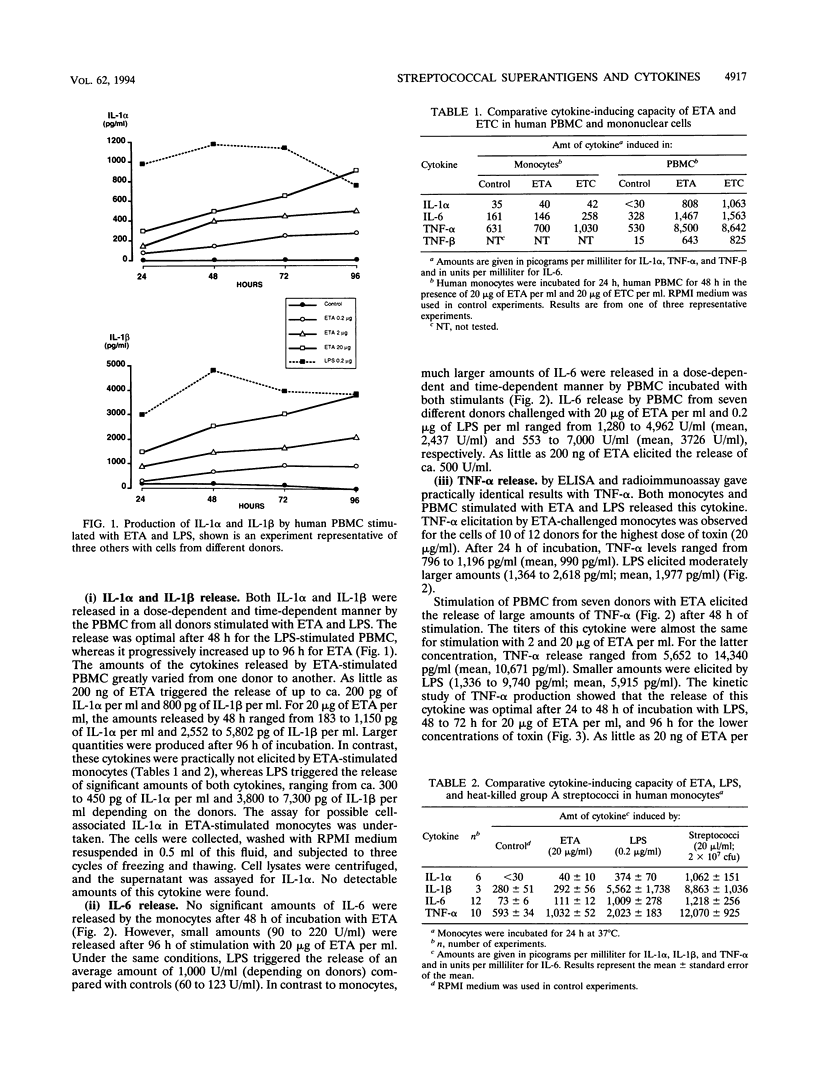
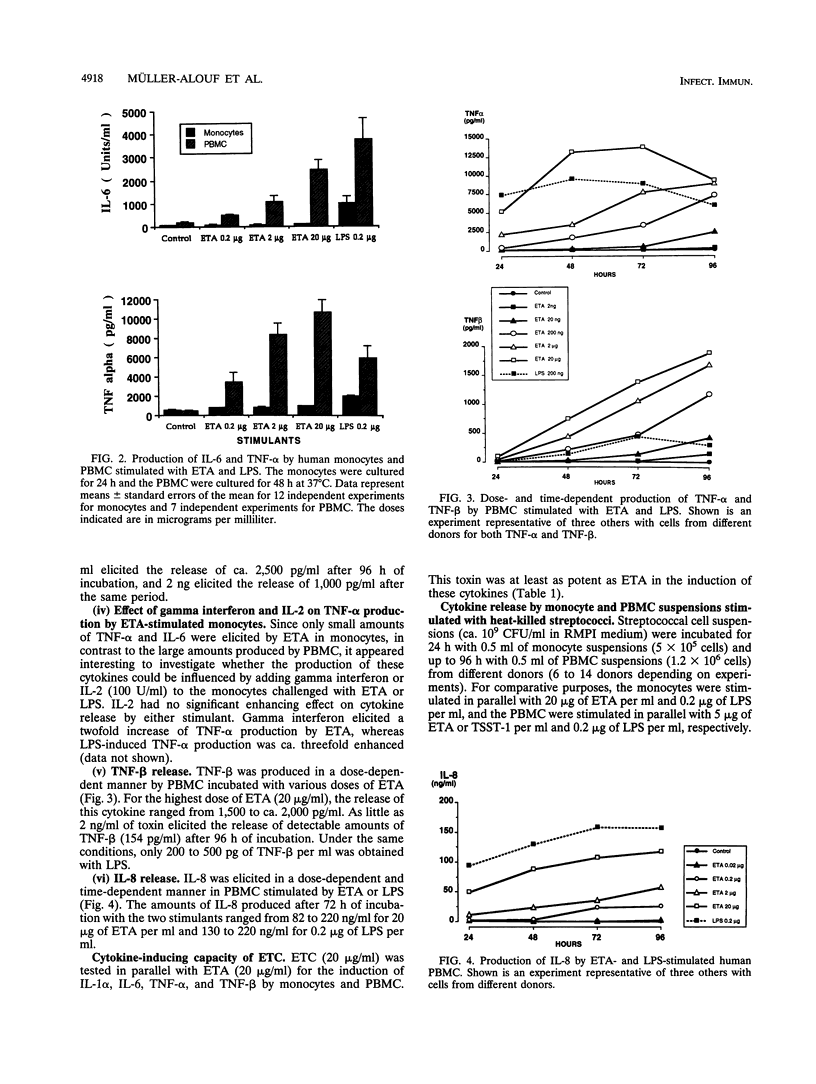
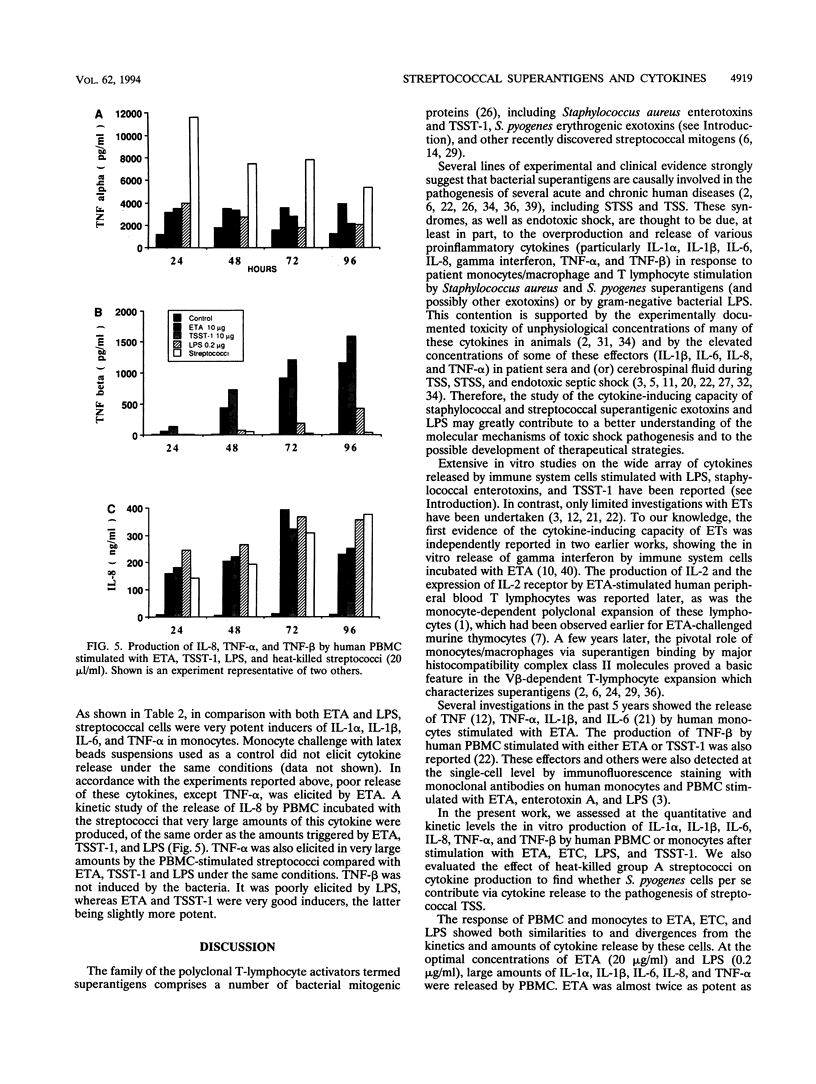
Abstract
The differences between toxic or septic shocks in humans during infections by streptococci and gram-negative bacteria remain to be fully characterized. For this purpose, a quantitative study of the cytokine-inducing capacity of Streptococcus pyogenes erythrogenic (pyrogenic) exotoxins (ETs) A and C, heat-killed S. pyogenes bacteria, and Neisseria meningitidis endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and monocytes has been undertaken. The levels of interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and TNF-beta induced by these bacterial products and bacteria were determined by using cell supernatants. The capacity of ETs to elicit the monocyte-derived cytokines IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha was found to depend on the presence of T lymphocytes, because of the failure of purified monocytes to produce significant amounts of these cytokines in response to ETs. PMBC elicited large amounts of these cytokines, as well as IL-8 and TNF-beta, with an optimal release after 48 to 96 h. The most abundant cytokine produced in response to ETA was IL-8. In contrast to the superantigens ETA and ETC, LPS and heat-killed streptococci stimulated the production of significant amounts of IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha, with optimal production after 24 to 48 h in monocytes, indicating no significant involvement of T cells in the process. ETs, but neither LPS nor streptococci, were potent inducers of TNF-beta in PBMC. This study outlines the differences in the pathophysiological features of shock evoked by endotoxins and superantigens during infection by gram-negative bacteria and group A streptococci, respectively. The production of TNF-alpha was a common pathway for LPS, streptococcal cells, and ETs, although cell requirements and kinetics of cytokine release were different.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E., Geoffroy C., Klatzmann D., Gluckman J. C., Gruest J., Montagnier L. High production of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome virus (lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by human T lymphocytes stimulated by streptococcal mitogenic toxins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):639–641. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.639-641.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Nagy S., Björk L., Abrams J., Holm S., Andersson U. Bacterial toxin-induced cytokine production studied at the single-cell level. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:69–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Group A streptococcal infections and acute rheumatic fever. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 12;325(11):783–793. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109123251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Gram-negative sepsis: a dilemma of modern medicine. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jan;6(1):57–68. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. A., Gerlach D., Hartwig U. F., Ozegowski J. H., Romagné F., Carrel S., Köhler W., Fleischer B. Stimulation of human T cells by streptococcal "superantigen" erythrogenic toxins (scarlet fever toxins). J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2457–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Alouf J. E. Mitogenicity of streptococcal extracellular products and antagonism with concanavalin A. Immunol Lett. 1982;5(6):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Polymyxin-B inhibition of LPS-induced interleukin-1 secretion by human monocytes is dependent upon the LPS origin. Mol Immunol. 1986 Sep;23(9):965–969. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Riviere Y., Svab J., Montagnier L., Alouf J. E. Induction of interferon by streptococcus pyogenes extracellular products. Immunol Lett. 1982;5(6):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomarat M., Chapuis C., Lepape A., Bernard F. Two cases of severe infection with beta-haemolytic group A streptococci associated with a toxic-shock-like syndrome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;9(12):901–903. doi: 10.1007/BF01967508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Toxic shock syndrome-associated staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor production. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):291–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Dohlsten M., Andersson U., Hedlund G., Ericsson P., Hansson J., Sjögren H. O. Production of TNF-alpha and TNF-beta by staphylococcal enterotoxin A activated human T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4663–4669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach D., Knöll H., Köhler W., Ozegowski J. H. Isolierung und Charakterisierung erythrogener Toxine von Streptococcus pyogenes 3. Mitteilung: Vergleichende Untersuchungen erythrogener Toxine vom Typ A. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Sep;250(3):277–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach D., Köhler W., Knöll H., Moravek L., Weeks C. R., Ferretti J. J. Purification and characterization of Streptococcus pyogenes erythrogenic toxin type A produced by a cloned gene in Streptococcus sanguis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Oct;266(3-4):347–358. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjörloff A., Fischer H., Hedlund G., Hansson J., Kenney J. S., Allison A. C., Sjögren H. O., Dohlsten M. Induction of interleukin-1 in human monocytes by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A requires the participation of T cells. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90056-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalo J. A., González-García A., Kalland T., Hedlund G., Martínez C., Kroemer G. Linomide, a novel immunomodulator that prevents death in four models of septic shock. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2372–2374. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougeon M. L., Dadaglio G., Garcia S., Müller-Alouf H., Roue R., Montagnier L. Is a dominant superantigen involved in AIDS pathogenesis? Lancet. 1993 Jul 3;342(8862):50–51. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hart M., van Schijndel R. J., Eerenberg A. J., Nuijens J. H., Thijs L. G., Aarden L. A. Interleukin-8 in sepsis: relation to shock and inflammatory mediators. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2835–2842. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2835-2842.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett S. P., Stevens D. L. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome: synthesis of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 by monocytes stimulated with pyrogenic exotoxin A and streptolysin O. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):879–885. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett S. P., Stevens D. L. Superantigens associated with staphylococcal and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor-beta synthesis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):232–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Cavaillon J. M., Moreau M., Szabó L. Interleukin 1 secretion by human monocytes stimulated by the isolated polysaccharide region of the Bordetella pertussis endotoxin. Mol Immunol. 1984 May;21(5):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi K., Igarashi H., Uchiyama T. Relative abilities of distinct isotypes of human major histocompatibility complex class II molecules to bind streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin types A and B. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5025–5029. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5025-5029.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Leung D. Y., Kappler J., Marrack P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:99–166. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60534-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty C., Misset B., Tamion F., Fitting C., Carlet J., Cavaillon J. M. Circulating interleukin-8 concentrations in patients with multiple organ failure of septic and nonseptic origin. Crit Care Med. 1994 Apr;22(4):673–679. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199404000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miethke T., Wahl C., Heeg K., Echtenacher B., Krammer P. H., Wagner H. T cell-mediated lethal shock triggered in mice by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: critical role of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):91–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollick J. A., Miller G. G., Musser J. M., Cook R. G., Grossman D., Rich R. R. A novel superantigen isolated from pathogenic strains of Streptococcus pyogenes with aminoterminal homology to staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):710–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI116641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz C., Carlet J., Fitting C., Misset B., Blériot J. P., Cavaillon J. M. Dysregulation of in vitro cytokine production by monocytes during sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1747–1754. doi: 10.1172/JCI115493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Alouf H., Alouf J. E., Gerlach D., Fitting C., Cavaillon J. M. Cytokine production by murine cells activated by erythrogenic toxin type A superantigen of Streptococcus pyogenes. Immunobiology. 1992 Nov;186(5):435–448. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal D., Lauener R. P., Braegger C. P., Kaufhold A., Simma B., Lütticken R., Seger R. A. T cell activation and cytokine release in streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome. J Pediatr. 1993 May;122(5 Pt 1):727–729. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(06)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozegowski J. H., Knöll H., Gerlach D., Köhler W. Isolierung und Charakterisierung von erythrogenen Toxinen. VII. Untersuchung des von Streptococcus pyogenes gebildeten erythrogenen Toxins Typ C. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 May;257(1):38–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt W., Müller-Alouf H., Alouf J. E., Köhler W. Erythrogenic toxins A, B and C: occurrence of the genes and exotoxin formation from clinical Streptococcus pyogenes strains associated with streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):313–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Role of superantigens in human disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):997–1002. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See R. H., Kum W. W., Chang A. H., Goh S. H., Chow A. W. Induction of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 by purified staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 requires the presence of both monocytes and T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2612-2618.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Tanner M. H., Winship J., Swarts R., Ries K. M., Schlievert P. M., Kaplan E. Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonew E., Gerlach D., Tonew M., Köhler W. Induktion von Immuninterferon durch erythrogene Toxine A und B des Streptococcus pyogenes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Sep;252(4):463–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby R., Greenberg R. N. The toxic shock syndrome and streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Apr;98(4):559–559. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-4-559_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



