Abstract
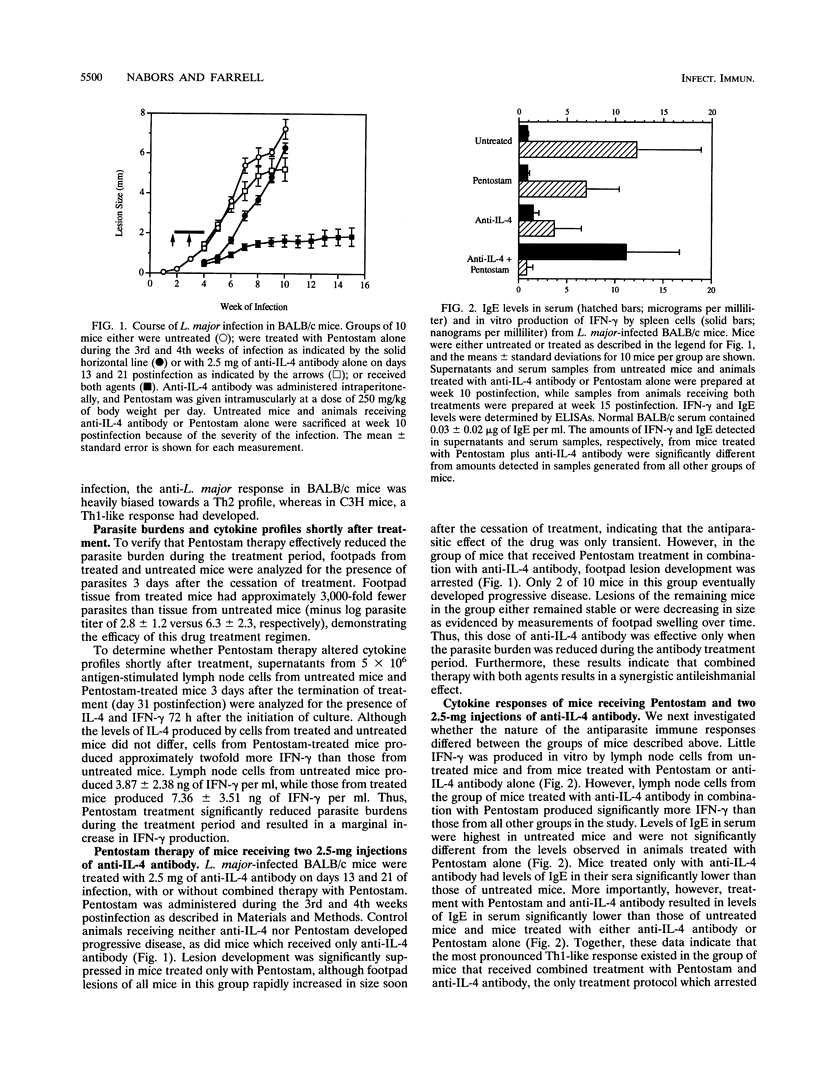
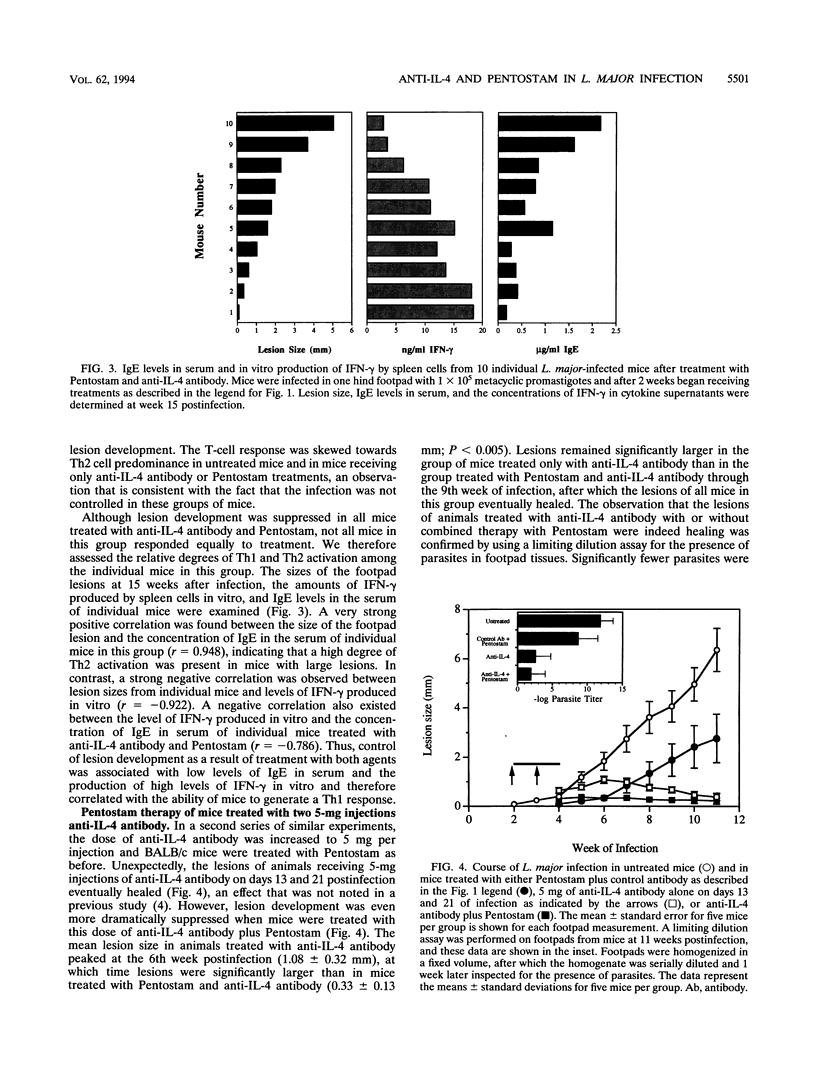
Whereas most inbred mouse strains mount a protective Th1 helper T-cell response following infection with Leishmania major, an ineffective Th2 response develops in BALB/c mice, leading to the development of disseminated, ultimately fatal disease. Interleukin-4 (IL-4) production is required for the initiation of the Th2 response, though little is known about the requirements for the long-term maintenance of this response. In order to investigate the role of the expanding parasite population on the Th2 response, mice infected for 2 weeks with L. major, which exhibited a Th2-like cytokine profile, were treated with a leishmanicidal agent (Pentostam) and/or various doses of anti-IL-4 antibody. Untreated mice, mice treated with Pentostam alone, or mice treated with 2.5 mg of anti-IL-4 antibody given at days 13 and 21 of infection developed progressive disease. However, in 8 of 10 mice treated with this dose of anti-IL-4 antibody plus Pentostam lesion development was arrested and lesions were either controlled or eventually healed. Healing was associated with the production of high levels of gamma interferon by spleen cells, and low levels of immunoglobulin E in serum compared with levels for control animals, indicating that a Th1-like response had developed in mice receiving both treatments. Thus, depletion of IL-4 only in combination with a reduction in the parasite burden allowed the expression of a Th1 response. When the dose of anti-IL-4 antibody was increased to 5 mg per injection, all mice treated with this dose of antibody, with or without Pentostam therapy, healed. However, combined therapy with Pentostam in mice treated with this dose of antibody had an additional protective effect. As expected, a Th1 response developed in mice treated with this dose of anti-IL-4 antibody with or without combined therapy with Pentostam, whereas a Th2 response developed in control mice. Thus, a significant effect on the course of disease is noted when mice with established L. major infections are treated with anti-IL-4 antibody in combination with Pentostam, suggesting that the combined effect of inhibiting IL-4 and reducing the parasite burden has a dramatic effect on the development of resistance to L. major.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afonso L. C., Scott P. Immune responses associated with susceptibility of C57BL/10 mice to Leishmania amazonensis. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2952–2959. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2952-2959.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorvatn B., Neva F. A. Experimental therapy of mice infected with Leishmania tropica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):480–485. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher P. A., Wei G., Menon J. N., Bielefeldt-Ohmann H. Establishment of stable, cell-mediated immunity that makes "susceptible" mice resistant to Leishmania major. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):539–542. doi: 10.1126/science.1636090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain R., Varkila K., Coffman R. L. IL-4 induces a Th2 response in Leishmania major-infected mice. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1182–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Varkila K., Scott P., Chatelain R. Role of cytokines in the differentiation of CD4+ T-cell subsets in vivo. Immunol Rev. 1991 Oct;123:189–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry R. C., Kiener P. A., Spitalny G. L. A sensitive immunochemical assay for biologically active MuIFN-gamma. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90497-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Fitch F. W. Anti-proliferative effect of IFN-gamma in immune regulation. I. IFN-gamma inhibits the proliferation of Th2 but not Th1 murine helper T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4245–4252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. IV. Prophylactic effect of sublethal irradiation as a result of abrogation of suppressor T cell generation in mice genetically susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. S., Heimberger A. B., Gold J. S., O'Garra A., Murphy K. M. Differential regulation of T helper phenotype development by interleukins 4 and 10 in an alpha beta T-cell-receptor transgenic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6065–6069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Severn A., Millott S., Schmidt J., Salter M., Moncada S. A possible novel pathway of regulation by murine T helper type-2 (Th2) cells of a Th1 cell activity via the modulation of the induction of nitric oxide synthase on macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2489–2494. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., O'Donnell C. A. Immunology of leishmaniasis. Adv Parasitol. 1993;32:161–259. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris L., Troutt A. B., Handman E., Kelso A. Changes in the precursor frequencies of IL-4 and IFN-gamma secreting CD4+ cells correlate with resolution of lesions in murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 15;149(8):2715–2721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Berman J. D., Wright S. D. Immunochemotherapy for intracellular Leishmania donovani infection: gamma interferon plus pentavalent antimony. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):973–978. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olliaro P. L., Bryceson A. D. Practical progress and new drugs for changing patterns of leishmaniasis. Parasitol Today. 1993 Sep;9(9):323–328. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powrie F., Correa-Oliveira R., Mauze S., Coffman R. L. Regulatory interactions between CD45RBhigh and CD45RBlow CD4+ T cells are important for the balance between protective and pathogenic cell-mediated immunity. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):589–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Hieny S., Sher A. Identification of cell surface carbohydrate and antigenic changes between noninfective and infective developmental stages of Leishmania major promastigotes. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Holaday B. J., Pu R. T., Dawkins R. S., Locksley R. M. Cure of murine leishmaniasis with anti-interleukin 4 monoclonal antibody. Evidence for a T cell-dependent, interferon gamma-independent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Street N., Mosmann T. R., Locksley R. M. Cytokine regulation of murine leishmaniasis: interleukin 4 is not sufficient to mediate progressive disease in resistant C57BL/6 mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4710–4714. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4710-4714.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. IFN-gamma modulates the early development of Th1 and Th2 responses in a murine model of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3149–3155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Natovitz P., Sher A. Vaccination against cutaneous leishmaniasis in a murine model. I. Induction of protective immunity with a soluble extract of promastigotes. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Chung C. L., Mayor S. E., Subramanyam J. M., Goldman S. J., Sieburth D. S., Wolf S. F., Schaub R. G. Resolution of cutaneous leishmaniasis: interleukin 12 initiates a protective T helper type 1 immune response. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1797–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Ceredig R., Cerottini J. C., Louis J. A. Therapeutic effect of anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibody GK1.5 on cutaneous leishmaniasis in genetically-susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



