Abstract
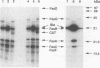
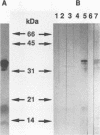
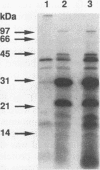
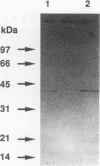
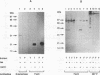
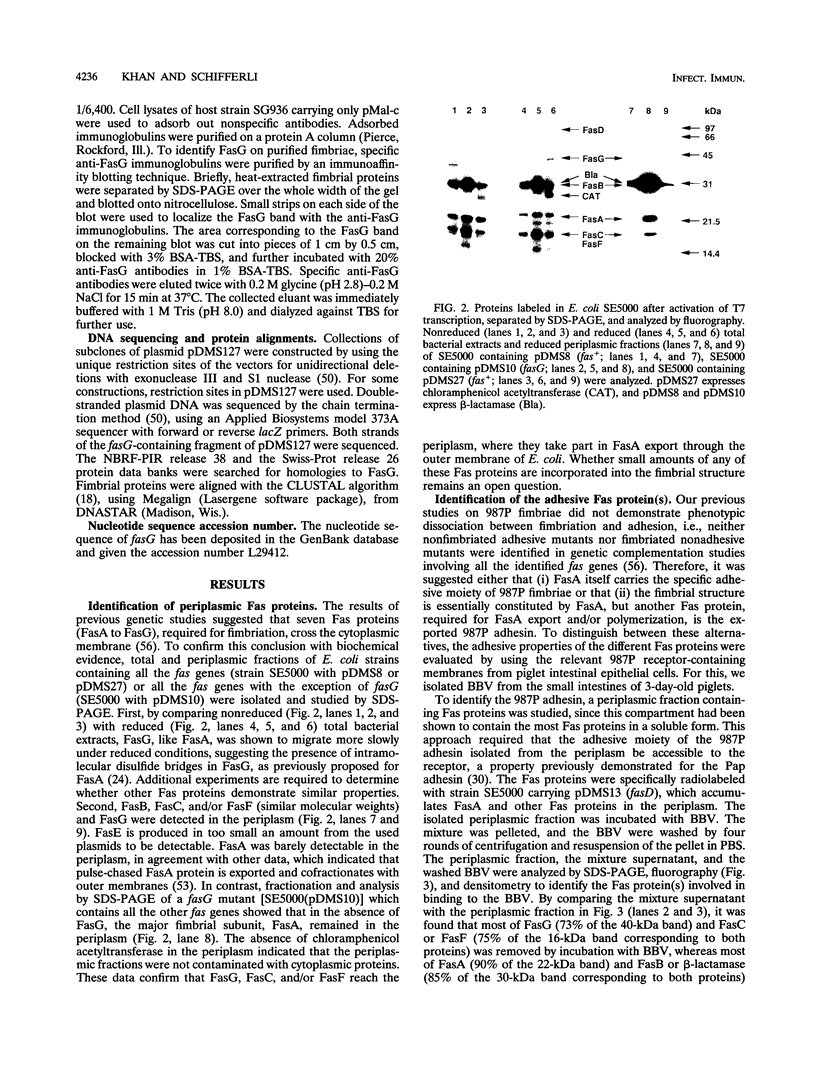
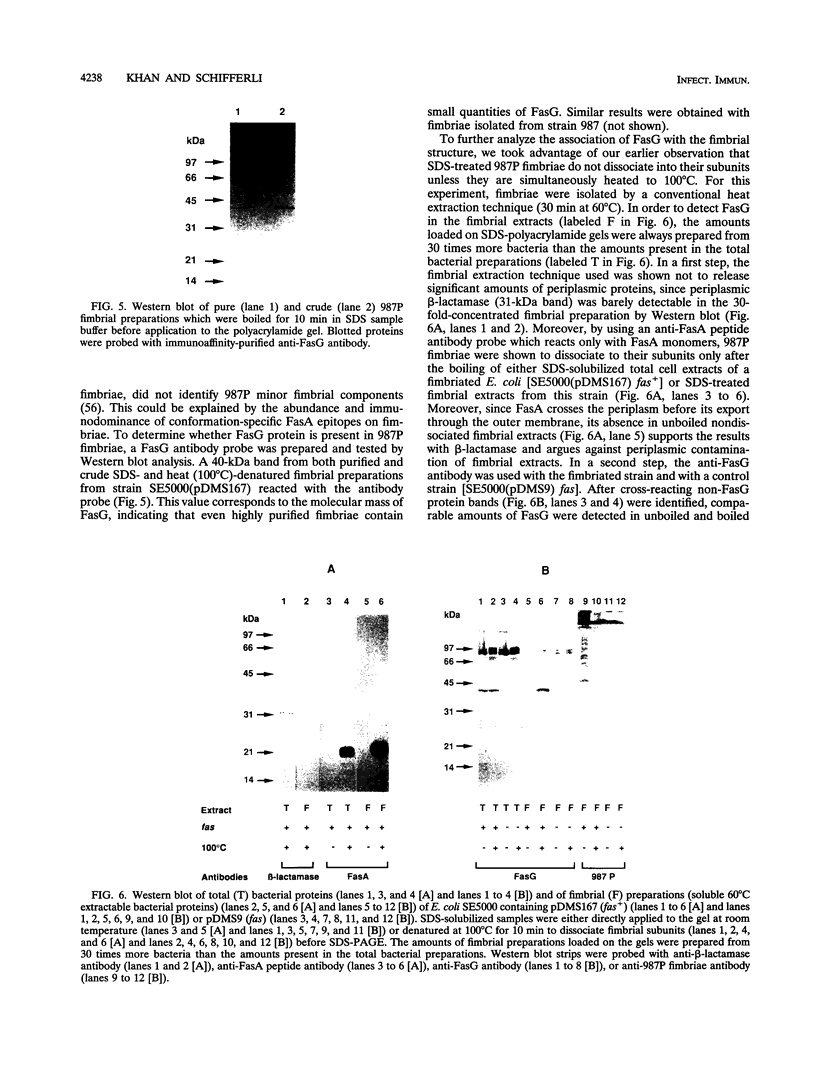
The 987P fimbriae produced by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from piglets mediate bacterial attachment to intestinal epithelial cells. These fimbriae consist essentially of a tight helical arrangement of one structural protein subunit encoded by fasA. Fimbriation and specific adhesion requires the expression of seven additional genes (fasB to fasH). In this study, we investigated whether FasA or another Fas protein, e.g., a potential minor fimbrial component, harbors the binding moiety for the pig 987P receptor glycoproteins. Fas proteins, specifically radiolabeled with an in vivo T7 expression system, were isolated from the periplasm and incubated with receptor-containing brush borders isolated from piglet intestinal epithelial cells. FasG bound best to brush borders, whereas no FasA adhered to them. Additional evidence that FasG, and not FasA, is the 987P adhesin was provided by ligand blotting inhibition assays indicating that FasG alone inhibited fimbrial binding to 987P receptors and that in the absence of FasG, other Fas proteins were not inhibitory. FasG was identified in purified fimbrial preparations with a specific anti-FasG antibody probe. Moreover, FasG was shown to be tightly associated with the fimbrial structure, since it was released only after disassembling fimbriae by heat and sodium dodecyl sulfate treatments. The primary structure of FasG, deduced from the DNA sequence, exhibited 19.1 to 24.4% similarity to FasA and large minor components and/or adhesins of other fimbriae. FasG is the first-described minor fimbrial subunit shown to be essential for both fimbrial biogenesis and specific adhesion.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Goguen J. D., Sun D., Klemm P., Beachey E. H. Identification of two ancillary subunits of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae by using antibodies against synthetic oligopeptides of fim gene products. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5530–5536. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5530-5536.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker D., Willemsen P. T., Simons L. H., van Zijderveld F. G., de Graaf F. K. Characterization of the antigenic and adhesive properties of FaeG, the major subunit of K88 fimbriae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler T., Hoschützky H., Jann K. Analysis of colonization factor antigen I, an adhesin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O78:H11: fimbrial morphology and location of the receptor-binding site. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3876–3882. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3876-3882.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey T. A., Schneider R. A., Dean-Nystrom E. A. Identification of plasmid and chromosomal copies of 987P pilus genes in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli 987. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2249–2252. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2249-2252.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A. Comparison of receptors for 987P pili of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the small intestines of neonatal and older pig. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4030–4035. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4030-4035.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. In vitro adhesion of piliated Escherichia coli to small intestinal villous epithelial cells from rabbits and the identification of a soluble 987P pilus receptor-containing fraction. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1192-1198.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. Location and distribution of a receptor for the 987P pilus of Escherichia coli in small intestines. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.345-348.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Whipp S. C., Moon H. W. Age-specific colonization of porcine intestinal epithelium by 987P-piliated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.82-87.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson K. W., Jacob-Dubuisson F., Striker R. T., Hultgren S. J. Outer-membrane PapC molecular usher discriminately recognizes periplasmic chaperone-pilus subunit complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3670–3674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Casson L. P., Goldberg A. L. Heat shock regulatory gene htpR influences rates of protein degradation and expression of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6647–6651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):151–153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Kuehn M. J., Brändén C. I., Hultgren S. J. Conserved immunoglobulin-like features in a family of periplasmic pilus chaperones in bacteria. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1617–1622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick D. B., Allen B. L., Horn M. A., Clegg S. Adherence to respiratory epithelia by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing Klebsiella pneumoniae type 3 fimbrial gene products. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1577–1588. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1577-1588.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoschützky H., Lottspeich F., Jann K. Isolation and characterization of the alpha-galactosyl-1,4-beta-galactosyl-specific adhesin (P adhesin) from fimbriated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):76–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.76-81.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Lindberg F., Magnusson G., Kihlberg J., Tennent J. M., Normark S. The PapG adhesin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli contains separate regions for receptor binding and for the incorporation into the pilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4357–4361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Normark S., Abraham S. N. Chaperone-assisted assembly and molecular architecture of adhesive pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:383–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Richter P. Escherichia coli 987P pilus: purification and partial characterization. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.784-789.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. A., Simons B. H., de Graaf F. K. The role of lysine-132 and arginine-136 in the receptor-binding domain of the K99 fibrillar subunit. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1805–1808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Hoschützky H. Nature and organization of adhesins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:55–70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaasen P., de Graaf F. K. Characterization of FapR, a positive regulator of expression of the 987P operon in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1779–1783. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lund B., Johansson L., Normark S. Localization of the receptor-binding protein adhesin at the tip of the bacterial pilus. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):84–87. doi: 10.1038/328084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Tennent J. M., Hultgren S. J., Lund B., Normark S. PapD, a periplasmic transport protein in P-pilus biogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6052–6058. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6052-6058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lintermans P. F., Bertels A., Schlicker C., Deboeck F., Charlier G., Pohl P., Norgren M., Normark S., van Montagu M., De Greve H. Identification, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the F17-G gene, which determines receptor binding of Escherichia coli F17 fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3366–3373. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3366-3373.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe M. A., Holt S. C., Eisenstein B. I. Immunoelectron microscopic analysis of elongation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):157–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.157-163.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund B. I., Tennent J. M., Garcia E., Hamers A., Båga M., Lindberg F., Gaastra W., Normark S. Horizontal gene transfer of the Escherichia coli pap and prs pili operons as a mechanism for the development of tissue-specific adhesive properties. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2225–2242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middeldorp J. M., Witholt B. An in vitro system to study interactions between bacteria and epithelial cells at the molecular level. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jan;129(1):179–190. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moch T., Hoschützky H., Hacker J., Kröncke K. D., Jann K. Isolation and characterization of the alpha-sialyl-beta-2,3-galactosyl-specific adhesin from fimbriated Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3462–3466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Bunn T. O. Vaccines for preventing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections in farm animals. Vaccine. 1993;11(2):213–200. doi: 10.1016/0264-410X(93)90020-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Colonization factor antigens of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in animals. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:147–165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine intestine by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: selection of piliated forms in vivo, adhesion of piliated forms to epithelial cells in vitro, and incidence of a pilus antigen among porcine enteropathogenic E. coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.344-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E., To C. C., Brinton C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enteric enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection by vaccinating dams with purified pili. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):269–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.269-274.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Normark S., Lark D., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S., Svanborg-Edén C., Båga M., Uhlin B. E. Mutations in E coli cistrons affecting adhesion to human cells do not abolish Pap pili fiber formation. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Courtney H. S., Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for adherence of bacteria to animal cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.512-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Sharon N. Adhesins as lectins: specificity and role in infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:91–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Serologic classification of fimbriae. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:71–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., De Graaf F. K. Genetic organization and biogenesis of adhesive fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(4):285–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00393521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., de Graaf M., de Boer L., Bakker D., Vader C. E., Mooi F. R., de Graaf F. K. Detection and identification of FaeC as a minor component of K88 fibrillae of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):645–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponniah S., Endres R. O., Hasty D. L., Abraham S. N. Fragmentation of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae exposes cryptic D-mannose-binding sites. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4195–4202. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4195-4202.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegman N., Hoschützky H., van Die I., Hoekstra W., Jann K., Bergmans H. Immunocytochemical analysis of P-fimbrial structure: localization of minor subunits and the influence of the minor subunit FsoE on the biogenesis of the adhesin. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1193–1198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegman N., van Die I., Leunissen J., Hoekstra W., Bergmans H. Biogenesis of F7(1) and F7(2) fimbriae of uropathogenic Escherichia coli: influence of the FsoF and FstFG proteins and localization of the Fso/FstE protein. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H. Use of monoclonal antibodies to probe subunit- and polymer-specific epitopes of 987P fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):923–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.923-930.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Alrutz M. A. Permissive linker insertion sites in the outer membrane protein of 987P fimbriae of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(4):1099–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.4.1099-1110.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H., Taylor R. K. 987P fimbrial gene identification and protein characterization by T7 RNA polymerase-induced transcription and TnphoA mutagenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):61–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H., Taylor R. K. Genetic analysis of 987P adhesion and fimbriation of Escherichia coli: the fas genes link both phenotypes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1230–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1230-1240.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H., Taylor R. K. The 987P fimbrial gene cluster of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli is plasmid encoded. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.149-156.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmoll T., Hoschützky H., Morschhäuser J., Lottspeich F., Jann K., Hacker J. Analysis of genes coding for the sialic acid-binding adhesin and two other minor fimbrial subunits of the S-fimbrial adhesin determinant of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1735–1744. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons B. L., Willemsen P. T., Bakker D., Roosendaal B., De Graaf F. K., Oudega B. Structure, localization and function of FanF, a minor component of K99 fibrillae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2041–2050. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokurenko E. V., Courtney H. S., Abraham S. N., Klemm P., Hasty D. L. Functional heterogeneity of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4709–4719. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4709-4719.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson T. N., Bilge S. S., Nowicki B., Moseley S. L. Molecular structure of the Dr adhesin: nucleotide sequence and mapping of receptor-binding domain by use of fusion constructs. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):261–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.261-268.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K. Genetics of adhesive fimbriae of intestinal Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:29–53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Guan C., Li P., Riggs P. D., Inouye H. Vectors that facilitate the expression and purification of foreign peptides in Escherichia coli by fusion to maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]