Abstract
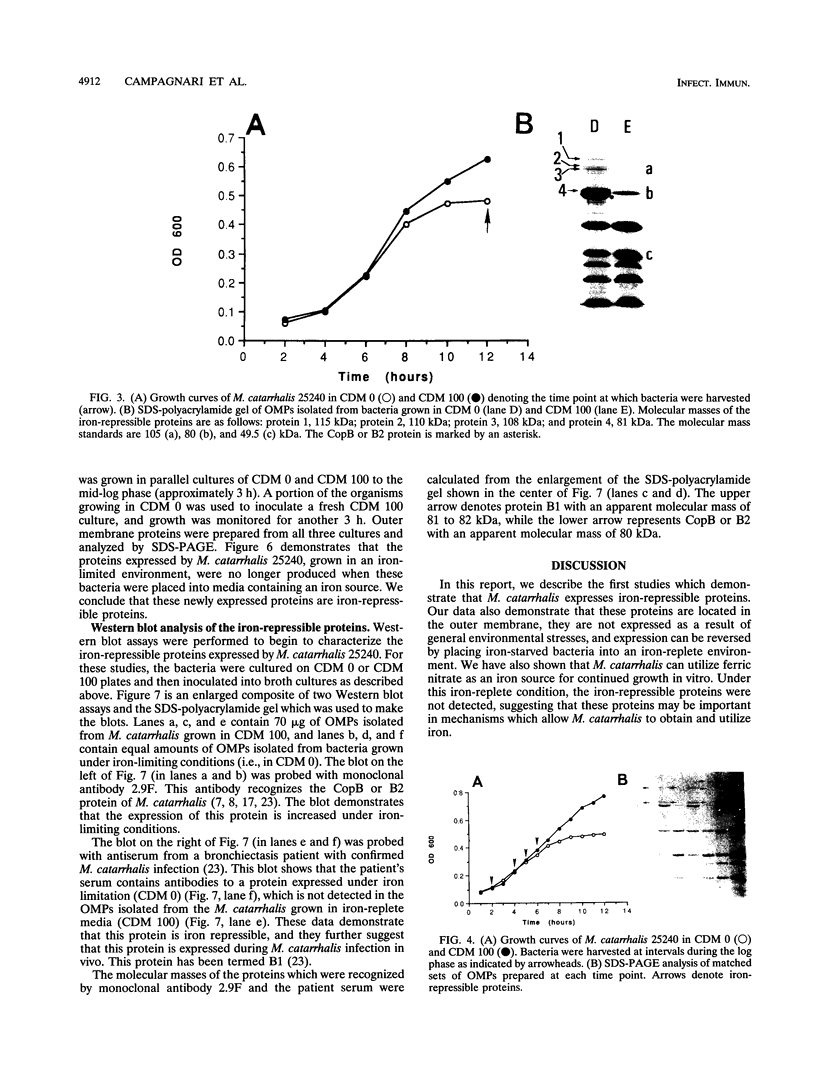
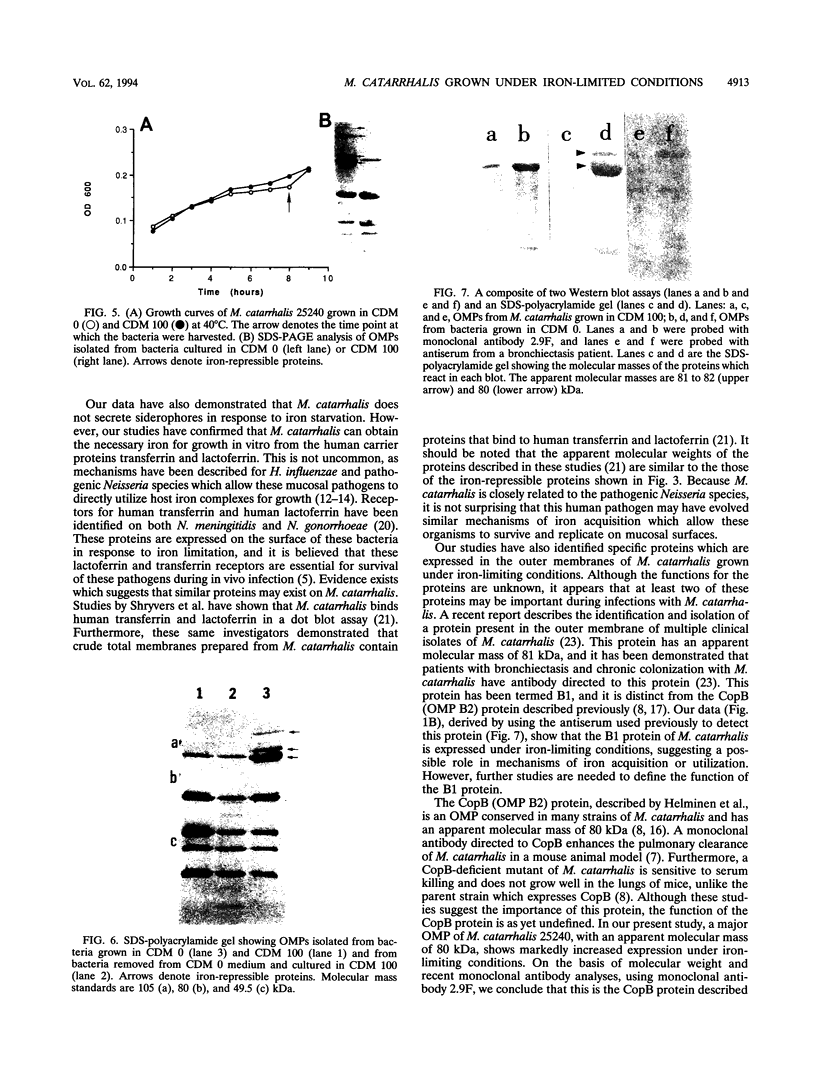
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, a mucosal pathogen closely related to Neisseria species, is a prominent cause of otitis media in young children and lower respiratory tract infections in adults. In this study, we investigated whether M. catarrhalis can compete for iron bound to human transferrin or human lactoferrin in a manner similar to that utilized by Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Our studies demonstrated that M. catarrhalis obtains iron from these serum carrier proteins and also maintains growth with ferric nitrate in vitro. Furthermore, we report that when M. catarrhalis is grown under iron-limited conditions, the bacteria express new outer membrane proteins that are not detected in membranes of organisms cultured in an iron-rich environment. We have shown that these are iron-repressible proteins since they are not induced by other environmental stresses and the expression of these proteins is repressed when a source of iron is provided for iron-limited bacteria. The iron-repressible proteins are expressed in the absence of any detectable siderophore production. These iron-repressible proteins may be important for the acquisition and utilization of iron in vivo, which could allow M. catarrhalis to colonize and survive on human mucosal surfaces.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartos L. C., Murphy T. F. Comparison of the outer membrane proteins of 50 strains of Branhamella catarrhalis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):761–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle F. M., Georghiou P. R., Tilse M. H., McCormack J. G. Branhamella (Moraxella) catarrhalis: pathogenic significance in respiratory infections. Med J Aust. 1991 May 6;154(9):592–596. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1991.tb121219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Branhamella catarrhalis: an organism gaining respect as a pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Oct;3(4):293–320. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., West E. P., McKenna W., Thompson S. A., Sparling P. F. A pleiotropic iron-uptake mutant of Neisseria meningitidis lacks a 70-kilodalton iron-regulated protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):977–983. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.977-983.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager H., Verghese A., Alvarez S., Berk S. L. Branhamella catarrhalis respiratory infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Nov-Dec;9(6):1140–1149. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.6.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helminen M. E., Maciver I., Latimer J. L., Cope L. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. A major outer membrane protein of Moraxella catarrhalis is a target for antibodies that enhance pulmonary clearance of the pathogen in an animal model. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2003–2010. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2003-2010.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helminen M. E., Maciver I., Paris M., Latimer J. L., Lumbley S. L., Cope L. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. A mutation affecting expression of a major outer membrane protein of Moraxella catarrhalis alters serum resistance and survival in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1194–1201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. O., Teele D. W., Pelton S. I. New concepts in otitis media: results of investigations of the Greater Boston Otitis Media Study Group. Adv Pediatr. 1992;39:127–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingman K. L., Murphy T. F. Purification and characterization of a high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis. Infect Immun. 1994 Apr;62(4):1150–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.4.1150-1155.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Calderwood S. B. Role of iron in regulation of virulence genes. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Apr;6(2):137–149. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Purine metabolism in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: the requirement for hypoxanthine. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):13–20. doi: 10.1139/m80-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Surface-exposed and antigenically conserved determinants of outer membrane proteins of Branhamella catarrhalis. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2938–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2938-2941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F. The surface of Branhamella catarrhalis: a systematic approach to the surface antigens of an emerging pathogen. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S75–S77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicotra B., Rivera M., Luman J. I., Wallace R. J., Jr Branhamella catarrhalis as a lower respiratory tract pathogen in patients with chronic lung disease. Arch Intern Med. 1986 May;146(5):890–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar J., Campagnari A. A., Kirkham C., Murphy T. F. Characterization of an antigenically conserved heat-modifiable major outer membrane protein of Branhamella catarrhalis. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):804–809. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.804-809.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Lee B. C. Comparative analysis of the transferrin and lactoferrin binding proteins in the family Neisseriaceae. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Mar;35(3):409–415. doi: 10.1139/m89-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]