Abstract
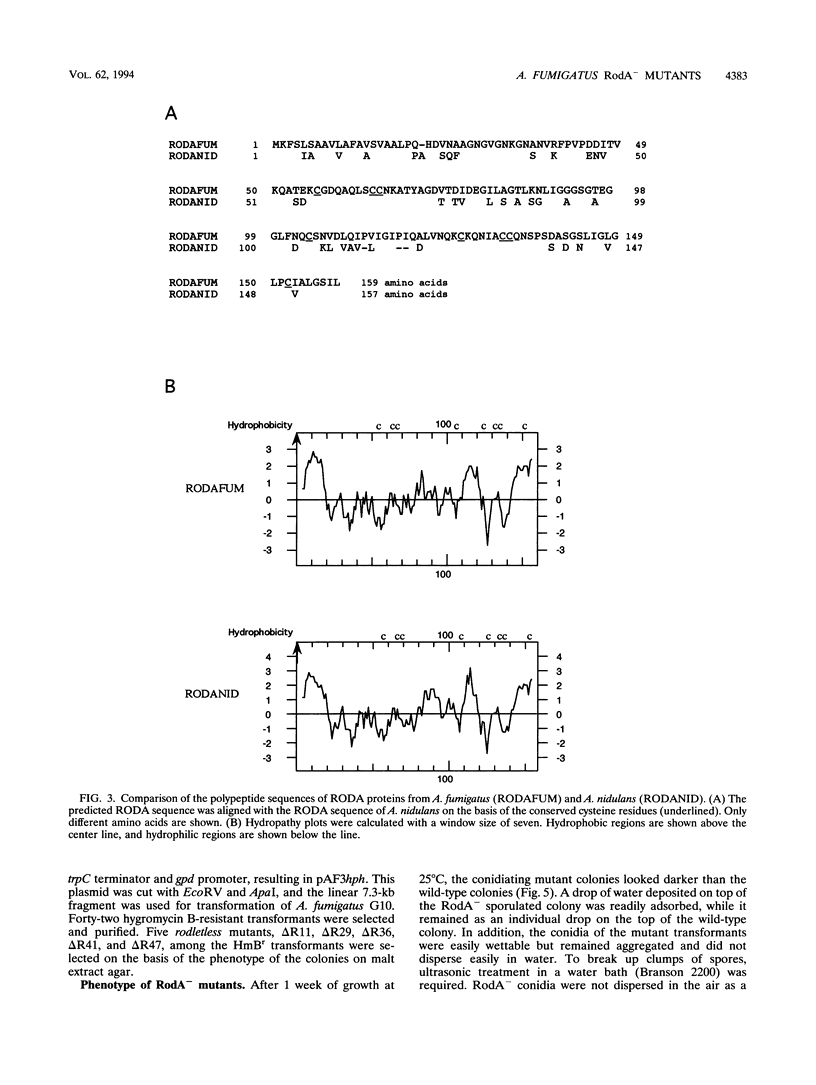
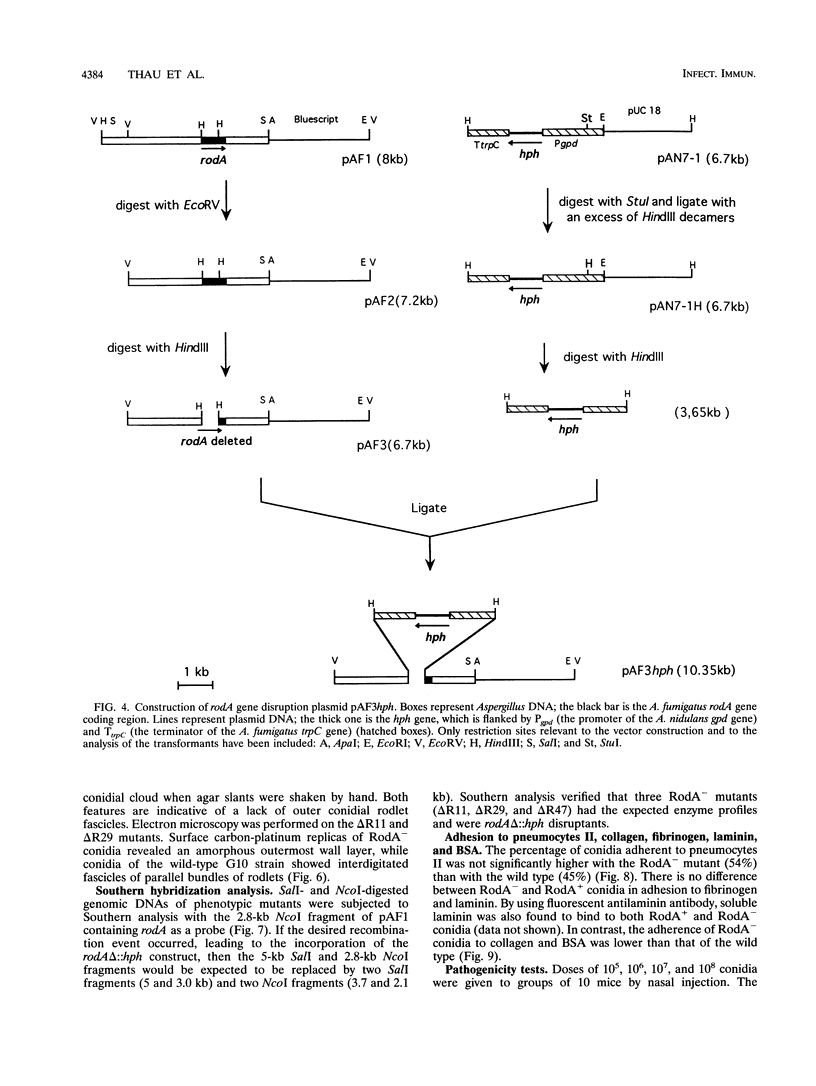
Conidia of Aspergillus fumigatus adhere in vitro to host proteins and cells via the outer cell wall layer. The rodA gene of A. fumigatus was cloned by homology with the rodA gene of Aspergillus nidulans, which is involved in the structure of the rodlets characteristic of the surface layer. The A. fumigatus RODA protein sequence has 85% similarity to that of A. nidulans RODA; the sequence codes for a hydrophobin, a low-molecular-weight protein moderately hydrophobic and rich in cysteines. The gene was disrupted with the hygromycin B resistance gene. By transformation of protoplasts with the disrupted gene, RodA- mutants were generated. These mutants are deficient in the ability to disperse their conidia; their conidia lack the rodlet layer and are hydrophilic. The adhesion of the rodletless conidia to collagen and bovine serum albumin was lower than that of the wild type; in contrast, there was no difference between RodA- and RodA+ conidia in adhesion to pneumocytes, fibrinogen, and laminin, suggesting that RODA is not the receptor for these cells and proteins. RodA- conidia were pathogenic for mice.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annaix V., Bouchara J. P., Larcher G., Chabasse D., Tronchin G. Specific binding of human fibrinogen fragment D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1747–1755. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1747-1755.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antley P. P., Hazen K. C. Role of yeast cell growth temperature on Candida albicans virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2884–2890. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2884-2890.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beever R. E., Dempsey G. P. Function of rodlets on the surface of fungal spores. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):608–610. doi: 10.1038/272608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beever R. E., Redgwell R. J., Dempsey G. P. Purification and chemical characterization of the rodlet layer of Neurospora crassa conidia. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1063-1070.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Dunlap J. C., Loros J. J. The Neurospora circadian clock-controlled gene, ccg-2, is allelic to eas and encodes a fungal hydrophobin required for formation of the conidial rodlet layer. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2382–2394. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Vartivarian S. Aspergillosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May;8(5):413–437. doi: 10.1007/BF01964057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchara J. P., Tronchin G., Annaix V., Robert R., Senet J. M. Laminin receptors on Candida albicans germ tubes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):48–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.48-54.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 11;113(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crestani B., Rolland C., Petiet A., Colas-Linhart N., Aubier M. Cell surface carbohydrates modulate neutrophil adherence to alveolar type II cells in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):L391–L400. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.264.4.L391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin H., Latgé J. P., Srikantha T., Morrow B., Soll D. R. Development of DNA probes for fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1547–1554. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1547-1554.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton-Ogay K., Suter M., Crameri R., Falchetto R., Fatih A., Monod M. Nucleotide sequence of a genomic and a cDNA clone encoding an extracellular alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Apr 15;71(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90506-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauter F. R., Russo V. E., Yanofsky C. Developmental and light regulation of eas, the structural gene for the rodlet protein of Neurospora. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2373–2381. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Paris S., Sarfati J., Jaton-Ogay K., Ave P., Latgé J. P. Virulence of alkaline protease-deficient mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jan 1;106(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutaouakil M., Monod M., Prévost M. C., Bouchara J. P., Paris S., Latgé J. P. Identification of the 33-kDa alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus in vitro and in vivo. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Nov;39(5):393–399. doi: 10.1099/00222615-39-5-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punt P. J., Oliver R. P., Dingemanse M. A., Pouwels P. H., van den Hondel C. A. Transformation of Aspergillus based on the hygromycin B resistance marker from Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;56(1):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer M. A., Dean R. A., Sewall T. C., Timberlake W. E. Rodletless, a new Aspergillus developmental mutant induced by directed gene inactivation. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1161–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant J. E., Latgé J. P. Interactions between conidia of Aspergillus fumigatus and human complement component C3. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1913–1918. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1913-1918.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Bouchara J. P., Larcher G., Lissitzky J. C., Chabasse D. Interaction between Aspergillus fumigatus and basement membrane laminin: binding and substrate degradation. Biol Cell. 1993;77(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(05)80189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]