Abstract
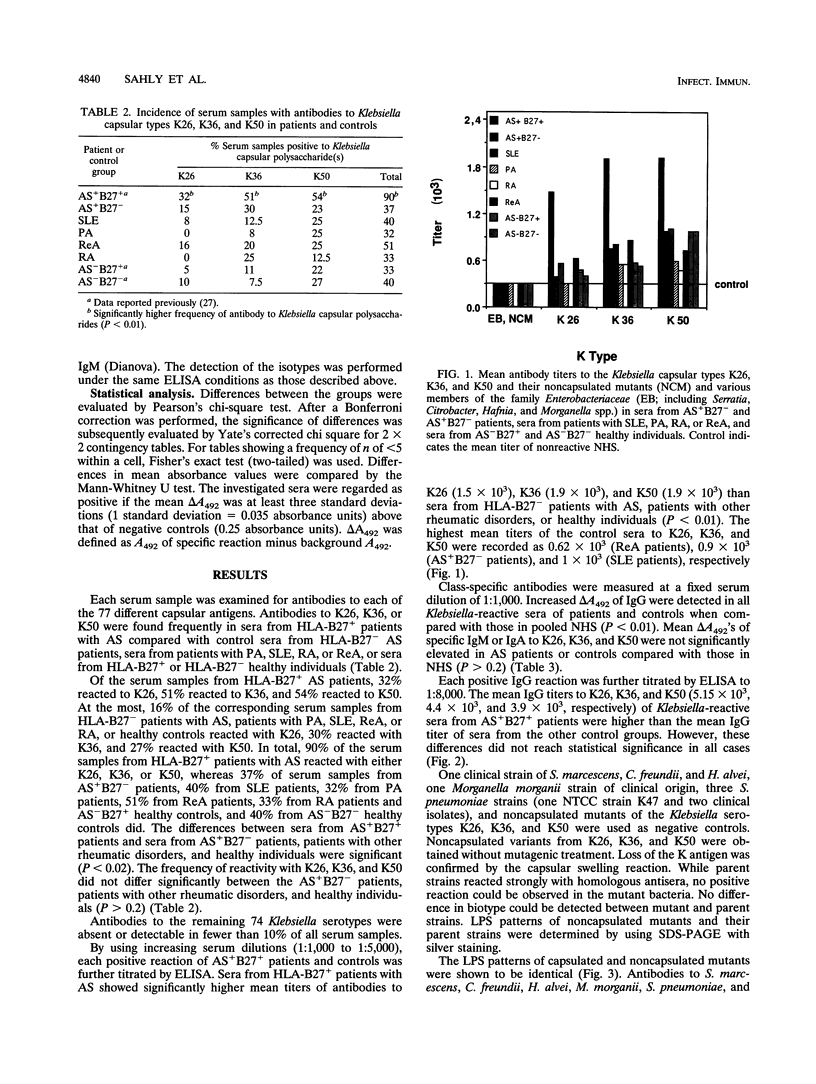
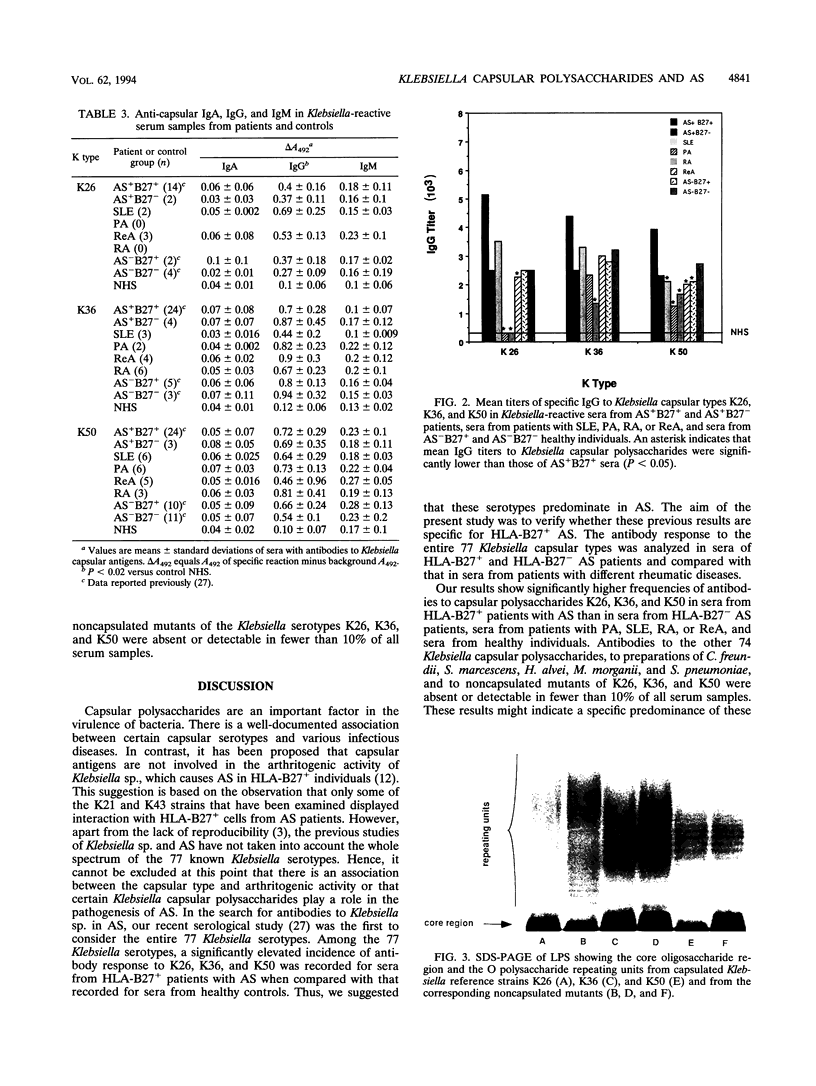
The production of antibodies to Klebsiella capsular polysaccharides was measured in sera from either HLA-B27-positive (HLA-B27+) or HLA-B27-negative (HLA-B27-) patients with classical ankylosing spondylitis (n = 54). These sera were compared with sera from patients with various rheumatic diseases (n = 82) and HLA-B27+ or HLA-B27- healthy individuals (n = 85). All sera were analyzed by means of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay specific to each of the 77 Klebsiella serotypes. The sera from HLA-B27+ patients with ankylosing spondylitis showed a significantly higher antibody frequency to the capsular types K26, K36, and K50 than the sera from HLA-B27- ankylosing spondylitis patients, patients with psoriatic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, or reactive arthritis after Yersinia enterocolitica infection, or healthy controls (P < 0.02). The antibodies were of the immunoglobulin G type. No significant antibody response to the other 74 Klebsiella serotypes, noncapsulated mutants of K26, K36, and K50, or preparations of Citrobacter, Serratia, Hafnia, or Morganella spp. or Streptococcus pneumoniae could be detected. The results might suggest a specific association between these capsular types and HLA-B27+ ankylosing spondylitis and might imply their predominance in this disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAER H., EHRENWORTH L. The pathogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae for mice: the relationship to the quantity and rate of production of type-specific capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.713-717.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines M., Ebringer A. HLA and disease. Mol Aspects Med. 1992;13(4):263–378. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(92)90003-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beukelman C. J., Quarles van Ufford H. C., van Bree F. P., Aerts P. C., Nieuwenhoff C., Reerink G., van Leeuwen A., van Dijk H. Trial and error in producing ankylosing-spondylitis-selective antisera according to Andrew Geczy. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1990;87:74–80. doi: 10.3109/03009749009097061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey M. F., James D. C. Human lymphocyte antigen association in ankylosing spondylitis. Nature. 1973 Mar 9;242(5393):121–121. doi: 10.1038/242121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer F., Germanier R. Experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae burn wound sepsis: role of capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):440–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.440-441.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Johanson W. G., Jr, Straus D. C. Lobar pneumonia in rats produced by clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):327–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.327-335.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer A. Ankylosing spondylitis is caused by Klebsiella. Evidence from immunogenetic, microbiologic, and serologic studies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Feb;18(1):105–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer A., Cox N. L., Abuljadayel I., Ghuloom M., Khalafpour S., Ptaszynska T., Shodjai-Moradi F., Wilson C. Klebsiella antibodies in ankylosing spondylitis and Proteus antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1988;27 (Suppl 2):72–85. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/xxvii.suppl_2.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy A. F., Alexander K., Bashir H. V., Edmonds J. A factor(s) in Klebsiella culture filtrates specifically modifies an HLA-B27 associated cell-surface component. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):782–784. doi: 10.1038/283782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffioen A. W., Rijkers G. T., Toebes E. A., Zegers B. J. The human in vitro anti-type 4 pneumococcal polysaccharide antibody response is regulated by suppressor T cells. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Aug;34(2):229–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb01541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Nimmich W., Eriksen J., Stirm S. More on cross-reactions of Pneumococci and Klebsiella. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1978 Dec;86B(6):313–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb00050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linssen A. B27+ disease versus B27- disease. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1990;87:111–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean L. HLA-B27 subtypes: implications for the spondyloarthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Aug;51(8):929–931. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.8.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki-Ikola O., Lehtinen K., Granfors K., Vainionpä R., Toivanen P. Bacterial antibodies in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):472–475. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podschun R., Heineken P., Ullmann U., Sonntag H. G. Comparative investigations of Klebsiella species of clinical origin: plasmid patterns, biochemical reactions, antibiotic resistances and serotypes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Sep;262(3):335–345. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podschun R., Penner I., Ullmann U. Interaction of Klebsiella capsule type 7 with human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Microb Pathog. 1992 Nov;13(5):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podschun R. Phenotypic properties of Klebsiella pneumoniae and K. oxytoca isolated from different sources. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1990 May;189(6):527–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Duncan I. B. Combined biochemical and serological typing of clinical isolates of Klebsiella. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):534–539. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.534-539.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser E., Noone P. Klebsiella capsular type versus site of isolation. J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;34(5):552–555. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.5.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Suarez Almazor M. E. Ankylosing spondylitis is not caused by Klebsiella. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Feb;18(1):95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahly H., Podschun R., Sass R., Bröker B., Kekow J., Gross W. L., Ullmann U. Serum antibodies to Klebsiella capsular polysaccharides in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 May;37(5):754–759. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shodjai-Moradi F., Ebringer A., Abuljadayel I. IgA antibody response to klebsiella in ankylosing spondylitis measured by immunoblotting. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Feb;51(2):233–237. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoons-Smit A. M., Verweij-Van Vught A. M., Kanis I. Y., MacLaren D. M. Biochemical and serological investigations on clinical isolates of klebsiella. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):265–276. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stodell M. A., Butler R. C., Zemelman V. A., Henry K., Brewerton D. A. Increased numbers of IgG-containing cells in rectal lamina propria of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Apr;43(2):172–176. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trull A. K., Ebringer R., Panayi G. S., Colthorpe D., James D. C., Ebringer A. IgA antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae in ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1983;12(3):249–253. doi: 10.3109/03009748309098543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trull A., Ebringer A., Panayi G., Ebringer R., James D. C. HLA-B27 and the immune response to enterobacterial antigens in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):74–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
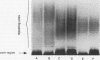
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]