Abstract
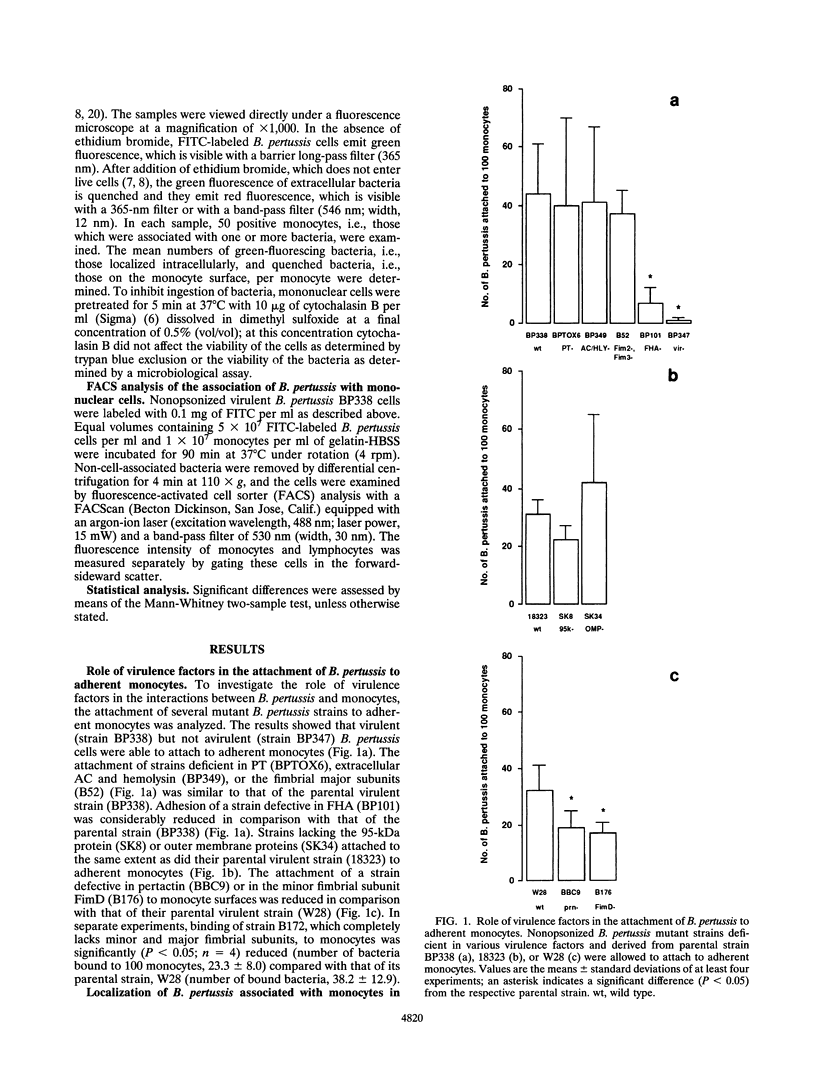
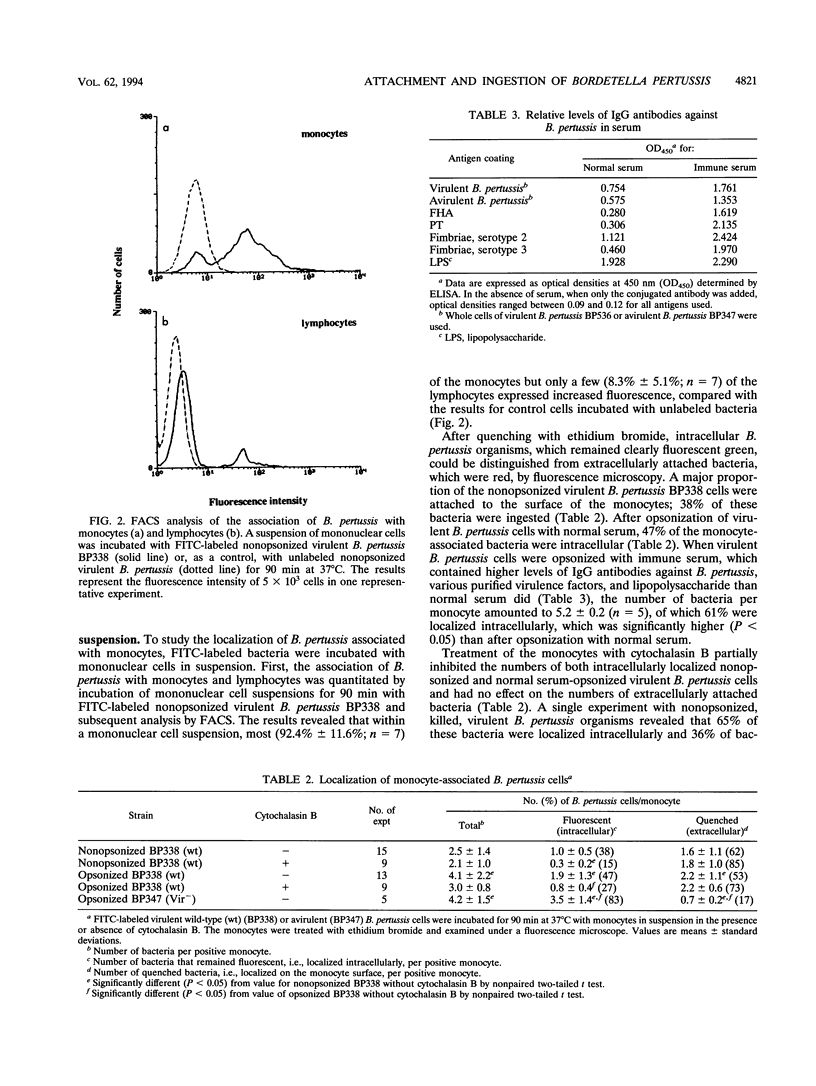
In the present study, the role of virulence factors in and the effect of opsonization on the interactions between Bordetella pertussis and human monocytes were investigated. The methods used facilitated the distinction between attachment and ingestion of bacteria by monocytes. Nonopsonized virulent B. pertussis cells attached to monocytes. Nonopsonized B. pertussis mutant strains deficient in filamentous hemagglutinin, fimbriae, or pertactin exhibited a reduced adherence to monocytes compared with that of their respective parental strains. Nonopsonized avirulent B. pertussis cells did not attach to monocytes. These results led to the conclusion that fimbriae and pertactin are involved in the adherence of nonopsonized virulent B. pertussis cells to monocytes and confirm the role of filamentous hemagglutinin in this process. In the absence of opsonins, about 40% of the monocyte-associated virulent B. pertussis cells were ingested. When B. pertussis cells were preopsonized with inactivated normal serum, about 50% of the monocyte-associated virulent B. pertussis cells were phagocytosed and about 80% of the monocyte-associated avirulent B. pertussis cells were ingested. These results indicate that virulence factors inhibit opsonin-mediated ingestion of B. pertussis by monocytes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blussé van Oud Alblas A., van der Linden-Schrever B., Van Furth R. Origin and kinetics of pulmonary macrophages during an inflammatory reaction induced by intra-alveolar administration of aerosolized heat-killed BCG. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2):276–281. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Gray D. F. Macrophage behaviour during the complaisant phase of murine pertussis. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):875–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Eaton J. W. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.6287574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Fox R. I., Polyzonis M., Allison A. C., Haswell A. D. The inhibition of phagocytosis and facilitation of exocytosis in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes by cytochalasin B. Lab Invest. 1973 Jan;28(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drevets D. A., Campbell P. A. Macrophage phagocytosis: use of fluorescence microscopy to distinguish between extracellular and intracellular bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Aug 28;142(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90289-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattorossi A., Nisini R., Pizzolo J. G., D'Amelio R. New, simple flow cytometry technique to discriminate between internalized and membrane-bound particles in phagocytosis. Cytometry. 1989 May;10(3):320–325. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feister A. J., Browder B., Willis H. E., Mohanakumar T., Ruddy S. Pertussis toxin inhibits human neutrophil responses mediated by the 42-kilodalton IgG Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn T. M., Shahin R., Mekalanos J. J. Characterization of vir-activated TnphoA gene fusions in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3273–3279. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3273-3279.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Fiederlein R. L., Glasser L., Galgiani J. N. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase: effects of affinity-purified adenylate cyclase on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.135-140.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Nordensson K., Wilson L., Akporiaye E. T., Yocum D. E. Uptake and intracellular survival of Bordetella pertussis in human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4578–4585. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4578-4585.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funnell S. G., Robinson A. A novel adherence assay for Bordetella pertussis using tracheal organ cultures. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jun 15;110(2):197–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazenbos W. L., van den Berg B. M., van Furth R. Very late antigen-5 and complement receptor type 3 cooperatively mediate the interaction between Bordetella pertussis and human monocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6274–6282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiemstra P. S., Annema A., Schippers E. F., van Furth R. Pertussis toxin partially inhibits phagocytosis of immunoglobulin G-opsonized Staphylococcus aureus by human granulocytes but does not affect intracellular killing. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):202–205. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.202-205.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Two trans-acting regulatory genes (vir and mod) control antigenic modulation in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5059–5066. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5059-5066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van Zwet T. L., van Furth R. Effect of extracellular serum in the stimulation of intracellular killing of streptococci by human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):421–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.421-426.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leininger E., Roberts M., Kenimer J. G., Charles I. G., Fairweather N., Novotny P., Brennan M. J. Pertactin, an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing Bordetella pertussis surface protein that promotes adherence of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Pai C. H. Plasmid-mediated resistance to phagocytosis in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1176-1183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., Jansen W. H., Brunings H., Gielen H., van der Heide H. G., Walvoort H. C., Guinee P. A. Construction and analysis of Bordetella pertussis mutants defective in the production of fimbriae. Microb Pathog. 1992 Feb;12(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Symes P., Conboy M., Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Inhibition of monocyte oxidative responses by Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2749–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Kuipers B., Vogel M. L., Hamstra H. J., Nagel J. Description of a hybridoma bank towards Bordetella pertussis toxin and surface antigens. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jun;8(6):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90024-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Domenighini M., Tuomanen E., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis: nucleotide sequence and crucial role in adherence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D., Tuomanen E., Falkow S., Golenbock D. T., Saukkonen K., Wright S. D. Recognition of a bacterial adhesion by an integrin: macrophage CR3 (alpha M beta 2, CD11b/CD18) binds filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1375–1382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90701-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Fairweather N. F., Leininger E., Pickard D., Hewlett E. L., Robinson A., Hayward C., Dougan G., Charles I. G. Construction and characterization of Bordetella pertussis mutants lacking the vir-regulated P.69 outer membrane protein. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1393–1404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Inhibition of phagocytosis in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: a virulence plasmid-encoded ability involving the Yop2b protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2139–2143. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2139-2143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Cabellos C., Burroughs M., Prasad S., Tuomanen E. Integrin-mediated localization of Bordetella pertussis within macrophages: role in pulmonary colonization. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1143–1149. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steed L. L., Setareh M., Friedman R. L. Intracellular survival of virulent Bordetella pertussis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Oct;50(4):321–330. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Weiss A. Characterization of two adhesins of Bordetella pertussis for human ciliated respiratory-epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):118–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urisu A., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Filamentous hemagglutinin has a major role in mediating adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human WiDr cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):695–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.695-701.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwey W. F., Thiele E. H., Sage D. N., Schuchardt L. F. A SIMPLIFIED LIQUID CULTURE MEDIUM FOR THE GROWTH OF HEMOPHILUS PERTUSSIS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Aug;58(2):127–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems R. J., Geuijen C., van der Heide H. G., Renauld G., Bertin P., van den Akker W. M., Locht C., Mooi F. R. Mutational analysis of the Bordetella pertussis fim/fha gene cluster: identification of a gene with sequence similarities to haemolysin accessory genes involved in export of FHA. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(2):337–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems R. J., van der Heide H. G., Mooi F. R. Characterization of a Bordetella pertussis fimbrial gene cluster which is located directly downstream of the filamentous haemagglutinin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2661–2671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Jong M. T. Adhesion-promoting receptors on human macrophages recognize Escherichia coli by binding to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1876–1888. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Capel P. J. Human IgG Fc receptor heterogeneity: molecular aspects and clinical implications. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90166-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van oud Alblas A. B., van Furth R. Origin, Kinetics, and characteristics of pulmonary macrophages in the normal steady state. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1504–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



