Abstract
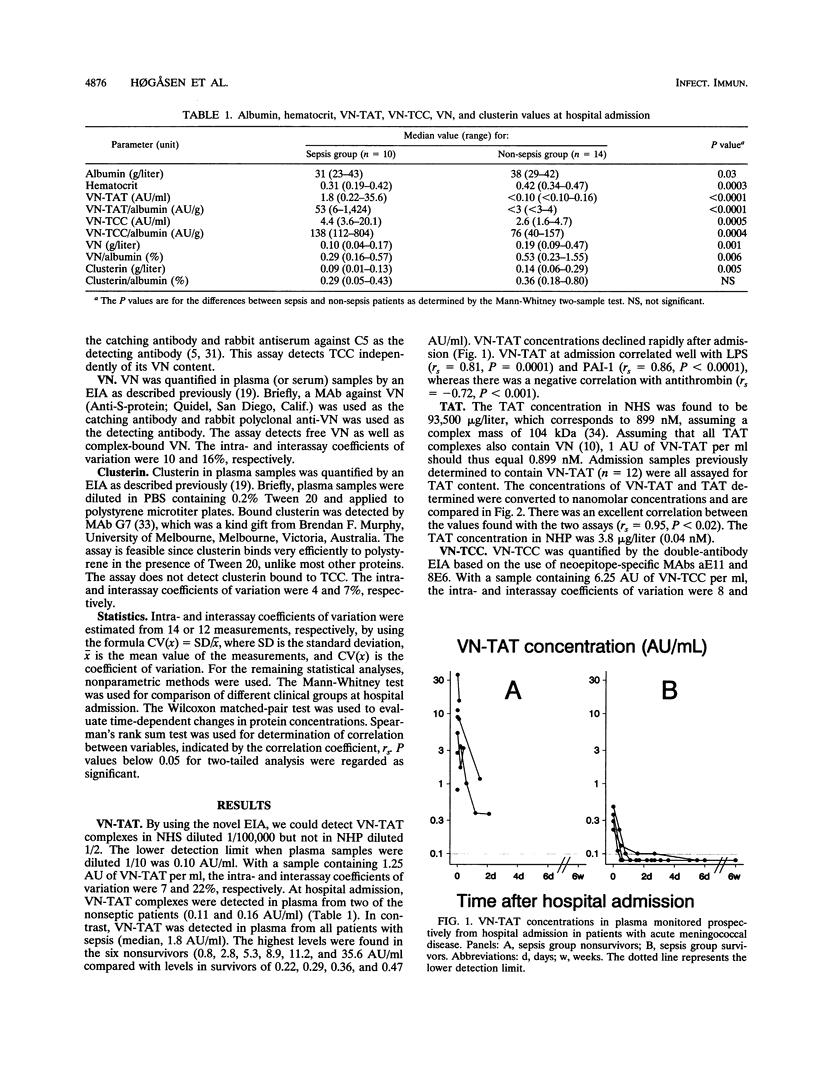
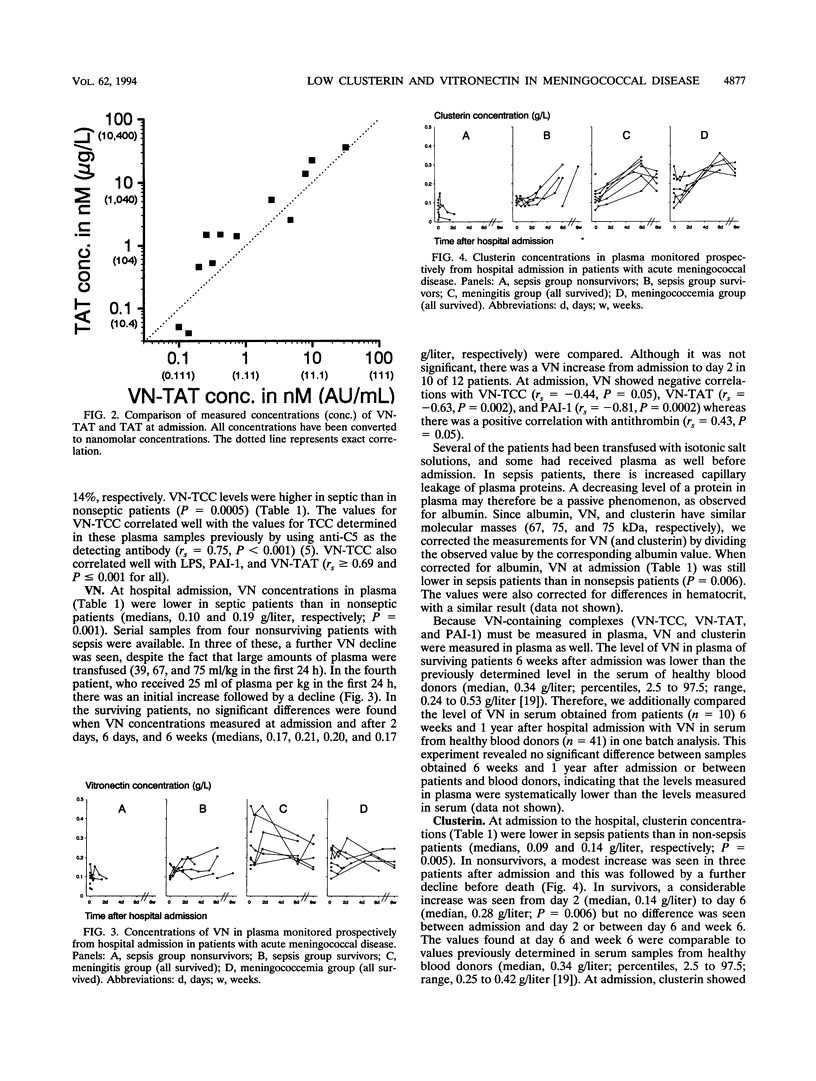
Patients with terminal complement deficiencies and thus impaired lytic efficiency have a highly increased likelihood of contracting invasive meningococcal infections but generally experience a mild disease course. Deficiencies of lysis inhibitors might therefore be associated with severe disease. We have quantified the complement lysis inhibitors vitronectin and clusterin, as well as complexes containing the proteins, in plasma from patients with acute meningococcal disease. At hospital admission, the median vitronectin concentrations were 0.10 (range, 0.04 to 0.17) g/liter in 10 septic patients and 0.19 (0.09 to 0.47) g/liter in 14 nonseptic patients (P = 0.001). The corresponding clusterin concentrations were 0.09 (0.01 to 0.13) and 0.14 (0.06 to 0.29) g/liter (P = 0.005). The vitronectin-thrombin-antithrombin complex concentration was 1.8 (0.22 to 35.6) arbitrary units (AU)/ml in septic patients, but the complex was not detectable in most nonseptic patients (< 0.10 to 0.16 AU/ml) (P < 0.0001). The corresponding levels of the terminal complement complex (contains vitronectin and clusterin) were 4.4 (3.6 to 20.1) and 2.6 (1.6 to 4.7) AU/ml (P = 0.0005). We found no evidence of constitutively low levels of vitronectin or clusterin in patients contracting meningococcal disease. The low levels of the proteins may partly be explained by hemodilution, extravasation, and increased consumption due to incorporation into complexes which are quickly removed from circulation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J., Chen C. Y., Schalla W. O., Sarafian S. K., Taylor C. L., Knapp J. S., Morse S. A. Binding of S protein by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and potential role in invasion. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.70-75.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. A., Warren J. S. Complement component C5 modulates the systemic tumor necrosis factor response in murine endotoxic shock. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1474–1481. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1474-1481.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Joø G. B., Brusletto B., Kierulf P. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and 2, alpha-2-antiplasmin, plasminogen, and endotoxin levels in systemic meningococcal disease. Thromb Res. 1990 Jan 15;57(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Kierulf P., Gaustad P., Skulberg A., Bruun J. N., Halvorsen S., Sørensen E. Plasma endotoxin as a predictor of multiple organ failure and death in systemic meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):195–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Mollnes T. E., Kierulf P. Complement activation and endotoxin levels in systemic meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):58–65. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Sandset P. M., Joø G. B., Ovstebø R., Abildgaard U., Kierulf P. The quantitative association of plasma endotoxin, antithrombin, protein C, extrinsic pathway inhibitor and fibrinopeptide A in systemic meningococcal disease. Thromb Res. 1989 Aug 15;55(4):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H. Specific binding of the human S protein (vitronectin) to streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1878–1883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1878-1883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi N. H., Nakano Y., Tobe T., Mazda T., Tomita M. Incorporation of SP-40,40 into the soluble membrane attack complex (SMAC, SC5b-9) of complement. Int Immunol. 1990;2(5):413–417. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.5.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan M. G., Tomasini B. R., Schultz R. L., Mosher D. F. Plasma vitronectin polymorphism in normal subjects and patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., Alessi M. C., Verstreken M., Kruithof E. K., Juhan-Vague I., Collen D. Measurement of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in biologic fluids with a murine monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., De Mol M., Alessi M. C., Baudner S., Pâques E. P., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Collen D. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 binding protein from human plasma. Identification as a multimeric form of S protein (vitronectin). J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15454–15461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P. Complement deficiencies and meningococcal disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Oct;86 (Suppl 1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb06209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederichsen P., Kierulf P. A more accurate dye-binding method for the routine determination of serum albumin. Clin Chem. 1979 Jun;25(6):1180–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ohgren Y., Ruoslahti E. Serum spreading factor (vitronectin) is present at the cell surface and in tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4003–4007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Suzuki S., Ruoslahti E. Vitronectin--a major cell attachment-promoting protein in fetal bovine serum. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Berstecher C., Krämer S., Fassbender W., Bhakdi S. In vivo clearance studies of the terminal fluid-phase complement complex in rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jul;77(1):112–116. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høgåsen K., Mollnes T. E., Harboe M. Heparin-binding properties of vitronectin are linked to complex formation as illustrated by in vitro polymerization and binding to the terminal complement complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23076–23082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høgåsen K., Mollnes T. E., Tschopp J., Harboe M. Quantitation of vitronectin and clusterin. Pitfalls and solutions in enzyme immunoassays for adhesive proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Mar 15;160(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ill C. R., Ruoslahti E. Association of thrombin-antithrombin III complex with vitronectin in serum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15610–15615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Clusterin: the intriguing guises of a widely expressed glycoprotein. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Hugo F., Bhakdi S. Interaction of complement S-protein with thrombin-antithrombin complexes: a role for the S-protein in haemostasis. Thromb Res. 1985 May 15;38(4):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Sharpe J. A., Murphy B., d'Apice A. J., Classon B., Hudson P., Walker I. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40,40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner P. J., Davies K. A., Walport M. J., Cope A. P., Würzner R., Orren A., Morgan B. P., Cohen J. Meningococcal septicaemia in a C6-deficient patient and effects of plasma transfusion on lipopolysaccharide release. Lancet. 1992 Dec 5;340(8832):1379–1381. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92561-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. L., Sigurdardottir O., Wiman B. Stability of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1). Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):748–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milis L., Morris C. A., Sheehan M. C., Charlesworth J. A., Pussell B. A. Vitronectin-mediated inhibition of complement: evidence for different binding sites for C5b-7 and C9. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Apr;92(1):114–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Ohkubo T. How vitronectin binds to activated glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex and its function in platelet aggregation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991 Nov;96(5):605–609. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/96.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Abrahamsen T. G., Garred P. Alterations in the terminal complement pathway in leukopenic children with malignant diseases during episodes with evidence of infection. Complement Inflamm. 1989;6(6):460–469. doi: 10.1159/000463115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E. Early- and late-phase activation of complement evaluated by plasma levels of C3d,g and the terminal complement complex. Complement. 1985;2(2-3):156–164. doi: 10.1159/000467856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Lea T., Frøland S. S., Harboe M. Quantification of the terminal complement complex in human plasma by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on monoclonal antibodies against a neoantigen of the complex. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P. Mechanisms of tissue damage by the membrane attack complex of complement. Complement Inflamm. 1989;6(2):104–111. doi: 10.1159/000463082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., d'Apice A. J. SP-40,40, a newly identified normal human serum protein found in the SC5b-9 complex of complement and in the immune deposits in glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1858–1864. doi: 10.1172/JCI113531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer H., Schwarz A., Heimburger N. Determination of human thrombin-antithrombin III complex in plasma with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):101–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The SC5b-7 complex: formation, isolation, properties, and subunit composition. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2024–2029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Preissner K. T., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Inhibition of C9 polymerization within the SC5b-9 complex of complement by S-protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1984;284:89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powars D., Larsen R., Johnson J., Hulbert T., Sun T., Patch M. J., Francis R., Chan L. Epidemic meningococcemia and purpura fulminans with induced protein C deficiency. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17(2):254–261. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T. Structure and biological role of vitronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:275–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarello V., Scheld W. M. Bacterial meningitis: pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and progress. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 17;327(12):864–872. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209173271208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. The in vivo metabolism of antithrombin III and antithrombin III complexes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3243–3248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasini B. R., Mosher D. F. Conformational states of vitronectin: preferential expression of an antigenic epitope when vitronectin is covalently and noncovalently complexed with thrombin-antithrombin III or treated with urea. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):903–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Chonn A., Hertig S., French L. E. Clusterin, the human apolipoprotein and complement inhibitor, binds to complement C7, C8 beta, and the b domain of C9. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2159–2165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Weigand P., Grulich-Henn J., Chhatwal G. S., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H., Preissner K. T. Mediation of adherence of streptococci to human endothelial cells by complement S protein (vitronectin). Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2851–2855. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2851-2855.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Almquist A., Sigurdardottir O., Lindahl T. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI) is bound to vitronectin in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80999-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. C., Preissner K. T., Bouma B. N., de Groot P. G. Binding of vitronectin-thrombin-antithrombin III complex to human endothelial cells is mediated by the heparin binding site of vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2264–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. C., de Groot P. G., Bouma B. N., Preissner K. T. Ternary vitronectin-thrombin-antithrombin III complexes in human plasma. Detection and mode of association. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1279–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



