Abstract
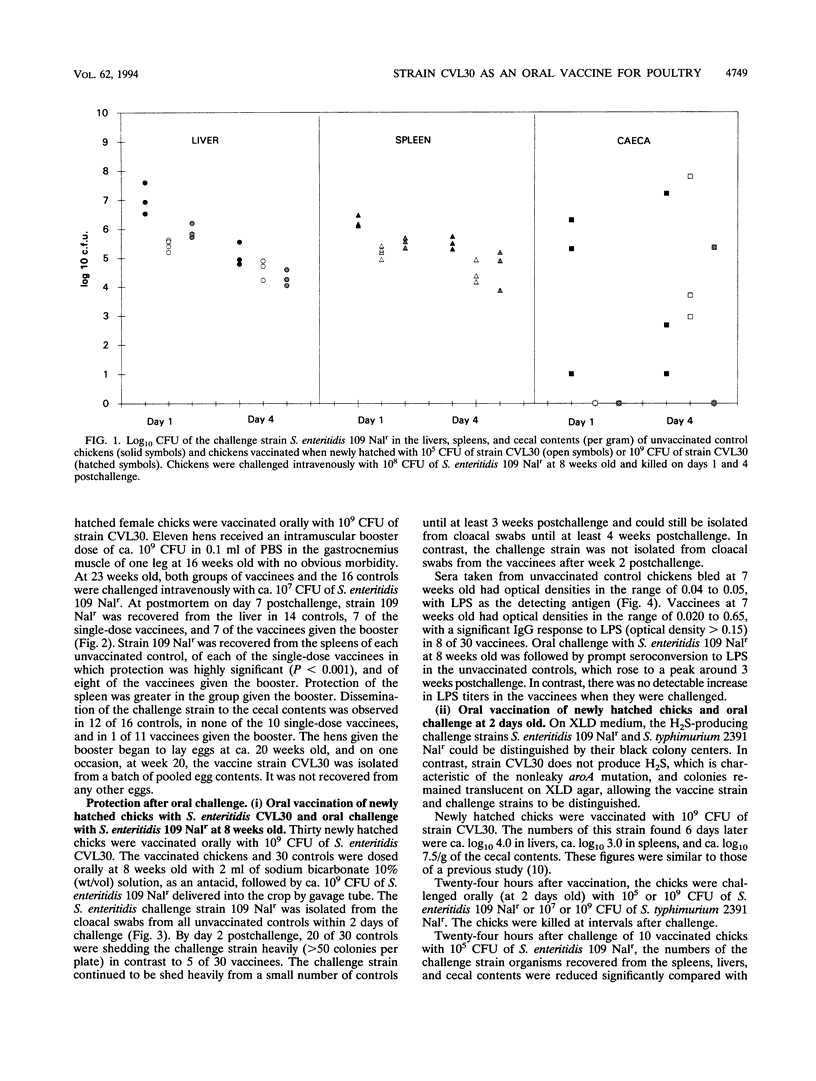
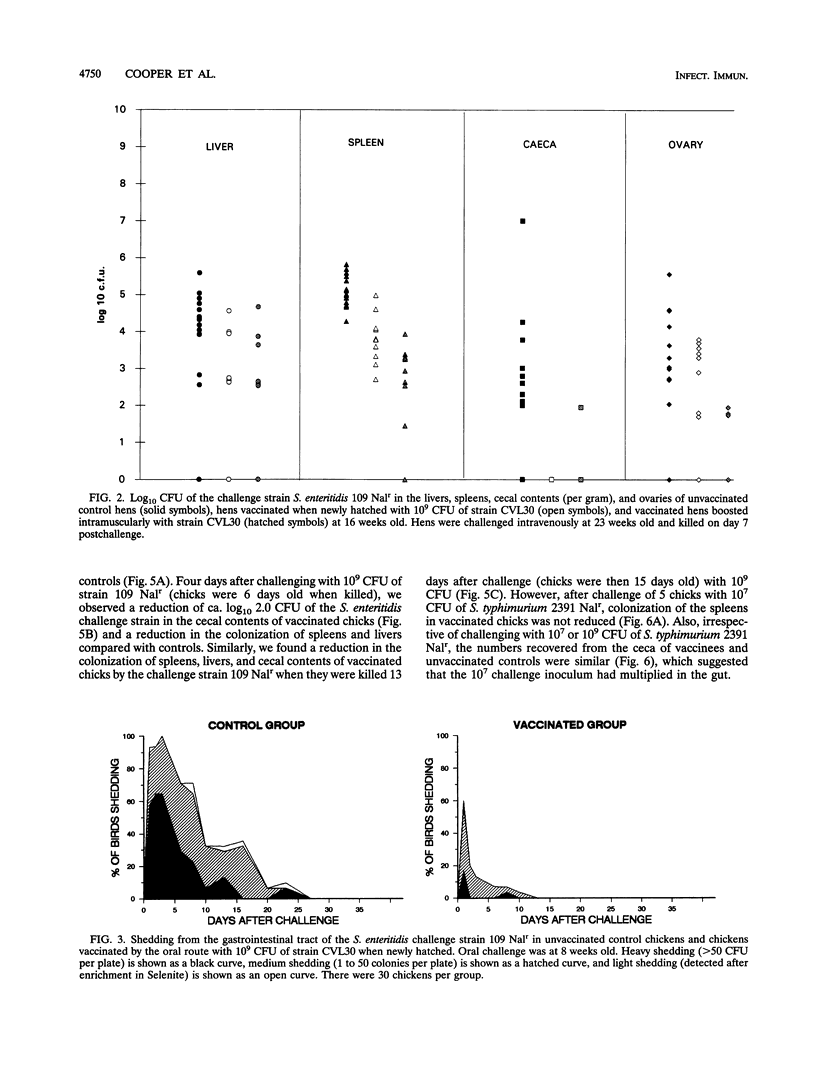
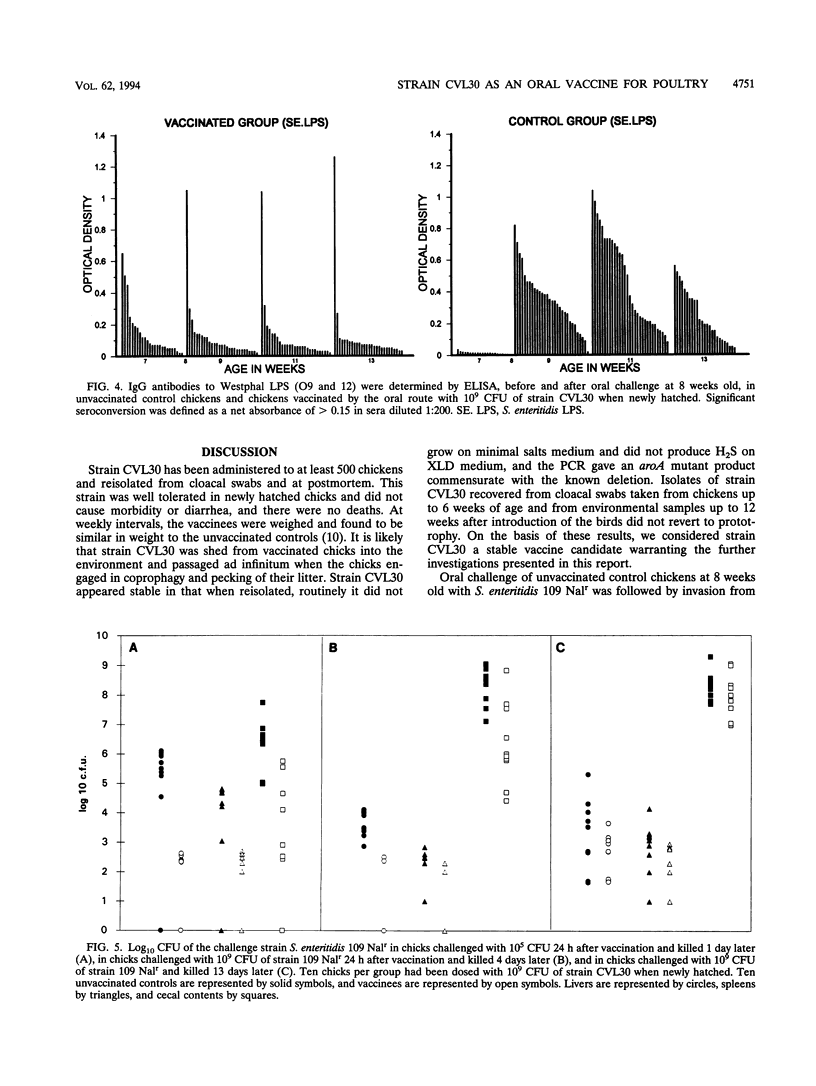
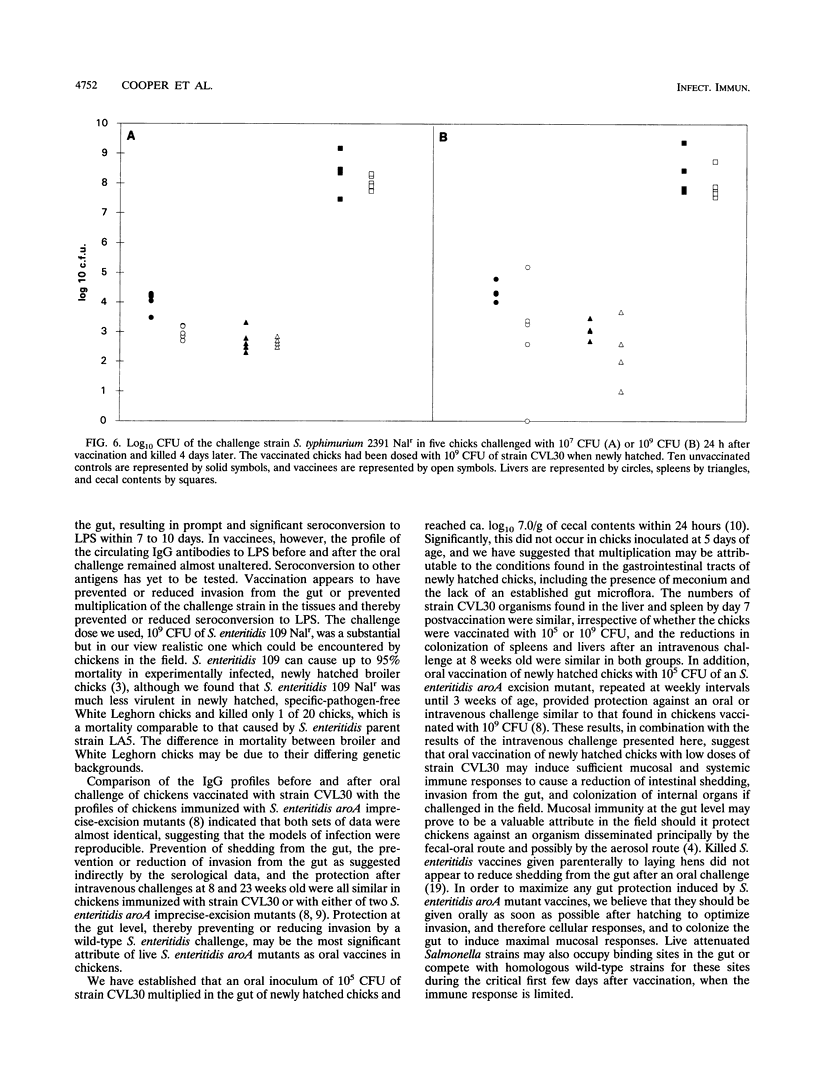
Newly hatched chicks were vaccinated orally with a genetically defined Salmonella enteritidis aroA candidate, strain CVL30. In chickens immunized with 10(5) or 10(9) CFU and challenged by the intravenous route with 10(8) CFU of S. enteritidis 109 Nalr at 8 weeks old, there were similar reductions in colonization of the spleens, livers, and ceca of vaccinees compared with unvaccinated controls. Two groups of newly hatched female chicks were vaccinated orally with 10(9) CFU of strain CVL30, and one group was revaccinated intramuscularly with 10(9) CFU at 16 weeks old. When challenged intravenously with S. enteritidis 109 Nalr at 23 weeks old, there was a reduction in the colonization of spleens, livers, ovaries, and ceca compared with unvaccinated controls. Inclusion of the intramuscular booster gave increased protection to the ovary, although the vaccine strain was isolated on one occasion from a batch of eggs laid at 20 weeks old. In chickens immunized with 10(9) CFU of strain CVL30 and challenged orally with 10(9) CFU of S. enteritidis 109 Nalr, there was a reduction in intestinal shedding of the challenge strain from vaccines compared with unvaccinated controls. Circulating immunoglobulin G antibodies to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were detected in unvaccinated controls within 7 to 10 days of oral challenge. In contrast, circulating immunoglobulin G antibodies to LPS in vaccinees were not altered by the oral challenge, which suggested that vaccination reduced or prevented invasion by the challenge strain from the gut or multiplication of the challenge strain in the tissues. Newly hatched chicks were vaccinated orally with ca. 10(9) CFU of strain CVL30, and 1 day later, the vaccines and unvaccinated controls were challenged orally with 10(5) or 10(9) CFU of S. enteritidis 109 Nalr. Colonization of the ceca and invasion from the gut by the S. enteritidis challenge strain was reduced in the vaccines up to 5 days postchallenge compared with controls. In a second trial, vaccinees and controls were challenged orally with 10(7) or 10(9) CFU of S. typhimurium 2391 Nalr. In contrast to the challenge with S. enteritidis, colonization of the ceca and invasion by the S. typhimurium strain were not greatly reduced.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskerville A., Humphrey T. J., Fitzgeorge R. B., Cook R. W., Chart H., Rowe B., Whitehead A. Airborne infection of laying hens with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4. Vet Rec. 1992 May 2;130(18):395–398. doi: 10.1136/vr.130.18.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binkin N., Scuderi G., Novaco F., Giovanardi G. L., Paganelli G., Ferrari G., Cappelli O., Ravaglia L., Zilioli F., Amadei V. Egg-related Salmonella enteritidis, Italy, 1991. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Apr;110(2):227–237. doi: 10.1017/s095026880006814x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield S., Roberts M., Londono P., Cropley I., Douce G., Dougan G. The development of oral vaccines based on live attenuated Salmonella strains. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993 Jun;7(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1993.tb00374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Nicholas R. A., Bracewell C. D. Serological and bacteriological investigations of chickens from flocks naturally infected with Salmonella enteritidis. Vet Rec. 1989 Dec 2;125(23):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Venables L. M., Nicholas R. A., Cullen G. A., Hormaeche C. E. Further studies of the application of live Salmonella enteritidis aroA vaccines in chickens. Vet Rec. 1993 Jul 10;133(2):31–36. doi: 10.1136/vr.133.2.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Venables L. M., Nicholas R. A., Cullen G. A., Hormaeche C. E. Vaccination of chickens with chicken-derived Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 aroA live oral Salmonella vaccines. Vaccine. 1992;10(4):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90160-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Venables L. M., Woodward M. J., Hormaeche C. E. Invasiveness and persistence of Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, and a genetically defined S. enteritidis aroA strain in young chickens. Infect Immun. 1994 Nov;62(11):4739–4746. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.11.4739-4746.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Chatfield S., Higgins C. F., Hayward C., Dougan G. Characterization of porin and ompR mutants of a virulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium: ompR mutants are attenuated in vivo. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2136–2140. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2136-2140.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Chatfield S., Pickard D., Bester J., O'Callaghan D., Maskell D. Construction and characterization of vaccine strains of Salmonella harboring mutations in two different aro genes. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1329–1335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gast R. K., Stone H. D., Holt P. S., Beard C. W. Evaluation of the efficacy of an oil-emulsion bacterin for protecting chickens against Salmonella enteritidis. Avian Dis. 1992 Oct-Dec;36(4):992–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Schroeter A. Molecular typing methods for S. enteritidis. Int J Food Microbiol. 1994 Jan;21(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(94)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper S. A., Mawer S. Salmonella enteritidis in a commercial layer flock. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 24;123(13):351–351. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.13.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E., Joysey H. S., Desilva L., Izhar M., Stocker B. A. Immunity conferred by Aro- Salmonella live vaccines. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90075-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin D. J., Rao M., Barham D. W., Pencheon D. C., Lofts C., Jones P. H., O'Mahony M., Soltanpoor N., Ward L. R., Threlfall E. J. An outbreak of infection with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 associated with the use of raw shell eggs. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1993 Dec 3;3(13):R179–R183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Robertsson J. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: cell-mediated and humoral immune reactions before and after challenge with live virulent bacteria in calves given live or inactivated vaccines. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):751–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.751-757.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Segall T., Weintraub A., Stocker B. A. Antibody response and protection against challenge in mice vaccinated intraperitoneally with a live aroA O4-O9 hybrid Salmonella dublin strain. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1211–1221. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1211-1221.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister S. A. Salmonella enteritidis infection in broilers and broiler breeders. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 24;123(13):350–350. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.13.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J. Salmonella serovars and phage types in humans and animals in Australia 1987-1992. Aust Vet J. 1994 Mar;71(3):78–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1994.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampling A., Anderson J. R., Upson R., Peters E., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 infection of broiler chickens: a hazard to public health. Lancet. 1989 Aug 19;2(8660):436–438. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue D. C., Tauxe R. V., Rowe B. International increase in Salmonella enteritidis: a new pandemic? Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Aug;105(1):21–27. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall T., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella dublin experimental infection in calves: protection after oral immunization with an auxotrophic aroA live vaccine. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1991 Mar;38(2):142–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Johnson E. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella dublin as a parenteral modified live vaccine for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Tucker J. F. The effect of antibiotic therapy on the faecal excretion of Salmonella typhimurium by experimentally infected chickens. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Oct;75(2):275–292. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeyenbos G. H., Smyser C. F., Van Roekel H. Salmonella infections of the ovary and peritoneum of chickens. Avian Dis. 1969 Aug;13(3):668–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Joseph C., Bruce J., Fenton D., O'Mahony M., Cunningham D., O'Connor B., Rowe B. A large outbreak of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 associated with eggs from overseas. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Dec;103(3):425–433. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003082x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A. Auxotrophic Salmonella typhi as live vaccine. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):141–145. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Hone D. M., Losonsky G. A., Guers L., Edelman R., Levine M. M. Clinical acceptability and immunogenicity of CVD 908 Salmonella typhi vaccine strain. Vaccine. 1992;10(7):443–446. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90392-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Hampton M. D., Chart H., Rowe B. Use of plasmid profile typing for surveillance of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 from humans, poultry and eggs. Epidemiol Infect. 1994 Feb;112(1):25–31. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800057381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams Smith H., Tucker J. F. The virulence of salmonella strains for chickens: their excretion by infected chickens. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Jun;84(3):479–488. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400027017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



