Abstract
Clostridium perfringens type A strains which differed in alpha-toxin (phospholipase C [PLC]) productivity were inoculated intraperitoneally or intravenously into mice, and then their 50% mouse lethal doses (LD50) were determined. Strain NCTC 8237 produced ninefold higher PLC activity than strain 13. The mean LD50 for the former was 1 log unit lower than that for the latter. Two isogenic strains were constructed from strain 13: strain 13(pJIR418 alpha) (pJIR418 alpha contains the plc gene), which produced ninefold higher PLC activity than strain 13; and strain 13 PLC-, which showed no PLC productivity at all because of transformation-mediated gene disruption. The mean LD50 for strain 13(pJIR418 alpha) was 1 log unit lower than those for strain 13 PLC- and strain 13. These results indicate that PLC functions as a virulence-determining factor when it is produced in a sufficient amount. Such a difference in LD50 was also observed between Bacillus subtilis with and without the cloned plc gene. Inoculation of B. subtilis PLC+ intravenously into mice caused marked thrombocytopenia and leukocytosis. Mice inoculated with B. subtilis at 2 LD50 died because of circulatory collapse. Histological examination revealed that intravascular coagulation and vascular congestion occurred most prominently in the lungs. These results suggest that PLC plays a key role in the systemic intoxication of clostridial myonecrosis, probably by affecting the functions of platelets and phagocytes.
Full text
PDF

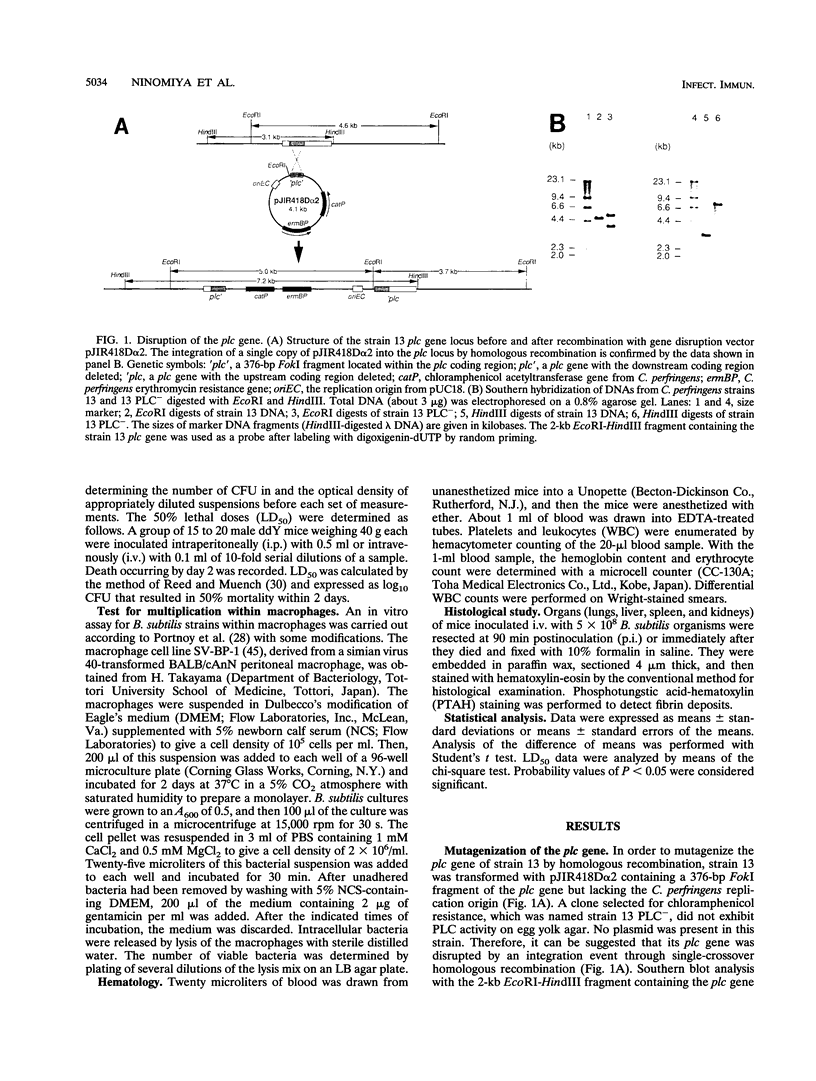

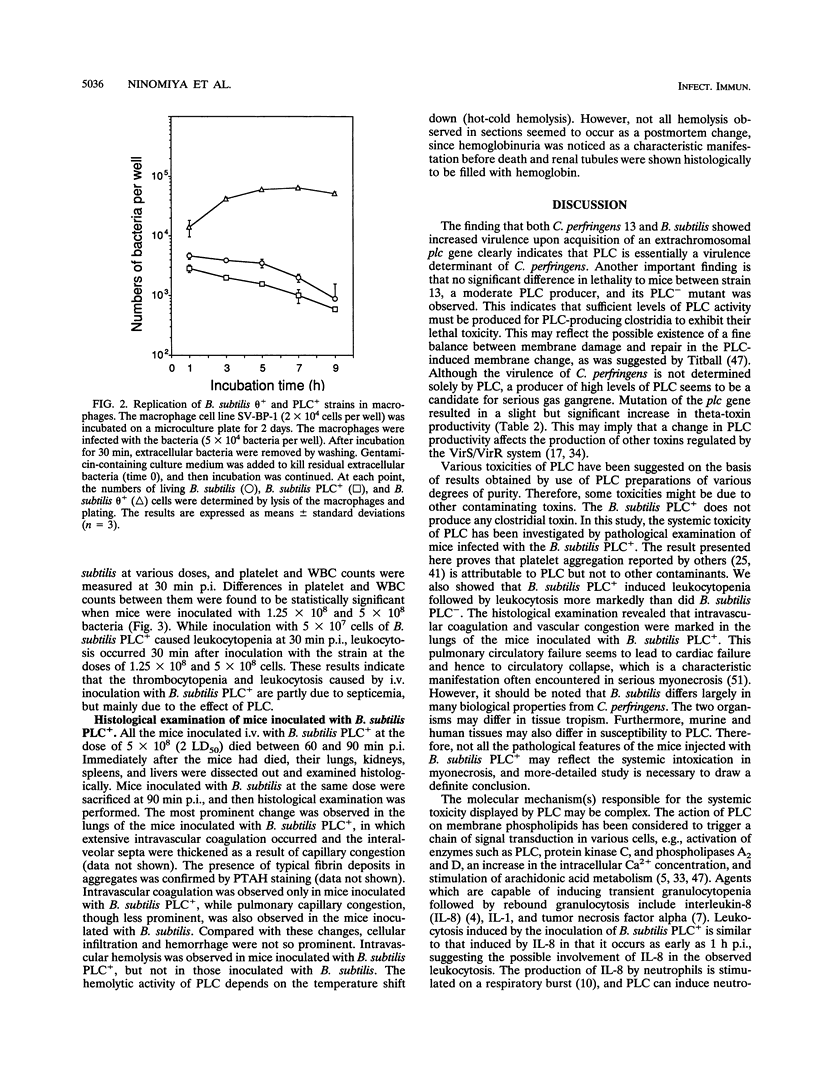



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener M., Eglème C., Rummel W. Phospholipase C-induced anion secretion and its interaction with carbachol in the rat colonic mucosa. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 6;200(2-3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90581-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Sakurai J. Contraction of the rat isolated aorta caused by Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin (phospholipase C): evidence for the involvement of arachidonic acid metabolism. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Yoneda K., Cohen D. A., McClain C. J. Provocation of pulmonary vascular endothelial injury in rabbits by human recombinant interleukin-1 beta. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2255–2263. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2255-2263.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatheway C. L. Toxigenic clostridia. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):66–98. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Des Prez R. M. Complement-dependent platelet injury by staphylococcal protein A. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi H., Mukaida N., Okamoto S., Teranishi H., Kasuya M., Matsushima K. Cadmium induces interleukin-8 production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with the concomitant generation of superoxide radicals. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1993 Dec;12(6):421–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houldsworth S., Andrew P. W., Mitchell T. J. Pneumolysin stimulates production of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta by human mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1994 Apr;62(4):1501–1503. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.4.1501-1503.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama S., Matsushita O., Minami J., Mizobuchi S., Okabe A. Comparison of the alpha-toxin genes of Clostridium perfringens type A and C strains: evidence for extragenic regulation of transcription. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):457–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.457-463.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug E. L., Kent C. Phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens: preparation and characterization of homogeneous enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyristis M., Bryant A. E., Sloan J., Awad M. M., Nisbet I. T., Stevens D. L., Rood J. I. Identification and molecular analysis of a locus that regulates extracellular toxin production in Clostridium perfringens. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jun;12(5):761–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony D. E., Moore T. I. Stable L-forms of Clostridium perfringens and their growth on glass surfaces. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jul;22(7):953–959. doi: 10.1139/m76-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita C., Matsushita O., Koyama M., Okabe A. A Clostridium perfringens vector for the selection of promoters. Plasmid. 1994 May;31(3):317–319. doi: 10.1006/plas.1994.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita O., Yoshihara K., Katayama S., Minami J., Okabe A. Purification and characterization of Clostridium perfringens 120-kilodalton collagenase and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.149-156.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Hiraoka K., Takaishi K., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Takai Y. Regulation of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase by a small GTP-binding protein and its stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10215–10218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Holme T., Nord C. E., Smyth C. J., Wadström T. Production of phospholipase C (alpha-toxin), haemolysins and lethal toxins by Clostridium perfringens types A to D. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Sep;96(1):137–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Thelestam M., Wadström T. Effect of Clostridium perfringens phospholipase C(alpha-toxin) on the human diploid fibroblast membrane. J Membr Biol. 1974;16(4):313–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01872421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsaka A., Tsuchiya M., Oshio C., Miyairi M., Suzuki K., Yamakawa Y. Aggregation of platelets in the mesenteric microcirculation of the rat induced by alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) of Clostridium perfringens. Toxicon. 1978;16(4):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(78)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson E. K. Phospholipase C mimics the differential effects of phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate on the colony formation and cornification of cultured normal and transformed human keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Jun;8(6):857–860. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.6.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Tweten R. K., Kehoe M., Bielecki J. Capacity of listeriolysin O, streptolysin O, and perfringolysin O to mediate growth of Bacillus subtilis within mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2710–2717. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2710-2717.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts I., Holmes W. M., Hylemon P. B. Modified plasmid isolation method for Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium absonum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):197–199. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.197-199.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood J. I., Cole S. T. Molecular genetics and pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Dec;55(4):621–648. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.4.621-648.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Ochi S., Tanaka H. Regulation of Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin-activated phospholipase C in rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1994 Feb;62(2):717–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.2.717-721.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Ba-Thein W., Tamaki M., Hayashi H. The virR gene, a member of a class of two-component response regulators, regulates the production of perfringolysin O, collagenase, and hemagglutinin in Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1616–1623. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1616-1623.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Okabe A., Minami J., Hayashi H. An upstream regulatory sequence stimulates expression of the perfringolysin O gene of Clostridium perfringens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):137–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.137-142.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan J., Warner T. A., Scott P. T., Bannam T. L., Berryman D. I., Rood J. I. Construction of a sequenced Clostridium perfringens-Escherichia coli shuttle plasmid. Plasmid. 1992 May;27(3):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spika J. S., Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Hammerschmidt D. E., Verbrugh H. A., Verhoef J., Quie P. G. Role of peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus in leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and complement activation associated with bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):227–234. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Mitten J., Henry C. Effects of alpha and theta toxins from Clostridium perfringens on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):324–333. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Troyer B. E., Merrick D. T., Mitten J. E., Olson R. D. Lethal effects and cardiovascular effects of purified alpha- and theta-toxins from Clostridium perfringens. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):272–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styrt B., Walker R. D., White J. C. Neutrophil oxidative metabolism after exposure to bacterial phospholipase C. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Jul;114(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara T., Takahashi T., Yamaya S., Ohsaka A. In vitro aggregation of platelets induced by alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) of Clostridium perfringens. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1976 Oct;29(5):255–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara T., Takahashi T., Yamaya S., Ohsaka A. Vascular permeability increase by alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) of Clostridium perfringens. Toxicon. 1977;15(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. TRANSDUCTION OF SPOROGENESIS IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:294–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.294-298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Sugahara T., Ohsaka A. Phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):710–725. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titball R. W. Bacterial phospholipases C. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):347–366. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.347-366.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyonaga T., Matsushita O., Katayama S., Minami J., Okabe A. Role of the upstream region containing an intrinsic DNA curvature in the negative regulation of the phospholipase C gene of Clostridium perfringens. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(6):603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Van Beeumen J., Opdenakker G., Billiau A. A novel, NH2-terminal sequence-characterized human monokine possessing neutrophil chemotactic, skin-reactive, and granulocytosis-promoting activity. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1364–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Some biological properties of purified staphylococcal haemolysins. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. VII. Studies on -haemolysin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):308–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




