Abstract
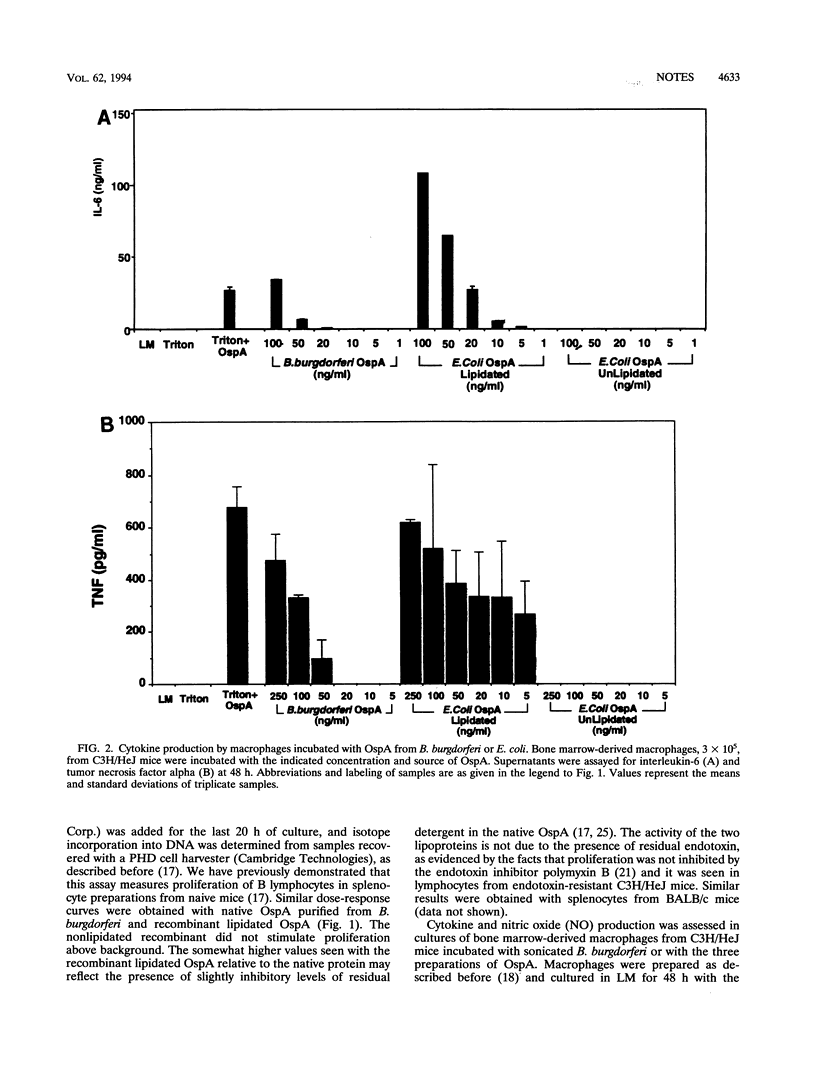
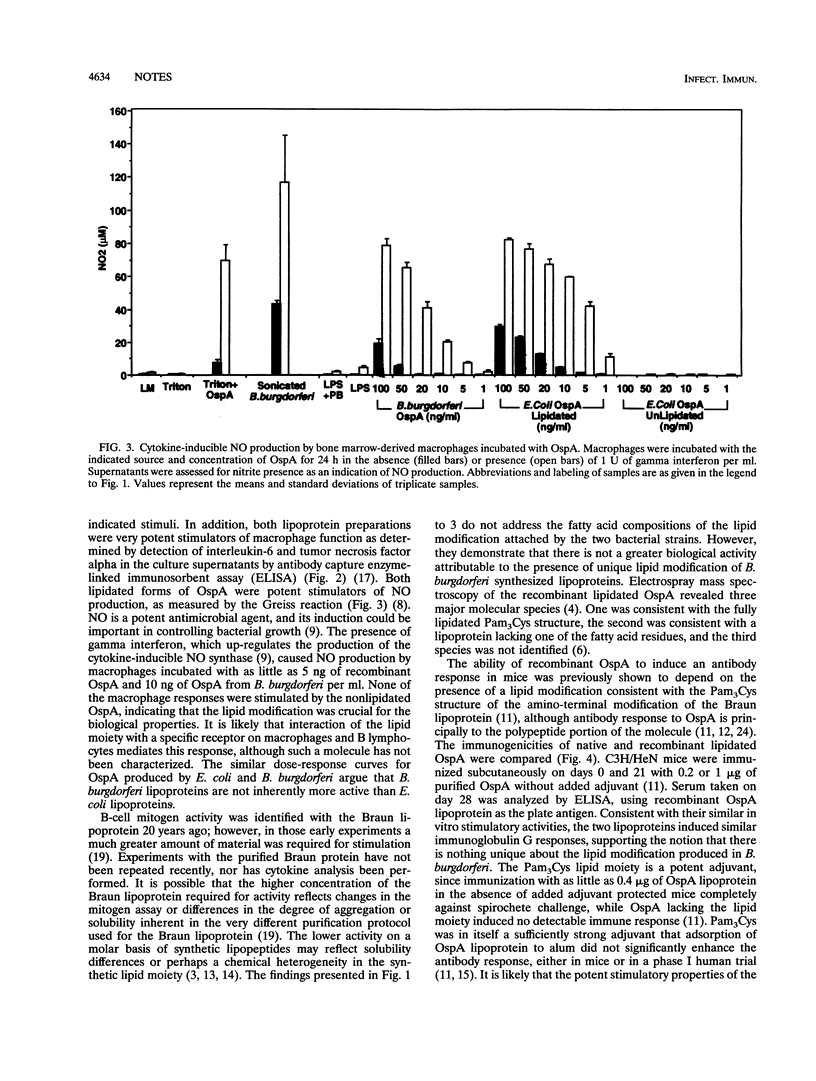
Borrelia burgdorferi lipoproteins are 50- to 500-fold more active as cytokine inducers and B-cell mitogens than Escherichia coli lipoproteins and synthetic peptides containing the tripalmitoyl-S-glyceryl-cysteine moiety. To investigate the source of this unique potency, we compared native OspA from B. burgdorferi with recombinant lipidated OspA produced in E. coli. As little as 10 ng of either protein per ml stimulated B-cell proliferation and production of cytokines and nitric oxide by macrophages. The two proteins induced comparable antibody responses in mice. Nonlipidated OspA made in E. coli had no stimulatory activity. Thus, lipid modification is essential both in vivo and in vitro for the immunological properties of OspA. The lipid moiety appears equally active whether produced in B. burgdorferi or in E. coli.
Full text
PDF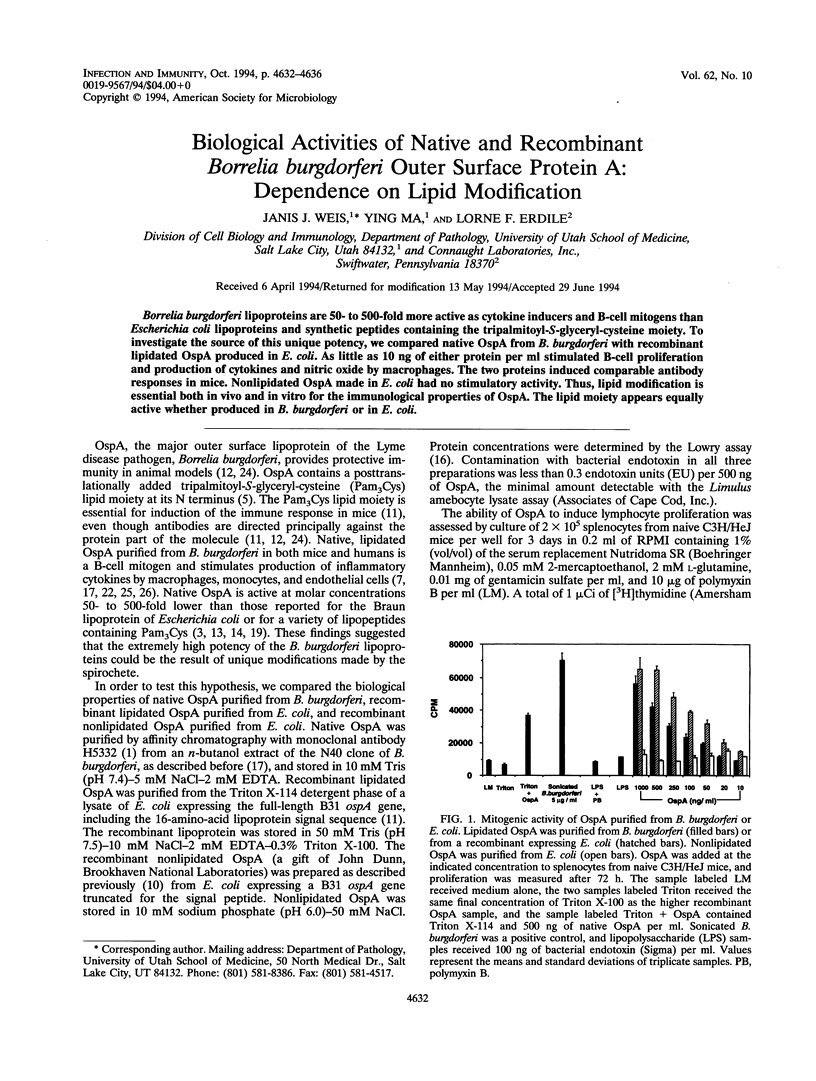


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Benach J. L., Habicht G. S. Isolation of interleukin 1 from joint fluids of patients with Lyme disease. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;16(6):800–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler W. G., Cox M., Lex A., Suhr B., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G. Synthetic lipopeptide analogs of bacterial lipoprotein are potent polyclonal activators for murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1900–1905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchon B., Van Dorsselaer A., Roitsch C. Characterization of multiple acylation sites on a recombinant protein by electrospray mass spectrometry. Biol Mass Spectrom. 1993 Jun;22(6):358–360. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200220608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defosse D. L., Johnson R. C. In vitro and in vivo induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha by Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1109–1113. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1109-1113.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Wietzerbin J., Hibbs J. B., Jr Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor induce the L-arginine-dependent cytotoxic effector mechanism in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1587–1592. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Lade B. N., Barbour A. G. Outer surface protein A (OspA) from the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi: high level expression and purification of a soluble recombinant form of OspA. Protein Expr Purif. 1990 Nov;1(2):159–168. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(90)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdile L. F., Brandt M. A., Warakomski D. J., Westrack G. J., Sadziene A., Barbour A. G., Mays J. P. Role of attached lipid in immunogenicity of Borrelia burgdorferi OspA. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.81-90.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Hoffmann P., Beuscher H. U., Dufhues G., Heinrich P., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Bessler W. G. Activation of bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by bacterial lipopeptide: cytokine production, phagocytosis and Ia expression. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P., Heinle S., Schade U. F., Loppnow H., Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D., Jung G., Bessler W. G. Stimulation of human and murine adherent cells by bacterial lipoprotein and synthetic lipopeptide analogues. Immunobiology. 1988 May;177(2):158–170. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(88)80036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller D., Koster F. T., Marks D. H., Hosbach P., Erdile L. F., Mays J. P. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant outer surface protein A Lyme vaccine. JAMA. 1994 Jun 8;271(22):1764–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Weis J. J. Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface lipoproteins OspA and OspB possess B-cell mitogenic and cytokine-stimulatory properties. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3843–3853. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3843-3853.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerpohl H. G., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Fischer H. Studies on the activation of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages by the macrophage cytotoxicity factor (MCF). Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):213–217. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Braun V., Galanos C. The lipoprotein of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli: a B-lymphocyte mitogen. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):473–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. C., Isa S., Vannier E., Georgilis K., Steere A. C., Dinarello C. A. Live Borrelia burgdorferi preferentially activate interleukin-1 beta gene expression and protein synthesis over the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):906–912. doi: 10.1172/JCI115966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Brandt M. E., Isaacs R. D., Thompson P. A., Beutler B. Lipoproteins of Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum activate cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis. Analysis using a CAT reporter construct. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H., Steere A. C., Dwyer J. M. In vivo and in vitro evidence of B cell hyperactivity during Lyme disease. J Rheumatol. 1988 Apr;15(4):648–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eckerskorn C., Museteanu C., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Wallich R. Recombinant outer surface protein a from Borrelia burgdorferi induces antibodies protective against spirochetal infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):123–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai K. F., Ma Y., Weis J. J. Normal human B lymphocytes and mononuclear cells respond to the mitogenic and cytokine-stimulatory activities of Borrelia burgdorferi and its lipoprotein OspA. Infect Immun. 1994 Feb;62(2):520–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.2.520-528.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmire W. M., Garon C. F. Specific and nonspecific responses of murine B cells to membrane blebs of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1460–1467. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1460-1467.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Ma Y., Schoenfeld R., Griffiths M., Eichwald E., Araneo B., Weis J. J. Evidence for B-lymphocyte mitogen activity in Borrelia burgdorferi-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3033–3041. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3033-3041.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoschke D. C., Skemp A. A., Defosse D. L. Lymphoproliferative responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 15;114(4):285–289. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-4-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza M. S., Fikrig E., Smith A. L., Flavell R. A., Barthold S. W. Nonspecific proliferative responses of murine lymphocytes to Borrelia burgdorferi antigens. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):471–478. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


