Abstract
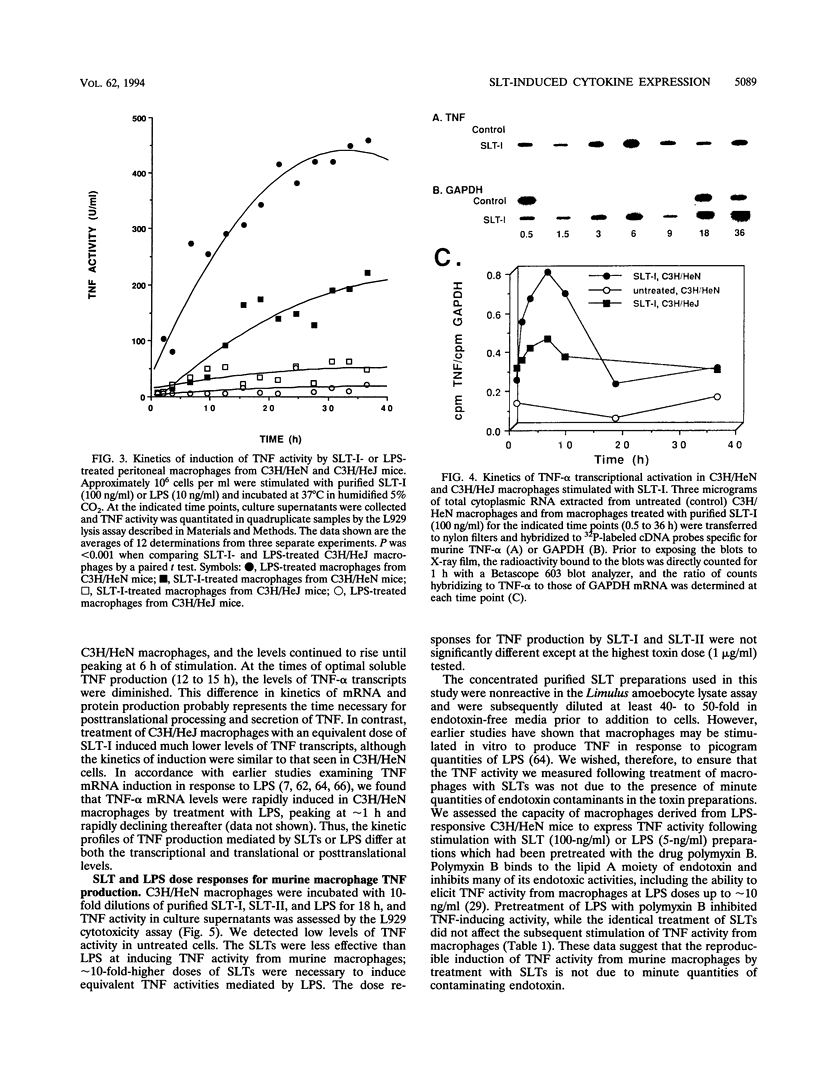
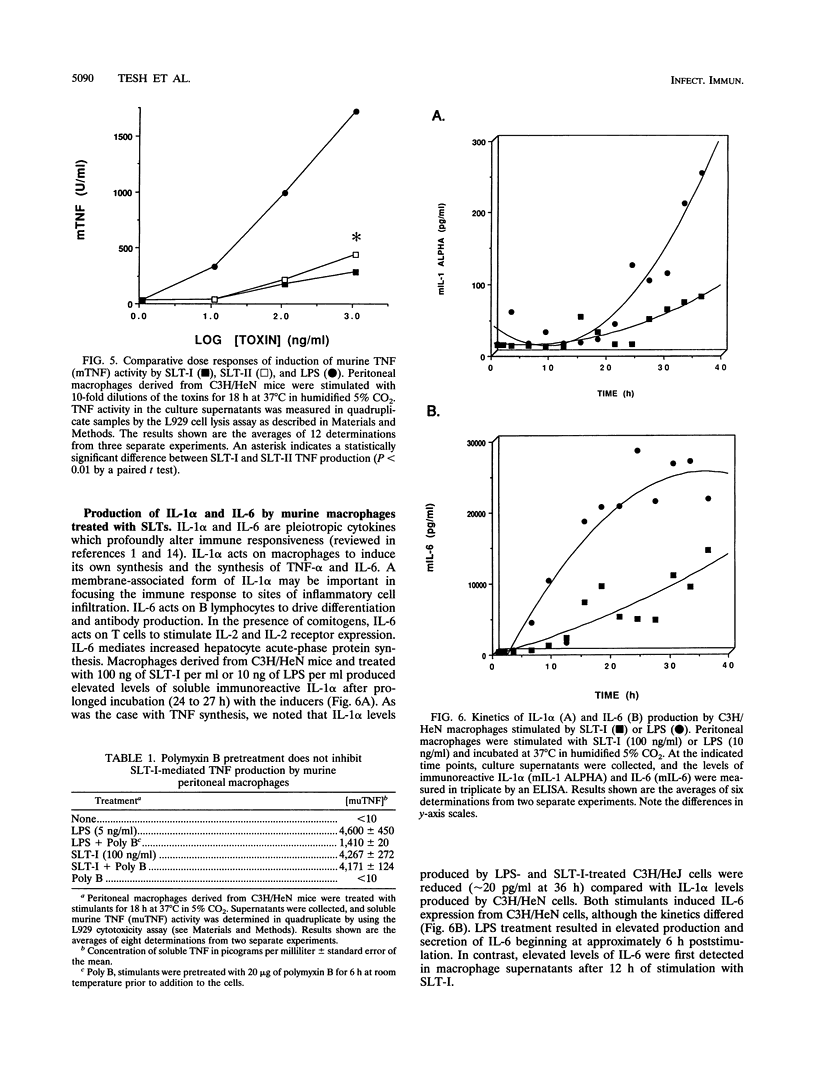
Infections with Shiga toxin-producing Shigella dysenteriae type 1 and Shiga-like toxin (SLT)-producing Escherichia coli cause outbreaks of bloody diarrhea in which patients are at risk for developing life-threatening complications involving the renal and central nervous systems. Histopathology studies and in vitro experiments suggested that the toxins damage toxin receptor-expressing endothelial cells (EC) lining glomerular and central nervous system capillaries. In the presence of inducible host factors (cytokines), EC sensitivity to SLT toxicity was increased approximately 1 million-fold. We hypothesized that to manifest the vascular lesions characteristic of infection with toxin-producing bacteria, two signals were needed: systemic toxins and elevated proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-alpha], interleukin 1 [IL-1], and IL-6). Human EC do not secrete these cytokines when stimulated with SLTs in vitro, suggesting that additional cells may be involved in pathogenesis. Therefore, we carried out comparative analyses of the capacity of purified (endotoxin-free) SLTs and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) to induce cytokine mRNA and proteins from murine macrophages. The cells were essentially refractory to SLT cytotoxicity, expressing low to undetectable levels of toxin receptor. SLTs and LPS induced TNF activity and IL-6 expression from macrophages, although dose response and kinetics of cytokine induction differed. LPS was a more effective inducing agent than SLTs. SLT-I-induced TNF activity and IL-6 expression were delayed compared with induction mediated by LPS. IL-1 alpha production required approximately 24 h of exposure to SLTs or LPS. Macrophages from LPS-hyporesponsive C3H/HeJ mice produced low levels of TNF activity when treated with SLT-I, suggesting that LPS and SLTs may utilize separate signaling pathways for cytokine induction.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale J. F., Jr, Brasher C., Siegler R. L. CNS manifestations of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Relationship to metabolic alterations and prognosis. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Sep;134(9):869–872. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130210053014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Potter M. E., Strockbine N. A. Evidence for participation of the macrophage in Shiga-like toxin II-induced lethality in mice. Microb Pathog. 1990 Aug;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Potter M. E., Wachsmuth I. K. Continuous peritoneal infusion of Shiga-like toxin II (SLT II) as a model for SLT II-induced diseases. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):774–777. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baud L., Oudinet J. P., Bens M., Noe L., Peraldi M. N., Rondeau E., Etienne J., Ardaillou R. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rat mesangial cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Kidney Int. 1989 May;35(5):1111–1118. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni F., Kruys V., Shakhov A., Jongeneel C. V., Beutler B. Analysis of tumor necrosis factor promoter responses to ultraviolet light. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):56–62. doi: 10.1172/JCI116984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Korom S., Schmidt G. Effects of Escherichia coli hemolysin on human monocytes. Cytocidal action and stimulation of interleukin 1 release. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1746–1753. doi: 10.1172/JCI114631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromander A., Holmgren J., Lycke N. Cholera toxin stimulates IL-1 production and enhances antigen presentation by macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Echeverria P., Lindberg A. A. Digalactosyl-containing glycolipids as cell surface receptors for shiga toxin of Shigella dysenteriae 1 and related cytotoxins of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13 (Suppl 4):S298–S303. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_4.s298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaby R., Morelec M. J., Ensergueix D., Girard R. Membrane glycolipid and phospholipid composition of lipopolysaccharide-responsive and -nonresponsive murine B lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):777–785. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.777-785.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Madrid-Marina V., Estrov Z., Freedman M. H., Lingwood C. A., Dosch H. M. Expression of glycolipid receptors to Shiga-like toxin on human B lymphocytes: a mechanism for the failure of long-lived antibody response to dysenteric disease. Int Immunol. 1990;2(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Müller F., Däubener W., Fischer H. G., Hadding U., Northoff H. Cytokine response by human monocytes to Clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3659–3666. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3659-3666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine A., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Role of Shiga toxin in the pathogenesis of bacillary dysentery, studied by using a Tox- mutant of Shigella dysenteriae 1. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3099–3109. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3099-3109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna P. C., Acosta D., Collier R. J. On the role of macrophages in anthrax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10198–10201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel Y., Silva M., Giroir B., Weinberg A., Cleary T. B., Beutler B. A reporter transgene indicates renal-specific induction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) by shiga-like toxin. Possible involvement of TNF in hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2110–2116. doi: 10.1172/JCI116811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda D. J., Lee J. C., Young P. R. The kinetics of interleukin 1 secretion from activated monocytes. Differences between interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8473–8479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., McCallum R. E. Identification of tumor necrosis factor as a transcriptional regulator of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene following endotoxin treatment of mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4040–4050. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4040-4050.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Okusawa S., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Induction by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 of a circulating tumor necrosis factor-like substance in rabbits and of immunoreactive tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 from human mononuclear cells. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1017–1025. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Feldman H. A., Donohue-Rolfe A., Balasubramanian K. A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. XIV. Analysis of Shiga toxin receptors on cloned HeLa cells. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):881–889. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevnikar A. M., Brennan D. C., Singer G. G., Heng J. E., Maslinski W., Wuthrich R. P., Glimcher L. H., Kelley V. E. Stimulated kidney tubular epithelial cells express membrane associated and secreted TNF alpha. Kidney Int. 1991 Aug;40(2):203–211. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth R. S., Edgington T. S. Tumor necrosis factor production by human monocytes is a regulated event: induction of TNF-alpha-mediated cellular cytotoxicity by endotoxin. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2585–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licastro F., Morini M. C., Bolognesi A., Stirpe F. Ricin induces the production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta by human peripheral-blood mononuclear cells. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):517–520. doi: 10.1042/bj2940517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman A. P., Pitha P. M., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines by astrocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or a neurotropic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louise C. B., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of shiga toxin and lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1536–1543. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1536-1543.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louise C. B., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin, interleukin-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4173–4179. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4173-4179.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Taguchi M., Kovacs E. J., Young H. A., Oppenheim J. J. Intracellular localization of human monocyte associated interleukin 1 (IL 1) activity and release of biologically active IL 1 from monocytes by trypsin and plasmin. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2883–2891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Legaard P. K., Howell S. E., Fornella M. H., LeGrand R. D. Induction of interleukin-1 from murine peritoneal macrophages by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):978–982. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.978-982.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Strockbine N. A., Miller S. F., O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Cloning of Shiga-like toxin structural genes from a toxin converting phage of Escherichia coli. Science. 1985 Oct 11;230(4722):179–181. doi: 10.1126/science.2994228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Tesh V. L., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jackson M. P., Olsnes S., Sandvig K., Lindberg A. A., Keusch G. T. Shiga toxin: biochemistry, genetics, mode of action, and role in pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;180:65–94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77238-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Del Vecchio P. J., Brown J. E., Moran T. P., Rowland B. M., Judge T. K., Rothman S. W. Direct cytotoxic action of Shiga toxin on human vascular endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2373–2378. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2373-2378.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Gillis Z. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes in response to toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1026–1033. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Ulevitch R. J., Wright S. D., Sibley C. H., Ding A., Nathan C. F. Gram-negative endotoxin: an extraordinary lipid with profound effects on eukaryotic signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Sep;5(12):2652–2660. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G. HUS and TTP: variable expression of a single entity. Kidney Int. 1987 Aug;32(2):292–308. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Karmali M. A., Becker L. E., Smith C. R. The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Hum Pathol. 1988 Sep;19(9):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Rotman T. A., Jay V., Smith C. R., Becker L. E., Petric M., Olivieri N. F., Karmali M. A. Experimental verocytotoxemia in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4154–4167. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4154-4167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Ward S., O'Brien A. D., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Comparison of the glycolipid receptor specificities of Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variants. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):611–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.611-618.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Garred O., Prydz K., Kozlov J. V., Hansen S. H., van Deurs B. Retrograde transport of endocytosed Shiga toxin to the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):510–512. doi: 10.1038/358510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santucci L. A., Gutierrez P. L., Silverman D. J. Rickettsia rickettsii induces superoxide radical and superoxide dismutase in human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5113–5118. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5113-5118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung L. M., Jackson M. P., O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Transcription of the Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variant operons of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6386–6395. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6386-6395.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Burris J. A., Owens J. W., Gordon V. M., Wadolkowski E. A., O'Brien A. D., Samuel J. E. Comparison of the relative toxicities of Shiga-like toxins type I and type II for mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3392–3402. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3392-3402.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., O'Brien A. D. The pathogenic mechanisms of Shiga toxin and the Shiga-like toxins. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1817–1822. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Sharefkin J. B., O'Brien A. D. Evaluation of the role of Shiga and Shiga-like toxins in mediating direct damage to human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):344–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadolkowski E. A., Sung L. M., Burris J. A., Samuel J. E., O'Brien A. D. Acute renal tubular necrosis and death of mice orally infected with Escherichia coli strains that produce Shiga-like toxin type II. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3959–3965. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3959-3965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yohe H. C., Berenson C. S., Cuny C. L., Ryan J. L. Altered B-lymphocyte membrane architecture indicated by ganglioside accessibility in C3H/HeJ mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2888–2894. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2888-2894.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W. W., Burke P. A., Hand A. T., Walsh M. J., Hughes L. A., Forse R. A. Regulation of cytokine mRNA expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human macrophages. Arch Surg. 1993 Feb;128(2):158–164. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420140035006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoja C., Corna D., Farina C., Sacchi G., Lingwood C., Doyle M. P., Padhye V. V., Abbate M., Remuzzi G. Verotoxin glycolipid receptors determine the localization of microangiopathic process in rabbits given verotoxin-1. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Aug;120(2):229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Shellhaas J., Butler L. D. Differential regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor synthesis: effects of endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids and the role of the pituitary-adrenal axis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):301–305. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Kar N. C., Monnens L. A., Karmali M. A., van Hinsbergh V. W. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 induce expression of the verocytotoxin receptor globotriaosylceramide on human endothelial cells: implications for the pathogenesis of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2755–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





