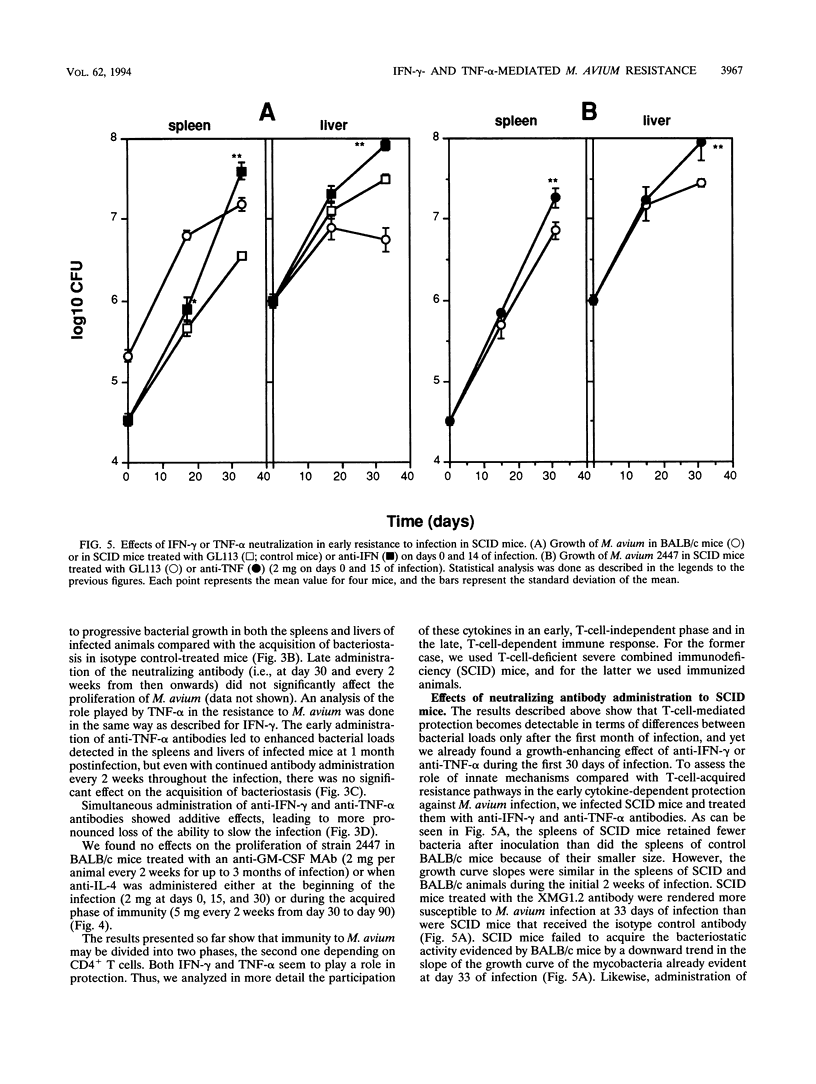
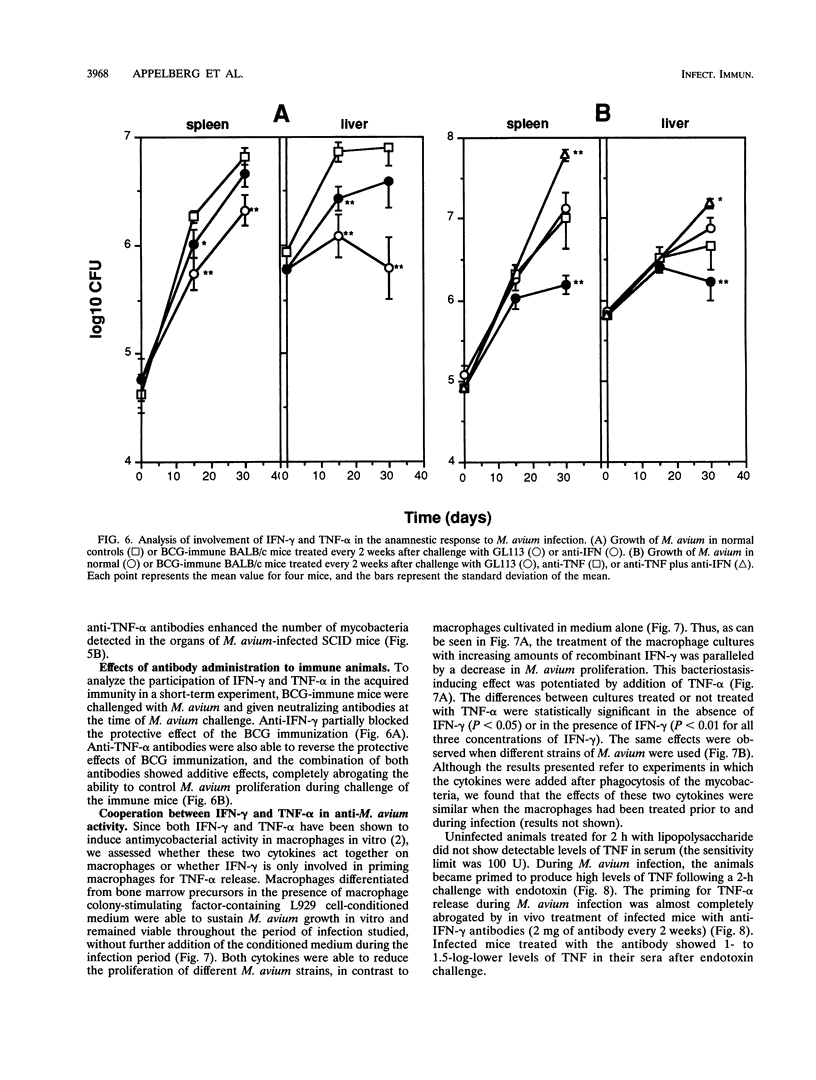
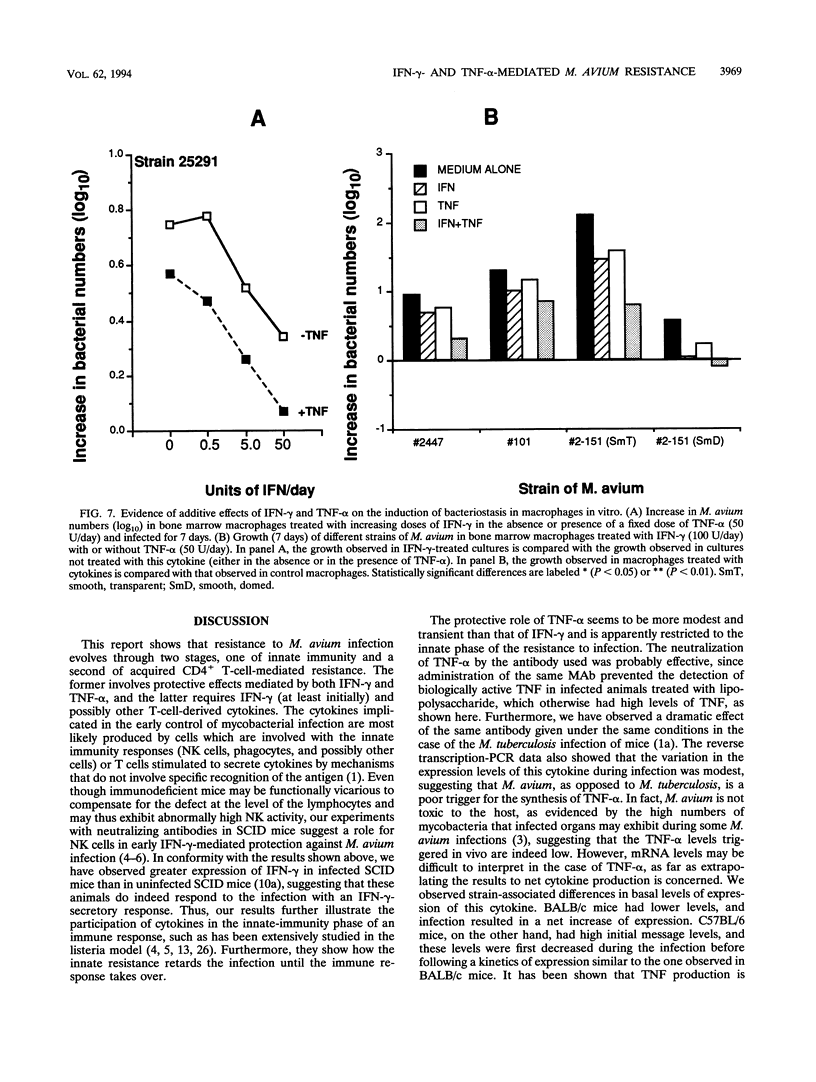
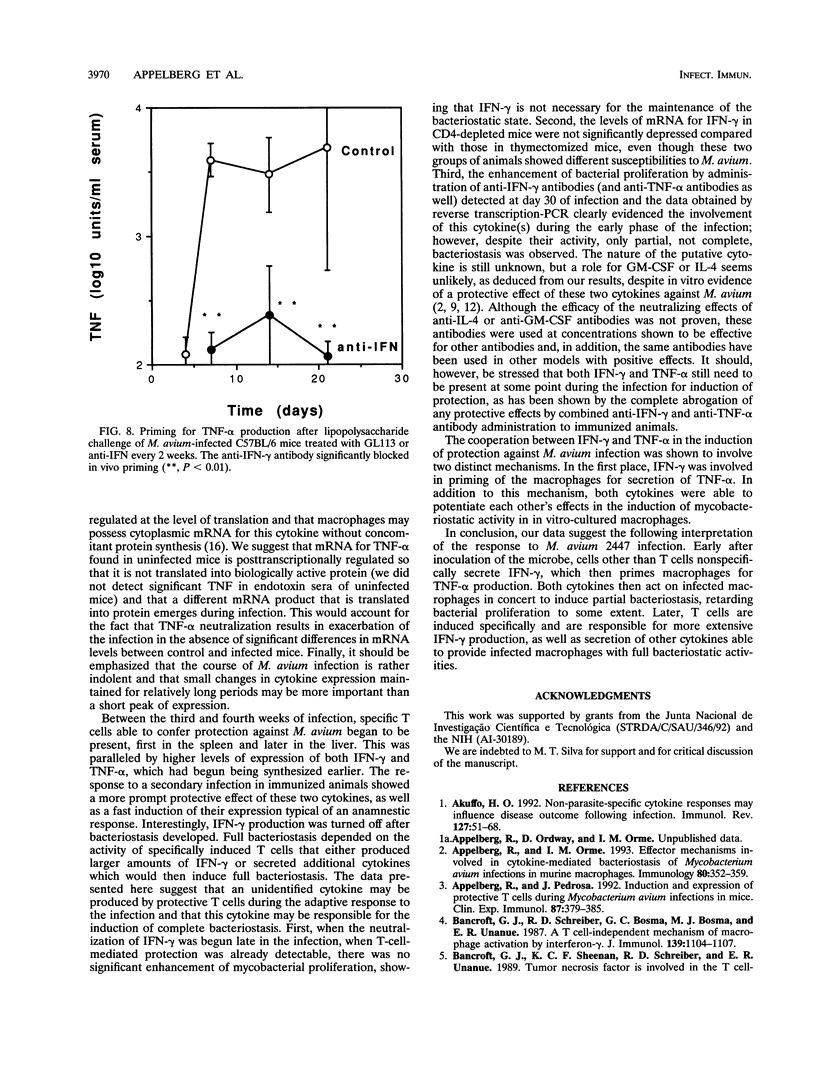
Abstract
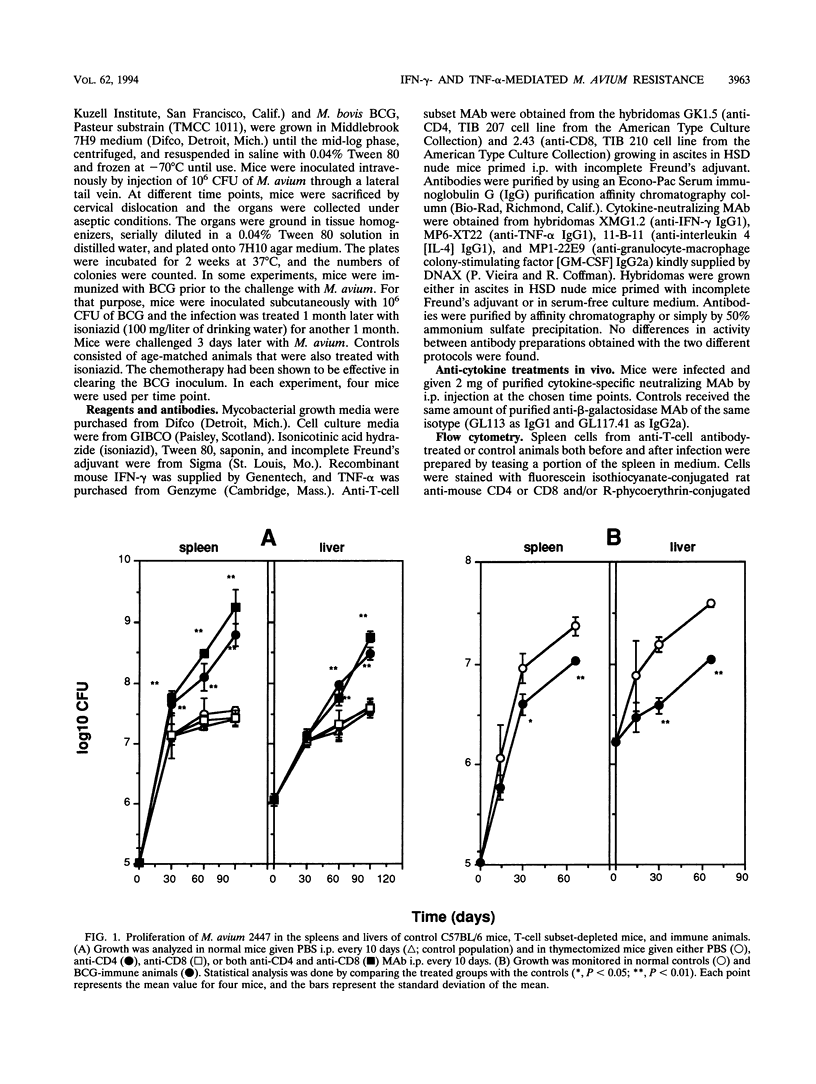
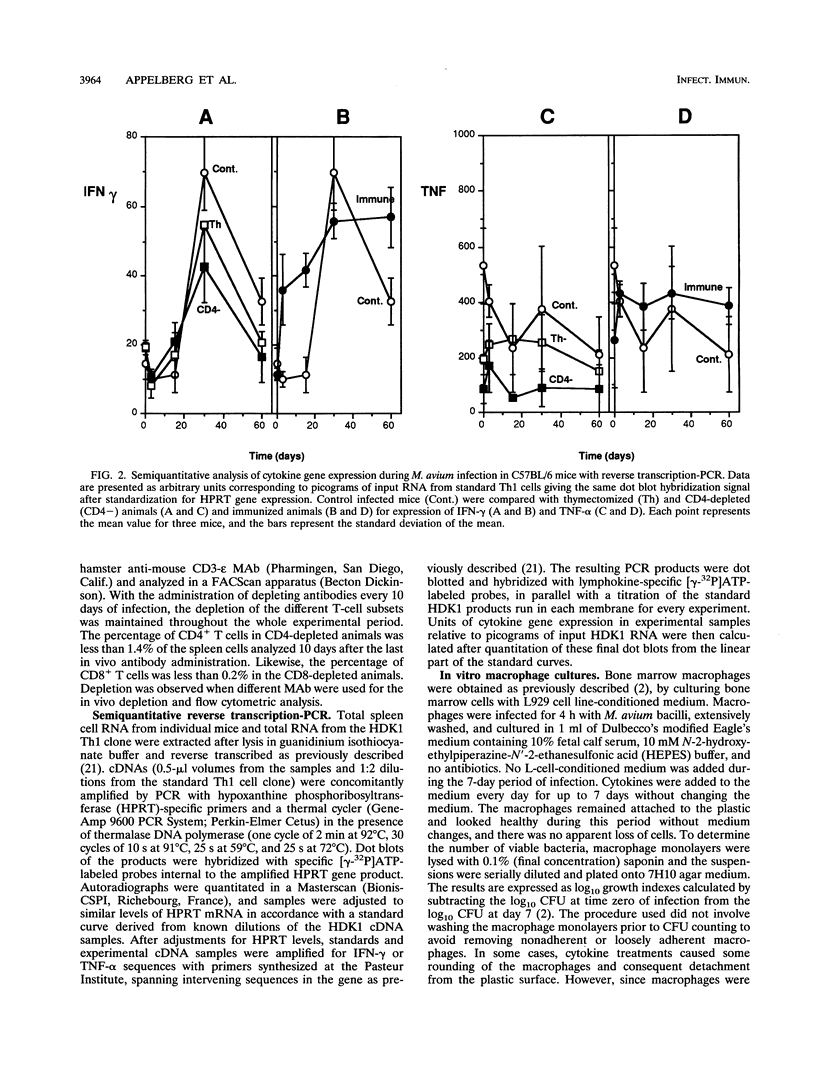
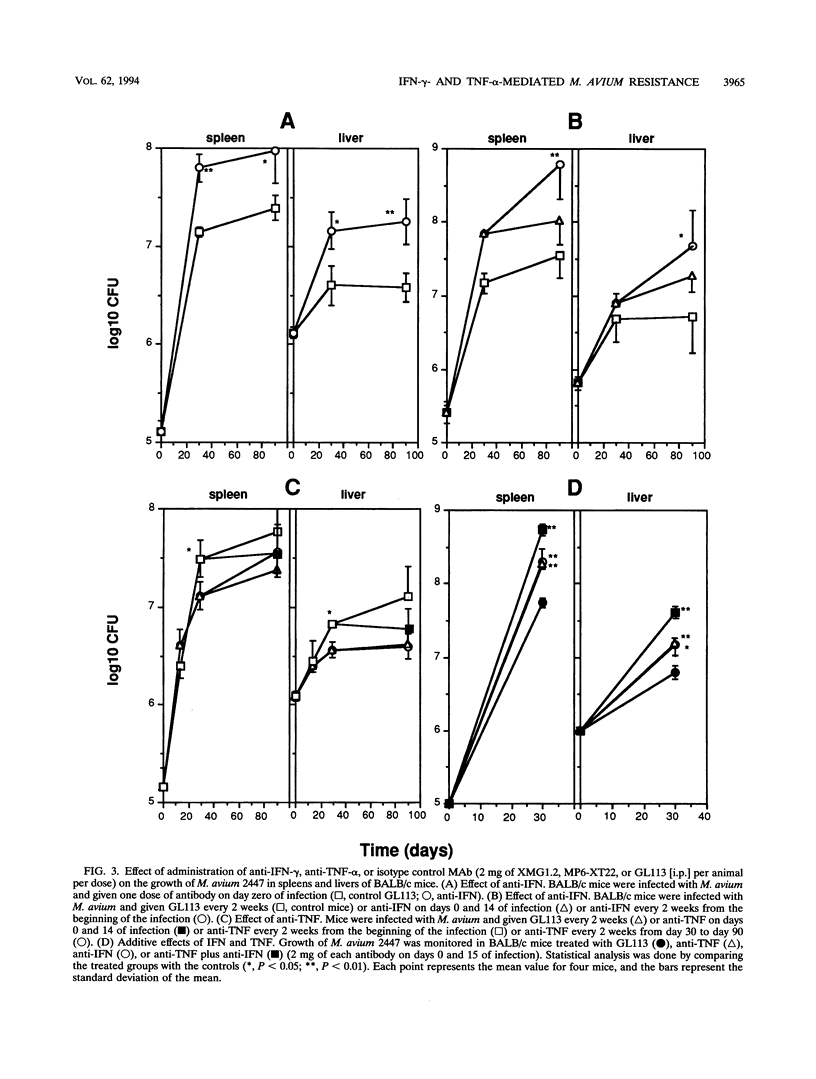
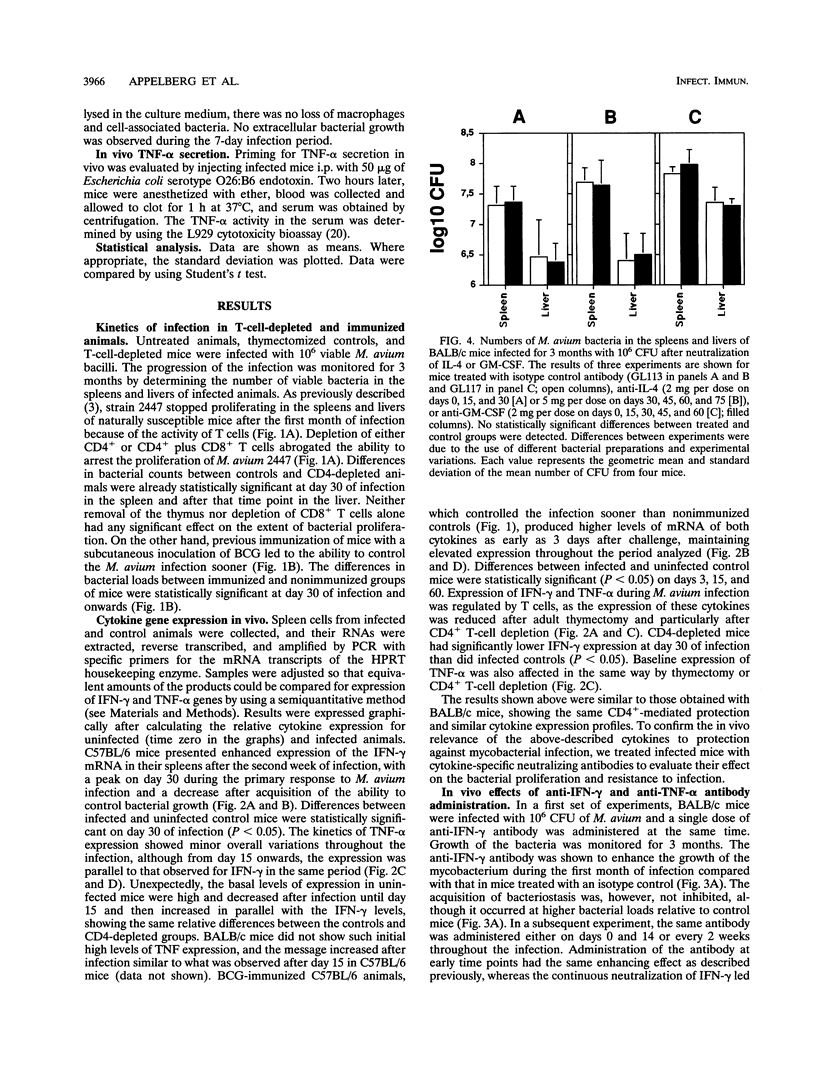
To design an effective immunotherapy for Mycobacterium avium infections, the protective host response to the infection must be known. Here we analyzed the role of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in the innate and acquired responses to M. avium infections in mice. T-cell depletion studies showed that CD4+ T cells were required for control of the infection. CD(4+)-depleted mice showed enhanced bacterial proliferation and at the same time showed a reduction in the level of expression of both IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha mRNAs in spleen cells. In contrast, M. bovis BCG immunization restricted M. avium proliferation and at the same time promoted expression of the mRNAs for the two cytokines. In vivo depletion studies using specific monoclonal antibodies showed that both IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha are involved in an early protection possibly involving NK cells, and furthermore, IFN-gamma is involved in the later T-cell-protective response to infection. In vivo neutralization of IFN-gamma during M. avium infection also blocked the priming for enhanced TNF-alpha secretion triggered by endotoxin. Both cytokines were found to be involved in the resistance expressed in BCG-immunized animals and exhibited additive bacteriostatic effects in vitro on bone marrow-derived macrophages infected with different strains of M. avium. These data suggest that both cytokines act in an additive or synergistic fashion in the induction of bacteriostasis and that IFN-gamma is also involved in priming TNF-alpha secretion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akuffo H. O. Non-parasite-specific cytokine responses may influence disease outcome following infection. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:51–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg R., Orme I. M. Effector mechanisms involved in cytokine-mediated bacteriostasis of Mycobacterium avium infections in murine macrophages. Immunology. 1993 Nov;80(3):352–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg R., Pedrosa J. Induction and expression of protective T cells during Mycobacterium avium infections in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Mar;87(3):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Schreiber R. D., Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Unanue E. R. A T cell-independent mechanism of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1104–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Tumor necrosis factor is involved in the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation in scid mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Kolonoski P., Young L. S. Natural killer cell activity and macrophage-dependent inhibition of growth or killing of Mycobacterium avium complex in a mouse model. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Feb;47(2):135–141. doi: 10.1002/jlb.47.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Stevens P., Kolonoski P., Wu M., Young L. S. Treatment of experimental disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in mice with recombinant IL-2 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2996–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activates human macrophages to inhibit growth or kill Mycobacterium avium complex. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Jul;48(1):67–73. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Michelini-Norris M. B., Djeu J. Y. Interferon decreases the growth inhibition of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex by fresh human monocytes but not by culture-derived macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):152–157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gregg E. O. Modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in murine macrophages: reversal of unresponsiveness to interferon-gamma by indomethacin or interleukin-4. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in vivo by cytokines: involvement of tumour necrosis factor in resistance to atypical mycobacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):466–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. L., North R. J. Early gamma interferon production by natural killer cells is important in defense against murine listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2892–2900. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2892-2900.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. K., 3rd, Hedegaard H. B., Zlotnik A., Gangadharam P. R., Johnston R. B., Jr, Pabst M. J. Chronic infection due to Mycobacterium intracellulare in mice: association with macrophage release of prostaglandin E2 and reversal by injection of indomethacin, muramyl dipeptide, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1820–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory C. M., Hubbard R. D., Collins F. M. Effects of in vivo T lymphocyte subset depletion on mycobacterial infections in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Mar;51(3):225–229. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Brown T., Beutler B. Endotoxin-responsive sequences control cachectin/tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis at the translational level. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):465–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshan K. V., Gangadharam P. R. In vivo depletion of natural killer cell activity leads to enhanced multiplication of Mycobacterium avium complex in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2818–2821. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2818-2821.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr Mycobacterium avium complex infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 9;324(19):1332–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105093241906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. A., Hopewell P. C., Yajko D. M., Hadley W. K., Lazarus E., Mohanty P. K., Modin G. W., Feigal D. W., Cusick P. S., Sande M. A. Natural history of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):994–998. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Hieny S., Sher A., O'Garra A. Detection of in vivo expression of interleukin-10 using a semi-quantitative polymerase chain reaction method in Schistosoma mansoni infected mice. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jun 18;162(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90386-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale S. D., Byrd L. T., Southern P. M., Jockusch J. D., Cal S. X., Wynne B. A. Incidence of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex bacteremia in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1082–1085. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Furney S. K., Roberts A. D. Dissemination of enteric Mycobacterium avium infections in mice rendered immunodeficient by thymectomy and CD4 depletion or by prior infection with murine AIDS retroviruses. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4747–4753. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4747-4753.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires K. E., Brown S. T., Armstrong D., Murphy W. F., Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma treatment for Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex bacillemia in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):686–687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toba H., Crawford J. T., Ellner J. J. Pathogenicity of Mycobacterium avium for human monocytes: absence of macrophage-activating factor activity of gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.239-244.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wherry J. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Regulation of gamma interferon production by natural killer cells in scid mice: roles of tumor necrosis factor and bacterial stimuli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1709–1715. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1709-1715.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


