Abstract
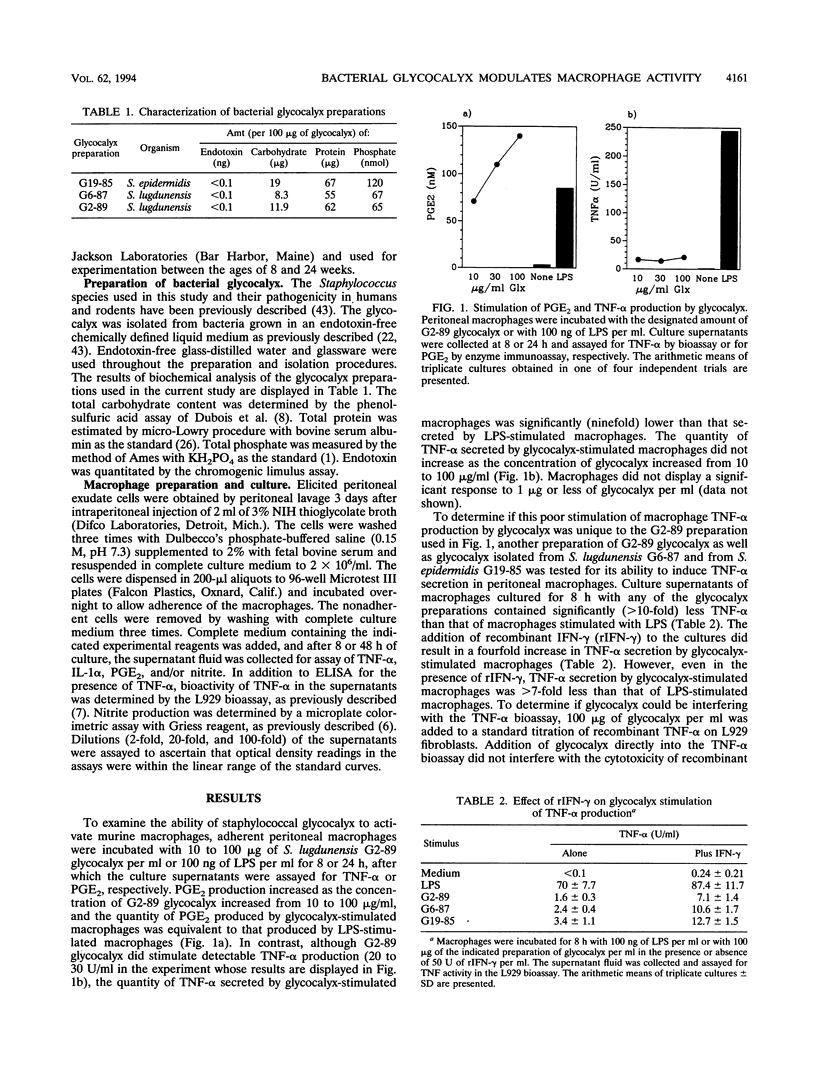
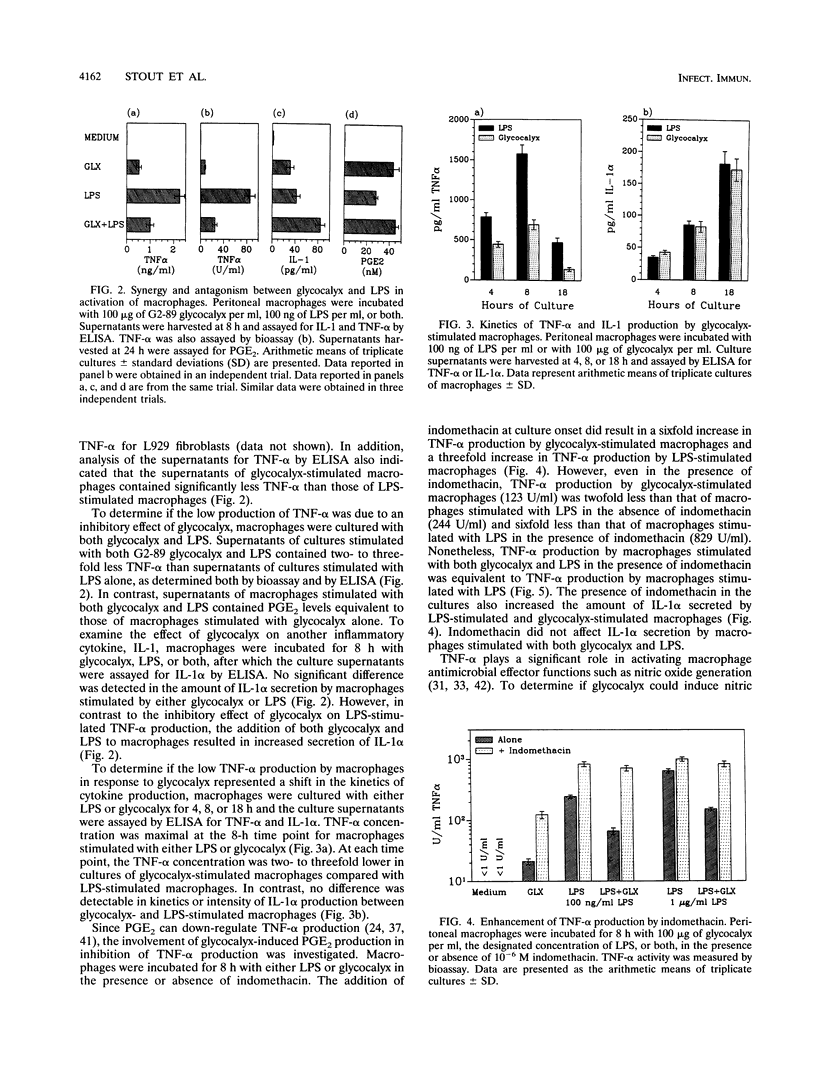
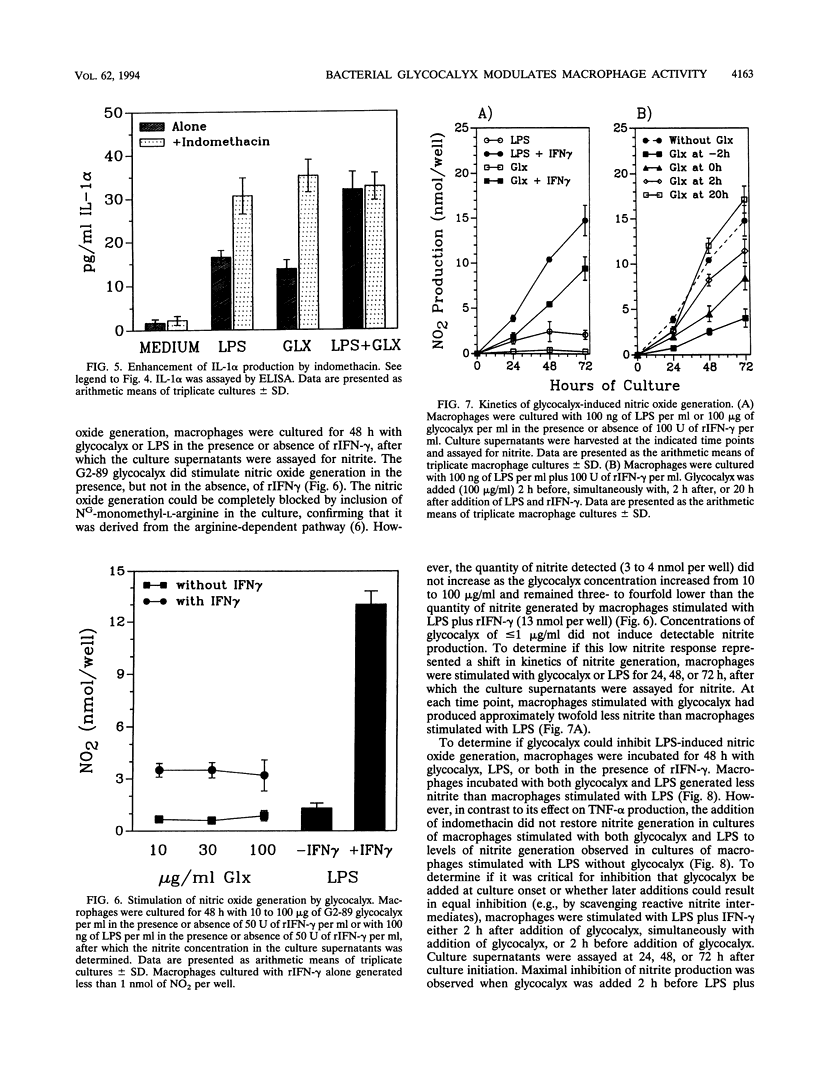
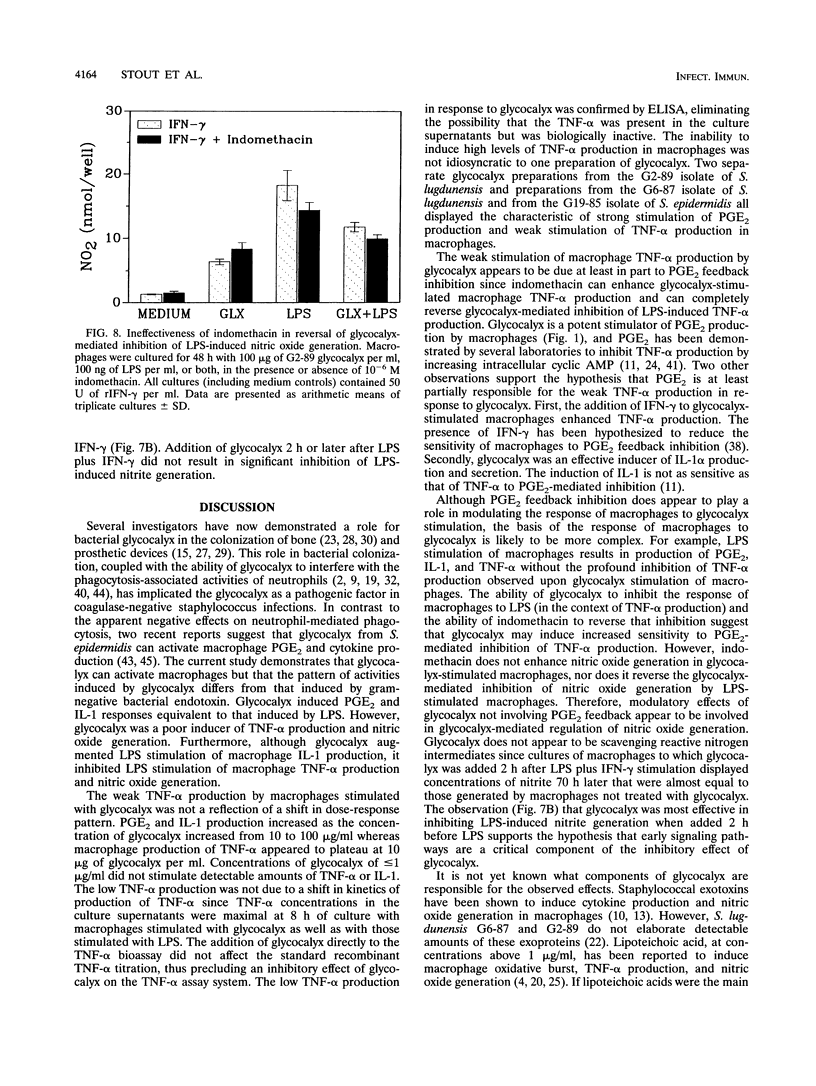
We have examined the effect of staphylococcal glycocalyces on the ability of murine peritoneal macrophages to produce prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and the inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and to generate nitric oxide. Glycocalyx partially purified under endotoxin-free conditions from defined liquid medium cultures of Staphylococcus lugdunensis or Staphylococcus epidermidis was a strong stimulator of PGE2 and IL-1 production. The addition of 10 to 100 micrograms of glycocalyx per ml induced levels of IL-1 and PGE2 production similar to that induced by 0.1 to 1 micrograms of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) per ml. In contrast, glycocalyx induced ninefold less TNF-alpha and three- to fourfold less nitrite than LPS. A modulatory effect was suggested by the observation that the amount of TNF-alpha and nitrite generated remained constant whether the macrophages were stimulated with 10 or 100 micrograms of glycocalyx per ml. A selective modulation of macrophage activation was confirmed by the demonstration that costimulation of macrophages with both glycocalyx and LPS resulted in a reduction in TNF-alpha and nitrite generation relative to stimulation with LPS alone even though costimulation had no effect on PGE2 production and increased IL-1 production. Involvement of PGE2 in this modulatory effect was suggested by the ability of indomethacin to augment glycocalyx-stimulated TNF-alpha production and to reverse the inhibitory effect of glycocalyx on LPS induction of TNF-alpha production. However, the inability of indomethacin to reverse the inhibitory effect of glycocalyx on LPS-induced nitric oxide generation suggests that the selective modulation of macrophage function by glycocalyx may be more complex than increased sensitivity to PGE2 feedback inhibition.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Klonisch T., Nuber P., Fischer W. Stimulation of monokine production by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4614–4620. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4614-4620.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Bailey P. J., Goldenberg M. M., Ford-Hutchinson A. W. The role of arachidonic acid oxygenation products in pain and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:335–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale B. E., Zacharchuk C. M., Shin H. S. Mechanism of macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity: production of a soluble cytotoxic factor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2362–2367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcieri E., Vaudaux P., Huggler E., Lew D., Waldvogel F. Role of bacterial exopolymers and host factors on adherence and phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus in foreign body infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):524–531. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Shannon B. J., Herriott M. J., Kennedy M. J., Rummage J. A., Leu R. W. Staphylococcal exotoxins stimulate nitric oxide-dependent murine macrophage tumoricidal activity. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2987–2993. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2987-2993.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieren M. W., van den Bemd G. J., Ben-Efraim S., Bonta I. L. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, rather than interleukin 1 beta, from human macrophages. Immunol Lett. 1992 Jan;31(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(92)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. H., Kessler R. E., Tabak L. A., Shockman G. D. Limulus lysate activity of lipoteichoic acids. J Dent Res. 1977 Dec;56(12):1500–1500. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560121501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S. D., Iandolo J. J., Chapes S. K. Murine macrophage activation by staphylococcal exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4049–4055. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4049-4055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages: role of reactive nitrogen intermediates. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3213–3218. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3213-3218.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson T. R., Sheth N. K., Rose H. D., Sohnle P. G. Scanning electron microscopy of bacteria adherent to intravascular catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. D., Peters G., Verstegen M., Regelmann W. E. Effect of extracellular slime substance from Staphylococcus epidermidis on the human cellular immune response. Lancet. 1984 Feb 18;1(8373):365–367. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Higashi N., Taki H., Osawa T. Cytolytic mechanisms of activated macrophages. Tumor necrosis factor and L-arginine-dependent mechanisms act synergistically as the major cytolytic mechanisms of activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1425–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. M., Lee D. A., Regelmann W. E., Gray E. D., Peters G., Quie P. G. Interference with granulocyte function by Staphylococcus epidermidis slime. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Fischer W., Keist R., Bassetti S. Macrophage response to bacteria: induction of marked secretory and cellular activities by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3664–3672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3664-3672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson K. P., Ferguson D. A., Jr The Bacteroides glycocalyx as visualized by differential interference contrast microscopy. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Nov;34(11):1189–1195. doi: 10.1139/m88-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson K. P., Keplinger J. L., Gemmell C. G., Kalbfleisch J. H. Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus lugdunensis, Staphylococcus schleiferi, and three other coagulase-negative staphylococci in a mouse model and possible virulence factors. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Jul;36(7):455–463. doi: 10.1139/m90-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson K. P., Mayberry-Carson K. J., Tober-Meyer B., Costerton J. W. Foreign-body-associated experimental osteomyelitis induced with Bacteroides fragilis and Staphylococcus epidermidis in rabbits. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991 May;(266):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmmann V., Benninghoff B., Dröge W. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of peritoneal macrophages is regulated by prostaglandin E2 and cAMP. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Kotb M., Nagauker O., Majumdar G., Alkan M., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Stimulation of oxidative burst in human monocytes by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):566–568. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.566-568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Mode of growth of bacterial pathogens in chronic polymicrobial human osteomyelitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):924–933. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.924-933.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Scanning electron microscopic study of uropathogen adherence to a plastic surface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1018-1024.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Nelligan J., Costerton J. W. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of an infected endocardial pacemaker lead. Circulation. 1982 Dec;66(6):1339–1341. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.6.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Tober-Meyer B., Smith J. K., Lambe D. W., Jr, Costerton J. W. Bacterial adherence and glycocalyx formation in osteomyelitis experimentally induced with Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):825–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.825-833.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Fernández M. A., Fernández M. A., Fresno M. Synergism between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma on macrophage activation for the killing of intracellular Trypanosoma cruzi through a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):301–307. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvik Q. N., Wagner W., Barth E., Wood P., Gristina A. G. Effects of extracellular slime produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis on oxidative responses of rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Invest Surg. 1989;2(4):381–389. doi: 10.3109/08941938909018263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald I. P., Wynn T. A., Sher A., James S. L. Interleukin 10 inhibits macrophage microbicidal activity by blocking the endogenous production of tumor necrosis factor alpha required as a costimulatory factor for interferon gamma-induced activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8676–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps R. P., Stein S. H., Roper R. L. A new view of prostaglandin E regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90064-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz H., Gong J. H., Schmidt A., Nain M., Gemsa D. Release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from macrophages. Enhancement and suppression are dose-dependently regulated by prostaglandin E2 and cyclic nucleotides. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2388–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., Pace J. L. Gamma interferon interferes with the negative regulation of macrophage activation by prostaglandin E2. Mol Immunol. 1984 Mar;21(3):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito S., Onozuka K., Shinomiya H., Nakano M. Sensitivity of bacteria to NaNO2 and to L-arginine-dependent system in murine macrophages. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(4):325–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler R. N., Spengler M. L., Lincoln P., Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L. Dynamics of dibutyryl cyclic AMP- and prostaglandin E2-mediated suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2837–2841. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2837-2841.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D., Ferguson K. P., Li Y. N., Lambe D. W., Jr Staphylococcal exopolysaccharides inhibit lymphocyte proliferative responses by activation of monocyte prostaglandin production. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):922–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.922-927.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D. Macrophage activation by T cells: cognate and non-cognate signals. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veringa E. M., Ferguson D. A., Jr, Lambe D. W., Jr, Verhoef J. Trospectomycin enhances surface phagocytosis of Bacteroides and Staphylococcus by altering the bacterial glycocalyx. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1989 Sep;271(3):311–320. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(89)80029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi G., Gelfand J. A., Jung W. K., Connolly R. J., Burke J. F., Dinarello C. A. Staphylococcus epidermidis induces complement activation, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1, a shock-like state and tissue injury in rabbits without endotoxemia. Comparison to Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1925–1935. doi: 10.1172/JCI115218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



