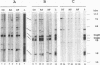
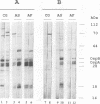
Abstract
Immune responses to Borrelia burgdorferi and their influence on spirochete transmission to Ixodes ricinus were analyzed in the natural European reservoir hosts; i.e., the mouse species Apodemus flavicollis (yellow-necked mouse) and Apodemus sylvaticus (wood mouse) and the vole species Clethrionomys glareolus (bank vole), and, in addition, in the laboratory mouse strain NMRI. Naive and preimmunized rodents were infected either by artificially infected I. ricinus larvae or by intradermal injection of spirochetes. Independent of the species, all animals developed antibodies to various spirochetal antigens. However, antibodies to the outer surface proteins A (OspA) and B (OspB) were not found in recipients infected via ticks. Rodents of the genus Apodemus and of the NMRI strain showed higher levels of B. burgdorferi-specific antibodies than those of the species C. glareolus. The rate of spirochete transmission to noninfected ticks correlated with both the quality and quantity of spirochete-specific antibodies generated in the various species: high levels of spirochete-specific immunoglobulins correlated with low transmission rates. Furthermore, lower transmission rates were observed with rodents expressing antibodies to OspA and OspB (i.e., intradermally infected or immunized) than with those lacking these specificities (i.e., infected via ticks). The study provides evidence that transmission of B. burgdorferi from natural hosts to ticks is controlled by the specificity and quantity of spirochete-reactive antibodies and suggests that immunity to B. burgdorferi in natural reservoir hosts is an important regulatory factor in the horizontal transmission of B. burgdorferi in nature.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baranton G., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C., Assous M., Grimont P. A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Terwilliger G. A., Moody K. D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):133–138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Schell R. F., Case K. L., Lovrich S. D., Day S. P. Characterization of the borreliacidal antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi in humans: a serodiagnostic test. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):158–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Rogers R. C., Benach J. L. Selection of an escape variant of Borrelia burgdorferi by use of bactericidal monoclonal antibodies to OspB. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3098–3104. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3098-3104.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer R., Hovius K. E., Nohlmans M. K., Gray J. S. The woodmouse (Apodemus sylvaticus) as a reservoir of tick-transmitted spirochetes (Borrelia burgdorferi) in The Netherlands. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Aug;279(3):404–416. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. G., Piesman J., Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Marcantonio N., Deponte K., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Roles of OspA, OspB, and flagellin in protective immunity to Lyme borreliosis in laboratory mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):657–661. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.657-661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Tao H., Kantor F. S., Barthold S. W., Flavell R. A. Evasion of protective immunity by Borrelia burgdorferi by truncation of outer surface protein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4092–4096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Telford S. R., 3rd, Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Spielman A., Flavell R. A. Elimination of Borrelia burgdorferi from vector ticks feeding on OspA-immunized mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5418–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Jauris S., Lottspeich F., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Soutschek E. Molecular analysis and expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi gene encoding a 22 kDa protein (pC) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gern L., Rais O., Capiau C., Hauser P., Lobet Y., Simoen E., Voet P., Pêtre J. Immunization of mice by recombinant OspA preparations and protection against Borrelia burgdorferi infection induced by Ixodes ricinus tick bites. Immunol Lett. 1994 Mar;39(3):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gern L., Schaible U. E., Simon M. M. Mode of inoculation of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi influences infection and immune responses in inbred strains of mice. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):971–975. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde W. T., Burkot T. R., Sviat S., Keen M. G., Mayer L. W., Johnson B. J., Piesman J. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted response of recombinant inbred strains of mice to natural tick transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):9–17. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. S., Kahl O., Janetzki C., Stein J. Studies on the ecology of Lyme disease in a deer forest in County Galway, Ireland. J Med Entomol. 1992 Nov;29(6):915–920. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/29.6.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. T., Walker R. L., Nicholson W. L., Heidner H. W., Levine J. F., Burgess E. C., Wyand M., Breitschwerdt E. B., Berkhoff H. A. Immunoblot analysis of immunoglobulin G response to the Lyme disease agent (Borrelia burgdorferi) in experimentally and naturally exposed dogs. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):648–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.648-653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzelberger D., Eichmann K. Genetic control of B-cell function. I. Two genes determine the magnitude of antibody responses of inbred mice to red blood cells. Immunobiology. 1982 Feb;160(5):454–471. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(82)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu C. M., Gern L., Aeschlimann A. Changes in the protein profile and antigenicity of different Borrelia burgdorferi strains after reintroduction to Ixodes ricinus ticks. Parasite Immunol. 1992 Jul;14(4):415–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1992.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. A., Engstrom S. M., Coleman L. A., Kodner C. B., Johnson R. C. Protective immunity is induced by a Borrelia burgdorferi mutant that lacks OspA and OspB. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5115–5122. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5115-5122.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humair P. F., Turrian N., Aeschilimann A., Gern L. Borrelia burgdorferi in a focus of Lyme borreliosis: epizootiologic contribution of small mammals. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1993;40(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Schaible U. E., Wallich R., Moter S. E., Petzoldt D., Simon M. M. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi associated antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Immunobiology. 1990 Nov;181(4-5):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Lim L. C., Schell R. F. Seroprotective groups among isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4367–4374. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4367-4374.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Konkel M. E., Garon C. F. Variability of osp genes and gene products among species of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2611–2617. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2611-2617.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Lubke L., Hauglum W., Garon C. F. Species-specific identification of and distinction between Borrelia burgdorferi genomic groups by using 16S rRNA-directed oligonucleotide probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.628-632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis N., Rosa P. A. Regulation of expression of major outer surface proteins in Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2207–2210. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2207-2210.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather T. N., Telford S. R., 3rd, Moore S. I., Spielman A. Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti: efficiency of transmission from reservoirs to vector ticks (Ixodes dammini). Exp Parasitol. 1990 Jan;70(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90085-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather T. N., Wilson M. L., Moore S. I., Ribeiro J. M., Spielman A. Comparing the relative potential of rodents as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Jul;130(1):143–150. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuschka F. R., Fischer P., Heiler M., Richter D., Spielman A. Capacity of European animals as reservoir hosts for the Lyme disease spirochete. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):479–483. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuschka F. R., Fischer P., Musgrave K., Richter D., Spielman A. Hosts on which nymphal Ixodes ricinus most abundantly feed. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jan;44(1):100–107. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.44.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. P., Lam T. T., Barthold S. W., Telford S. R., 3rd, Flavell R. A., Fikrig E. Partial destruction of Borrelia burgdorferi within ticks that engorged on OspE- or OspF-immunized mice. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):2079–2084. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.2079-2084.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Kissel V., Bittker S., Cabello F., Levine S. Antiborrelial activity of serum from rats injected with the Lyme disease spirochete. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):656–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J. Intensity and duration of Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti infectivity in rodent hosts. Int J Parasitol. 1988 Jul;18(5):687–689. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(88)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Maupin G. O., Campos E. G., Happ C. M. Duration of adult female Ixodes dammini attachment and transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi, with description of a needle aspiration isolation method. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):895–897. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph S. E. Density-dependent acquired resistance to ticks in natural hosts, independent of concurrent infection with Babesia microti. Parasitology. 1994 May;108(Pt 4):413–419. doi: 10.1017/s003118200007596x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph S. E. Population regulation in ticks: the role of acquired resistance in natural and unnatural hosts. Parasitology. 1979 Aug;79(1):141–156. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000052033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph S. E. The effect of Babesia microti on feeding and survival in its tick vector, Ixodes trianguliceps. Parasitology. 1991 Feb;102(Pt 1):9–16. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000060285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M. Role of saliva in tick/host interactions. Exp Appl Acarol. 1989 Jun;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF01200449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Piesman J., Hunt A. R., Keen M. G., Happ C. M., Johnson B. J. The hamster immune response to tick-transmitted Borrelia burgdorferi differs from the response to needle-inoculated, cultured organisms. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3648–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Barbour A. G., Rosa P. A., Thomas D. D. An OspB mutant of Borrelia burgdorferi has reduced invasiveness in vitro and reduced infectivity in vivo. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3590–3596. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3590-3596.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Jonsson M., Bergström S., Bright R. K., Kennedy R. C., Barbour A. G. A bactericidal antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi is directed against a variable region of the OspB protein. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):2037–2045. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.2037-2045.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Thompson P. A., Barbour A. G. In vitro inhibition of Borrelia burgdorferi growth by antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):165–172. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Gay S., Museteanu C., Kramer M. D., Zimmer G., Eichmann K., Museteanu U., Simon M. M. Lyme borreliosis in the severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mouse manifests predominantly in the joints, heart, and liver. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):811–820. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Gern L., Wallich R., Kramer M. D., Prester M., Simon M. M. Distinct patterns of protective antibodies are generated against Borrelia burgdorferi in mice experimentally inoculated with high and low doses of antigen. Immunol Lett. 1993 May;36(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(93)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eichmann K., Modolell M., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi prevent Lyme borreliosis in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3768–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Justus C. W., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Demonstration of antigen-specific T cells and histopathological alterations in mice experimentally inoculated with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.41-47.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Wallich R., Tran T., Simon M. M. Experimental Borrelia burgdorferi infection in inbred mouse strains: antibody response and association of H-2 genes with resistance and susceptibility to development of arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2397–2405. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Wallich R., Kramer M. D., Nerz G., Stehle T., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Protection against Borrelia burgdorferi infection in SCID mice is conferred by presensitized spleen cells and partially by B but not T cells alone. Int Immunol. 1994 May;6(5):671–681. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.5.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Schell R. F. Depletion of complement and effects on passive transfer of resistance to infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3815–3818. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3815-3818.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A. G., England D. M. Passive immunization prevents induction of Lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):144–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.144-148.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Coe J. E. Characterization of the protective antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1916–1921. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1916-1921.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Kime K. K., Schrumpf M. E., Coe J. E., Simpson W. J. Antibody response in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) experimentally infected with the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3445–3451. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3445-3451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. M., Spielman A. Accelerated transmission of Lyme disease spirochetes by partially fed vector ticks. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Nov;31(11):2878–2881. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.11.2878-2881.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eckerskorn C., Museteanu C., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Wallich R. Recombinant outer surface protein a from Borrelia burgdorferi induces antibodies protective against spirochetal infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):123–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sădziene A., Rosa P. A., Thompson P. A., Hogan D. M., Barbour A. G. Antibody-resistant mutants of Borrelia burgdorferi: in vitro selection and characterization. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):799–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford S. R., 3rd, Urioste S. S., Spielman A. Clustering of host-seeking nymphal deer ticks (Ixodes dammini) infected by Lyme disease spirochetes (Borrelia burgdorferi). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Jul;47(1):55–60. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Ribeiro J. M. The role of vector saliva in transmission of arthropod-borne disease. Parasitol Today. 1990 May;6(5):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tälleklint L., Jaenson T. G., Mather T. N. Seasonal variation in the capacity of the bank vole to infect larval ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J Med Entomol. 1993 Jul;30(4):812–815. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.4.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Helmes C., Schaible U. E., Lobet Y., Moter S. E., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Evaluation of genetic divergence among Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by use of OspA, fla, HSP60, and HSP70 gene probes. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4856-4866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Jauris S., Hofmann A., Pradel I., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Will G., Wanner G. Immunological and molecular polymorphisms of OspC, an immunodominant major outer surface protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2182–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2182-2191.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wéry M. Les lents progrès du contrôle de la maladie du sommeil. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1990;65 (Suppl 1):89–93. doi: 10.1051/parasite/1990651089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]