Abstract
To investigate the immune response to human infection with the fungus Coccidioides immitis, we measured cytokine production from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and plastic-adherent monocytes/macrophages (Mphi) isolated from healthy subjects who were skin test positive to spherulin, healthy subjects who were skin test negative, and patients with active coccidioidomycosis. PBMC and Mphi from all these donor groups secreted increased levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-6 in response to stimulation with formalin-killed spherules (FKS), as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Viable C. immitis spherules also stimulated PBMC and Mphi from healthy subjects and patients to secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-6, although at levels lower than those induced by FKS. The production of these acute inflammatory cytokines may contribute to the immunopathogenesis of active coccidioidomycosis and could account for the toxicity of the FKS vaccine in humans.
Full text
PDF
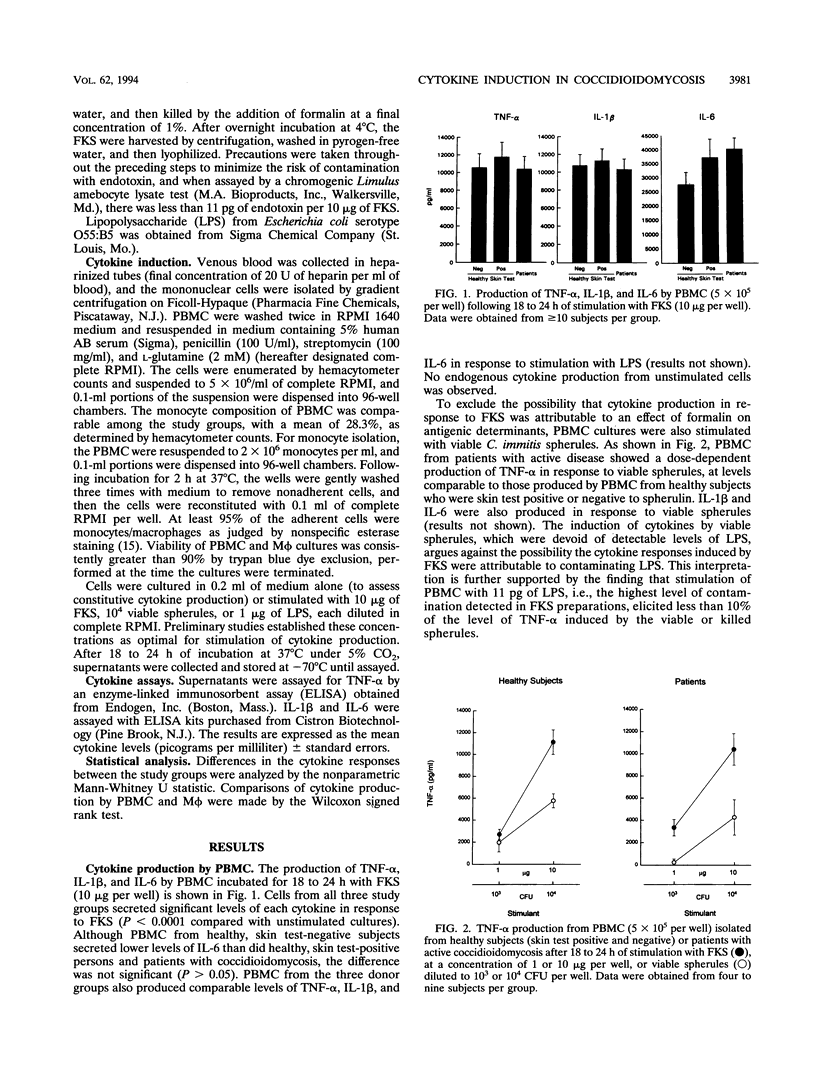
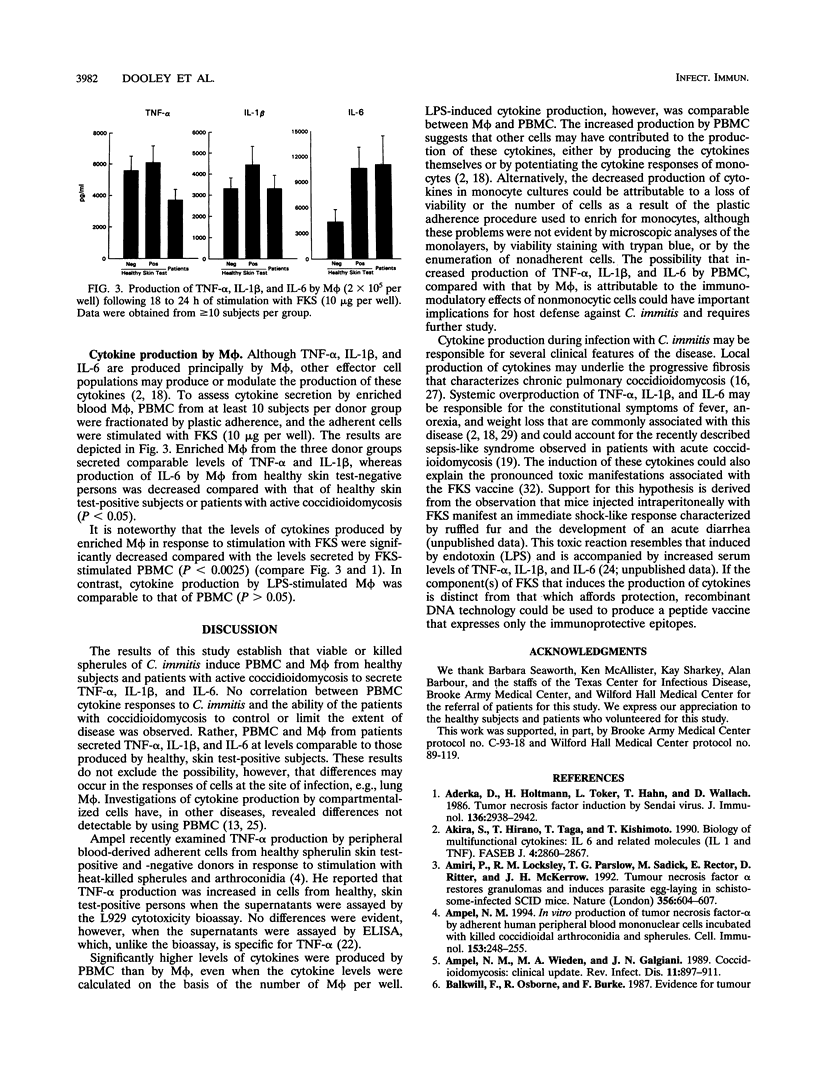

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Holtmann H., Toker L., Hahn T., Wallach D. Tumor necrosis factor induction by Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2938–2942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiri P., Locksley R. M., Parslow T. G., Sadick M., Rector E., Ritter D., McKerrow J. H. Tumour necrosis factor alpha restores granulomas and induces parasite egg-laying in schistosome-infected SCID mice. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):604–607. doi: 10.1038/356604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M. In vitro production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by adherent human peripheral blood mononuclear cells incubated with killed coccidioidal arthroconidia and spherules. Cell Immunol. 1994 Jan;153(1):248–255. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Wieden M. A., Galgiani J. N. Coccidioidomycosis: clinical update. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;11(6):897–911. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F., Osborne R., Burke F., Naylor S., Talbot D., Durbin H., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Evidence for tumour necrosis factor/cachectin production in cancer. Lancet. 1987 Nov 28;2(8570):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Fong S. J., Brennan P. J., Twomey P. E., Mazumder A., Modlin R. L. Local production of tumor necrosis factor and IFN-gamma in tuberculous pleuritis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L. Effects of recombinant gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor on in vitro interactions of human mononuclear phagocytes with Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4227–4229. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4227-4229.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L. Fungicidal activation of murine macrophages by recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2951–2955. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2951-2955.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Mar;117(3):559–585. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part II. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):727–771. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Bukasa K., Sindic C. J., Van Damme J., Van Snick J. Elevated levels of the 26K human hybridoma growth factor (interleukin 6) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute infection of the central nervous system. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):320–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël-Biet D., Cadranel J., Beldjord K., Andrieu J. M., Jeffrey A., Even P. Tumor necrosis factor production in HIV-seropositive subjects. Relationship with lung opportunistic infections and HIV expression in alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):490–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs E. J. Fibrogenic cytokines: the role of immune mediators in the development of scar tissue. Immunol Today. 1991 Jan;12(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. M., Williams P. L., Ampel N. M. Acute pulmonary coccidioidomycosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia and septic shock: a report of two cases. Am J Med. 1993 Aug;95(2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90267-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Cytokines and HIV infection: is AIDS a tumor necrosis factor disease? AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1405–1417. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Leung H., Woolley J. Assays for tumour necrosis factor and related cytokines. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 6;116(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Taverne J., Mehlert A., Bate C. A., Brealey R. J., Meager A., Rook G. A., Playfair J. H. Lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the production of tumour necrosis factor from human and murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):240–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Aung H., Takeuchi M., Kusume K., Izumi T. IL-1 and IL-1 inhibitory activity in the culture supernatants of alveolar macrophages from patients with interstitial lung diseases. Chest. 1991 Mar;99(3):674–680. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.3.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeh M. The role of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Intern Med. 1990 Dec;228(6):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Collart M. A., Grau G. E., Kapanci Y., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin plays a key role in bleomycin-induced pneumopathy and fibrosis. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):655–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slagle D. C., Cox R. A., Kuruganti U. Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1916–1921. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1916-1921.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Cachectin: a hormone that triggers acute shock and chronic cachexia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):413–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



