Abstract
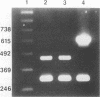
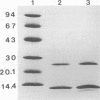
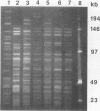
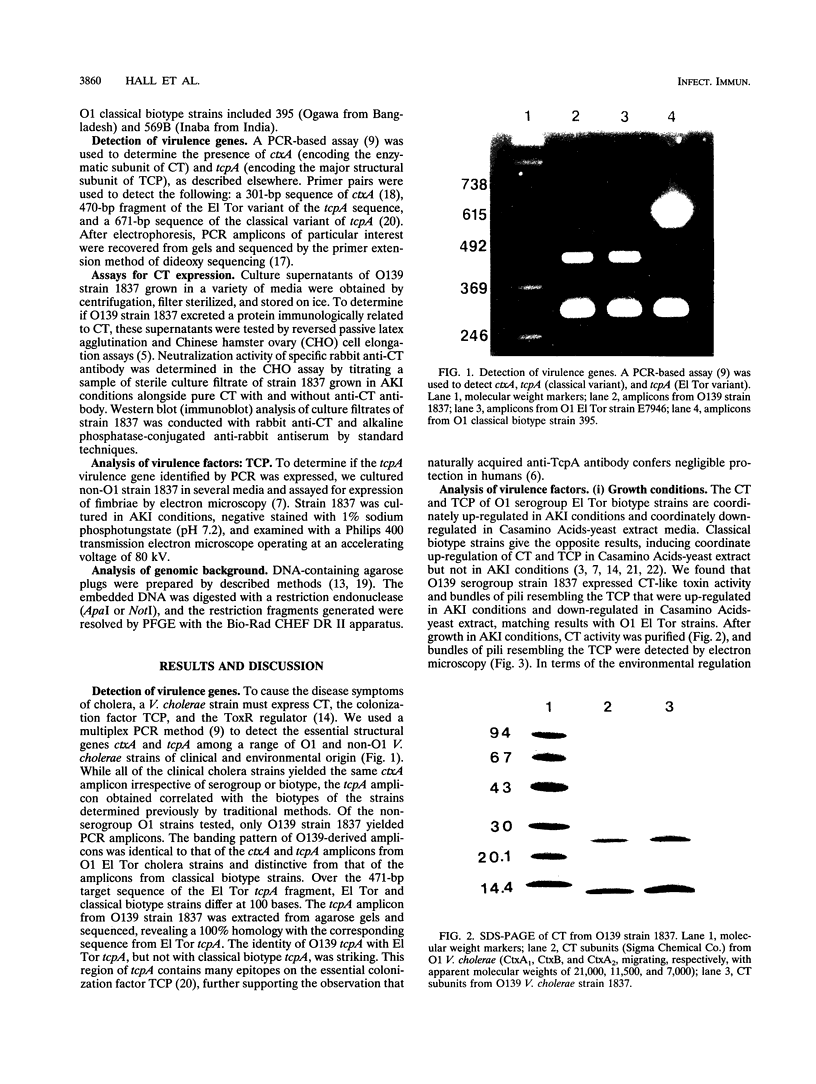
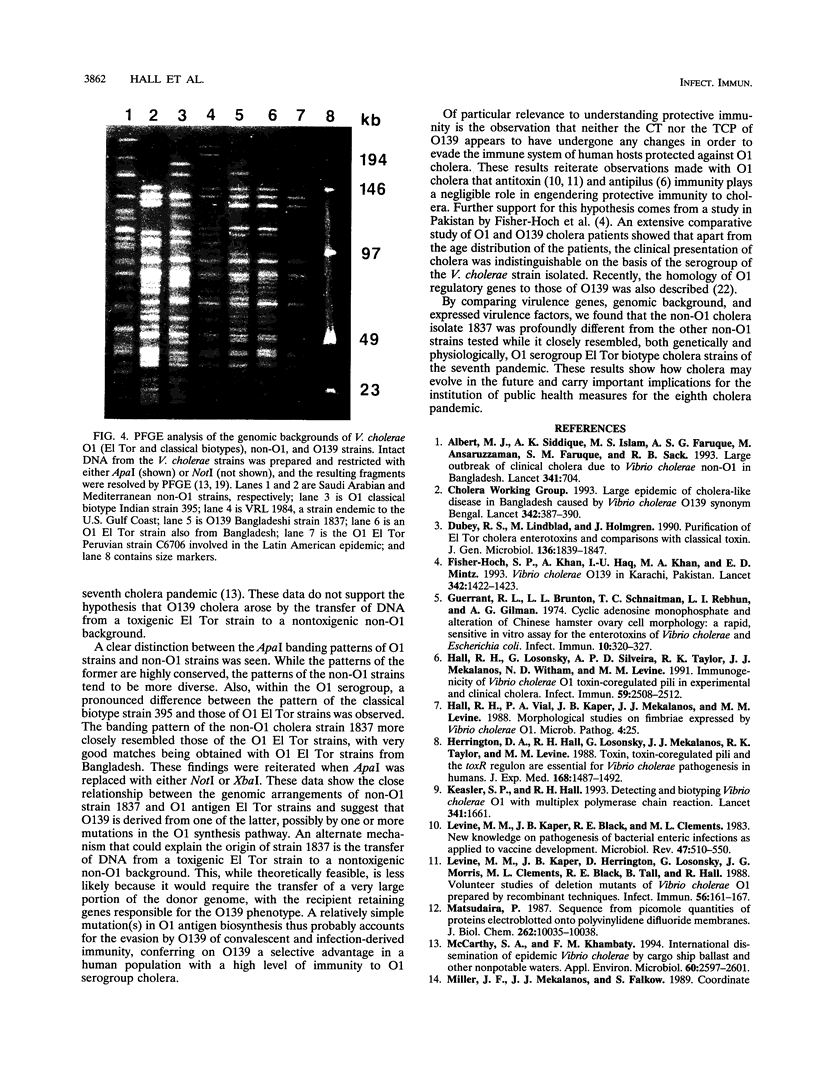
Until recently, only Vibrio cholerae strains of the O1 serogroup have been associated with epidemic cholera. In December 1992, an outbreak of cholera gravis in Vellore, India, was attributed to a new serogroup of V. cholerae recently designated O139. Serogroup O139 cholera has since spread to 13 countries and has reached pandemic proportions. Serogroup O139 cholera evades immunity to O1 cholera and is not detected by the standard O1 antigen test. Understanding the origins of O139 cholera and determining the relatedness of O139 to O1 cholera are necessary to device strategies for detecting, reporting, and controlling this new pandemic. In order to determine the origins of this novel cholera serogroup, O139 was analyzed for virulence genes, for virulence proteins and their regulation, and for its genomic background. We found that O139 and O1 V. cholera strains of the E1 Tor biotype possess highly homologous virulence genes encoding cholera toxin and toxin-coregulated pili and that the regulation of virulence protein expression likewise was indistinguishable between O139 and O1. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) revealed the restriction digest pattern of O139 strains to be closely related to that of O1 serogroup E1 Tor biotype cholera strains from the Indian subcontinent. However, PFGE showed minor differences among individual O139 cholera isolates, suggesting that O139 V. cholerae is evolving.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Siddique A. K., Islam M. S., Faruque A. S., Ansaruzzaman M., Faruque S. M., Sack R. B. Large outbreak of clinical cholera due to Vibrio cholerae non-O1 in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1993 Mar 13;341(8846):704–704. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90481-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey R. S., Lindblad M., Holmgren J. Purification of El Tor cholera enterotoxins and comparisons with classical toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Sep;136(9):1839–1847. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-9-1839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher-Hoch S. P., Khan A., Inam-ul-Haq, Khan M. A., Mintz E. D. Vibrio cholerae O139 in Karachi, Pakistan. Lancet. 1993 Dec 4;342(8884):1422–1423. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92780-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Silveira A. P., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J., Witham N. D., Levine M. M. Immunogenicity of Vibrio cholerae O1 toxin-coregulated pili in experimental and clinical cholera. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2508–2512. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2508-2512.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keasler S. P., Hall R. H. Detecting and biotyping Vibrio cholerae O1 with multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1993 Jun 26;341(8861):1661–1661. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90792-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S. A., Khambaty F. M. International dissemination of epidemic Vibrio cholerae by cargo ship ballast and other nonpotable waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jul;60(7):2597–2601. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.7.2597-2601.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae: a look at the epidemiology of an occasional pathogen. Epidemiol Rev. 1990;12:179–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthy T., Garg S., Sharma R., Bhattacharya S. K., Nair G. B., Shimada T., Takeda T., Karasawa T., Kurazano H., Pal A. Emergence of novel strain of Vibrio cholerae with epidemic potential in southern and eastern India. Lancet. 1993 Mar 13;341(8846):703–704. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90480-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai H., Nishibuchi M., Ramamurthy T., Bhattacharya S. K., Pal S. C., Takeda Y. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of the cholera enterotoxin operon of Vibrio cholerae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2517–2521. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2517-2521.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Seyer J. M., Kovari I., Sumrada R. A., Taylor R. K. Localization of protective epitopes within the pilin subunit of the Vibrio cholerae toxin-coregulated pilus. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):114–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.114-118.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Mekalanos J. J. ToxR regulates virulence gene expression in non-O1 strains of Vibrio cholerae that cause epidemic cholera. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.72-78.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]