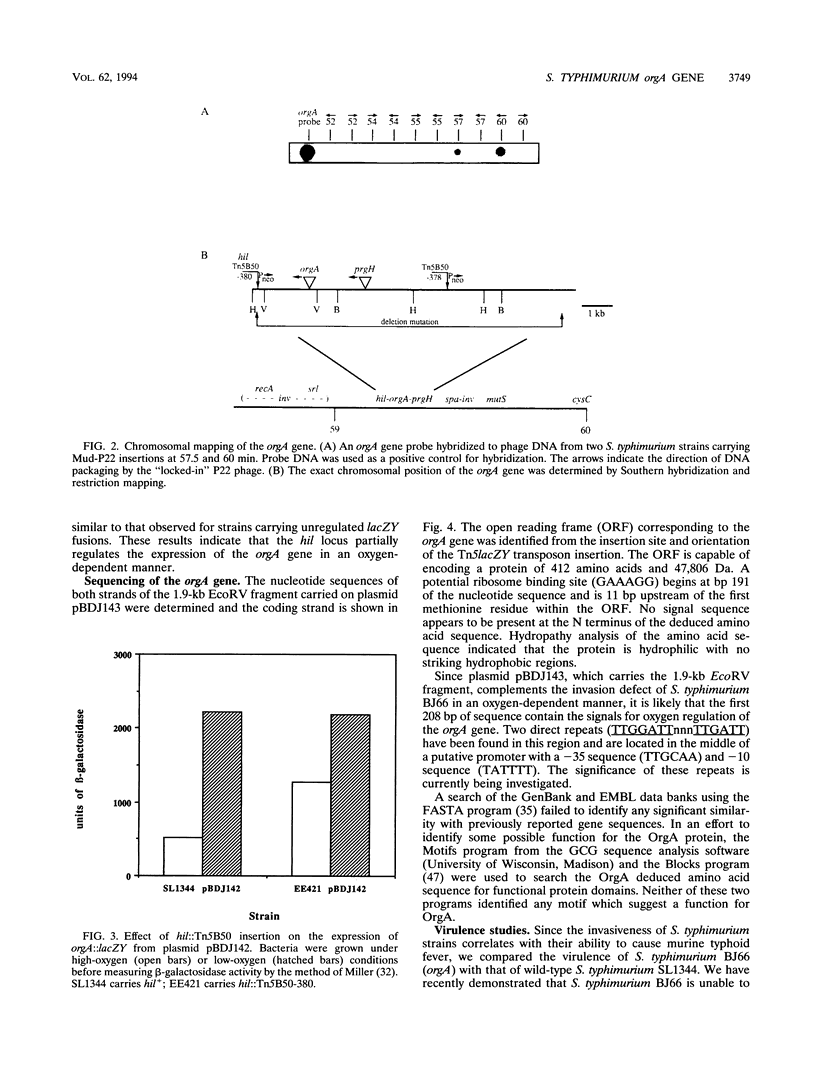
Abstract
Growth of Salmonella typhimurium in a low-oxygen environment induces the ability of these bacteria to enter mammalian cells. We have carried out a search for invasion genes that are expressed under low-oxygen conditions by using Tn5lacZY transcriptional fusions. Several noninvasive oxygen-regulated lacZY insertion strains have been identified. The invasion defect in one of these noninvasive S. typhimurium strains, BJ66, has been complemented by introduction of a cosmid (pBDJ125) from an S. typhimurium SL1344 gene bank. A 1.9-kb EcoRV DNA fragment subcloned from this cosmid, containing a single open reading frame (orgA), restores the ability of BJ66 to invade mammalian cells. Comparative searches of the GenBank and EMBL sequence data banks with the nucleotide sequence of the gene and deduced amino acid sequence of the protein reveal no significant similarities. Interestingly, hybridization of an orgA gene probe with a P22 chromosomal mapping library demonstrated that the orgA gene maps to a region on the chromosome between 57.5 and 60 min where other Salmonella invasion genes have been mapped. Other enteroinvasive bacteria (Shigella flexneri, Escherichia coli, Yersinia spp., and Listeria monocytogenes) lack sequences which cross hybridize to the probe. We have compared the virulence of S. typhimurium SL1344 and an isogenic orgA mutant in a mouse model of typhoid fever. The orgA mutant was as virulent as the wild-type strain was when inoculated intraperitoneally but is significantly reduced (> 60-fold) in its ability to cause disease by an oral route of infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmeyer R. M., McNern J. K., Bossio J. C., Rosenshine I., Finlay B. B., Galán J. E. Cloning and molecular characterization of a gene involved in Salmonella adherence and invasion of cultured epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):89–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlau I., Miller S. I. A PhoP-repressed gene promotes Salmonella typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4475–4484. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4475-4484.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1189–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiglmeier K., Honoré N., Iuchi S., Lin E. C., Cole S. T. Molecular genetic analysis of FNR-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):869–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst R. K., Dombroski D. M., Merrick J. M. Anaerobiosis, type 1 fimbriae, and growth phase are factors that affect invasion of HEp-2 cells by Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):2014–2016. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.2014-2016.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Ryan T. A., Jones B. D., Smith S. J., Falkow S. Ruffles induced by Salmonella and other stimuli direct macropinocytosis of bacteria. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):639–642. doi: 10.1038/364639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Starnbach M. N., Falkow S. Morphological and cytoskeletal changes in epithelial cells occur immediately upon interaction with Salmonella typhimurium grown under low-oxygen conditions. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3077–3087. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Ginocchio C., Costeas P. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella invasion gene invA: homology of InvA to members of a new protein family. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4338–4349. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4338-4349.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginocchio C., Pace J., Galán J. E. Identification and molecular characterization of a Salmonella typhimurium gene involved in triggering the internalization of salmonellae into cultured epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Ochman H. Cognate gene clusters govern invasion of host epithelial cells by Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3779–3787. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A. W., Schmidt G., Rowley D. Intestinal colonization and virulence of Salmonella in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Ghori N., Falkow S. Salmonella typhimurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the Peyer's patches. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):15–23. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Lee C. A., Falkow S. Invasion by Salmonella typhimurium is affected by the direction of flagellar rotation. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2475–2480. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2475-2480.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Paterson H. F., Hall A., Falkow S. Salmonella typhimurium induces membrane ruffling by a growth factor-receptor-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10390–10394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A., Uhlman D. The invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: reversible and irreversible bacterial attachment and the role of bacterial motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):351–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Nilsson L. Endocytosis of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR10 by HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):322–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Reichardt K., Botstein D. Inversions and deletions of the Salmonella chromosome generated by the translocatable tetracycline resistance element Tn10. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 5;127(1):89–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Yokoyama H., Yabuuchi E. Cytopathogenic effect of Salmonella typhi GIFU 10007 on M cells of murine ileal Peyer's patches in ligated ileal loops: an ultrastructural study. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(12):1225–1237. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Falkow S. The ability of Salmonella to enter mammalian cells is affected by bacterial growth state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Jones B. D., Falkow S. Identification of a Salmonella typhimurium invasion locus by selection for hyperinvasive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE A. E., SABACHEWSKY L., TOOLAN H. W. Culture characteristics of four permanent lines of human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1955 Oct;15(9):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manis J. J., Kline B. C. Restriction endonuclease mapping and mutagenesis of the F sex factor replication region. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00268815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J., Hayman M. J., Galán J. E. Signal transduction and invasion of epithelial cells by S. typhimurium. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruschkowski S., Rosenshine I., Finlay B. B. Salmonella typhimurium induces an inositol phosphate flux in infected epithelial cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 15;74(2-3):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90416-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Shope S. R. Anaerobic growth of Salmonella typhimurium results in increased uptake by Henle 407 epithelial and mouse peritoneal cells in vitro and repression of a major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):437–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.437-440.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., Quandt J., Klipp W. New derivatives of transposon Tn5 suitable for mobilization of replicons, generation of operon fusions and induction of genes in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1989 Aug 1;80(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Aliabadi Z., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Global control in Salmonella typhimurium: two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of starvation-, anaerobiosis-, and heat shock-inducible proteins. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):420–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.420-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. FNR and its role in oxygen-regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):399–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Black W., Falkow S. The construction of a cloning vector designed for gene replacement in Bordetella pertussis. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch K. L., Lenk J. B., Gamble B. L., Miller C. G. Oxygen regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):673–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.673-680.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. C., Henikoff S. PATMAT: a searching and extraction program for sequence, pattern and block queries and databases. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Jun;8(3):249–254. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray C., Sojka W. J. Experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Sep;25(2):139–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Sugiono P., Brewer K. L., Higgins N. P., Elliott T. Packaging specific segments of the Salmonella chromosome with locked-in Mud-P22 prophages. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):581–592. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]