Abstract
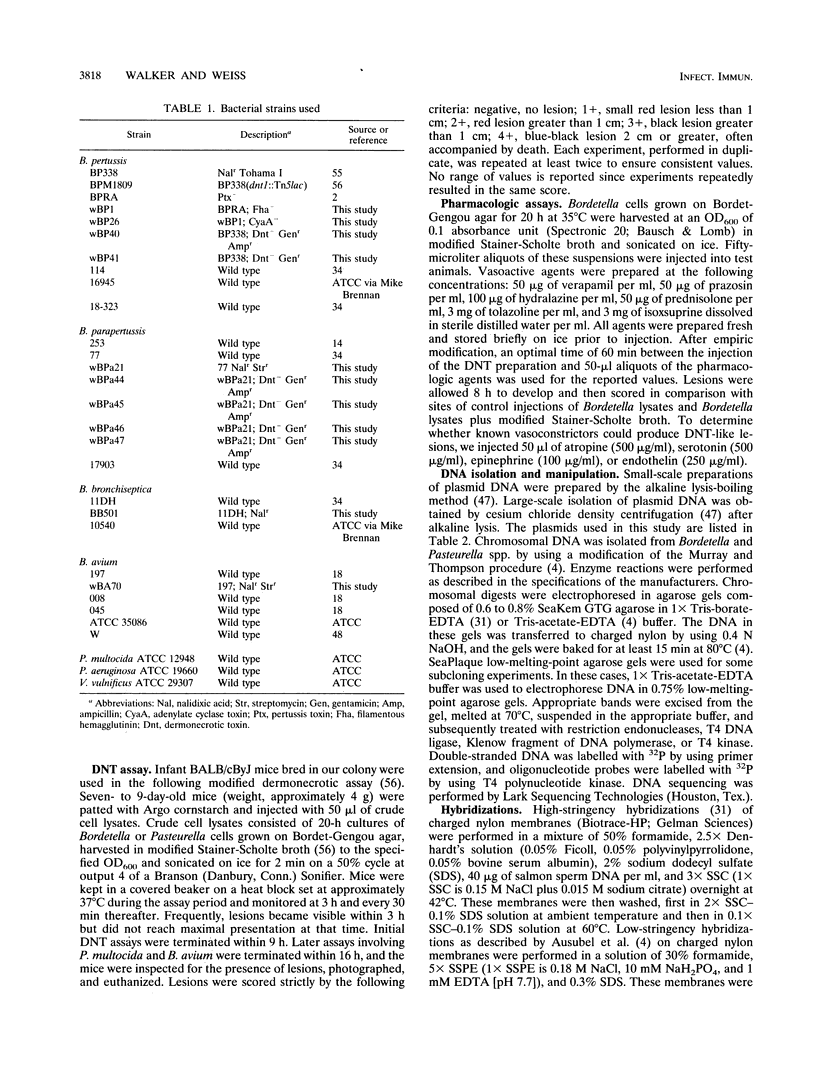
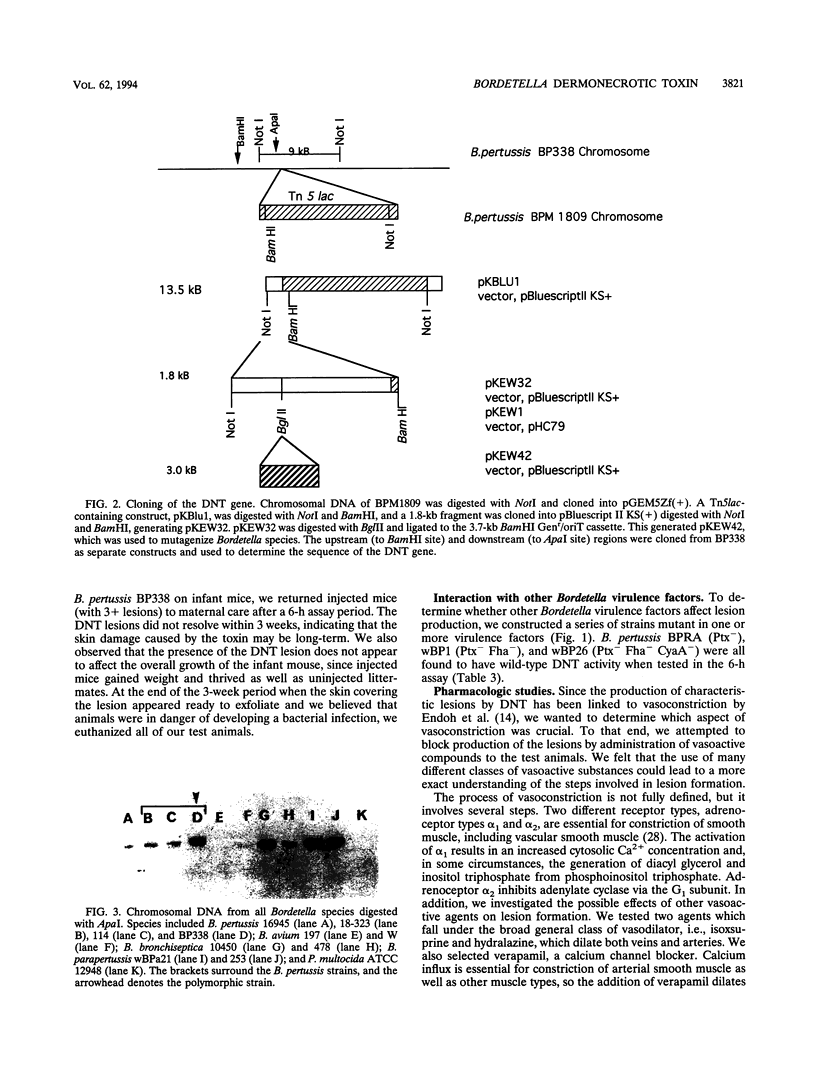
All members of the genus Bordetella and Pasteurella multocida (a gram-negative bacillus genetically unrelated to Bordetella spp., yet often sharing the same ecological niche) produce a dermonecrotic toxin (DNT). The amount of toxin produced and the time required for appearance of the lesions are identical for Bordetella pertussis, B. parapertussis, and B. bronchiseptica but different for P. multocida and B. avium. DNT has been reported to act by promoting vasoconstriction; however, vasoactive compounds (verapamil, prazosin, hydralazine, tolazoline, or isoxsuprine) are able to reverse the action of the toxin only slightly. Vasoconstrictors (atropine, serotonin, epinephrine, or endothelin) did not produce DNT-like lesions. We have characterized a region of DNA essential for DNT expression. We have determined by Southern analysis that the restriction map of the DNT gene is nearly identical in B. pertussis, B. parapertussis, and B. bronchiseptica, but the sequences are not present in toxigenic B. avium and P. multocida strains. A gentamicin resistance-origin of transfer cassette cloned into a 1.8-kb NotI-BamHI fragment results in constructs which can be mobilized and recombined into the Bordetella chromosome, rendering the resultant B. pertussis, B. parapertussis, and B. bronchiseptica strains negative for DNT. A 5-kb BamHI-ApaI fragment from the B. pertussis chromosome was sequenced and revealed homology to the Escherichia coli CNF1 (cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1) toxin.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Boguski M. S., Gish W., Wootton J. C. Issues in searching molecular sequence databases. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):119–129. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoine R., Locht C. Roles of the disulfide bond and the carboxy-terminal region of the S1 subunit in the assembly and biosynthesis of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1518–1526. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1518-1526.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aullo P., Giry M., Olsnes S., Popoff M. R., Kocks C., Boquet P. A chimeric toxin to study the role of the 21 kDa GTP binding protein rho in the control of actin microfilament assembly. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):921–931. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli A., Donelli G., Falbo V., Possenti R., Roda L. G., Roscetti G., Ruggeri F. M. A cell division-active protein from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli A., Falbo V., Roda L. G., Ruggeri F. M., Zona C. Partial purification and characterization of an escherichia coli toxic factor that induces morphological cell alterations. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1300–1306. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1300-1306.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Dougan G., Pickard D., Chatfield S., Smith M., Novotny P., Morrissey P., Fairweather N. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of protective outer membrane protein P.69 from Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3554–3558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. X., Alley M. R., Manktelow B. W. Experimental induction of pneumonia in mice with Bordetella parapertussis isolated from sheep. J Comp Pathol. 1989 Jan;100(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(89)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L., Hewlett E. L., Manclark C. R. Intracellular localization of the dermonecrotic toxin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.896-901.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke J., González E. A., Blanco J., Oswald E., Blanco M., Boivin R. Evidence for two types of cytotoxic necrotizing factor in human and animal clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):694–699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.694-699.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Amitani M., Nakase Y. Purification and characterization of heat-labile toxin from Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):659–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Nagai M., Nakase Y. Contractile action of heat-labile toxin of Bordetella parapertussis on aortic smooth muscles of pigs. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(8):755–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falbo V., Pace T., Picci L., Pizzi E., Caprioli A. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4909–4914. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4909-4914.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzano L., Fiorentini C., Donelli G., Michel E., Kocks C., Cossart P., Cabanié L., Oswald E., Boquet P. Induction of phagocytic behaviour in human epithelial cells by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1247–1254. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentini C., Arancia G., Caprioli A., Falbo V., Ruggeri F. M., Donelli G. Cytoskeletal changes induced in HEp-2 cells by the cytotoxic necrotizing factor of Escherichia coli. Toxicon. 1988;26(11):1047–1056. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry-Weeks C. R., Cookson B. T., Goldman W. E., Rimler R. B., Porter S. B., Curtiss R., 3rd Dermonecrotic toxin and tracheal cytotoxin, putative virulence factors of Bordetella avium. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1698–1707. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1698-1707.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow R. A. Biology of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):722–738. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.722-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Ras-related proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Nakai T., Kume K. Effects of Bordetella bronchiseptica dermonecrotic toxin on the structure and function of osteoblastic clone MC3T3-e1 cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1112–1116. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1112-1116.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Nakai T., Kume K. Purification and characterization of Bordetella bronchiseptica dermonecrotic toxin. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Nakai T., Kume K. Simplified procedure for purification of Bordetella bronchiseptica dermonecrotic toxin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90255-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Sugimoto N., Matsuda M. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells by Bordetella bronchiseptica dermonecrotic toxin. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3611–3615. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3611-3615.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshijima M., Kondo J., Kikuchi A., Yamamoto K., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain membranes of a GTP-binding protein with a Mr of 21,000, ADP-ribosylated by an ADP-ribosyltransferase contaminated in botulinum toxin type C1--identification as the rhoA gene product. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Jan;7(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90067-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh Y. J., Weiss A. A. A 23-kilodalton protein, distinct from BvgA, expressed by virulent Bordetella pertussis binds to the promoter region of vir-regulated toxin genes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2389–2395. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2389-2395.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Sugai M., Murooka Y., Paik S. Y., Hong Y. M., Ohgai H., Suginaka H. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the epidermal cell differentiation inhibitor gene from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):459–464. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91438-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livey I., Wardlaw A. C. Production and properties of Bordetella pertussis heat-labile toxin. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Feb;17(1):91–103. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell D. J., Morrissey P., Dougan G. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the aroA gene of Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2467–2471. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2467-2471.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. C., Rozengurt E. Pasteurella multocida toxin selectively facilitates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin. Requirement for a functional G protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25296–25303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Hewlett E. L., Peppler M. S., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships in populations of Bordetella spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):230–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.230-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Kume K. Intracellular locations of dermonecrotic toxins in Pasteurella multocida and in Bordetella bronchiseptica. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Apr;46(4):870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Tsuji M., Samejima Y., Kume K. Purification of dermonecrotic toxin from a sonic extract of Pasteurella multocida SP-72 serotype D. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):429–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.429-434.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald E., Sugai M., Labigne A., Wu H. C., Fiorentini C., Boquet P., O'Brien A. D. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 2 produced by virulent Escherichia coli modifies the small GTP-binding proteins Rho involved in assembly of actin stress fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3814–3818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parton R. Effect of prednisolone on the toxicity of Bordetella pertussis for mice. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):391–400. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen S. K., Foged N. T. Cloning and expression of the Pasteurella multocida toxin gene, toxA, in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3907–3913. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3907-3913.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimler R. B. Turkey coryza: toxin production by Bordetella avium. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1043–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Falkow S. Identification of Bordetella pertussis regulatory sequences required for transcriptional activation of the fhaB gene and autoregulation of the bvgAS operon. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2385–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2385-2392.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Higgins T., Chanter N., Lax A. J., Staddon J. M. Pasteurella multocida toxin: potent mitogen for cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):123–127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Mackenzie A. Pathogenesis of atrophic rhinitis in pigs: a new perspective. Vet Rec. 1984 Jan 28;114(4):89–90. doi: 10.1136/vr.114.4.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. G., Dees C., Rose L. P. A heat-stable toxin isolated from the turkey coryza agent, Bordetella avium. Avian Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;30(4):761–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Black W., Falkow S. The construction of a cloning vector designed for gene replacement in Bordetella pertussis. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai M., Hashimoto K., Kikuchi A., Inoue S., Okumura H., Matsumoto K., Goto Y., Ohgai H., Moriishi K., Syuto B. Epidermal cell differentiation inhibitor ADP-ribosylates small GTP-binding proteins and induces hyperplasia of epidermis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2600–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga T., Sugie K., Hirata M., Morii N., Fukata J., Uchida A., Imura H., Narumiya S. Inhibition of PMA-induced, LFA-1-dependent lymphocyte aggregation by ADP ribosylation of the small molecular weight GTP binding protein, rho. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1529–1537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Goodwin M. S. Lethal infection by Bordetella pertussis mutants in the infant mouse model. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3757–3764. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3757-3764.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Melton A. R., Walker K. E., Andraos-Selim C., Meidl J. J. Use of the promoter fusion transposon Tn5 lac to identify mutations in Bordetella pertussis vir-regulated genes. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2674–2682. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2674-2682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems R., Paul A., van der Heide H. G., ter Avest A. R., Mooi F. R. Fimbrial phase variation in Bordetella pertussis: a novel mechanism for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2803–2809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. L., Sekura R. D. Purification and characterization of the heat-labile toxin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3754–3759. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3754-3759.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. R., Eggen R. I., Zehnder A. J., de Vos W. M. Sequence analysis of the Pseudomonas sp. strain P51 tcb gene cluster, which encodes metabolism of chlorinated catechols: evidence for specialization of catechol 1,2-dioxygenases for chlorinated substrates. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2425-2434.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





