Abstract
We report the assembly of the 14,054 bp near complete sequencing of the mitochondrial genome of the legume pod borer (LPB), Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), which we subsequently used to estimate divergence and relationships within the lepidopteran lineage. The arrangement and orientation of the 13 protein-coding, 2 rRNA, and 19 tRNA genes sequenced was typical of insect mitochondrial DNA sequences described to date. The sequence contained a high A+T content of 80.1% and a bias for the use of codons with A or T nucleotides in the 3rd position. Transcript mapping with midgut and salivary gland ESTs for mitochondrial genome annotation showed that translation from protein-coding genes initiates and terminates at standard mitochondrial codons, except for the coxI gene, which may start from an arginine CGA codon. The genomic copy of coxII terminates at a T nucleotide, and a proposed polyadenylation mechanism for completion of the TAA stop codon was confirmed by comparisons to EST data. EST contig data further showed that mature M. vitrata mitochondrial transcripts are monocistronic, except for bicistronic transcripts for overlapping genes nd4/nd4L and nd6/cytb, and a tricistronic transcript for atp8/atp6/coxIII. This processing of polycistronic mitochondrial transcripts adheres to the tRNA punctuated cleavage mechanism, whereby mature transcripts are cleaved only at intervening tRNA gene sequences. In contrast, the tricistronic atp8/atp6/coxIII in Drosophila is present as separate atp8/atp6 and coxIII transcripts despite the lack of an intervening tRNA. Our results indicate that mitochondrial processing mechanisms vary between arthropod species, and that it is crucial to use transcriptional information to obtain full annotation of mitochondrial genomes.
Introduction
The mitochondrial genome encodes genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation and a unique translation system of 2 rRNAs and 22 tRNAs used for synthesis of the 13 inclusive protein coding genes (PCGs). Within animal species the mitochondrial genome shows a lack of introns and little intergenic space, the exception being the AT nucleotide rich displacement loop (D-loop) which encodes the origin of replication and promoters for the translation of both the heavy (H) and the light (L) strands (heavy strand promoter, HSP; light strand promoter, LSP) [1]. Thus, both H and L strands of the mitochondrial genome are transcriptionally active, and produce polycistronic RNA transcripts (cistrons) [2], [3], [4]. The tRNA regions form characteristic cloverleaf secondary structure within the initial polycistronic transcripts, and they are recognized by cleavage mechanisms that result in processed transcripts that encode one or more PCGs [5]. This mode of gene expression is reminiscent of the bacterial cistronic mode of gene expression from which eukaryotic mitochondria are believed to have been derived. As a consequence of gene order in the mitochondrial genome, the tRNA-punctuated mode of transcript processing can result in mature transcripts that encode more than one PCG [5], where bicistronic transcripts are predicted for mitochondrial PCG sequences (cds) that overlap within the genomic sequence, which includes atp8/atp6 and nd4/nd4L within insect mitochondria.
Mitochondrial genomes have been sequenced for insect species within the order Lepidoptera: the first ones sequenced were from the silk moth Bombyx mori [6] and the corn borer Ostrinia spp. [7]. Lepidopteran mitochondrial genomes have a relatively conserved gene order and orientation [8], which is shared with that of Drosophila species [9]. Despite the generation of full mitochondrial genome sequences, the corresponding annotation of gene coding regions in Lepidoptera has largely relied upon comparison to Drosophila gene models. There are discrepancies in mitochondrial gene boundaries in Lepidoptera, among them (1) the ambiguity in the translation start site of cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (coxI) at either a proposed arginine codon (CGR) or a TTAG site [6], and (2) the assumed polyadenylation following a T nucleotide at the terminus of coxII that would complete a truncated stop codon [9]. Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) are a source of gene expression information, and are typically inclusive of mitochondrial-derived transcripts. The use of EST data to assemble mitochondrial-derived transcripts has proven valuable in characterization of gene boundaries, polycistronic transcripts, and differential transcript processing among tissues, as well as for the quantification of mitochondrial transcript stability [10],[11]. Despite the utility of ESTs in the annotation of mitochondrial genomes, these data are rarely incorporated into annotation efforts.
In this paper, we describe the nearly complete mitochondrial DNA sequence for the legume pod borer (LPB), Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyraloidea: Crambidae). This insect species is a crop pest found throughout tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Larval stages of LPB feed upon leaves, flowers and pods of leguminous plants [12], [13], [14], [15] and cause significant yield loss to legume crops cultivated in Southeast Asia [16], [17], [18], South Asia [19], [20], [21], and Central America and South Americas [22], [23]. Its most significant impact is in sub-Saharan Africa [24], [25], [26], [27], where between 20–80% yield reductions are incurred [25]. Accordingly, M. vitrata has been identified as a major emerging threat to legume production in developing and under-developed nations. The mitochondrial genome information provided here complements the mitochondrial coxI DNA markers developed by Margam et al. (2010) [28], by providing additional sequence data to assist in defining population structure, and gene flow, which will hopefully lead to sustainable and economically viable methods of pest management. With the exception of Drosophila melanogaster, this study provides the first instance where (i) mitochondrial genome annotations have been validated by transcribed sequence data, and (ii) predictions of processed mitochondrial transcripts (cistron) have been used for both structural and functional annotation of genes. This added value information suggests that available EST information is a valuable resource for mitochondrial genome annotations.
Materials and Methods
Sequence and annotation of the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome
Genomic DNA was isolated from a M. vitrata specimen (from Burkina Faso; BUR38) [28] using a DNeasy animal tissue kit following the manufacturer's instructions (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). A total of 100 ng genomic DNA was used as the template in 50 µl PCR volumes that also contained 10 pmol primers, 5 µl 10× PCR buffer, 0.4 µl Taq polymerase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA), and 1.2 µl 10mM dNTP. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out in an Eppendorf Mastercycler thermocycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) using the thermal cycling profile of 95°C denaturation for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95°C for 30 s, 52°C for 45 s, 72°C for 1 m, as well as a final cycle of 72°C for 8 m. The PCR products were cleaned to remove any residual primers and nucleotides using Qiaquick PCR purification kits (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) following the manufacturer's protocols. The PCR products were cycle sequenced using 1 µl of purified template, 1 µl of 10× BigDye™ (ABI PRISM™ BigDye™ Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction Kit; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA), 1 pmol forward or reverse primer (Table 1), and 6 µl of ddH2O using the conditions: 95°C for 2 min, followed by 98 cycles of 95°C for 10 s, 50°C for 5 s, and 60°C for 4 min. Cycle-sequencing products were precipitated using an ethanol-sodium acetate procedure. Precipitates were dissolved in 35 µl of ddH2O. From this solution, 15 µl was separated on an ABI 3500 Sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Sequences from PCR fragments obtained from BUR38 and PR08 were assembled independently using the NextGENe software (Softgenetics®, State College, PA), and the assemblies were exported in FASTA format.
Table 1. Oligonucleotide primers used for amplification of overlapping fragments used to reconstruct the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome sequence (Fig. 2).
| Primer pair | Forward | Reverse |
| ND2 | TCTTGATTTGGWTGYTGAATTGG | GTWCCAATATCTTTATGATTTGTTGAG |
| COI | TCGCTTATAACGTCAGCCATTT | CTAATCAATTTCCAAATCCTCCAA |
| COII3p | TTAATCGATTTTTATTAGAAGGTCAAA | TTGCACCACAAATTTCAGAACA |
| ND3a | TCCCTTAAATTTTCTATTTATTGATGAGG | GGAATTAAACCACTAAAAATTAAGTTAGC |
| ND3b | TTATTTTACTTTTAGGATTATTTCACG | CCTTATCCTTATATAATTTATTTGCCTTT |
| ND5 | GCTAAATCAGGTAATCCCATTCTT | TTTATTAGGTTGAGATGGTTTAGGTTT |
| Cytb-a | CCAATTCGAAAAACACACCCTA | TTCGAGGGACTTTACCTCGTT |
| Cytb-b | TCCTTTAGGAATCAATAGAAATTTAG | TTCGAGGGACTTTACCTCGTT |
| ND1 | TCATATCGATAACGAGGTAAAGTCC | CCTGTCATTAGATTTATTTTGTCTTT |
| gap1 | AGGGGGTTTACCTCCATTTA | AATAAATGCATGAGCTGTTACAATA |
| gap2 | TTACCACCTGCAGAACATTCA | CGTAATGAAGGTAAAGCAATAAAAA |
| gap3 | GCAAGTACTGGTCTCTTAAACCAT | AGATGGGTCAAAAATTGAAAAA |
| gap4 | CAGCCAATATAATTGCAGGACA | TCTCGACAAATATCTCGTCATCA |
| gap5 | ATTTGAAGCTGCTGCCTGAT | CGAGCAGAAGATTTAGGGTCA |
| gap6 | GACCCTAAATCTTCTGCTCGAA | GAGAAGTTTATAGCGGTTATGGAA |
| gap7 | AACCACTGAAGAAATTAATATAACAAA | CATGGTAAATATTATTCAGGAATTT |
| gap8 | GCTCCCTCACAAACTGAGAAA | TTTCATTTGATGCAATTCTAGATACA |
| gap9 | TTAGGCCCTTTACGAATTTGA | GCGACCTCGATGTTGGATTA |
| gap10 | CAACATCGAGGTCGCAAAC | TTGACTGTACAAAGGTAGCATAAT |
| gap11 | TTATGCTACCTTTGTACAGTCA | TGTATCTTGTGTATCAGAGTTTATT |
The FASTA-formatted BUR38 mitochondrial sequence was imported into a local database using BioEdit [29], and was queried with O. nubilalis protein and tRNA sequences from GenBank ID: AF442957.1. Protein cds were defined based on invertebrate mitochondrial translation table using the Virtual Ribosome (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/VirtualRibosome/) [30]. The tRNA gene boundaries and folded structures were defined using tRNAscan-SE (http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE/) [31] with the following parameters: (i) search mode – organellar; (ii) search type – cove only; (iii) cove cut off score −15; (iv) translation code used – invertebrate mitochondrial; (v) maximum intron length – 40; and (vi) pseudogene checking – disabled. The mitochondrial sequences were imported into the Artemis visualization and annotation tool [32], positional information of sequence features was added, and the annotated data exported in GenBank(.gb) format.
Phylogenetics
The FASTA-formatted mitochondrial genome assembly for M. vitrata was used in a query in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant nucleotide database (nr) with the blastn search algorithm [33]. The resulting hits to full mitochondrial genome sequences for species of Lepidoptera were downloaded in FASTA format. The FASTA formatted mitochondrial genome sequences were imported into the MEGA 4.0 software package sequence alignment application [34] and a multiple sequence alignment was performed with the ClustalW algorithm using default parameters (gap opening penalty 15, gap extension penalty 6.66, weight matrix IUB, and transition weight of 0.5). The nucleotide diversity (p), base composition, transition to transversion bias (R; [35]), disparity in substitution among nucleotide sites (Disparity Index), and test substitution homogeneity [36] of the aligned sequence was analyzed by MEGA 4.0 [34].
Maximum likelihood analysis of derived amino acid sequences, to infer the phylogenetic relationships among mitochondrial genome sequences, was performed using the PHYLIP software package [37]. Concatenated protein sequences from each species of Lepidoptera that has a complete mitochondrial genome within GenBank (current December 7, 2010) were imported into the MEGA 4.0 sequence alignment suite, aligned using the ClustalW algorithm (default parameters using the PAM protein weight matrix), and all gaps deleted manually. One thousand bootstrap pseudo-datasets were constructed using the program seqboot, which was used as input into ProML that used a Hidden Markov Model method to infer evolutionary rates among residue positions [38] with the Jones, Talyor, and Thorton [39] probability matrix. An unrooted majority rule consensus tree was generated using Consense, and viewed using TreeView 1.6.6 [40].
454 EST sequencing and mitochondrial transcript mapping
A total of 60 LPB larvae comprising of 3rd, 4th and 5th instars (20 each from Taiwan, Puerto Rico and Australia) were dissected to obtain the midgut and the salivary-gland tissues. Total RNA was extracted from these tissues using a TRIzol® Reagent protocol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA was quantified on a NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, DE). First-strand cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg of total RNA using a BD Smart PCR cDNA synthesis kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). The first-strand cDNA was then amplified by a BD mix for 15 cycles (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) following the manufacturer's protocol except that a modified CDS II/3′ primer 5′ – TAG AGG CCG AGG CGG CCG ACA TGT TTT GTT TTT TTT TCT TTT TTT TTT VN -3′ (IDT Inc.) was used to avoid long homopolymer repeats. Subsequent to first-strand synthesis, the cDNA was then amplified using PCR Advantage II polymerase (Clontech Inc.) with the following thermal cycling program: (i) 1 min at 95°C, (ii) 21 cycles of 95°C for 7 sec, and 68°C for 6 min. A 2 µl aliquot of the PCR product was analyzed on a 1% agarose gel to determine the amplification efficiency. The PCR product was then subjected to SfiI digestion (10 units) for 2 h at 50°C to remove the concatemers formed by CDSIII/3′ and the SMART IV primers. A Qiaquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) was used to remove the leftover primers and nucleotides from the amplified cDNA. The quality and quantity of the cDNA library was evaluated by both spectrophotometry and gel electrophoresis.
Sequencing and assembly: Amplified cDNA was submitted to the Keck Genomic Center (University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign) for library construction and sequencing. Two µg of amplified cDNA was used for library construction followed by pyro-sequencing on a Roche 454 GS-FLX (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using established protocols [41]. The adaptor sequences were identified and the trim positions changed in .sff files using cross-match (http://www.phrap.org), sff tools from Roche (https://www.rocheapplied-science.com) and custom-built Java scripts. Sequences shorter than 50 nucleotides or containing homopolymers (in which 60% over the entire length of the read is represented by one nucleotide) were not included for assembly. The sequences were assembled with the Lasergene software (http://www.dnastar.com), using the modified .sff files. Raw sequence data were obtained from .sff files, and assembled into contigs using the Roche GS De Novo Assembler (i.e., Newbler assembler), and data comprising all non-redundant contigs were exported to FASTA format.
A local database, MvEST01, containing all Newbler-assembled non-redundant contigs was constructed using BioEdit [29]. MvEST01 was queried with 13 Ostrinia nubilalis mitochondrial protein sequences and 21 tRNA sequences obtained from GenBank accession AF442957 using the tblastn search algorithms [33]. The results were then filtered for hits with ≥90% identity, and inclusive contigs were retrieved from MvEST1.
Scaffolding of M. vitrata ESTs and transcript mapping
The EST reads were scaffolded against the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome assembly using the NextGENe software (Softgenetics®, State College, PA; parameters used were – matching base number > = 8 and matching base percent > = 70), and contiguous overlapping sequences exported as consensus contigs in FASTA format. The coding region(s) of contig sequences were annotated manually via blastx search of the M. vitrata mitochondrial gene model developed previously, and derived peptide sequence were predicted using the Virtual Ribosome v.1.1 [30].
Results and Discussion
Sequence and annotation of the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome
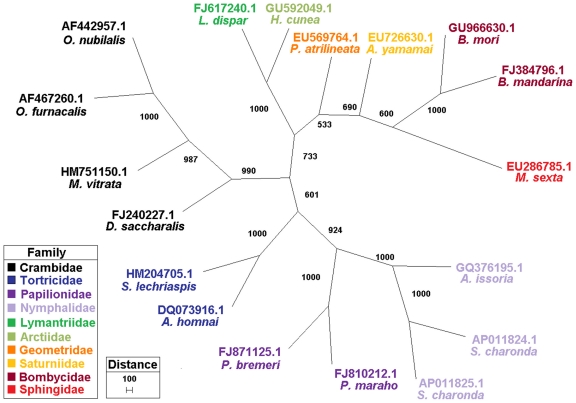
Nineteen overlapping PCR products generated using the oligonucleotide primer pairs shown in Table 1 yielded a total of 15,385 bp of sequence data. The data were assembled into a 14,054 bp partial sequence of the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome that was submitted to GenBank (HZ751150). This sequence lacks only the displacement loop (D-loop) that encodes the origin of replication or heavy strand promoter (HSP) and light strand promoter (LSP). The M. vitrata mitochondrial genome showed a high A+T nucleotide content of 80.0%, typical of animal and insect mitochondrial genome sequences [42], [43]. The A+T bias in M. vitrata is lower than that in any other mitochondrial genome sequence from Lepidoptera (Fig. 1), but this likely is the consequence of our partial sequence that does not contain the A-T rich D-loop. Although it does not include the entire mitochondrial genome, the M. vitrata assembly allowed for the identification and analysis of 2 rRNAs, 13 protein coding genes, and 19 of 22 tRNA genes (Fig. 2). The gene order and orientation seen in M. vitrata is typical for insect mitochondrial genomes (Table 2) [9], and is identical to that of the other Crambid species O. nubilalis and O. furnacalis [7]. Phylogenetic analyses indicated that the M. vitrata mitochondrial DNA grouped with a clade containing other species from the lepidopteran Family Crambidae, and clustered with other Families. A clear distinction between moth and butterfly species was apparent (Fig 1; alignment not shown). Thus, the use of the entire mitochondrial genome may clarify phylogenetic relationships that could not be determined using smaller sequence sampling methods [44].
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationships among mitochondrial genomes sequences.
Phylogenetic relationships among complete mitochondrial genome sequences from the insect Order Lepidoptera using maximum likelihood estimations from a Hidden Markov Model, and branch support shown for 1000 bootstrap pseudoreplicates in a majority rule tree. The GenBank accession no., species, and Family assignment are indicated.
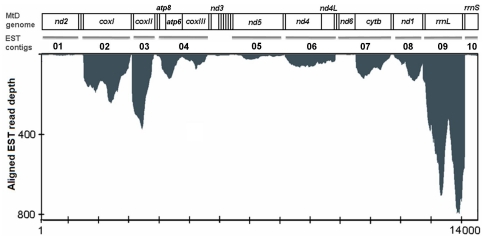
Figure 2. Transcript mapping to the mitochondrial genome.
Transcript mapping of raw EST read data to respective positions on the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome (GenBank accession HZ751150), and assembled contigs representing polycistronic transcripts. The gene annotation and expression profile data for each of the contigs are presented in Table 4. Light strand encoded genes are indicated by asterisks (*), and arrows indicate the direction of transcription for polycistronic RNAs from the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome.
Table 2. Summary of Maruca vitrata predicted tRNAs.
| Gene | Strand | 5′ start | 3′ stop | Length (bp) | Start | Stop |
| Nd2 | H | 1 | 999 | 999 | TTA | TAA |
| tRNATrpUGR | H | 1007 | 1074 | 68 | ||
| tRNACys UGY | H | 1068 | 1131 | 64 | ||
| tRNATyrUAY | L | 1199 | 1137 | 61 | ||
| coxI | H | 1207 | 2739 | 1533 | CGA | TAA |
| tRNALeuUUR | H | 2735 | 2801 | 67 | ||
| coxII | H | 2802 | 3486 | 685 | ATG | T |
| tRNALysAAR | H | 3484 | 3554 | 71 | ||
| tRNAAspGAY | L | 3557 | 3624 | 68 | ||
| atp8 | H | 3624 | 3785 | 162 | ATT | TAA |
| atp6 | H | 3779 | 4453 | 675 | ATG | TAA |
| coxIII | H | 4461 | 5249 | 789 | ATG | TAA |
| tRNAGlyGGN | H | 5252 | 5317 | 66 | ||
| Nd3 | H | 5318 | 5671 | 354 | ATT | TAA |
| tRNAAlaGCN | H | 5673 | 5738 | 66 | ||
| tRNAArgCGN | H | 5737 | 5802 | 66 | ||
| tRNAAsnAAY | H | 5801 | 5866 | 66 | ||
| tRNASerAGN | H | 5869 | 5936 | 68 | ||
| tRNAGluGAR | H | 5937 | 6001 | 65 | ||
| tRNAPheUUY | L | 6069 | 6004 | 64 | ||
| Nd 5 | L | 7790 | 6260 | 1529 | ATT | TAA |
| tRNAHisCAY | L | 7872 | 7806 | 65 | ||
| Nd 4 | L | 9213 | 7872 | 1340 | ATG | TAA |
| Nd 4L | L | 9491 | 9213 | 277 | ATG | TAA |
| tRNAThrACN | H | 9465 | 9532 | 68 | ||
| tRNAProCCN | L | 9591 | 9531 | 59 | ||
| Nd 6 | H | 9611 | 10040 | 430 | ATT | TAA |
| cytb | H | 10377 | 11364 | 988 | ||
| tRNASerUCN | H | 11367 | 11432 | 66 | ||
| Nd 1 | L | 12378 | 11449 | 928 | TTG | TAG |
| tRNALeuCUN | L | 12455 | 12388 | 66 | ||
| rrnL | L | 13780 | 12476 | 1303 | ||
| tRNAValGUN | L | 13852 | 13804 | 47 | ||
| rrnS | L | 13863 | 14139 | 277 |
The tRNAs are presented in the order they occur on the mitogenome along with their beginning and ending nucleotide positions. The anticodon region detected and the corresponding amino acid the predicted tRNA transfer are presented. The orientation is indicated with respect to the heavy (H) or light (L) strand is indicated.
Protein coding regions encompassed 10,266 of the 14,052 bp assembled sequence (75.5%) and showed an A+T content of 82.9%, which is slightly higher than that of the entire sequence, but both were consistent with the high A+T content of insect [9], [43] and lepidopteran mitochondrial DNAs [45]. This AT-bias was reflected in the codon usage of the 14 PCGs (Table 3), where phenylalanine (F; UUU), isoleucine (I; AUU), leucine (L; UUA), methionine (M; AUA), and tyrosine (Y; UAU) were proportionately the most represented. The AT-bias in codon usage also was likewise observed in that 3218 of 3422 codons had third positions with either an A or T nucleotide (94.0%), and was significantly higher proportion than at the first codon positions (73%; χ2 = 4.69, P-value = 0.030) and second codon positions (69.8%; χ2 = 6.23, P-value = 0.013). This difference may reflect the selection for optimal codon usage [46] or codons that match the anti-codons of tRNAs [47].
Table 3. Codon usage in the Maruca vitrata mitochondrial genome showing a high A-T nucleotide bias in the 3rd (wobble) position (94.0%).
| UUU(F) | 315.0(1.82) | | | UCU(S) | 98.0(2.69) | | | UAU(Y) | 169.0(1.88) | | | UGU(C) | 28.0(1.87) |
| UUC(F) | 31.0(0.18) | | | UCC(S) | 8.0(0.22) | | | UAC(Y) | 11.0(0.12) | | | UGC(C) | 2.0(0.13) |
| UUA(L) | 426.0(5.26) | | | UCA(S) | 12.0(2.06) | | | UAA(*) | 10.0(1.82) | | | UGA(W) | 88.0(1.96) |
| UUG(L) | 9.0(0.11) | | | UCG(S) | 1.0(0.05) | | | UAG(*) | 1.0(0.18) | | | UGG(W) | 2.0(0.04) |
| CUU(L) | 26.0(0.32) | | | CCU(P) | 74.0(2.47) | | | CAU(H) | 60.0(1.82) | | | CGU(R) | 12.0(0.94) |
| CUC(L) | 2.0(0.02) | | | CCC(P) | 8.0(0.27) | | | CAC(H) | 6.0(0.18) | | | CGC(R) | 0.0(0.00) |
| CUA(L) | 23.0(0.28) | | | CCA(P) | 38.0(1.27) | | | CAA(Q) | 54.0(1.96) | | | CGA(R) | 37.0(2.90) |
| CUG(L) | 0.0(0.00) | | | CCG(P) | 0.0(0.00) | | | CAG(Q) | 1.0(0.04) | | | CGG(R) | 2.0(0.16) |
| AUU(I) | 394.0(1.91) | | | ACU(T) | 83.0(2.35) | | | AAU(N) | 202.0(1.87) | | | AGU(S) | 31.0(0.85) |
| AUC(I) | 18.0(0.09) | | | ACC(T) | 8.0(0.23) | | | AAC(N) | 14.0(0.13) | | | AGC(S) | 1.0(0.03) |
| AUA(M) | 240.0(1.85) | | | ACA(T) | 49.0(1.39) | | | AAA(K) | 73.0(1.70) | | | AGA(S) | 76.0(2.09) |
| AUG(M) | 19.0(0.15) | | | ACG(T) | 1.0(0.03) | | | AAG(K) | 13.0(0.30) | | | AGG(S) | 0.0(0.00) |
| GUU(V) | 71.0(2.07) | | | GCU(A) | 75.0(2.52) | | | GAU(D) | 55.0(1.75) | | | GGU(G) | 57.0(1.19) |
| GUC(V) | 4.0(0.12) | | | GCC(A) | 9.0(0.30) | | | GAC(D) | 8.0(0.25) | | | GGC(G) | 0.0(0.00) |
| GUA(V) | 59.0(1.72) | | | GCA(A) | 35.0(1.18) | | | GAA(E) | 68.0(1.89) | | | GGA(G) | 117.0(2.45) |
| GUG(V) | 3.0(0.09) | | | GCG(A) | 0.0(0.00) | | | GAG(E) | 4.0(0.11) | | | GGG(G) | 17.0(0.36) |
The methionine start codons, UTG, were used by 6 of 13 protein coding genes (46.2%). In contrast, an atypical Ile codon (AUU) was used to initiate protein synthesis in the atp8, nd3, nd5, and nd6 genes, and Phe (UUR) was used in the nd1 and nd2 genes, and Arg (CGA) was used for the coxI gene. The use of Ile for initiation of peptide synthesis has previously been reported in other insects [48] including Lepidoptera [6], [7], which suggests that it is common in this insect Order. Additionally, the cox1 gene was first annotated with an Arg (CGA) initiation codon for protein synthesis in Drosophila yakuba [9], and the same codon was also subsequently shown for the Lepidopteran species B. mori [6], O. nubilalis and O. furnacalis [7], Adoxophyes honmai [49], Coreana rephaelis [50], Antheraea pernyi [45], B. mandarina [51], Ochrogaster lunifer [52], Artogeia melete [53], Eriogyna pyretorum [54], and Hyphantria cunea [8]. The nucleotide sequence, TTAG, located immediately upstream of the putative Arg CGR start codon of coxI was proposed to serve in a non-standard initiation process [6]. Our alignment of the mitochondrial genome sequence from 19 species of Lepidoptera (Fig. 1; alignment not shown) indicated that this putative TTAG initiation was conserved among 15 of 27 (55.6%) coxI genes from full lepidopteran mitochondrial genomes (Fig. 1). The lack of absolute conservation of the TTAG suggests that there may be flexibility in the function of the sequence, or that it may not serve as an initiation codon. In any case, further study is required to determine the mechanism of coxI initiation, but transcript information provided by Stewart and Beckenback (2009) [55] and our data described below indicate that the Arg (CGR) indeed functions as the initiation codon.
The corresponding stop codons used by M. vitrata mitochondrial genes were predicted to be TAA in all instances except for coxII and ND1 where T and TAG motifs were observed, respectively (Table 2). Based on invertebrate mitochondrial genetics, we predict that the UAG codon serves as a stop codon, and it has only been observed in M. vitrata, Ostrinia sp. [7], Parnassius bremeri (GenBank ID: FJ871125.1), and Parnassius maraho (GenBank ID: FJ810212.1) mitochondrial genomes. The infrequent use of the TAG stop codon is likely a consequence of the high A+T bias at the third codon position [43]. The incomplete stop codon of coxII (T nucleotide only) was previously reported in insects [7], [9], and for other mitochondrial genes in bivalves [56] and mammalian species [3]. Mitochondrial RNA processing occurs by the tRNA punctuation model [3], wherein the cloverleaf-like secondary structures of tRNAs are required for the cleavage of polycistronic transcripts into mRNAs. Maturation of the mitochondrial mRNAs occur by the addition of poly(A) tails, and results in completion of the TAA stop codon for coxII (A nucleotides added via polyadenylation are underlined; [55]). Similarly, we present EST data in the following section that indicate that mature M. vitrata coxII transcripts are also polyadenylated.
M. vitrata EST assembly and mitochondrial cistronic transcripts
The de novo assembly of the M. vitrata larval midgut and salivary EST read data resulted in a total of 3729 contigs (mean length 459.6±287.3 bp; range 96 to 3299 bp), of which 10 contigs were annotated as derived from the mitochondrial genome (1335.7±510.3 bp; Supplemental Data S1); these contigs resulted from the clustering of 7608 raw reads (Supplemental Data S2). The arrangement of genes within assembled contigs likely represent mature transcripts that are derived from tRNA punctuated cleavage of a polycistronic transcript [3], [57], and in M. vitrata it showed that three contigs had more than one gene (contig 4: atp8, atp6, and coxIII; contig 6: nd4 and nd4L; and contig 7: nd6 and cytb; Fig 2; Table 4). The atp6 and atp8 genes, as well as the nd4 and nd4L genes, were located upon the same mature mitochondrial transcript within the Dipteran insects D. melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura [55], [57], [58] and the swine Sus scofa [10]. According to the tRNA punctuated model, all M. vitrata mitochondrial polycistronic transcripts are cleaved at junctions with tRNAs, such that the 3′ end of cistrons are each interspersed by a tRNA gene [3], [5]. By default, mitochondrial genes on the same cistron that are contiguous within the genome lack an intervening tRNA. This contiguous structural arrangement of the atp8/atp6/coxIII, nd4/nd4L, and nd6/cytb genes was observed in the M. vitrata mitochondrial genome, and was also predicted within the resulting mature transcripts (cistrons; Fig. 2; Table 4).
Table 4. The quantitative expression profile of cistrons transcribed from Maruca vitrata mitochondrial genome.
| Contig (cistron) | Genes within contig | Contig length | Total nt | Mean depth (nt) | Read no. | Proportion |
| MvMtD_01 | nd2 | 1,033 | 7,829 | 7.58 | 24 | 0.2 |
| MvMtD_02 | coxI | 1,532 | 265,789 | 290.16 | 916 | 6.9 |
| MvMtD_03 | coxII | 713 | 239,189 | 300.49 | 796 | 6.0 |
| MvMtD_04 | atp8, atp6, coxIII | 2,049 | 171,490 | 83.69 | 558 | 4.2 |
| MvMtD_05 | nd5 | 1,736 | 27,891 | 16.07 | 81 | 0.6 |
| MvMtD_06 | nd4 | 1,640 | 89,043 | 54.29 | 297 | 2.2 |
| MvMtD_07 | nd6, cytb | 1,768 | 117,208 | 66.29 | 359 | 2.7 |
| MvMtD_08 | nd1 | 1,022 | 86,645 | 84.48 | 278 | 2.1 |
| MvMtD_09 | rrnL (16s rDNA) | 1,408 | 1,053,548 | 748.29 | 4,288 | 32.1 |
| MvMtD_10 | rrnS (12s rDNA) | 456 | 2870 | 6.29 | 11 | 0.1 |
The number of raw reads (Read no.) that were scaffolded to each contig (cistron) was used to calculate the relative proportion of mitochondrial transcripts within the pooled M. vitrata midgut and salivary gland EST library.
The overlap of the gene coding sequence between those of M. vitrata atp8 and atp6 (7 bp), and nd4 and nd4L (1 bp), would logically dictate that the mature transcripts remain intact in order to preserve their respective coding sequences. This scenario was also predicted due to the absence of an intervening tRNA that would be necessary for transcript cleavage [3], [5]. To our knowledge, the polycistronic atp8/atp6/coxIII transcript identified from M. vitrata has yet to be reported in insects despite ancestral genome arrangements that likely would lead to this tricistronic transcript. Drosophila melanogaster showed polyadenylation at the 3′ terminus of bicistronic atp8/atp6 and monocistronic coxIII mitochondrial transcripts [55], which suggests that variation in mitochondrial transcript cleavage events may exist among insect species. Indeed, differences occur between species of salamander, where a tricistronic atp8/atp6/coxIII transcript from Ambystoma tigrinum is processed into atp8/atp6 and coxIII transcripts within A. mexicanum [59]. Our mitochondrial transcript mapping data are the first to be reported for a lepidopteran, so direct comparison with data from other species cannot readily be made. Undoubtedly the inclusion of mitochondrial transcript mapping data from additional species will allow us to understand the functional variation in mitochondrial transcript processing.
Only two out of the eight (25%) mature processed M. vitrata mitochondrial transcripts have possible poly(A) tails (coxII and atp8/atp6/coxIII cistrons; Supplemental Data S1), which is in contrast to the observation of 3′ polyadenlyation for all cistronic transcripts in Drosophila [55]. Generation of initial M. vitrata cDNA by use of a poly(T) oligonucleotide would indicate that adenlyated forms of each cistron would be within the EST assemblies, if indeed present within the biological samples. The post-transcriptional 3′ addition of adenosine nucleotides results in increased transcript stability in many systems, but it has been linked to increased degradation in plant mitochondria [60]. RNAi knockdown of the enzymatic machinery involved in polyadenylation was previously reported to produce no apparent change in mitochondrial transcript stability in humans [61], [62]. Hence, the role of adenylation in mitochondrial transcript stability remains unknown [63]. Adenylation is required by the coxII transcript for the completion of its termination codon, but the functional or protective role of poly(A) tails remains uncertain given the absence from most cistronic transcripts in M. vitrata.
Scaffolding of M. vitrata ESTs and transcript mapping
Since polycistronic transcripts are cleaved to generate mRNAs for each mitochondrial gene-derived cistron, the initial molar ratios are equal and subsequent variation in processed transcript quantities result from differences in mRNA stability [64]. The scaffolds comprised of short read EST data from M. vitrata were representative of full-length transcripts (Fig. 2), and appear not to be significantly influenced by reported over-representations of the 3′ end of fragments sometimes observed from 454 data [57]. Furthermore, the scaffolds aligned with our previous contig (cistron) assemblies that were representative of mature processed mitochondrial transcripts, and showed a read depth of 1 to 784 (Fig. 2; Table 4). Similar data from Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies has been used to characterize gene expression [57], and applied to describe the sequence and relative quantities of processed mitochondrial-derived transcripts [10], [11]. The quantification described in those studies used simple calculations of the proportion of raw sequence reads mapped to each transcript (cistron) as a relative measure of cellular transcript level, which was used as an estimation of gene expression [57], [65].
A similar quantification of M. vitrata mitochondrial-derived transcript levels from scaffolded EST data indicated a ∼321-fold variance in cistron level, where the rrnL gene was present in the highest proportion (Table 4). The rrnL transcript was also present in the highest proportion of D. melanogaster [11] and porcine cistrons [10], and the analogous large abundance of rrnL transcripts in human expression data was attributed to the presence of a second HSP upstream of the gene that terminates in proximity near the tRNALeuUUR downstream of the 16 S rRNA [66], [67], [68]. The HSP and LSP sequences have diverged rapidly in mammalian systems [69], such that defining these functional regions is difficult by comparative sequence analyses [70]. The proportional range of cistron levels for those that encode for proteins involved in the same process showed ≤11.15-fold difference in cistron quantities for the NADH dehydrogenase complex (nd1 vs. nd2), and a ≤3.59-fold variance among cistrons for the cytochrome c oxidase (coxII vs. coxIII). The estimated expression levels of coxI and coxII were approximately equal in M. vitrata ESTs. An overall lack of correlation between transcript levels within a protein complex has been observed among species of Drosophila [11], and likely can be attributed to differences in individual transcript stabilities [64]. Furthermore, these estimates do not take into account any differences in protein stability or turnover in the cell that would influence cellular metabolic processes [71]. The expression data represent additional data for annotation, but comparison with ESTs derived from different M. vitrata tissues or growth stages are likely to provide valuable information regarding metabolic variation.
Conclusions
This is the first study of a species of Lepidoptera to provide functional annotation of a complete mitochondrial genome using gene expression data. These results will be valuable for future studies to provide comparisons for other species of Lepidoptera and to describe tissue-specific mitochondrial transcript processing pathways. This study provides a paradigm for the mating of EST and functional mitochondrial genome annotations that can be accomplished for any species for which both data sets are present.
Supporting Information
Maruca vitrata mitochondrial DNA assembled contigs.
(TXT)
Maruca vitrata 454 raw reads corresponding to the mitochondrial genome assembly.
(TXT)
Acknowledgments
We thank Susan Balfe, Department of Entomology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, for her technical assistance on this project.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This research has been made possible through support provided to the Dry Grains Pulses Collaborative Research Support Program (CRSP) by the Bureau for Economic Growth, Agriculture, and Trade, U.S. Agency for International Development, under the terms of Grant No. EDH-A-00-07-00005. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the U.S. Agency for International Development or the U.S. government. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Kasamatsu H, Robberson DL, Vinograd J. A novel closed-circular mitochondrial DNA with properties of a replicating intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1971;68 doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fernandez-Silva P, Enriquez JA, Montoya J. Replication and transcription of mammalian mitochondrial DNA. Exp Physiol. 2003;88:41–56. doi: 10.1113/eph8802514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ojala D, Montoya J, Attardi G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature. 1981;290:470–474. doi: 10.1038/290470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Taanman JW. The mitochondrial genome: structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1410:103–123. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(98)00161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ojala D, Merkel C, Gelfand R, Attardi G. The tRNA genes punctuate the reading of genetic information in human mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1980;22:393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90350-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yukuhiro K, Sezutsu H, Itoh M, Shimizu K, Banno Y. Significant levels of sequence divergence and gene rearrangements have occurred between the mitochondrial genomes of the wild mulberry silkmoth, Bombyx mandarina, and its close relative, the domesticated silkmoth, Bombyx mori. Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:1385–1389. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Coates BS, Sumerford DV, Hellmich RL, Lewis LC. Partial mitochondrial genome sequences of Ostrinia nubilalis and Ostrinia furnacalis. Int J Biol Sci. 2005;1:13–18. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liao F, Wang L, Wu S, Li YP, Zhao L, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Int J Biol Sci. 2010;6:172–186. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Clary DO, Wolstenholme DR. The mitochondrial DNA molecular of Drosophila yakuba: nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J Mol Evol. 1985;22:252–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Scheibye-Alsing K, Cirera S, Gilchrist MJ, Fredholm M, Gorodkin J. EST analysis on pig mitochondria reveal novel expression differences between developmental and adult tissues. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:367. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Torres TT, Dolezal M, Schlotterer C, Ottenwalder B. Expression profiling of Drosophila mitochondrial genes via deep mRNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:7509–7518. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Huang CC, Peng WK, Talekar NS. Parasitoids and other natural enemies of Maruca vitrata feeding on Sesbania cannabina in Taiwan. BioControl. 2003;48:407–416. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Arodokoun DY, Tamo M, Cloutier C, Brodeur J. Larval parasitoids occurring on Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in Benin, West Africa. Agric Ecosyst Environ. 2006;113:320–325. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sharma HC, Saxena KB, Bhagwat VR. The legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata: bionomics and management. 1999. Information bulletin 55 International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), Patancheru, India.
- 15.Singh SR, van Emden HF. Insect pests of grain legumes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1979;24:255–278. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chinh NT, Dzung DT, Long TD, Tam HM, Ramakrishna A, et al. Legumes in Viet Nam: constraints and opportunities. In: Gowda CLLRA, Rupela OP, Wani SP, editors. Legumes in rice-based cropping systems in tropical Asia: constraints and opportunities. Hyderabad, India: ICRISAT; 2000. pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Soeun MSM. Legumes in rice-based cropping systems in Cambodia: constraints and opportunities. In: Gowda CLL, Ramakrishna A, Rupela OP, Wani SP, editors. Legumes in rice-based cropping systems in tropical Asia: constraints and opportunities. Hyderabad, India: ICRISAT; 2001. pp. 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ulrichs C, Mewis I, Schnitzler WH, Burleigh JR. Parasitoids of the bean podborer, Maruca vitrata F. (Lepidoptera: Pyraustinae), a pest of Vigna sesquipedalis in the Philippine lowlands. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft fur allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie. 2001;13(1–6):283–288. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bindra OS. A note on the study of varietal resistance in pulses to different insect pests. Second annual workshop on pulse crops. 1968. Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi.
- 20.Patnaik HP, Samolo AP, Samolo BN. Susceptibility of some early varieties of pigeonpea for pod borers under protected conditions. Legum Res. 1986;9:7–10. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rahman MM. Pest complex of flower and pods of pigeonpea and their control through insecticide application. Bang J Sci Res. 1989;7:27–32. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leonard MD, Mills A. A preliminary report on the lima bean pod borer and other legume pod borers in Puerto Rico. J Econ Entomol. 1931;24:466–473. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ruppel RF, Idrobo E. Lista preliminar de insectos yotros animales que danan frijoles en America. Agricultura Trop. 1962;18:650–678. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Katayama J, Suzuki I. Seasonal prevalence of pod borers [Ostrinia scapulalis, Maruca testulalis and Matsumuraeses sp.] in azuki-beans and injury caused by larval infestation. Bull Kyoto Prefect Inst Agric. 1984;12:27–34. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Raheja AI. Report on the insect pests of grain legumes in northern Nigeria. 1974. pp. 295–299. 1st IITA grain legume improvement workshop 1973 International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Ibadan, Nigeria.
- 26.Sharma HC. Bionomics, host plant resistance, and management of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata—a review. Crop Prot. 1998;17:373–386. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Taylor TA. The bionomics of Maruca testulalis Gey. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), a major pest of cowpeas in Nigeria. J W Afr Sci Assoc. 1967;12:111–129. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Margam VM, Coates BS, Ba MN, Sun W, Binso-Dabire CL, et al. Geographic distribution of phylogenetically-distinct legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Pyraloidea: Crambidae). Mol Biol Rep. 2010 doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hall TA. BioEdit:a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–98. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wernersson R. Virtual Ribosome–a comprehensive DNA translation tool with support for integration of sequence feature annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:W385–388. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:955–964. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, et al. Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics. 2000;16:944–945. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.10.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–1599. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004;101:11030–11035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404206101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kumar S, Gadagkar SR. Disparity Index: a simple statistic to measure and test the homogeneity of substitution patterns between molecular sequences. Genetics. 2001;158:1321–1327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/158.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Felsenstein J. PHYLIP-Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics. 1989;5:164–166. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Churchill GA. Stochastic models for heterogeneous DNA sequences. Bull of Math Biol. 1989;51:79–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02458837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM. The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992;8:275–282. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Page RDM. TREEVIEW: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci. 1996;12:357–358. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/12.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Margulies M, Egholm M, Altman WE, Attiya S, Bader JS, et al. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature. 2005;437:376–380. doi: 10.1038/nature03959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Boore JL. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:1767–1780. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.8.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Crozier RH, Crozier YC. The mitochondrial genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera: complete sequence and genome organization. Genetics. 1993;133:97–117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zardoya R, Meyer A. On the origin of and phylogenetic relationships among living amphibians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:7380–7383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111455498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Liu Y, Li Y, Pan M, Dai F, Zhu X, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Chinese oak silkmoth, Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2008;40:693–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Xia X. Maximizing transcription efficiency causes codon usage bias. Genetics. 1996;144:1309–1320. doi: 10.1093/genetics/144.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kanaya S, Yamada Y, Kinouchi M, Kudo Y, Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA genes in eukaryotes: correlation of codon usage diversity with translation efficiency and with CG-dinucleotide usage as assessed by multivariate analysis. J Mol Evol. 2001;53:290–298. doi: 10.1007/s002390010219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lessinger AC, Martins Junqueira AC, Lemos TA, Kemper EL, da Silva FR, et al. The mitochondrial genome of the primary screwworm fly Cochliomyia hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Insect Mol Biol. 2000;9:521–529. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2583.2000.00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lee ES, Shin KS, Kim MS, Park H, Cho S, et al. The mitochondrial genome of the smaller tea tortrix Adoxophyes honmai (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Gene. 2006;373:52–57. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim I, Lee EM, Seol KY, Yun EY, Lee YB, et al. The mitochondrial genome of the Korean hairstreak, Coreana raphaelis (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Insect Mol Biol. 2006;15:217–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pan M, Yu Q, Xia Y, Dai F, Liu Y, et al. Characterization of mitochondrial genome of Chinese wild mulberry silkworm, Bomyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Sci China C Life Sci. 2008;51:693–701. doi: 10.1007/s11427-008-0097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Salvato P, Simonato M, Battisti A, Negrisolo E. The complete mitochondrial genome of the bag-shelter moth Ochrogaster lunifer (Lepidoptera, Notodontidae). BMC Genomics. 2008;9:331. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hong G, Jiang S, Yu M, Yang Y, Li F, et al. The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the cabbage butterfly, Artogeia melete (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2009;41:446–455. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmp030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jiang S, Hong G, Yu M, Li N, Yang Y, Liu Y, Wei Z. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of the giant silkworm moth, Eriogyna pyretorum (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Int J Biol Sci. 2009;5:351–365. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stewart JB, Beckenbach AT. Characterization of mature mitochondrial transcripts in Drosophila, and the implications for the tRNA punctuation model in arthropods. Gene. 2009;445:49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jiang WP, Li JL, Zheng RL, Wang GL. Analysis of complete mitochondrial genome of Cristaria plicata. Yi Chuan. 2010;32:153–162. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Torres TT, Metta M, Ottenwalder B, Schlotterer C. Gene expression profiling by massively parallel sequencing. Genome Res. 2008;18:172–177. doi: 10.1101/gr.6984908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Berthier F, Renaud M, Alziari S, Durand R. RNA mapping on Drosophila mitochondrial DNA: precursors and template strands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14:4519–4533. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Samuels AK, Weisrock DW, Smith JJ, France KJ, Walker JA, et al. Transcriptional and phylogenetic analysis of five complete ambystomatid salamander mitochondrial genomes. Gene. 2005;349:43–53. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.12.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gagliardi D, Stepien PP, Temperley RJ, Lightowlers RN, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM. Messenger RNA stability in mitochondria: different means to an end. Trends Genet. 2004;20:260–267. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2004.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Piwowarski J, Grzechnik P, Dziembowski A, Dmochowska A, Minczuk M, et al. Human polynucleotide phosphorylase, hPNPase, is localized in mitochondria. J Mol Biol. 2003;329:853–857. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tomecki R, Dmochowska A, Gewartowski K, Dziembowski A, Stepien PP. Identification of a novel human nuclear-encoded mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:6001–6014. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bobrowicz AJ, N. Lightowlers RN, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers Z. Polyadenylation and degradation of mRNA in mammalian mitochondria: a missing link? Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:517–519. doi: 10.1042/BST0360517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Piechota J, Tomecki R, Gewartowski K, Szczesny R, Dmochowska A, et al. Differential stability of mitochondrial mRNA in HeLa cells. Acta Biochim Pol. 2006;53:157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5:621–628. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Christianson TW, Clayton DA. In vitro transcription of human mitochondrial DNA: accurate termination requires a region of DNA sequence that can function bidirectionally. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:6277–6281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Montoya J, Christianson T, Levens D, Rabinowitz M, Attardi G. Identification of initiation sites for heavy-strand and light-strand transcription in human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982;79:7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Montoya J, Gaines GL, Attardi G. The pattern of transcription of the human mitochondrial rRNA genes reveals two overlapping transcription units. Cell. 1983;34:151–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Fisher RP, Parisi MA, Clayton DA. Fisher RP, Parisi MA, Clayton DA. 1989. Flexible recognition of rapidly evolving promoter sequences by mitochondrial transcription factor 1. Gene Devel. 1989;8:2202–2217. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bravo JP, Felipe J, Zanatta DB, Silva JLC, Fernandez MA. Sequence analysis of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the sugarcane borer Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Braz Arch Biol Technol. 2008;51:671–677. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pratt JM, Petty J, Riba-Garcia I, Robertson DH, Gaskell SJ, Oliver SG, Beynon RJ. Dynamics of protein turnover, a missing dimension in proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2002;1:579–591. doi: 10.1074/mcp.m200046-mcp200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Maruca vitrata mitochondrial DNA assembled contigs.
(TXT)
Maruca vitrata 454 raw reads corresponding to the mitochondrial genome assembly.
(TXT)