Abstract
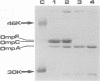
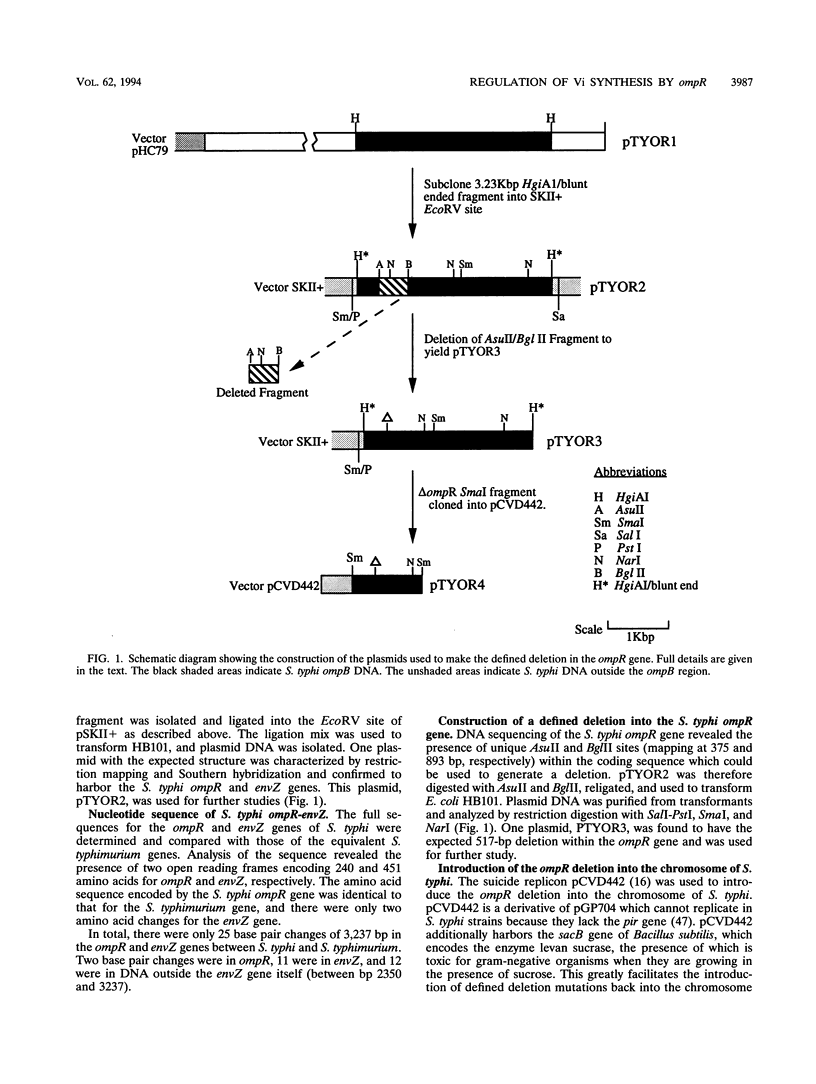
The ompB operon, comprising the ompR and envZ genes, was cloned from a Salmonella typhi Ty2 cosmid bank and characterized by DNA sequence analysis. The S. typhi ompR and envZ genes contained open reading frames encoding proteins of 240 and 451 amino acids, respectively. Comparison with the Salmonella typhimurium OmpB protein sequences revealed 99.5% homology. The DNA sequence data were used to identify appropriate restriction sites for generating a defined deletion of 517 bp within the open reading frame of the ompR gene. This deletion was introduced by homologous recombination into the chromosomes of two S. typhi strains which already harbored defined deletions in both the aroC and aroD genes. The presence of the deletions within ompR was confirmed by Southern hybridization and sequencing of the DNA fragments surrounding the deleted regions by PCR. The S. typhi ompR mutants displayed a marked decrease in OmpC and OmpF porin expression as demonstrated by examination of outer membrane preparations. It was also found that S. typhi strains harboring the defined ompR deletions no longer agglutinated with Vi antiserum. However, when a functional ompB operon was introduced back into the S. typhi ompR mutants, either on a multicopy plasmid or as a single-copy chromosomal replacement, the Vi+ phenotype was restored. The levels of Vi synthesis were also found to be sensitive to different concentrations of sodium chloride present in the growth medium, although the levels of sensitivity varied between different isolates of S. typhi. It is therefore concluded that the ompR-envZ two component regulatory system plays an important role in the regulation of Vi polysaccharide synthesis in S. typhi and that one of the environmental signals for this regulation may be osmolarity.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpuche Aranda C. M., Swanson J. A., Loomis W. P., Miller S. I. Salmonella typhimurium activates virulence gene transcription within acidified macrophage phagosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10079–10083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlau I., Miller S. I. A PhoP-repressed gene promotes Salmonella typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4475–4484. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4475-4484.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Fontaine A., Sansonetti P. J. The two-component regulatory system ompR-envZ controls the virulence of Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6274–6281. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6274-6281.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Sanna M. G., Fontaine A., Sansonetti P. J. OmpC is involved in invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3625–3635. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3625-3635.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A., DeVault J. D., Chakrabarty A. M. High osmolarity is a signal for enhanced algD transcription in mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2312–2317. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2312-2317.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield S. N., Dorman C. J., Hayward C., Dougan G. Role of ompR-dependent genes in Salmonella typhimurium virulence: mutants deficient in both ompC and ompF are attenuated in vivo. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.449-452.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield S. N., Strahan K., Pickard D., Charles I. G., Hormaeche C. E., Dougan G. Evaluation of Salmonella typhimurium strains harbouring defined mutations in htrA and aroA in the murine salmonellosis model. Microb Pathog. 1992 Feb;12(2):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield S., Roberts M., Londono P., Cropley I., Douce G., Dougan G. The development of oral vaccines based on live attenuated Salmonella strains. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993 Jun;7(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1993.tb00374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Dikshit R., Konyecsni W. M., Chakrabarty A. M., Misra T. K. The algR gene, which regulates mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, belongs to a class of environmentally responsive genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1278-1283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional regulation of the algD gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4567–4581. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Mohr C. D., Martin D. W. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: signal transduction and histone-like elements in the regulation of bacterial virulence. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1577–1583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Chatfield S., Higgins C. F., Hayward C., Dougan G. Characterization of porin and ompR mutants of a virulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium: ompR mutants are attenuated in vivo. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2136–2140. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2136-2140.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J. DNA supercoiling and environmental regulation of gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):745–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.745-749.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Chatfield S., Pickard D., Bester J., O'Callaghan D., Maskell D. Construction and characterization of vaccine strains of Salmonella harboring mutations in two different aro genes. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1329–1335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Hall H. K. Adaptive acidification tolerance response of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.771-778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Stout V. Regulation of capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1599–1606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeme-Cook K. A., May G., Bremer E., Higgins C. F. Osmotic regulation of porin expression: a role for DNA supercoiling. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1287–1294. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Li N., Yokoyama H., Ezaki T. Complete nucleotide sequence and molecular characterization of ViaB region encoding Vi antigen in Salmonella typhi. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4456–4465. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4456-4465.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde M., Portalier R. Regulation of major outer membrane porin proteins of Escherichia coli K 12 by pH. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):511–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00328148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hone D. M., Harris A. M., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Levine M. M. Construction of genetically defined double aro mutants of Salmonella typhi. Vaccine. 1991 Nov;9(11):810–816. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90218-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houng H. S., Noon K. F., Ou J. T., Baron L. S. Expression of Vi antigen in Escherichia coli K-12: characterization of ViaB from Citrobacter freundii and identity of ViaA with RcsB. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5910–5915. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5910-5915.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaratne P., Keenleyside W. J., MacLachlan P. R., Dodgson C., Whitfield C. Characterization of rcsB and rcsC from Escherichia coli O9:K30:H12 and examination of the role of the rcs regulatory system in expression of group I capsular polysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5384–5394. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5384-5394.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Charles I., Dougan G., Pickard D., O'Gaora P., Costa G., Ali T., Miller I., Hormaeche C. The role of a stress-response protein in Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. W., Dougan G., Hayward C., Mackensie N., Collins P., Chatfield S. N. Oral vaccination of calves against experimental salmonellosis using a double aro mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Vaccine. 1991 Jan;9(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90313-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Misra T. K., Chakrabarty A. M. AlgR3, a protein resembling eukaryotic histone H1, regulates alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2887–2891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B. Live oral vaccines against cholera: an update. Vaccine. 1993;11(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90019-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Laamanen I., Palva E. T. Structure and expression of the ompB operon, the regulatory locus for the outer membrane porin regulon in Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 20;201(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Kärnell A., Stocker B. A., Katakura S., Sweiha H., Reinholt F. P. Development of an auxotrophic oral live Shigella flexneri vaccine. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):146–150. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Steigbigel R. T. Role of the Vi antigen of Salmonella typhi in resistance to host defense in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Nov;108(5):506–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Reversible phosphorylation of an enhancer binding protein regulates the transcription of bacterial nitrogen utilization genes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Dec;13(12):475–479. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastroeni P., Villarreal-Ramos B., Hormaeche C. E. Adoptive transfer of immunity to oral challenge with virulent salmonellae in innately susceptible BALB/c mice requires both immune serum and T cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3981–3984. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3981-3984.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Environmental signals controlling expression of virulence determinants in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.1-7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Mekalanos J. J. Constitutive expression of the phoP regulon attenuates Salmonella virulence and survival within macrophages. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2485–2490. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2485-2490.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Mekalanos J. J. Strategies for the development of vaccines for typhoid fever, shigellosis, and cholera. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;569:145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb27365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Kanamaru K., Aiba H., Mizuno T. Signal transduction and osmoregulation in Escherichia coli. A novel type of mutation in the phosphorylation domain of the activator protein, OmpR, results in a defect in its phosphorylation-dependent DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10775–10780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni Bhriain N., Dorman C. J., Higgins C. F. An overlap between osmotic and anaerobic stress responses: a potential role for DNA supercoiling in the coordinate regulation of gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):933–942. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D., Maskell D., Liew F. Y., Easmon C. S., Dougan G. Characterization of aromatic- and purine-dependent Salmonella typhimurium: attention, persistence, and ability to induce protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):419–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.419-423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puente J. L., Verdugo-Rodríguez A., Calva E. Expression of Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli OmpC is influenced differently by medium osmolarity; dependence on Escherichia coli OmpR. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1205–1210. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. D., Robbins J. B. Reexamination of the protective role of the capsular polysaccharide (Vi antigen) of Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):436–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo T. A., Singh G. An extraintestinal, pathogenic isolate of Escherichia coli (O4/K54/H5) can produce a group 1 capsule which is divergently regulated from its constitutively produced group 2, K54 capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7617–7623. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7617-7623.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Arondel J. Construction and evaluation of a double mutant of Shigella flexneri as a candidate for oral vaccination against shigellosis. Vaccine. 1989 Oct;7(5):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W. The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen D., Jones C., Schofield J. P. A rapid method for isolating high quality plasmid DNA suitable for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7463–7464. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Hone D. M., Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M., Losonsky G., Guers L., Harris A. M., Edelman R., Levine M. M. Comparison of the safety and immunogenicity of delta aroC delta aroD and delta cya delta crp Salmonella typhi strains in adult volunteers. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):536–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.536-541.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Losonsky G., Taylor D. N., Baron L. S., Kopecko D., Cryz S., Levine M. M. Lack of immune response to the Vi component of a Vi-positive variant of the Salmonella typhi live oral vaccine strain Ty21a in human studies. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):901–904. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartera C., Metcalf E. S. Osmolarity and growth phase overlap in regulation of Salmonella typhi adherence to and invasion of human intestinal cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3084–3089. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3084-3089.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. An optimized freeze-squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90419-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Is cross regulation by phosphorylation of two-component response regulator proteins important in bacteria? J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2053–2058. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2053-2058.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak D. J., Ohman D. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgB, a two-component response regulator of the NtrC family, is required for algD transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1406–1413. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1406-1413.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]