Abstract
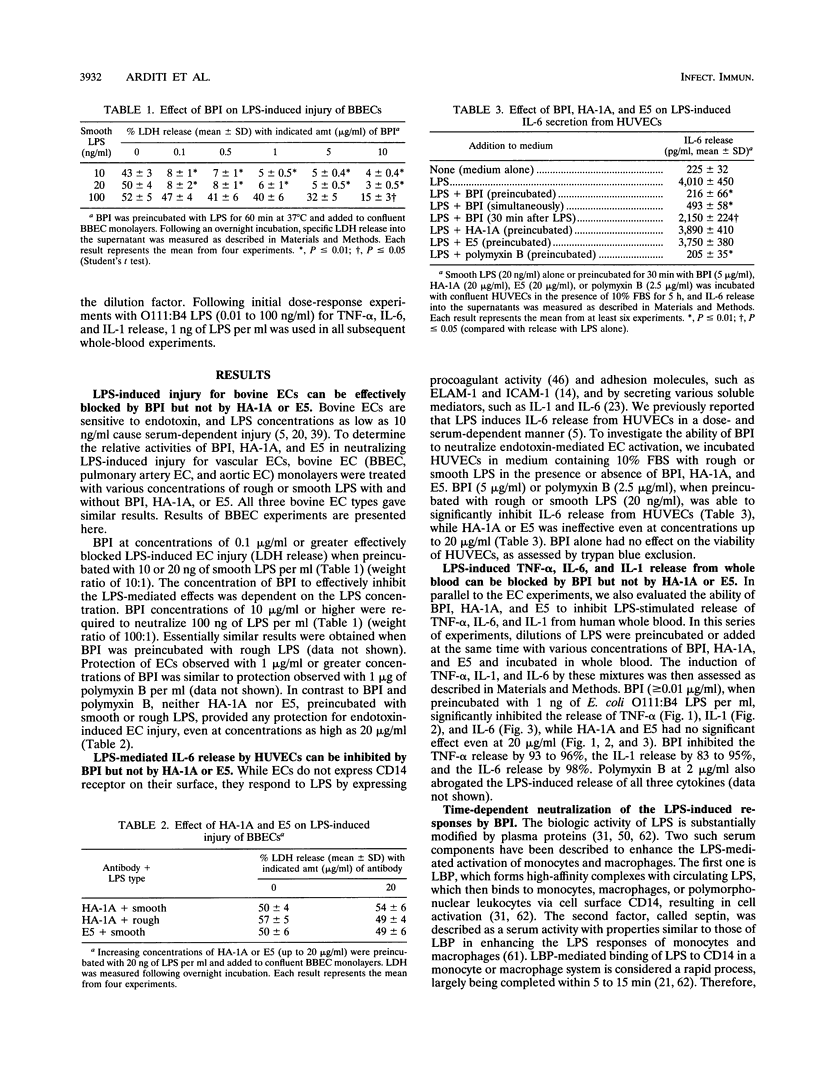
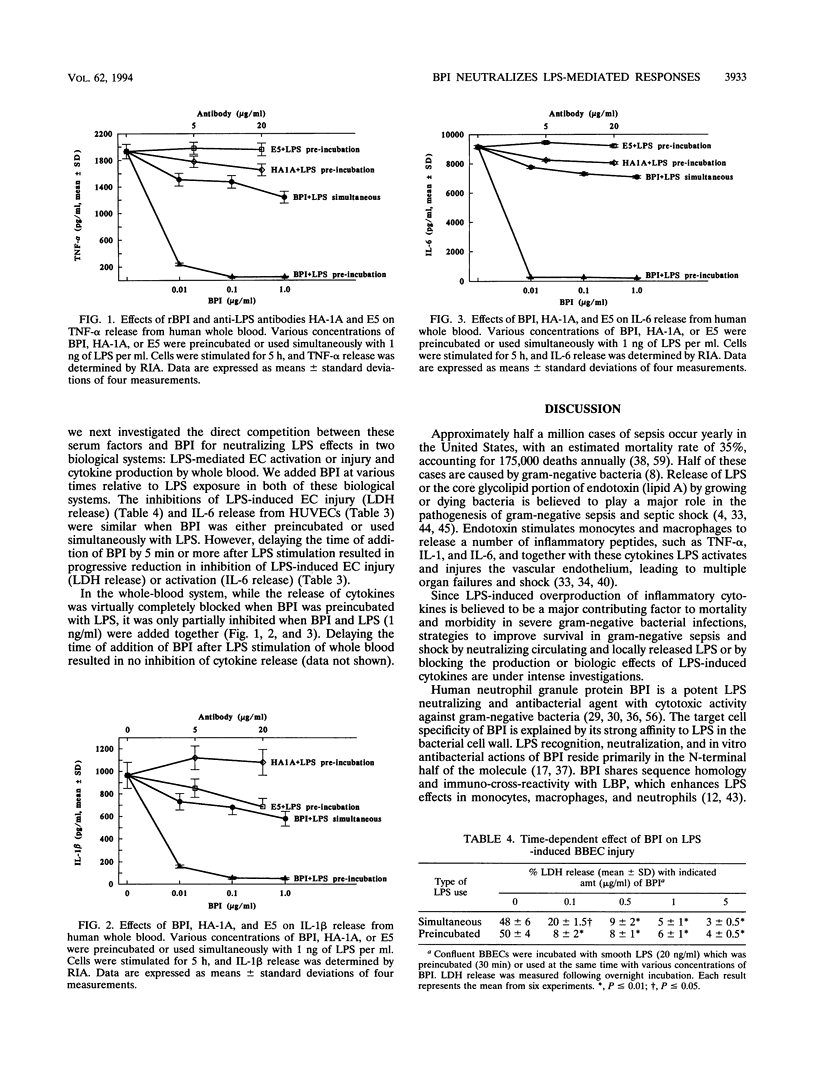
Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI), a human neutrophil granule protein, has been shown to bind lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and neutralize LPS-mediated cytokine production in adherent monocytes and the whole-blood system. In this study we investigated the ability of recombinant human BPI (rBPI) to inhibit LPS-induced vascular endothelial cell (EC) injury and activation. rBPI inhibited significantly both rough and smooth LPS-mediated injury for cultured bovine brain microvessel ECs, as measured by lactic dehydrogenase release, and blocked the LPS-induced interleukin-6 (IL-6) release from human umbilical vein ECs in a dose-dependent manner. BPI was able to inhibit LPS-mediated EC injury or activation whether it was added before or at the same time with LPS, but delaying the time of addition of rBPI resulted only in a partial inhibition. BPI also inhibited LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 release from human whole blood. This inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 release from whole blood was maximal when BPI was premixed with LPS before addition to blood and was partial when BPI was added simultaneously with LPS, but no inhibition was observed when the addition of rBPI was delayed for 5 min. These findings suggest that rBPI is a potent inhibitor of LPS-mediated responses in ECs and whole blood and underscore the potential use of BPI in treatment or prevention of endotoxic shock. In contrast, the anti-lipid A monoclonal antibodies HA-1A and E5 were ineffective in inhibiting LPS-mediated EC injury and activation as well as LPS-induced cytokine release in whole blood.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arditi M., Ables L., Yogev R. Cerebrospinal fluid endotoxin levels in children with H. influenzae meningitis before and after administration of intravenous ceftriaxone. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1005–1011. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arditi M., Kabat W., Yogev R. Antibiotic-induced bacterial killing stimulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha release in whole blood. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):240–244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arditi M., Kabat W., Yogev R. Serum tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1-beta, p24 antigen concentrations and CD4+ cells at various stages of human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Jun;10(6):450–455. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199106000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arditi M., Manogue K. R., Caplan M., Yogev R. Cerebrospinal fluid cachectin/tumor necrosis factor-alpha and platelet-activating factor concentrations and severity of bacterial meningitis in children. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):139–147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arditi M., Zhou J., Dorio R., Rong G. W., Goyert S. M., Kim K. S. Endotoxin-mediated endothelial cell injury and activation: role of soluble CD14. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3149–3156. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3149-3156.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner J. D., Eggimann P., Glauser M. P. Management of septic shock: new approaches. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1992;12:165–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekhuizen H., Blokland I., Corsèl-van Tilburg A. J., Koning F., van Furth R. CD14 contributes to the adherence of human monocytes to cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3761–3767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):653–658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperstock M. S. Inactivation of endotoxin by polymyxin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):422–425. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan J. J., Jr, Bell B. M. Endotoxin-induced intravascular coagulation: prevention with polymyxin B sulfate. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):802–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Fürer E. Synthesis and characterization of Escherichia coli O18 O-polysaccharide conjugate vaccines. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):373–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.373-377.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentener M. A., Von Asmuth E. J., Francot G. J., Marra M. N., Buurman W. A. Antagonistic effects of lipopolysaccharide binding protein and bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein on lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release by mononuclear phagocytes. Competition for binding to lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4258–4265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desch C. E., Kovach N. L., Present W., Broyles C., Harlan J. M. Production of human tumor necrosis factor from whole blood ex vivo. Lymphokine Res. 1989 Summer;8(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) interaction with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is one of at least three mechanisms for lymphocyte adhesion to cultured endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):321–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Schneider A., Harris L. Separation and purification of a potent bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a closely associated phospholipase A2 from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Observations on their relationship. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11000–11009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey E. A., Miller D. S., Jahr T. G., Sundan A., Bazil V., Espevik T., Finlay B. B., Wright S. D. Soluble CD14 participates in the response of cells to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1665–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzano-Santoro H., Parent J. B., Grinna L., Horwitz A., Parsons T., Theofan G., Elsbach P., Weiss J., Conlon P. J. High-affinity binding of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a recombinant amino-terminal fragment to the lipid A region of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4754–4761. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4754-4761.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz I. E., Warren J., Estrada C., Roberts E., Krause D. N. Long-term serial cultivation of arterial and capillary endothelium from adult bovine brain. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1985 Mar;21(3 Pt 1):172–180. doi: 10.1007/BF02621355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman R. L., Schein R. M., Martin M. A., Wenzel R. P., MacIntyre N. R., Emmanuel G., Chmel H., Kohler R. B., McCarthy M., Plouffe J. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Reidy M. A., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated bovine endothelial cell injury in vitro. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann D., Gallay P., Barras C., Zaech P., Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S., Glauser M. P., Baumgartner J. D. Control of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding and LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor secretion in human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3505–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann D., Gallay P., Betz-Corradin S., Barras C., Baumgartner J. D., Glauser M. P. Competition between bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein for lipopolysaccharide binding to monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1351–1357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Podor T. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Loskutoff D. J., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory mediators augment IL-6 secretion by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn F. R., Ammons W. S., Horwitz A., Grinna L., Theofan G., Weickmann J., Kung A. H. Protective effect of a recombinant amino-terminal fragment of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein in experimental endotoxemia. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1307–1310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laug W. E., Tokes Z. A., Benedict W. F., Sorgente N. Anchorage independent growth and plasminogen activator production by bovine endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):281–293. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Thornton M. B., Snable J. L., Leong S., Lane J., Wilde C. G., Scott R. W. Regulation of the response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide by endogenous and exogenous lipopolysaccharide binding proteins. Blood Purif. 1993;11(2):134–140. doi: 10.1159/000170107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Wilde C. G., Collins M. S., Snable J. L., Thornton M. B., Scott R. W. The role of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein as a natural inhibitor of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Wilde C. G., Griffith J. E., Snable J. L., Scott R. W. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein has endotoxin-neutralizing activity. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J., Tobias P., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. Regulatory mechanisms of host responsiveness to endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide). Pathobiology. 1991;59(3):185–188. doi: 10.1159/000163641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa M. M., Ramilo O., Mertsola J., Risser R. C., Beutler B., Hansen E. J., McCracken G. H., Jr Modulation of inflammation and cachectin activity in relation to treatment of experimental Hemophilus influenzae type b meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):818–825. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Doerfler M. E., Elsbach P. Endotoxin-neutralizing properties of the 25 kD N-terminal fragment and a newly isolated 30 kD C-terminal fragment of the 55-60 kD bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):649–655. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Frangione B., Mannion B. A 25-kDa NH2-terminal fragment carries all the antibacterial activities of the human neutrophil 60-kDa bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14891–14894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick D., Betts J., Frey E. A., Prameya R., Dorovini-Zis K., Finlay B. B. Haemophilus influenzae lipopolysaccharide disrupts confluent monolayers of bovine brain endothelial cells via a serum-dependent cytotoxic pathway. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):865–872. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. Cytokines and endothelial cell biology. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):427–451. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugin J., Schürer-Maly C. C., Leturcq D., Moriarty A., Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S. Lipopolysaccharide activation of human endothelial and epithelial cells is mediated by lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and soluble CD14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2744–2748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D. Prevention by polymyxin B of endotoxin lethality in mice. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1463–1464. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1463-1464.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Barton R. P., Mogan K. A. Role of antibiotic class in the rate of liberation of endotoxin during therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1012–1018. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Flynn P. M., Barrett F. F., Stidham G. L., Westenkirchner D. F. Serial quantitation of endotoxemia and bacteremia during therapy for gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):565–568. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Bank I., Nawroth P. P., Cassimeris J., Kisiel W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Dinarello C., Chess L., Jaffe E. A. Self-regulation of procoagulant events on the endothelial cell surface. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1223–1235. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng N. N., Kaplan H. S., Hebert J. M., Moore C., Douglas H., Wunderlich A., Braude A. I. Protection against gram-negative bacteremia and endotoxemia with human monoclonal IgM antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Vukajlovich S. W., Morrison D. C. Endotoxin interactions with serum proteins relationship to biological activity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;272:47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Shibl A. M., Hackbarth C. J., Larrick J. W., Sande M. A. Antibiotic therapy, endotoxin concentration in cerebrospinal fluid, and brain edema in experimental Escherichia coli meningitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):456–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R. The modification of biophysical and endotoxic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharides by serum. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1313–1324. doi: 10.1172/JCI109252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Amato S. F., Fitting C., Black K. M., Loiselle P. M., Pasternack M. S., Cavaillon J. M. Assessment of ability of murine and human anti-lipid A monoclonal antibodies to bind and neutralize lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):89–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Danner R. L., Munford R. S. Anti-endotoxin monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1153–1157. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Glennon M. L., Wainwright N., Amato S. F., Black K. M., Kirsch S. J., Riveau G. R., Whyte R. I., Zapol W. M., Novitsky T. J. Binding and neutralization of endotoxin by Limulus antilipopolysaccharide factor. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2506–2513. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2506-2513.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weersink A. J., van Kessel K. P., van den Tol M. E., van Strijp J. A., Torensma R., Verhoef J., Elsbach P., Weiss J. Human granulocytes express a 55-kDa lipopolysaccharide-binding protein on the cell surface that is identical to the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Shu C., Castillo J., Grinna L., Horwitz A., Theofan G. Human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a recombinant NH2-terminal fragment cause killing of serum-resistant gram-negative bacteria in whole blood and inhibit tumor necrosis factor release induced by the bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1122–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI115930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Olsson I. Cellular and subcellular localization of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of neutrophils. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):652–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P. The mortality of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections: need for a new vital statistic? Int J Epidemiol. 1988 Mar;17(1):225–227. doi: 10.1093/ije/17.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Patel M., Miller D. S. Septin: a factor in plasma that opsonizes lipopolysaccharide-bearing particles for recognition by CD14 on phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):719–727. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Ramos R. A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding protein opsonizes LPS-bearing particles for recognition by a novel receptor on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1231–1241. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Fisher C. J., Jr, Sprung C. L., Straube R. C., Sadoff J. C., Foulke G. E., Wortel C. H., Fink M. P., Dellinger R. P., Teng N. N. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 14;324(7):429–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102143240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A., Fierer J., Glauser M. P., Sadoff J. C., Douglas H., Braude A. I. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutant Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



