Abstract
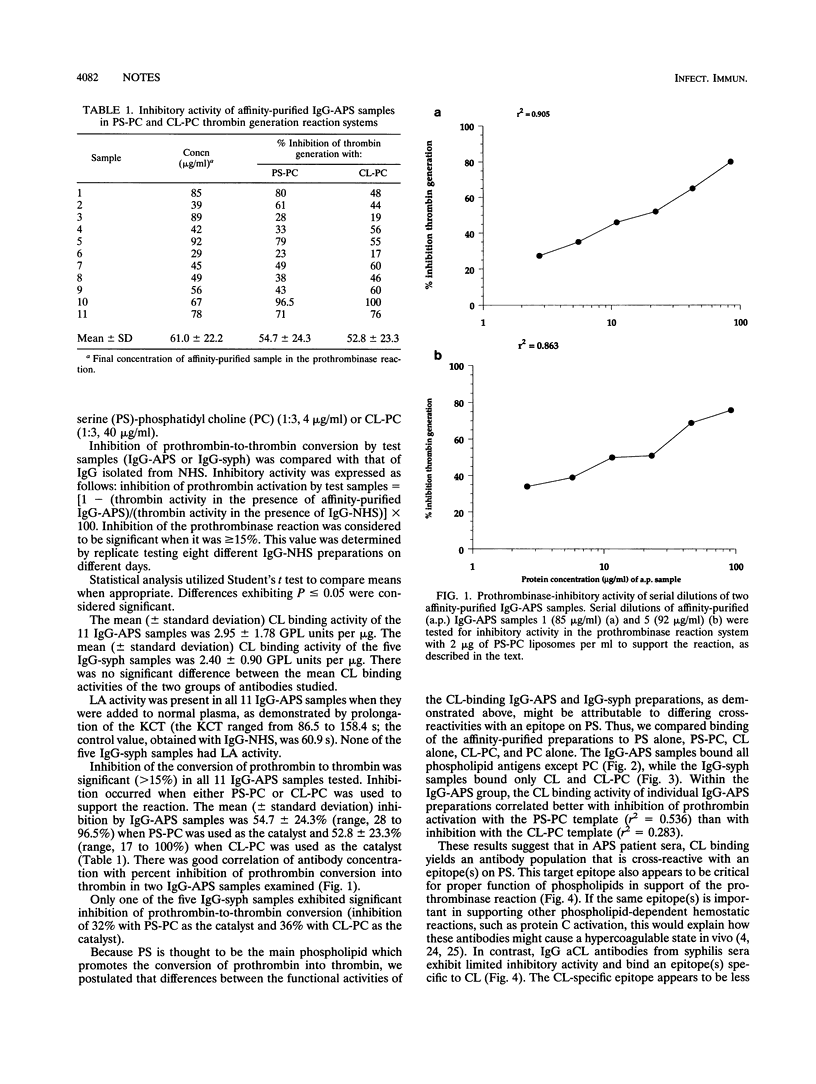
Anticardiolipin antibodies are produced both in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and in patients with syphilis, but lupus anticoagulant activity has been reported only for the former group. To understand these differences, affinity-purified immunoglobulin G anticardiolipin antibodies from APS (n = 11) and syphilis (n = 5) patients were compared. Only the antibodies from the APS group inhibited prothrombin conversion to thrombin and cross-reacted with phosphatidylserine. These findings may enable better definition of the phospholipid epitopes involved in the hemostatic abnormalities of APS.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevers E. M., Galli M., Barbui T., Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. Lupus anticoagulant IgG's (LA) are not directed to phospholipids only, but to a complex of lipid-bound human prothrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Dec 2;66(6):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J. T. Assays for phospholipid-dependent formation of thrombin and Xa: a potential method for quantifying lupus anticoagulant activity. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Oct 1;66(4):453–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cariou R., Tobelem G., Bellucci S., Soria J., Soria C., Maclouf J., Caen J. Effect of lupus anticoagulant on antithrombogenic properties of endothelial cells--inhibition of thrombomodulin-dependent protein C activation. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Aug 30;60(1):54–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaço C. B., Male D. K. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in syphilis and a thrombotic subset of SLE: distinct profiles of epitope specificity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):449–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello P. B., Green F. A. Reactivity patterns of human anticardiolipin and other antiphospholipid antibodies in syphilitic sera. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):771–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T., Rickard K. A., Kronenberg H. A sensitive test demonstrating lupus anticoagulant and its behavioural patterns. Br J Haematol. 1978 Sep;40(1):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Béguin S., Lindhout T., Hemker C. H. Inhibition of phospholipid and platelet-dependent prothrombinase activity in the plasma of patients with lupus anticoagulants. Br J Haematol. 1989 Aug;72(4):549–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb04322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticoagulant activity of beta 2-glycoprotein I is potentiated by a distinct subgroup of anticardiolipin antibodies. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Sep 7;68(3):297–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: isotype distribution and phospholipid specificity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N. Antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jan;74(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Anti-phospholipid antibodies. Clin Rheum Dis. 1985 Dec;11(3):591–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Patel S. P., Hughes G. R. Evaluation of the anti-cardiolipin antibody test: report of an international workshop held 4 April 1986. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):215–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Tincani A., Chan J. K., Englert H., Mantelli P., Allegro F., Ballestrieri G., Hughes G. R. Affinity purified anti-cardiolipin and anti-DNA antibodies. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1985 Aug;17(4):155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Wasley G. D., Hughes G. R. Use of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and of inhibition studies to distinguish between antibodies to cardiolipin from patients with syphilis or autoimmune disorders. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Pierangeli S., Birch D. Anticardiolipin wet workshop report. Fifth International Symposium on antiphospholipid antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;101(5):616–624. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N. Syndrome of the black swan. Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Oct;26(5):324–326. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.5.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson E. A., Lassus A. The occurrence of circulating anticoagulants in patients with syphilitic and biologically false positive antilipoidal antibodies. Ann Clin Res. 1974 Apr;6(2):105–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. V. Antiphospholipid antibodies: new perspectives on antigenic specificity. J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):1774–1777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A., Gharavi A. E., Sammaritano L. R., Habina L., Qamar T., Lockshin M. D. Characteristics of IgG antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and syphilis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Aug;17(8):1036–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou S., Mackworth-Young C. G., Cofiner C., Walport M. J. Heterogeneity of binding reactivity to different phospholipids of antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and with syphilis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malia R. G., Kitchen S., Greaves M., Preston F. E. Inhibition of activated protein C and its cofactor protein S by antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E., Romond E. H. Impaired catalytic function of activated protein C: a new in vitro manifestation of lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2426–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Fujimoto M., Ichikawa K., Suzuki T., Sumida T., Yasuda T., Koike T. Heterogeneity of anticardiolipin antibodies defined by the anticardiolipin cofactor. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3885–3891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S., Høier-Madsen M., Wiik A., Orum O., Strandberg Pedersen N. The specificity of anti-cardiolipin antibodies from syphilis patients and from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):178–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosting J. D., Derksen R. H., Bobbink I. W., Hackeng T. M., Bouma B. N., de Groot P. G. Antiphospholipid antibodies directed against a combination of phospholipids with prothrombin, protein C, or protein S: an explanation for their pathogenic mechanism? Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2618–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Harris E. N., Davis S. A., DeLorenzo G. Beta 2-glycoprotein 1 (beta 2GP1) enhances cardiolipin binding activity but is not the antigen for antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1992 Nov;82(3):565–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb06468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Thiagarajan P. Lupus anticoagulants. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1982;6:263–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett D. A., Brandt J. T. Lupus anticoagulants: misnomer, paradox, riddle, epiphenomenon. Hematol Pathol. 1988;2(3):121–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett D. A., Brandt J. Laboratory identification of the lupus anticoagulant. Br J Haematol. 1989 Oct;73(2):139–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



