Abstract
Proteins containing the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) motif comprise a conserved family, postulated to act as cell protectors. However, their function and mechanisms of action remain unclear. Here we show that PRELI, a mammalian LEA-containing homolog of yeast Ups1p, can associate with dynamin-like GTPase Optic Atrophy-1 (OPA1) and contribute to the maintenance of mitochondrial morphology. Accordingly, PRELI can uphold mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and enhance respiratory chain (RC) function, shown by its capacity to induce complex-I/NADH dehydrogenase and ATP synthase expression, increase oxygen consumption and reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. PRELI can also inhibit cell death induced by STS, TNF-α or UV irradiation. Moreover, in vitro and in vivo dominant-negative overexpression of mutant PRELI/LEA− (lacking the LEA motif) and transient in vitro PRELI-specific knockdown can render lymphocytes vulnerable to apoptosis, cause mouse embryo lethality and revert the resistance of lymphoma cells to induced death. Collectively, these data support the long-presumed notion of LEA protein-dependent mechanisms of cytoprotection and suggest that PRELI interacts with OPA1 to maintain mitochondria structures intact, sustain balanced ion−/proton+ gradients, promote oxidative phosphorylation reactions, regulate pro- and antiapoptotic protein traffic and enable cell responses to induced death. These findings may help to understand how bioenergetics is mechanistically connected with cell survival cues.
Keywords: cell survival, cancer, mouse genetics, evolution, LEA family
Cells respond to death-inducing stimuli by adaptive mechanisms that trigger stress-response gene expression.1 Among those, the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) genes comprise a unique family characterized by tandem LEA (A/TAEKAK) repeats, originally detected in plant embryos after exposure to environmental stress.2, 3 Remarkably, LEA-containing proteins are evolutionarily conserved4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and are predicted to reside in the mitochondria,5, 6, 8 the organelles that control energy production and programmed cell death or apoptosis. However, the relevance of LEA-containing proteins and the mechanisms determining their function are still unclear.
Our search for mechanisms that control B-lymphocyte selection, led to the identification of PRELI, a mammalian LEA-containing gene, selectively expressed by germinal-centre (GC) B-lymphocytes.7 The present study shows that PRELI opposes programmed cell death by intrinsic mechanisms that sustain mitochondrial structure, which in turn support the respiratory chain (RC), reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and prevent the release of molecules that trigger caspase-dependent and independent apoptosis. We also show that functional interference by dominant-negative expression of mutant PRELI/LEA− proteins and transient siRNA-mediated PRELI knockdown can render chemoresistant lymphoma cell lines sensitive to apoptosis. These findings are also supported in vivo by the functional interference effects of PRELI/LEA− expression in ubiquitous and leukocyte-specific transgenic (Tg) mice, which led to embryo and neonatal lethality, thus suggesting that PRELI's function may be vital for embryonic and hematopoietic development.
Results
PRELI localizes in the mitochondrial IMS and associates with OPA1
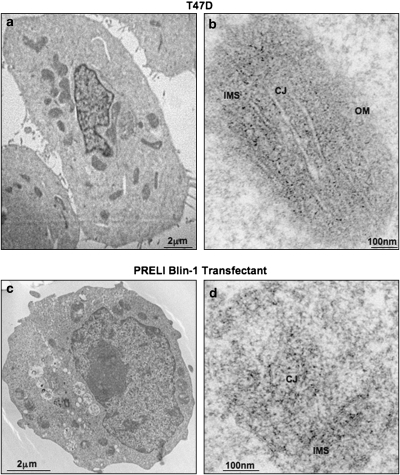
In agreement with the cited structural predictions,9, 10, 11 earlier studies have shown that MSF1-like/LEA-containing proteins are expressed in the mitochondria.5, 6, 8 As PRELI's yeast homolog Ups1p localizes within the mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS), interacts with Mgm1, a yeast dynamin-associated GTPase equivalent of OPA1, and regulates mitochondrial shape,8 we sought to determine whether comparable features apply to the mammalian protein. Congruent with the evolutionary parallel, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) shows that PRELI localizes in the IMS along mitochondrial cristae junctions, in which detection appears indistinguishable between the endogenous expression of the T47D breast carcinoma cell line12 and enforced PRELI overexpression in the acute lymphocytic leukemia Blin-1 transfectant (Figure 1).13
Figure 1.
Detection of PRELI expression by TEM. (a) A 2-μm image of T47D breast carcinoma cells, which have been observed to express high endogenous PRELI levels. (b) A 100-nm image taken from the centered T47D cell shown in panel a, depicting a detailed organization of mitochondrial structures, including the outer membrane (OM), IMS and cristae junctions (CJ). PRELI expression is notable by the dark immunogold dots within the IMS in intimate proximity to cristae membranes at the CJ. (c) A 2-μm image of a stable PRELI Blin-1 transfectant. (d) A 100-nm image taken from the same PRELI Blin-1 transfectant that also reveals significant PRELI expression within the IMS/CJ boundaries, albeit at lower resolution, given the fact that morphology and internal structures of suspension cells are not as well preserved as those in adhered T47D monolayers. The magnification bars are indicated and proportional to original caption of TEM images
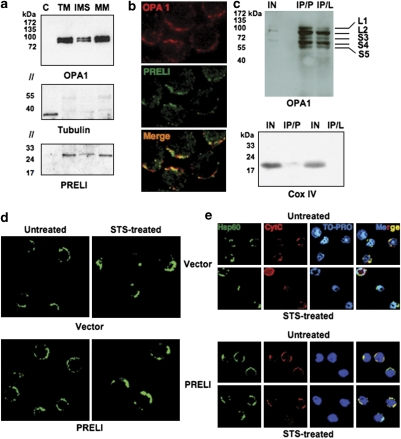
PRELI expression was additionally examined by comparative immunoblots of cytosol, total mitochondria (TM), IMS and mitochondrial membrane (MM) protein fractions. We found that both PRELI and OPA1 are detectable in the IMS and prominently present in the MM fraction (Figure 2a). The observed OPA1 doublet bands are consistent with large (L) and small (S) protein isoforms,14 of which L2 and S4 are prominent. By fluorescence microscopy, we also observed that PRELI and OPA1 colocalize in the mitochondria (Figure 2b), insinuating their potential biochemical interactions. Immunoprecipitation (IP)/immunoblot experiments reveal that PRELI can co-immunoprecipitate with prominent OPA1 isoforms and thus provide support to their predicted biochemical interactions (Figure 2c). These interactions could be relevant to maintain mitochondrial cristae junctions tight and prevent cytochrome c (CytC) release. Consistent with this reasoning, treatment of vector transfectants with the kinase inhibitor staurosporine (STS) caused alterations of mitochondrial morphology (Figure 2d), which lead to quantitative redistribution of CytC to the cytosol (Figure 2e, and Supplementary Figure S1). Such alterations were routinely prevented in PRELI-expressing cells (Figure 2d and e, and Supplementary Figure S1). Of note, IP results show that both full-length PRELI and mutant PRELI/LEA− (which lacks the LEA motif) can associate with OPA1 isoforms. This implies that whereas the LEA sequence is dispensable for protein binding, it may be required for PRELI-dependent functions.
Figure 2.
PRELI's and OPA1's colocalization, association and putative cooperation. (a) Immunoblot results assessing the expression of OPA1 (top blot), tubulin (middle blot) and PRELI (bottom blot) in cytosolic (C) total mitochondria (TM), inter-membrane space (IMS) and mitochondrial membrane (MM) protein fractions. The molecular weight markers are indicated. // indicates that the same immunoblot was sectioned to enable the simultaneous probe of OPA1, tubulin and PRELI, according with their respective molecular mass. (b) Immunofluorescence microscopy revealing OPA1 expression (top, red fluorescence) and PRELI (middle, green fluorescence). The micrograph at the bottom depicts the merge of red and green fluorescence. (c) Comparative IP/immunoblot experiments to investigate putative interactions of PRELI or PRELI/LEA− with OPA1, using V5-tagged protein lysates from PRELI/LEA− or untagged PRELI Blin-1 transfectants. IP was respectively performed with agarose-conjugated anti-V5 antibody or rabbit polyclonal anti-PRELI IgG, whose immunocomplexes were subsequently precipitated by agarose-conjugated protein-A. Immunoblots were revealed with monoclonal anti-OPA-1 IgG. Control input protein lysate (IN) was used to the minimum to simply control for positive immunoreaction, whereas a total precipitate from 1.0 mg of protein lysate was loaded onto the respective IP lanes. The distinct OPA1 protein L1, L2, S3, S4 and S5 isoforms present in both PRELI and PRELI/LEA− immunocomplexes are indicated. The IP specificity was routinely controlled by the exclusive detection of mitochondrial COX-IV in the input but not in the IP lanes. (d) Comparative immunofluorescent detection of mitochondrial Hsp60 (green fluorescence) between vector and PRELI Blin-1 transfectants to monitor the morphology of mitochondria in the absence (left frames) or presence (right frames) of STS. (e) Confocal microscopy to compare CytC's (in red) sub-cellular distribution between vector and PRELI Blin-1 transfectants incubated in the absence (upper panels) or presence (lower panels) of STS. The detection of Hsp60 (in green) was used as a mitochondrial reference and the TO-PRO fluorochrome (shown herein in blue) served as nuclear counterstain
PRELI but not PRELI/LEA− can uphold mitochondrial ΔΨm
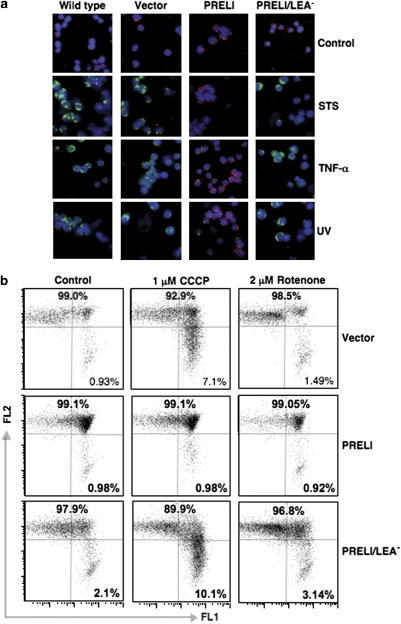
Under homeostatic conditions, the ΔΨm-sensitive JC-1 probe aggregates in the mitochondria and emits red fluorescence (Figure 3a). However, exposure to STS causes mitochondria to dissipate the ΔΨm, preventing JC-1 aggregation and resulting in green fluorescence emission. The STS-triggered red-to-green fluorescence shift was detectable in the wild type (WT) and in vector transfectants, yet was absent in PRELI Blin-1 transfectants (Figure 3a). Similar effects were observed with TNF-α and UV radiation (Figure 3a). In striking contrast to full-length PRELI, mutant PRELI/LEA− expression was completely incapable to uphold mitochondrial ΔΨm, induced by STS, TNF-α and UV radiation (Figure 3a). As it can be also corroborated in Figure 3a, mutant PRELI/LEA− could not prevent the mitochondrial damage caused by the apoptosis-inducing stimuli. These data collectively suggest that although PRELI/LEA− retains protein binding capacity, its altered structure resulting from loss of the LEA motif could hamper the required conformation for physiological cooperation with OPA1 to preserve mitochondrial cristae junctions intact.
Figure 3.
Effect of PRELI on mitochondrial ΔΨm. (a) Fluorescence microscopy results of WT and vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA− Blin-1 transfectants after exposure to STS, TNF-α and UVB radiation. Red (unaltered)-to-green (depolarized) JC-1 fluorescence shift measures altered ΔΨm. The DNA-binding blue fluorescent probe Hoechst 33342 served as a nuclear counterstain. (b) Flow cytometric analyses of ΔΨm after incubation of Blin-1 transfectants (vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA−) without (control) or with 1 μM CCCP or 2 μM rotenone. x/y flow cytometry dot plots represent ΔΨm changes as log(s) of red (FL2) and green (FL1) JC-1 fluorescence. The numbers indicate the percentage of cell events
Disruption of energy production by RC inhibitors and uncouplers alters mitochondrial ΔΨm and causes apoptosis.15 For instance, rotenone inhibits RC complex-I and depletes ATP pools,16, 17 whereas carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) pumps protons through mitochondrial inner membrane, thus uncoupling RC and hampering ATP production.18, 19 Hence, to investigate whether PRELI can uphold mitochondrial ΔΨm challenged by the complex-I inhibitor and the protonophore, vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA− Blin-1 transfectants were treated with rotenone or CCCP. Flow cytometric experiments show that although PRELI-expressing cells can effectively counter rotenone- and CCCP-induced mitochondrial depolarization, the vector and PRELI/LEA− transfectants could not prevent the effects of the complex-I inhibitor and protonophore (Figure 3b).
PRELI effects on mitochondrial respiration
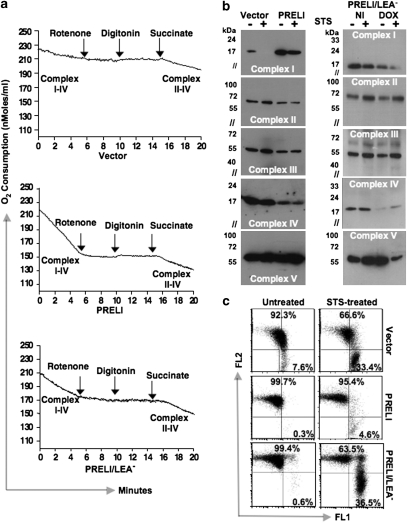
RC drives protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the IMS and creates a ΔΨm.19 As rotenone is applied to assess RC contribution to mitochondrial ΔΨm and apoptosis,16, 17 we sought to investigate whether PRELI's capacity to uphold mitochondrial ΔΨm against complex-I inhibition is mechanistically connected to oxidative phosphorylation. To test this, we measured oxygen consumption in vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA− transfectants in the absence or presence of rotenone. After rotenone treatment, cells were permeabilized for substrate (succinate) uptake to assess RC complex II-to-IV progression. We observed that in comparison with vector and PRELI/LEA−, PRELI Blin-1 transfectants exhibited higher respiration rates (Figure 4a and Supplementary Figure S2) and progressed more efficiently through complex II–IV (Figure 4a and Supplementary Figure S2). Logical to the notion that CCCP's effects are independent of mitochondrial ΔΨm and apoptosis,16, 17, 18, 19 PRELI's influence on the protonophore RC uncoupling appeared unremarkable (data not shown).
Figure 4.
Effect of PRELI on cell respiration. (a) A comparison of oxygen consumption (nmoles/ml/min) by vector (upper graph), PRELI (middle graph) and mutant PRELI/LEA− (lower graph) Blin-1 transfectants in the absence or presence of 2 μM rotenone. Measurements were taken before (complex I–IV) and after cell permeabilization and addition of succinate to assess complex II–IV progression. (b) Left panel: Immunoblot experiments to compare the expression of RC complex I–V proteins (NADH dehydrogenase, succinate dehydrogenase, CytC oxydoreductase, CytC oxidase and ATP synthase) between the vector and PRELI Blin-1 transfectants in the absence (−) or presence (+) of STS. Right panel: Immunoblot experiments to compare the expression of RC complex I–V proteins in non-induced (NI) and DOX-induced (DOX) Tet-ON PRELI/LEA Blin-1 transfectants in the absence (−) or presence (+) of STS. (c) Control flow cytometry to physiologically monitor the effects of STS on vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA− transfectants, using mitochondrial ΔΨm as a functional reference. The protein lysates that were used to obtain the results shown in panel b originated from the corresponding cells tested here
Mitochondria generate energy through RC oxidative phosphorylation, which transfers electrons from NADH to O2 molecules and leads to ATP synthesis.20 RC reactions depend on complex-I redox functions to create asymmetric electron/proton gradients across the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM).20 These gradients produce a mitochondrial ΔΨm, critical to restrain O2 or H2O2 (ROS) surges, and prevent the release of apoptogenic molecules.21 To investigate whether PRELI plays any role in the mechanisms that connect bioenergetics with cell survival/death signals, genome-wide expression analyses were performed between vector and PRELI transfectants. We found that PRELI selectively induced RC complex-I NADH dehydrogenase expression, which, in contrast with vector transfectants, was virtually unaffected by STS treatment (Figure 4b and c). STS was used in these experiments to underscore the putative connection between the RC and apoptosis-mediated signaling.
Strikingly, whereas compensatory reductions of complex-II, III and IV expression were evident in PRELI transfectants, ATP synthase (complex-V) expression proceeded with higher efficiency (Figure 4b). Notably, the reduced complex-IV expression observed in PRELI transfectants agrees with the notion that at high ATP/ADP ratios, COX-IV is allosterically inhibited22 (Figure 4b). Moreover, the finding that PRELI enhances complex-I expression is relevant because as a central entry site of electrons, COX-I is vulnerable to RC inhibitors16, 17 and a major source of premature O2 leakage and ROS production.23 Remarkably, induction of PRELI/LEA− expression resulted in substantive STS-mediated decrease of complex-I, IV and ATP synthase (complex-V) in conjunction with massive mitochondrial depolarization (Figure 4b and c), further supporting the physiological requirement of PRELI's LEA motif.
Effect of PRELI on caspase activation and apoptosis
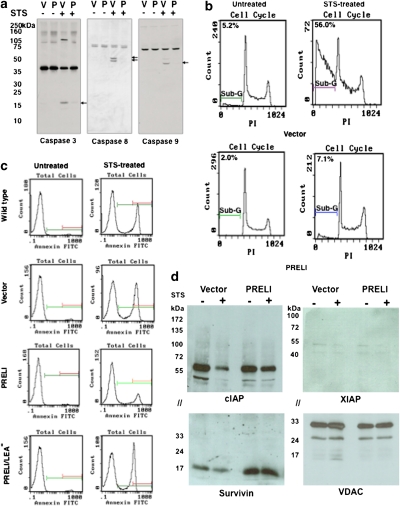
CytC is a molecular component of RC electron transfer reactions,24, 25 which resides in the mitochondria but is released to the cytosol upon induction of apoptosis (Figure 2e and Supplementary Figure S1a). Released CytC binds to the apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 (Apaf-1) and triggers Apaf-1 oligomerization26 to recruit procaspase-9 molecules, which undergo autocatalytic cleavage activation.26 Caspase-9 then activates the downstream caspases and promotes DNA fragmentation.27 To determine the effect of PRELI's expression on caspase activity, vector and PRELI transfectants were subjected to STS treatment. Figure 5a shows that vector but not PRELI transfectants undergo STS-induced, cleavage-dependent activation of caspase-9, 8 and 3. As caspase-3 activation mediates endonuclease-dependent DNA cleavage,27 we tested the effect of PRELI on this function. We found that whereas 56% of vector transfectants undergo sub-G1 DNA fragmentation after STS exposure, only 7.1% of PRELI cells exhibited DNA fragments (Figure 5b).
Figure 5.
Effect of PRELI on mitochondrial caspase activation, apoptosis and survivin expression. (a) Comparative immunoblots between vector (V) and PRELI (P) transfectants to assess the autocatalytic cleavage of caspase-3, 8 and 9 in the absence (−) or presence (+) of STS. The arrows indicate the predicted molecular sizes of the cleaved caspases. (b) Cell-cycle histograms revealing the differential accumulation of propidium iodide-stained DNA fragments at the sub-G stage between untreated or STS-treated vector and PRELI transfectants. The percentage of cells undergoing DNA fragmentation is indicated. (c) Flow cytometry of WT and vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA−transfectants comparing the percentage of Annexin-V− (viable) or Annexin-V+ (dead) cells incubated in the absence (untreated) or presence of STS (STS-treated). (d) Immunoblots assessing the expression of IAP proteins survivin, cIAP and XIAP. Of note, the anti-cIAP antibody detected two reactive bands that likely correspond to isoforms-1 and 2. The molecular weight markers are indicated. // indicates that the same immunoblot was sectioned to enable simultaneous probe of cIAP and survivin, or XIAP and VDAC, which served here as protein loading control
Signs of apoptosis include disruption of the plasma membrane, characterized by exposure of phosphatidylserine (PS) residues.28 Accordingly, increased numbers of Annexin-V+ WT and vector transfectants were detected after STS treatment, whereas the number of Annexin-V+ cells in PRELI transfectants was significantly reduced (Figure 5c). The functional requirement of the LEA motif was further noted by the evidence that PRELI/LEA− expression was completely unable to confer cytoprotection (Figure 5c). In added support of PRELI's contribution to cell survival, genome-wide expression analyses revealed a selective increase in survivin expression by PRELI-expressing cells. Figure 5d shows that, whereas survivin level is low and undergoes further decrease in the STS-treated vector transfectants, its levels were routinely enhanced in PRELI transfectants and virtually unaffected by STS. The level of cIAP, which like survivin is a member of the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) family, was decreased in the STS-treated vector transfectants, but was only minimally stabilized by PRELI expression (Figure 5d). Moreover, levels of XIAP, a third member of the IAPs, were consistently low and virtually unaffected under all the conditions examined (also depicted in Figure 5d). Together these results underscore the selective impact of PRELI on survivin's expression.
Effect of PRELI on caspase-independent apoptosis
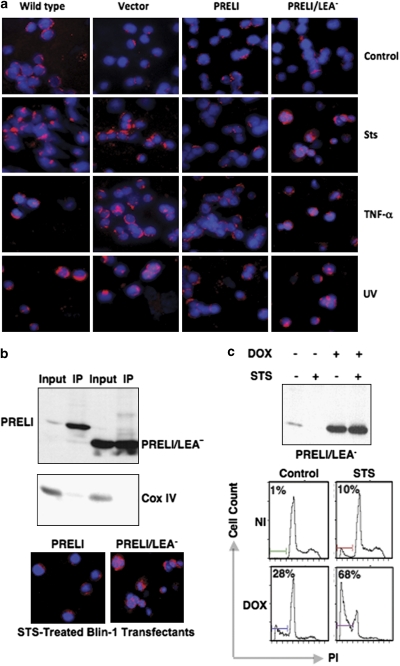
Death signals can trigger both caspase-dependent and independent apoptosis, and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is the best-characterized mediator of the latter.29 To investigate whether PRELI plays any role in caspase-independent mechanisms, WT and vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA− transfectants were subjected to apoptosis treatments and analyzed for AIF's sub-cellular distribution. Figure 6a shows that treatment of WT and vector transfectants with STS, TNF-α and UV radiation caused alterations in mitochondrial morphology and induced AIF nuclear translocation. Conversely, PRELI expression appeared to be sufficient to preserve mitochondrial structures and prevent AIF nuclear translocation (Figure 6a). We also found that though both PRELI and PRELI/LEA− could bind to AIF (Figure 6b), only the full-length protein could counter mitochondrial damage and prevent AIF nuclear translocation caused by STS, TNF-α and UV radiation (Figure 6a and replicate insert in Figure 6b). These results are consistent with the capacity of PRELI and PRELI/LEA− to bind to OPA1 and therefore provide additional support to the hypothesis that sustains that the LEA motif is dispensable for protein binding, but essential for PRELI-mediated mitochondrial structure and function stability and for ultimate cytoprotection.
Figure 6.
Effect of PRELI on AIF nuclear translocation and on the response of the B-cell lymphoma line JY to apoptosis. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy comparing AIF's sub-cellular distribution in WT and vector, PRELI and PRELI/LEA− Blin-1 transfectants after incubation without treatment (control) or after exposure to STS, TNF-α and UV radiation. AIF's localization was monitored by concomitant detection of AIF (red fluorescence) and using the nuclear probe Hoechst 33342 (blue fluorescence). (b) Combined anti-AIF IP and anti-V5 immunoblot experiments to test the potential binding of AIF with V5-tagged PRELI or PRELI/LEA− proteins. A 100-μg weight of total protein lysate was applied onto each input lane, whereas a total precipitate from 1.0 mg of protein lysate was loaded in respective IP lanes. Immunocomplex specificity was routinely controlled by exclusive detection of mitochondrial COX-IV in the input but not in the IP lanes. It is worth mentioning that endogenous AIF expression is constitutively high in most tumor cells tested (not shown) and hence not limited to bind to all available PRELI or PRELI/LEA− molecules, irrespective of their transient or induced level of expression. Also included here are replicate immunofluorescence images from panel a to further emphasize the functional differences on the response to STS treatment between PRELI-expressing and PRELI/LEA− cells. (c) From left to right, the immunoblot (upper panel) shows non-induced (first and second lanes from left) and DOX-induced (third and fourth subsequent lanes) V5-tagged PRELI/LEA− expression by Tet-ON JY B-cells in the absence (−) or presence (+) of STS. The lower panels show DNA fragmentation results from JY cells tested under identical experimental conditions
Endogenous PRELI expression may confer resistance to apoptosis
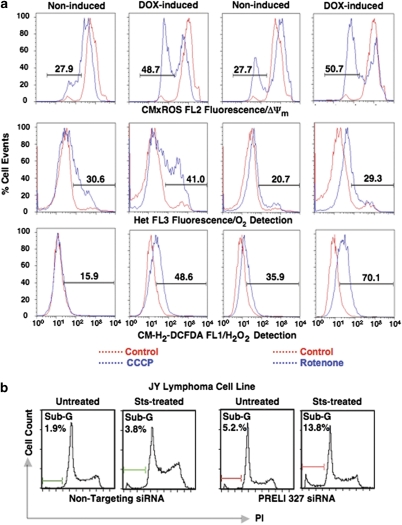
The observation that enforced PRELI overexpression prevents STS, TNF-α and UV radiation-induced apoptosis, prompted the hypothesis of PRELI-dependent mechanisms of cell resistance against induced death. After a comprehensive screening, we found that PRELI's expression is variable among leukemia and lymphoma cell lines (Supplementary Figure S3a). For instance, the Burkitt's B-cell lymphoma line Raji had high endogenous PRELI levels and was relatively resistant to STS-induced apoptosis. Conversely, its counterpart Daudi expressed low PRELI levels and was highly sensitive to STS (Supplementary Figure S3b). Moreover, the B-cell lymphoma line JY30 exhibited high endogenous levels and was virtually insensitive to STS-, TNF-α- and Fas-induced apoptosis (Supplementary Figure S3c). Thus, in view of the seemingly futile PRELI/LEA− function, we reasoned that enforced overexpression of the mutant protein could potentially interfere with endogenous PRELI expression. To test this hypothesis, tetracycline-inducible (Tet-ON)-PRELI/LEA− JY cell lines (JY/Tet-ON) were generated and tested (Supplementary Figure S3d). We observed that without induction there was neither significant PRELI/LEA− detection nor relevant JY/Tet-ON response to STS-induced apoptosis (Figure 6c). However, treatment of JY/Tet-ON with the tetracycline analog doxycycline (DOX) concomitantly resulted in robust PRELI/LEA− expression and strong STS-mediated DNA fragmentation (Figure 6c). Similarly, DOX-induced PRELI/LEA− expression rendered JY/Tet-ON cells susceptible to CCCP- and rotenone-mediated ΔΨm depolarization, manifested by reduction in CMxROS/FL2 fluorescence (Figure 7a, upper panel). We also tested whether induced PRELI/LEA− expression could alter ROS production. Figure 7a shows that induction of PRELI/LEA− expression causes high O2 and H2O2 production after CCCP and rotenone treatments, revealed by the respective shift in hydroethidine (HEt)/FL3 and 5-(-6)-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorohydrofluoresceindiacetate (CM-H2-DCFDA)/FL2 fluorescence. These data concur with the capacity of PRELI/LEA− expression to interfere with endogenous PRELI's capacity to uphold mitochondrial ΔΨm, inhibit ROS production and confer JY resistance to STS, rotenone and CCCP treatments.
Figure 7.
Effects of inducible PRELI/LEA− expression and transient PRELI knockdown. (a) Flow cytometric analyses to monitor mitochondrial ΔΨm (upper histograms) and ROS production (center and lower histograms) in Tet-ON JY cells without (non-induced) or with induced PRELI/LEA− expression (DOX-induced), in the absence (red-dotted lines in all the panels) or presence of either CCCP (blue-dotted lines in the panels on the left) or rotenone (blue-dotted lines in the panels on the right). Alterations in ΔΨm are reported as the log of CMxROS (FL2) fluorescence shift and ROS changes are monitored by the change in the log value of FL3/HEt and FL2/CM-H2-DCFDA fluorescence, which respectively measure O2 and H2O2 levels. The numbers represent the percentage of cellular events. (b) Cell-cycle histograms revealing the differential accumulation of propidium iodide-stained DNA fragments at the sub-G stage between JY cells transiently transfected with either non-targeting siRNA control or experimentally selected PRELI-specific siRNA 327 (denotes the relative position of the targeted PRELI mRNA sequence) after incubation in the absence (untreated) or presence of STS (STS-treated). The numbers indicate the percentage of cells undergoing DNA fragmentation
PRELI knockdown renders cells susceptible to apoptosis
To further support PRELI's involvement in JY lymphoma resistance to apoptosis, small interference RNAs (siRNAs) were designed and tested for their capacity to knockdown endogenous PRELI expression and counter its cytoprotective function (Supplementary Figure S4). After loading JY cells with non-targeting or PRELI-specific siRNAs by transitional pinocytosis,31 cells were tested for apoptosis-induced DNA fragmentation. Flow cytometry shows that only 3.8% of JY cells loaded with non-targeting siRNA exhibited sub-G DNA fragments after STS treatment (Figure 7b). In contrast, PRELI siRNA increased the number of JY cells undergoing DNA fragmentation to 13.8% (Figure 7b). These data support the involvement of PRELI in the mechanisms that confer JY lymphoma resistance to apoptosis.
LEA requirement for in vivo PRELI's function
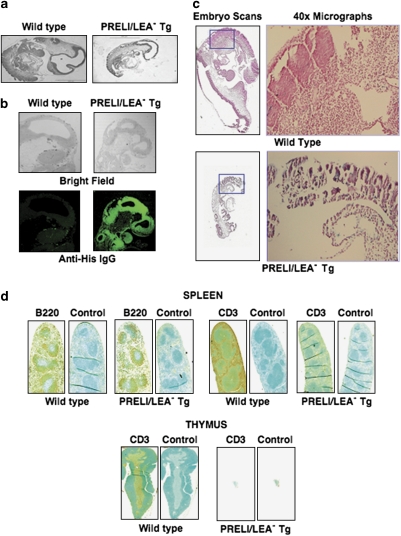
PRELI is ubiquitously expressed throughout embryo development (data not shown) and possesses in vitro LEA-dependent capacity to oppose apoptosis. Thus, to investigate in vivo the physiological significance of PRELI's expression, we generated Tg mice in which PRELI/LEA− expression is under the control of the SR-α promoter32 and histidine (His)-tagged to ensure ubiquitous detection. After failing to obtain viable Tg mice (three pro-nuclear injections and 11 Tg embryos), we found that, contrary to WT littermates, PRELI/LEA− Tg mice did not survive past 10 days post coitus (dpc). We noted that while WT embryos developed normally, PRELI/LEA− Tg embryos were significantly smaller and underdeveloped (Figure 8a). To assess PRELI/LEA− expression, whole-mount WT and PRELI/LEA− Tg mouse sections were stained with anti-His antibodies and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. WT embryo sections depicted only background fluorescence, whereas PRELI/LEA− Tg sections showed strong and ubiquitous detection of the mutant protein (Figure 8b). To determine the cause of PRELI/LEA− embryo deaths, TUNEL assays were performed using WT and PRELI/LEA− Tg sections. Figure 8c (upper panels) shows discreet apoptosis levels in WT littermates, which is congruent with normal tissue remodeling during embryo development. Conversely, massive apoptosis was detected in PRELI/LEA− Tg mice (Figure 8c, lower panels), suggesting a dominant-negative interference of mutant PRELI/LEA− with endogenous PRELI function.
Figure 8.
In vivo effects of mutant PRELI/LEA− expression. (a) Representative × 4 micrographs (gray field) of whole-mount 10 dpc embryo sections comparing the development of WT (left frame) with PRELI/LEA− Tg intrauterine littermates (right frame). (b) Detection of mutant PRELI/LEA− protein expression by anti-His immunofluorescence staining. The upper and lower panels on the left respectively show bright-field and green fluorescence of the WT embryo, whereas those on the right show the results from PRELI/LEA− Tg littermate. (c) TUNEL assays of 10 dpc WT and PRELI/LEA− Tg embryos. The upper (WT) and lower (Tg) panels on the left are section scans of whole-mount embryos and the corresponding panels on the right are × 40 microscopically magnified images of the framed areas. Positive TUNEL signal is revealed by a purple stain, resulting from the dark blue reactivity of the chromogenic TACS substrate against the nuclear Fast Red counterstain. (d) Immunohistochemistry of 5-week-old WT (left panels) and PRELI/LEA− Tg mice (right panels). The top panels show spleen tissue sections, respectively tested for detection of CD45R/B220+ B-cells and CD3+ T-cells (Brown reaction). The bottom panels depict thymus tissue sections analyzed for size, morphology and presence of CD3+ thymocytes. Isotype-matched IgGs are shown in the spleen and thymus panels as negative controls
PRELI has been detected in the thymus, spleen and peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs) and appears to be prominently expressed by B and T lymphocytes in adult mice (data not shown). We therefore examined in vivo the consequence of PRELI/LEA− overexpression on lymphocyte development. Mice (eight Tg pups from two pronuclear injections) carrying the PRELI/LEA− transgene under the control of the hematopoiesis-specific vav promoter33 died perinatally. The deaths ranged from a majority (high copy number) succumbing immediately after birth (data not shown) to a few (low-copy number) Tg mice that survived 4–5 weeks. Compared with WT littermates, vav-driven PRELI/LEA− Tg mice exhibited profound lymphopenia (data not shown), had smaller spleens and showed decreased numbers of CD45R/B220+ B lymphocytes (Figure 8d). In agreement with the notion of vav preferential expression within the T-lymphocyte compartment33 and consistent with the virtual absence of CD3+ T-cells in the spleen (Figure 8d), only thymus remnants were found in vav-driven PRELI/LEA− Tg mice, without detectable CD3+ thymocytes (Figure 8d).
Together, these data highlight the vital PRELI physiology and the essential requirement of its LEA motif.
Discussion
Eukaryotes respond to stress stimuli by adaptive mechanisms that activate stress-response gene expression.1 Among those, the LEA genes encode an evolutionarily conserved family of proteins long presumed to protect cells from stress and death.2, 3 However, the physiology of LEA-containing proteins and the mechanisms connecting to cytoprotection remained unsolved.
The present study postulates that PRELI, a mammalian LEA-containing protein, may play a role in conserved mechanisms that integrate mitochondrial energy functions with cell responses to death-inducing stimuli. In keeping with this premise, phylogenetic evidence of LEA-like mediated cytoprotection continues to mount. For instance, expression of the avian PRELI ortholog pX19 can be triggered in response to stress-inducing bromodeoxyuridine and appears critical for hematopoietic development;4 Drosophila prel (PRELI-like), slmo (slowmo) and retm (real-time) constitute a novel family of mitochondrial proteins that share PRELI/MSF1-like domains and are activated during embryo development;5 Ups1p, a yeast PRELI ortholog, is expressed within mitochondrial IMS and required for sorting and topogenesis of Mgm1p (yeast OPA1),8, 34, 35 which is known to regulate mitochondrial shape.8 Like Mgm1p, OPA1 is a dynamin-associated protein that protects cells from apoptosis by maintaining mitochondrial cristae integrity and keeping their junctions tight during induction of apoptosis, thereby preventing the release of CytC.34, 35
Coherent with the evolutionary parallels, the present study shows that PRELI is expressed within the IMS in intimate proximity to mitochondrial cristae junctions. We also show that PRELI can associate with OPA1 and support mitochondria morphology. We therefore contend that PRELI's cooperation with OPA1 to maintain mitochondria cristae junctions tight is fundamental to maintain electron/proton gradients,36 transduce signals relevant to RC oxidative phosphorylation/ATP synthesis and ROS production,36 and regulate the sorting of pro- and antiapoptotic molecules. Notably, we show that PRELI expression can uphold mitochondrial ΔΨm, enhance RC complex-I NADH dehydrogenase and ATP synthase expression, increase O2 consumption, reduce ROS production and sustain robust survivin protein levels, while preventing CytC and AIF exit from the mitochondria.
These findings suggest that analogous to other proteins, PRELI could exert both nuclear and mitochondrial functions. Congruent with this reasoning, bioinformatics data reveal that PRELI possesses nuclear localization signals (NLS) and DNA/RNA-binding domains.37 Alternatively, PRELI/OPA1 interactions at cristae junctions could transduce intra-mitochondrial signals, leading to activation of NADH dehydrogenase transcription from mtDNA loci. The evidence that oxidative phosphorylation subunits are also encoded by mtDNA suggests that alternative mechanisms are at least plausible for RC gene regulation.38 Then, to reconcile the enhanced survivin expression with PRELI's functions in the mitochondria, we must note that previous studies have shown that Hsp60, a mitochondrial chaperon, can bind to survivin and increase its stability.39 Accordingly, we speculate that in its MSF1-like protein-sorting capacity, PRELI could cooperate with Hsp60 to enhance survivin stability and coordinate its mitochondrial release. Coherently, PRELI and Hsp60 colocate in the mitochondria (not shown), which makes the potential cooperation persuasive.
In assessing the nature of potential PRELI interactions with other proteins, we sought to investigate whether the LEA sequence was required for protein binding and function. Since the experiments revealed that the LEA motif is dispensable for protein binding, the results appeared to be conflicting with PRELI's LEA-dependent cytoprotection. However, PRELI possesses PH, PTB, ENTH-like and FERM protein-binding capacity within the MSF1-like region,9, 10 which could help reconcile LEA-independent PRELI protein binding with LEA-dependent functions. Furthermore, PRELI's low-complexity α-helix structure at the LEA domain appears to be attuned with homodimer protein conformations. Thus, congruent with the functional requirement of the LEA sequence, we postulate that PRELI could form α-helix-dependent homodimers to achieve functions relevant to mitochondrial activity and cytoprotection (Supplementary Figure S5a). Preliminary protein purification experiments suggest that PRELI dimmer configuration may be plausible (not shown).
Of note, the present study finds that in most leukemia and lymphoma cell lines examined, the levels of PRELI expression are inversely proportional to the cell's response to apoptosis-inducing stimuli, namely, low PRELI expression equals sensitivity and high levels square with resistance. In keeping with these observations, we found that dominant interference with endogenous PRELI function by inducible PRELI/LEA− overexpression or transient PRELI-specific knockdown can revert the resistance of lymphoid tumors, like the JY lymphoma cells, to apoptosis.
Lastly, a recent study reports that PRELI induces apoptosis in human primary T-helper (Th) cells.40 Whereas it may be tenable that T and B lymphocytes respond to death-inducing stimuli through independent mechanisms, the findings and conclusions of the report appear at odds with the evolutionarily conserved cytoprotection associated to all LEA-containing proteins studied thus far.
In conclusion, this work provides experimental support to the long-standing prediction that LEA-containing proteins function as cell protectors. We also propose that, in view of the striking evolutionary conservation, PRELI and its homologs in other eukaryotes are bona fide antagonists of programmed cell death. While we remain cautious, we submit that our collective data might shed new information on how mitochondrial bioenergetics may be connected with mechanisms of cytoprotection and resistance to induced death.
Materials and Methods
Transfectants
Stable vector (pME18S-Neo), WT PRELI or mutant PRELI/LEA− Blin-1 transfectants were generated and G418-selected. Inducible Tet-ON HeLa and JY B-cell lymphoma clones expressing mutant V5-tagged PRELI/LEA− protein were generated as follows: cells were transduced with the pBMN-TetR-BSR vector and antibiotic-selected (blastocydin, 10 μg/ml). The JY-TetRhigh clones were then transduced with pRetroCMV/TO-PRELI/LEA−/V5 (LEA motif replacement by the V5 tag). After selection (puromycin, 1 μg/ml), the clones were induced with 20 μg/ml DOX (24 and 48 h) and assessed for PRELI/LEA−/V5 expression by immunoblotting, using HRP-conjugated monoclonal anti-V5 antibody (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
Mitochondrial ΔΨm and ROS production
WT and Blin-1 transfectants were incubated for 4 h at 37°C, with or without 1 μM STS or 20 ng/ml TNF-α. For UV radiation experiments, cells were suspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and exposed for 20 min to 1.5 kJ/m2 of UVB radiation (290–320 nm) and incubated at 37°C in fresh culture media for 4 h. Cells were next stained with a JC-1 probe (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA) for 20 min at 37°C, washed, cytocentrifuged onto slides (Thermo Shandon, Oak Park, MI, USA), fixed and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. In alternate experiments, transfectants were incubated for 4 h at 37°C, in the absence or presence of either 1 μM CCCP or 2 μM rotenone. After JC-1 staining, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The red-to-green fluorescence shift was monitored in FL1 and FL2 channels. ROS production by PRELI/LEA−/V5/Tet-ON JY B-cells was measured with or without DOX induction (24 h), followed by 16-h incubation in the absence or presence of 1 μM CCCP or 2 μM rotenone. The cells were stained with ROS-sensitive fluorescent HEt or CM-H2DCFDA probes (Invitrogen) for 20 min at 37°C to assess O2 (FL3) and H2O2 (FL2) production. Data were captured by flow cytometry and analyzed with FlowJo (Tree Star, Ashland, OR, USA).
Respiration rate analysis
Oxygen consumption was performed as previously described.36 Briefly, 20 million Blin-1 transfectants were resuspended in 1 ml respiration buffer (20 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2, 250 mM sucrose), placed in a sealed respiration chamber equipped with a thermostat control and a micro-stirring device (Oxytherm; Hansatech Instrument, Norfolk, UK). Oxygen consumption was measured polarographically at 37°C using a Clark-type oxygen electrode disc, using the conditions recommended by the manufacturer. Rotenone (100 nM) was added at 5-min intervals, followed by digitonin (30 μg/ml) permeabilization and succinate (5 μM) addition.
Annexin-V analysis
WT and Blin-1 transfectants were incubated with or without 1 μM STS for 8 h. Cells were stained with FITC–Annexin-V (Clontech), washed and analyzed by flow cytometry.
Immunofluorescence microscopy
Blin-1 transfectants were treated with or without 1 μM STS for 8 h. Cells were cytocentrifuged and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Slide preparations were independently reacted with monoclonal anti-Hsp60 and polyclonal anti-CytC (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) or anti-AIF (Chemicon, Billerica, MA, USA). Reactivities were respectively revealed using Alexa-488-conjugated anti-mouse and Alexa-594-conjugated anti-rabbit IgGs (Invitrogen). In other experiments, AIF detection was accomplished with a monoclonal IgG and revealed with anti-mouse Alexa-594. TO-PRO (Invitrogen) or Heochst33342 was used as nuclear counterstain. Green, red and blue-fluorescence images were captured by confocal microscopy (Olympus 1X71; PMT 0-900v; scan speed 0.005184 s per line). Similar procedures were used for OPA1 and PRELI detection, with the exception of STS treatment. Monoclonal anti-OPA1 (BD Biosciences) and rabbit anti-PRELI antibodies (custom generated by Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX, USA) were used here.
DNA fragmentation
Blin-1- and JY DOX-inducible transfectants were incubated for 8 h with or without 1 μM STS. Propidium iodide-stained DNA fragments at the sub-G1 stage were assessed by flow cytometry.
Immunoblots
Proteins were resolved on 10% SDS-PAGE gels, blotted, reacted with specific antibodies and revealed by chemiluminiscence (DNA Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Antibodies for caspase detection were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, whereas monoclonal antibodies used for respective detection of specific RC complex I–V subunits and OPA1 were purchased from BD Biosciences. For AIF/PRELI or PRELI/LEA− interactions, 1.0 mg V5-tagged PRELI or V5-tagged PRELI/LEA− protein lysates from transient HeLa and DOX-induced Blin-1 transfectants were immunoprecipitated with agarose-conjugated anti-AIF antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and blotted. For OPA1/PRELI or PRELI/LEA− interactions, 1.0 mg of the above cited protein lysates were immunoprecipitated with agarose-conjugated anti-V5 antibody (Invitrogen) and blotted. The blots were reacted with HRP-conjugated anti-V5 monoclonal antibody (Invitrogen) or anti-OPA1 monoclonal antibody followed by an HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG reaction.
Transmission electron microscopy
Monolayer breast carcinoma T47D cells grown on glass slides or PRELI Blin-1 transfectants grown in suspension were fixed with a solution containing 0.2% formaldehyde and 0.1% glutaraldehyde. The fixed cells were reacted overnight (ON) at 4°C with rabbit polyclonal anti-PRELI antibody, washed three times with PBS and 0.1% Tween (PBST) and then reacted ON at 4°C with gold-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. After subsequent washes with PBST and PBS alone, samples were further fixed with a solution containing 3% glutaraldehyde, 2% formaldehyde and 0.1 M cacodylate (pH 7.3) for 1 h at room temperature (RT). The samples were then washed with cacodylate-buffered tannic acid, post-fixed with 1% osmium tetra-oxide for 1 h at RT and stained in block with 1% uranyl acetate. After dehydration with increasing concentrations of ethanol, samples were embedded in Spurr's low-viscosity solution. Ultra-thin sections were obtained using a microtome (Leica, Bannockburn, IL, USA) and examined with a JEM 1010 transmission electron (JEOL) at an accelerating voltage of 80 kV. Digital images were obtained using an AMT imaging system (Advance Microscopy Techniques Corp., Danvers, MA, USA).
Tg mice
PRELI/LEA− cDNA was cloned into the pME18S vector41 for ubiquitous transgene expression, or a 2.3/4.4 (HS21/45) vector30 for hematopoietic-cell-specific expression. Tg mice were generated by the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) genetic engineering mouse core facility and housed at the MDACC vivarium in compliance with IACUC.
Genotyping
PRELI/LEA− Tg embryo tail or resorption site DNA was prepared by standard methods and amplified with an Accuprime polymerase kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions; forward SR-α promoter primer 5′CGCCCAGTTCCGCCCATTCT3′ and reverse PRELI/LEA−-6X His primer 5′TGTGTCTAGATCAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGAGCTGCCGCTGCTGCTG3′ were used for the procedures. Five-week PRELI/LEA− Tg mouse tail snip DNA preparations were made as described above, according to IACUC guidelines. PCR was performed using AmpliTaq Gold (Applied Biosystems) with forward Vav-Promoter primer 5′CGGTGGTGGTGCAAATCAA3′ and reverse V5-tagged PRELI/LEA− primer 5′CACAGCGGCCGCTCACGTAGAATCGAG ACCGAGGAGAGGGTTAGGGATAGGCTTACC AACAAGTGTTTTGGAAGGGCCTCGCC3′.
Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence
After paraformaldehyde fixing and paraffin embedding, whole-mount embryo sections were prepared for hematoxylin/eosin staining or reaction with anti-His monoclonal antibody (Novagen, Gibbstown, NJ, USA), subsequently revealed by anti-mouse Alexa-488-conjugated IgG (Invitrogen). Paraffin-embedded 5-week Tg mouse spleen and thymus sections were prepared, rehydrated, blocked with SuperBlock (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) and reacted ON at 4°C with anti-CD3 (BD Biosciences), anti-CD45R/B220 (BD Biosciences) or isotype control antibodies (eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA). After stringent washes, antibody reactions were revealed using biotinylated anti-species-specific antibodies (BD Biosciences), HRP-conjugated streptavidin (BD Biosciences) and stable DAB (Invitrogen), and using methyl green (Sigma) as counterstain. Images were captured with a pathology enabled Microtek 4000tf scanner (Meyer Instruments, Houston, TX, USA; scan speed 0.005184 s per line) or by confocal microscopy (Olympus 1X71; PMT 0-900v).
In situ apoptosis detection
TUNEL staining was performed using whole-mount embryo section, using a TACS TdT apoptosis assay, according to the protocol of R&D Systems. Scans were captured using the pathology enabled Microtek 4000tf scanner.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Drs Tucker LeBien, Kevin Moore, Jerry Adams and Vu Ngo provided, respectively, the Blin-1 cells, the pME18S-Neo vector, the vav 2.3/4.4 (HS21/45) vector and Tet-ON vectors. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) R01 grants AI056125-01 and AI065796-01. JCS-M and MRM were, respectively, supported by the Smith fellowship and NIH training grant T32 CA009598-15. WM is supported by the Odyssey Program and the Cockrell Foundation Award for Scientific Achievement at MD Anderson Cancer Center. GK is supported by grants from the Ligue National Contre le Cancer and European Union. KKS is supported by NIH R01grants CA121904 and CA113655. LMP is a student at The University of Texas Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. MD Anderson's Genetically Engineered Mouse, DNA Sequencing and High Resolution Electron Microscopy Core Facilities are supported by NIH grant CA-16672.
Glossary
- PRELI
protein of relevant evolutionary and lymphoid interest
- LEA
late embryogenesis abundant
- OPA1
optical atrophy-1
- AIF
apoptosis inducing factor
- CytC
cytochrome c
- VDAC
voltage dependent anion channel
- IAP
inhibitor of apoptosis
- cIAP
baculovirus IAP repeat-containing
- XIAP
X-linked IAP
- CG
germinal centre
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- TNF
tumor necrosis factor
- STS
staurosporine
- UV
ultraviolet
- FITC
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- PI
propidium idodide
- HEt
hydroethidine
- CM-H2-DCFDA
5-(-6)-chloromethyl-2′7′-dichlorohydrofluoresceindiacetate
- CMxROS
dichloromethyl-tetramethyl-rosamine
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Disease website (http://www.nature.com/cddis)
Supplementary Material
References
- Goh CH, Nam HG, Park YS. Stress memory in plants: a negative regulation of stomatal response and transient induction of rd22 gene to light in abscisic acid-entrained Arabidopsis plants. Plant J. 2003;36:240–255. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espelund M, Bedout JA, Outlaw WH, Jakobsen KS. Environmental and hormonal regulation of barley late-embryogenesis-abundant (Lea) mRNAs is via different signal transduction pathways. Plant Cell Environ. 1995;18:943–949. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy RA, Aalen RB. Identification of sequence homology between the internal hydrophilic repeated motifs of group 1 late-embryogenesis-abundant proteins in plants and hydrophilic repeats of the general stress protein GsiB of Bacillus subtilis. Planta. 1998;206:476–478. doi: 10.1007/s004250050424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu S, Antin PB, Morkin E. Cloning and sequencing of a developmentally regulated avian mRNA containing the LEA motif found in plant seed proteins. Gene. 1996;175:187–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(96)00146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dee CT, Moffat KG. A novel family of mitochondrial proteins is represented by the Drosophila genes slmo, preli-like and real-time. Dev Genes Evol. 2005;215:248–254. doi: 10.1007/s00427-005-0470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox EJ, Stubbs SA, Kyaw Tun J, Leek JP, Markham AF, Wright SC. PRELI (protein of relevant evolutionary and lymphoid interest) is located within an evolutionarily conserved gene cluster on chromosome 5q34-q35 and encodes a novel mitochondrial protein. Biochem J. 2004;378:817–825. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman-Rojas L, Sims JC, Rangel R, Guret C, Sun Y, Alcocer JM, et al. PRELI, the human homologue of the avian px19, is expressed by germinal center B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 2000;12:607–612. doi: 10.1093/intimm/12.5.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesaki H, Dunn CD, Iijima M, Shepard KA, Yaffe MP, Machamer CE, et al. Ups1p, a conserved intermembrane space protein, regulates mitochondrial shape and alternative topogenesis of Mgm1p. J Cell Biol. 2006;173:651–658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200603092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995;373:573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman J, Chen H, Di Fiore PP, De Camilli P, Brunger AT. Epsin 1 undergoes nucleocytosolic shuttling and its eps15 interactor NH(2)-terminal homology (ENTH) domain, structurally similar to Armadillo and HEAT repeats, interacts with the transcription factor promyelocytic leukemia Zn(2)+ finger protein (PLZF) J Cell Biol. 2000;149:537–546. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein RR. Abscisic acid-insensitive mutations provide evidence for stage-specific signal pathways regulating expression of an Arabidopsis late embryogenesis-abundant (lea) gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;238:401–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00291999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guseva NV, Rokhlin OW, Taghiyev AF, Cohen MB. Unique resistance of breast carcinoma cell line T47D to TRAIL but not anti-Fas is linked to p43cFLIP(L) Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;107:349–357. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9563-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormann B, Anderson JM, Liberty JA, Gajl-Peczalska K, Brunning RD, Silberman TL, et al. Establishment of a leukemic cell model for studying human pre-B to B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1989;142:110–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvezin-Caubet S, Koppen M, Wagener J, Zick M, Israel L, Bernacchia A, et al. OPA1 processing reconstituted in yeast depends on the subunit composition of the m-AAA protease in mitochondria. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:3582–3590. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-02-0164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong JS, Steinauer KK, French J, Killoran PL, Walleczek J, Kochanski J, et al. Bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis induced by mitochondrial uncoupling but does not prevent mitochondrial transmembrane depolarization. Exp Cell Res. 2001;262:170–179. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.5091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong JS, Hornung B, Lecane P, Jones DP, Knox SJ. Rotenone-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a human B lymphoma cell line PW. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289:973–978. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N, Ragheb K, Lawler G, Sturgis J, Rajwa B, Melendez JA, et al. Mitochondrial complex I inhibitor rotenone induces apoptosis through enhancing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:8516–8525. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210432200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari AA, Seol JW, Kim SJ, Lee YJ, Kang HS, Kim IS, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate Bax translocation and mitochondrial transmembrane potential, a possible mechanism for enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis by CCCP. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsinger G, Wilhelm S, Wagner H, Hacker G. Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation can enhance a Fas death signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:3299–3311. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.5.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M. Oxidative phosphorylation at the fin de siecle. Science. 1999;283:1488–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5407.1488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:99–163. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadenbach B, Huttemann M, Arnold S, Lee I, Bender E. Mitochondrial energy metabolism is regulated via nuclear-coded subunits of cytochrome c oxidase. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;29:211–221. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G, Chen Y, Lu H, Cao X. Coupling mitochondrial respiratory chain to cell death: an essential role of mitochondrial complex I in the interferon-beta and retinoic acid-induced cancer cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:327–337. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li K, Li Y, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Spencer E, Chen ZJ, et al. Cytochrome c deficiency causes embryonic lethality and attenuates stress-induced apoptosis. Cell. 2000;101:389–399. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80849-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 1996;86:147–157. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J, Lazebnik Y. Caspase-9 and APAF-1 form an active holoenzyme. Genes Dev. 1999;13:3179–3184. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.24.3179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf BB, Schuler M, Echeverri F, Green DR. Caspase-3 is the primary activator of apoptotic DNA fragmentation via DNA fragmentation factor-45/inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:30651–30656. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.43.30651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clodi K, Kliche KO, Zhao S, Weidner D, Schenk T, Consoli U, et al. Cell-surface exposure of phosphatidylserine correlates with the stage of fludarabine-induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and expression of apoptosis-regulating genes. Cytometry. 2000;40:19–25. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0320(20000501)40:1<19::aid-cyto3>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande C, Vahsen N, Garrido C, Kroemer G. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): caspase-independent after all. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:591–595. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolanus W, Nagel W, Schiller B, Zeitlmann L, Godar S, Stockinger H, et al. Alpha L beta 2 integrin/LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 induced by cytohesin-1, a cytoplasmic regulatory molecule. Cell. 1996;86:233–242. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada CY, Rechsteiner M. Introduction of macromolecules into cultured mammalian cells by osmotic lysis of pinocytic vesicles. Cell. 1982;29:33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y, Seiki M, Fujisawa J, Hoy P, Yokota K, Arai K, et al. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988;8:466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvy S, Louis-Dit-Sully C, Cooper J, Cassady RL, Alexander DR, Holmes N. Either of the CD45RB and CD45RO isoforms are effective in restoring T cell, but not B cell, development and function in CD45-null mice. J Immunol. 2003;171:1792–1800. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.4.1792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cipolat S, Rudka T, Hartmann D, Costa V, Serneels L, Craessaerts K, et al. Mitochondrial rhomboid PARL regulates cytochrome c release during apoptosis via OPA1-dependent cristae remodeling. Cell. 2006;126:163–175. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frezza C, Cipolat S, Martins de Brito O, Micaroni M, Beznoussenko GV, Rudka T, et al. OPA1 controls apoptotic cristae remodeling independently from mitochondrial fusion. Cell. 2006;126:177–189. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicano H, Xu RH, Du M, Feng L, Sasaki R, Carew JS, et al. Mitochondrial respiration defects in cancer cells cause activation of Akt survival pathway through a redox-mediated mechanism. J Cell Biol. 2006;175:913–923. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200512100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise MJ. LEAping to conclusions: a computational reanalysis of late embryogenesis abundant proteins and their possible roles. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003;4:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiana C, Pagliarini DJ, McKenzie M, Kirby DM, Salemi R, Abu-Amero KK, et al. Mutation of C20orf7 disrupts complex I assembly and causes lethal neonatal mitochondrial disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83:468–478. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh JC, Dohi T, Kang BH, Altieri DC. Hsp60 regulation of tumor cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:5188–5194. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705904200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahvanainen J, Kallonen T, Lähteenmäki H, Heiskanen KM, Westermarck J, Rao KV, et al. PRELI is a mitochondrial regulator of human primary T-helper cell apoptosis, STAT6, and Th2-cell differentiation. Blood. 2009;113:1268–1277. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-166553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao G, Xing J, Xiao X, Liou AK, Gao Y, Yin XM, et al. Critical role of calpain I in mitochondrial release of apoptosis-inducing factor in ischemic neuronal injury. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9278–9293. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2826-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.