Abstract
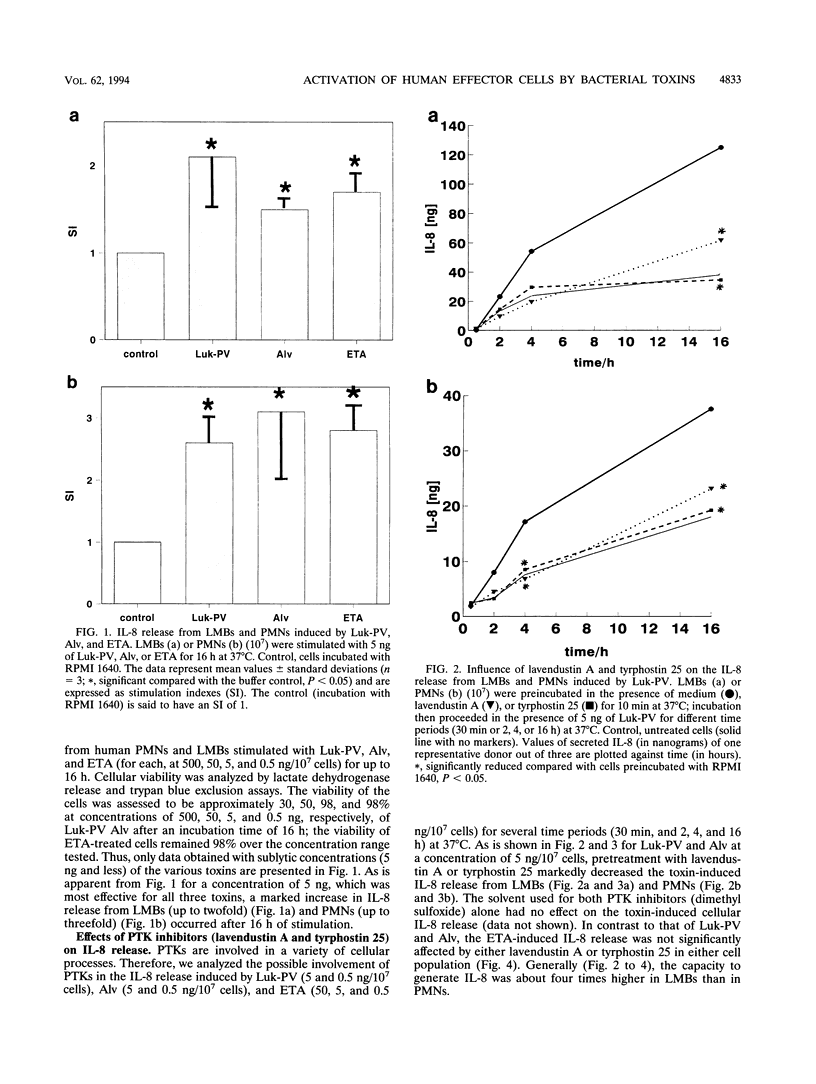
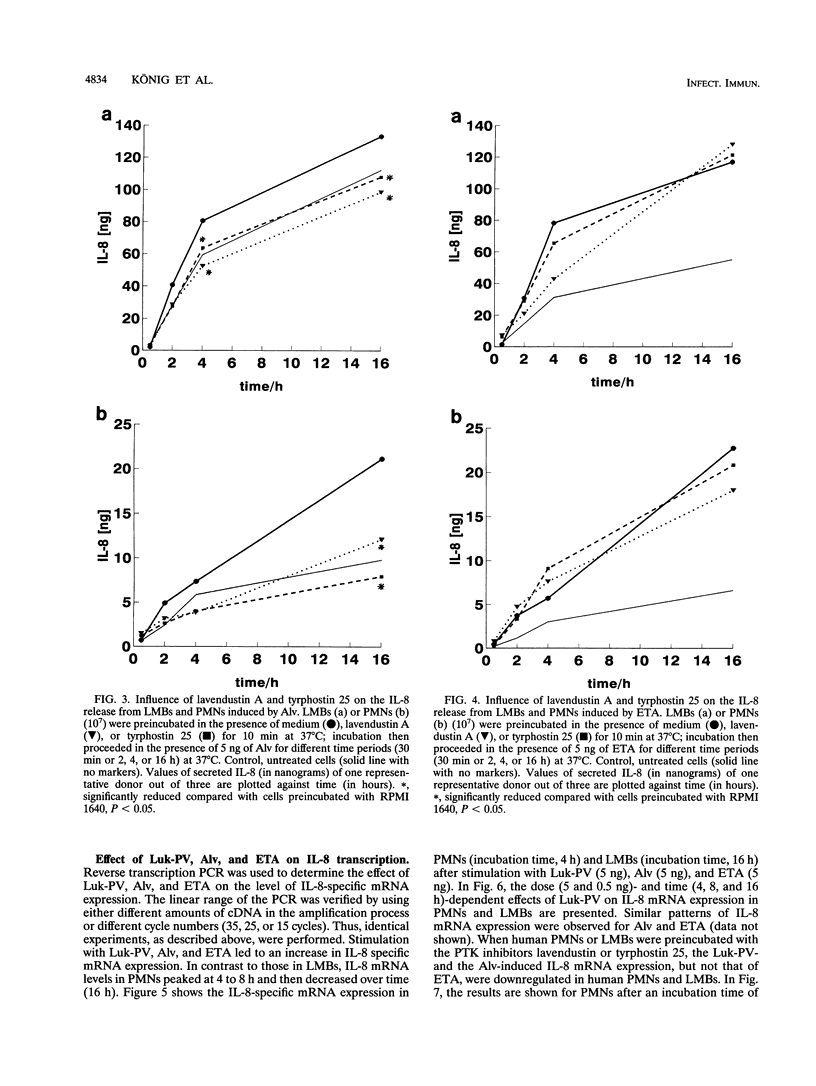
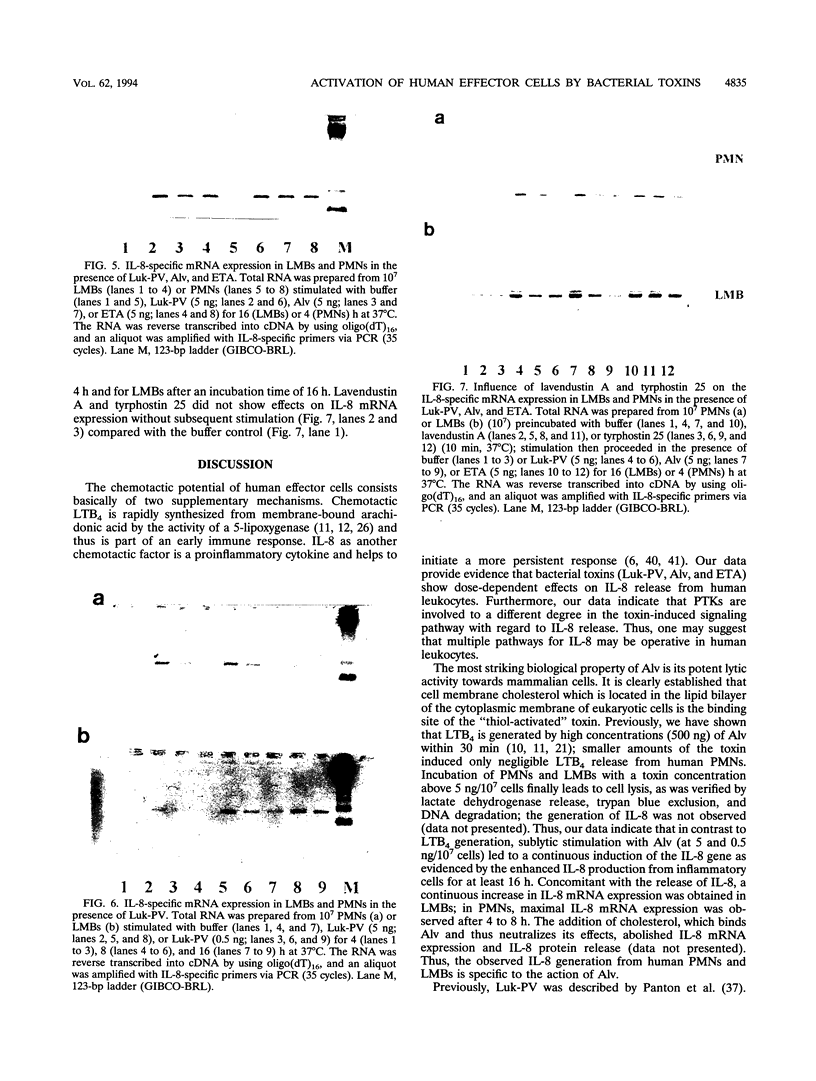
We analyzed the transcription and release of interleukin-8 (IL-8) from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMNs) and a lymphocyte-monocyte-basophil (LMB) cell population stimulated for different time periods (30 min to 16 h) with pore-forming bacterial toxins (Panton-Valentine leukocidin [Luk-PV] and alveolysin [Alv]) as well as with the erythrogenic toxin A (ETA) as a superantigen. At high toxin concentrations (500 ng/10(7) cells), Luk-PV and Alv led to a decreased IL-8 generation from LMBs within the first 30 min; with PMNs, a slight increase in IL-8 release was observed. Under these conditions, stimulation with ETA did not lead to an altered cellular IL-8 release. At lower concentrations (5 and 0.5 ng/10(7) cells), all three toxins led to a continuous increase (over 16 h) in IL-8 release and IL-8 mRNA expression of PMNs and LMBs. Preincubation of the cells with the protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors lavendustin A and tyrphostin 25 led to a reduction of the toxin-mediated effects on IL-8 release and IL-8 mRNA expression when Luk-PV and Alv were used as stimuli. In contrast, IL-8 synthesis in cells which were stimulated with ETA was not influenced by protein tyrosine kinase inhibition. From our data, one may suggest that multiple pathways for IL-8 production are operative in human leukocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe J., Forrester J., Nakahara T., Lafferty J. A., Kotzin B. L., Leung D. Y. Selective stimulation of human T cells with streptococcal erythrogenic toxins A and B. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3747–3750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham R. T., Karnitz L. M., Secrist J. P., Leibson P. J. Signal transduction through the T-cell antigen receptor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):434–438. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to cell membranes by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Prog Allergy. 1988;40:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., Brom H. J., Alouf J. E., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Peters W. Generation of leukotrienes from human granulocytes by alveolysin from Bacillus alvei. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):188–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.188-193.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., König W., Pfeiffer P., Rauschen I., Theobald K., Thelestam M., Alouf J. E. Effect of thiol-activated toxins (streptolysin O, alveolysin, and theta toxin) on the generation of leukotrienes and leukotriene-inducing and -metabolizing enzymes from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):844–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.844-851.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibb C. R., Strieter R. M., Burdick M., Kunkel S. L. Expression of interleukin-8 by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3052–3058. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3052-3058.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Toxic shock syndrome-associated staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor production. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):291–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finck-Barbançon V., Prévost G., Piémont Y. Improved purification of leukocidin from Staphylococcus aureus and toxin distribution among hospital strains. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jan;142(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90099-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujishima S., Hoffman A. R., Vu T., Kim K. J., Zheng H., Daniel D., Kim Y., Wallace E. F., Larrick J. W., Raffin T. A. Regulation of neutrophil interleukin 8 gene expression and protein secretion by LPS, TNF-alpha, and IL-1 beta. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Mar;154(3):478–485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLADSTONE G. P., VAN HEYNINGEN W. E. Staphylococcal leucocidins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Apr;38(2):123–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Yaish P., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins I: synthesis and biological activity of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1989 Oct;32(10):2344–2352. doi: 10.1021/jm00130a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Selective purification by thiol-disulfide interchange chromatography of alveolysin, a sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Bacillus alvei. Toxin properties and interaction with cholesterol and liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9968–9972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensler T., Köller M., Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E., König W. Staphylococcus aureus toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and Streptococcus pyogenes erythrogenic toxin A modulate inflammatory mediator release from human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.1055-1061.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Reichwein J., Arvand M., Krämer S., Bhakdi S. Use of a monoclonal antibody to determine the mode of transmembrane pore formation by streptolysin O. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):641–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.641-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Morinaga N., Muneto R. Non-thiol-activated cytolytic bacterial toxins: current status. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Feb;5(2):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Kroegel C., Kunau H. W., Borgeat P. Comparison of the eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF) with endogeneous hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids of leukocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;66 (Suppl 1):168–171. doi: 10.1159/000232895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. Tyrphostins: tyrosine kinase blockers as novel antiproliferative agents and dissectors of signal transduction. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3275–3282. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Harada N., Yokota T., Arai K. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:295–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeyer W. Interaction of streptolysin-O with biomembranes: kinetic and morphological studies on erythrocyte membranes. Toxicon. 1985;23(3):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(85)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Hirayama T., Kato I., Matsuda F. Crystallization and properties of staphylococcal leukocidin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 17;633(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Hirayama T., Matsuda F., Kato I. An early effect of the S component of staphylococcal leukocidin on methylation of phospholipid in various leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):142–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.142-145.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Kato I., Hirayama T., Matsuda F. Mode of action of staphylococcal leukocidin: effects of the S and F components on the activities of membrane-associated enzymes of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):38–45. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.38-45.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Iwamoto M., Mitsui K., Ando S., Nagai Y. Protease-nicked theta-toxin of Clostridium perfringens, a new membrane probe with no cytolytic effect, reveals two classes of cholesterol as toxin-binding sites on sheep erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Harris P. The effect of inhibition of leukotriene B4 release on lipopolysaccharide-induced production of neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1 (interleukin-8) by human alveolar macrophages. Prostaglandins. 1993 Jan;45(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(93)90091-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Purification and partial biologic characterization of a human lymphocyte-derived peptide with potent neutrophil-stimulating activity. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3534–3540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. B., Gamble J. R., Clark-Lewis I., Vadas M. A. Chemotactic desensitization of neutrophils demonstrates interleukin-8 (IL-8)-dependent and IL-8-independent mechanisms of transmigration through cytokine-activated endothelium. Immunology. 1993 Mar;78(3):491–497. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vairo G., Hamilton J. A. Signalling through CSF receptors. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):362–369. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODIN A. M. Purification of the two components of leucocidin from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:158–165. doi: 10.1042/bj0750158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]