Abstract
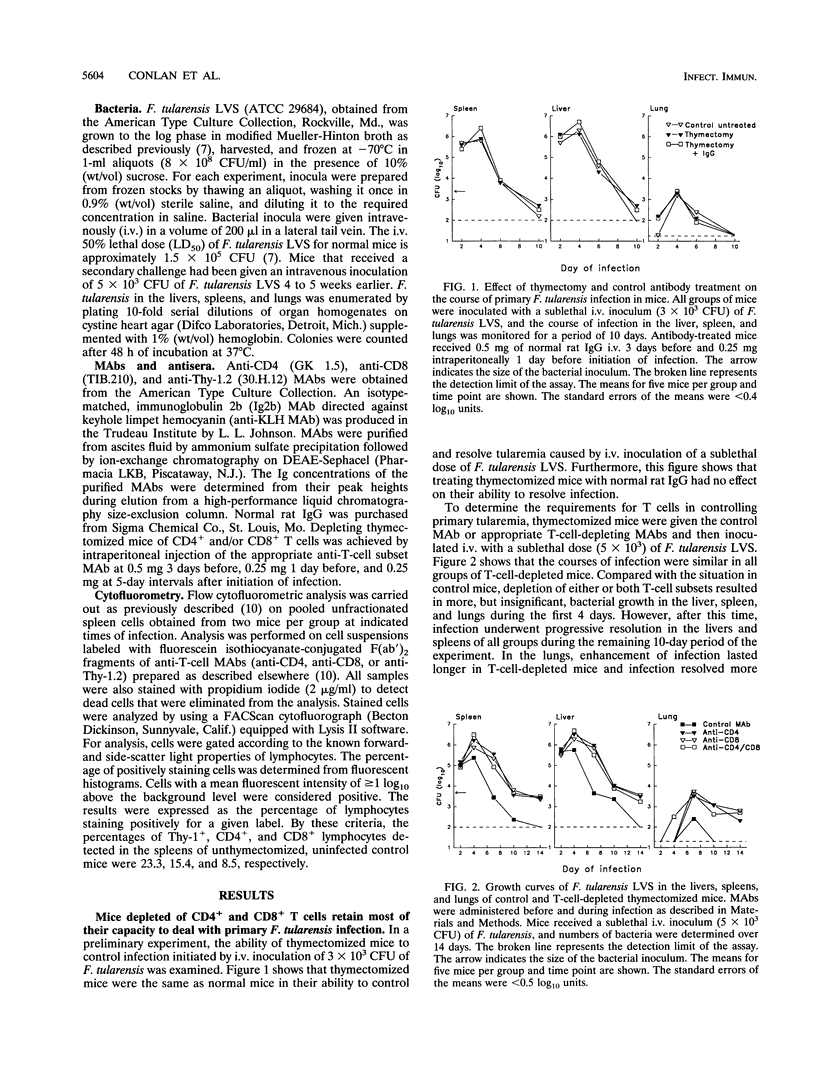
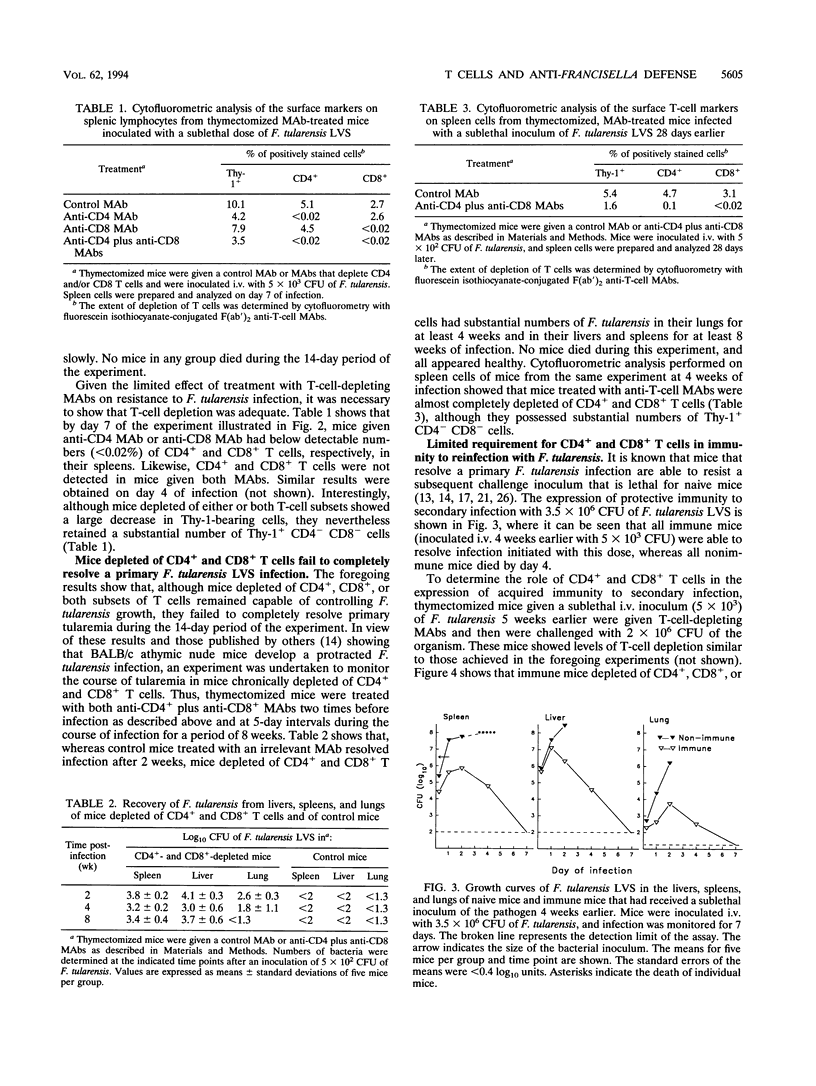
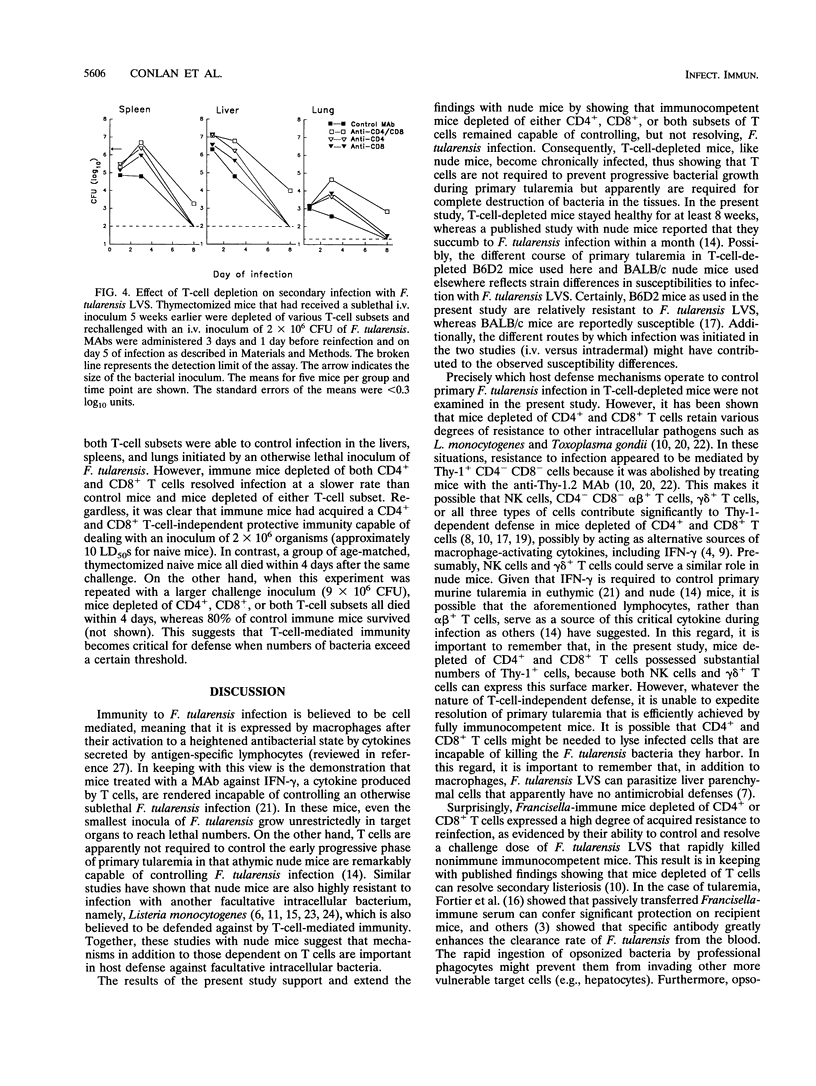
Immunity to experimental infection with the facultative intracellular bacterium Francisella tularensis is generally considered an example of T-cell-mediated, macrophage-expressed immunity. However, the results of the present study indicate that T-cell-independent mechanisms are also important in anti-Francisella defense. They show that mice selectively depleted of CD4+, CD8+, or both T-cell populations by treatment with T-cell subset-specific monoclonal antibodies remained capable of controlling and partly resolving a primary sublethal Francisella infection. Similarly, it was found that Francisella-immune mice depleted of either or both subsets of T cells retain a high degree of acquired immunity to reinfection. Together, these findings imply that resistance to primary and secondary tularemia can be mediated by cells other than CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony L. D., Burke R. D., Nano F. E. Growth of Francisella spp. in rodent macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3291–3296. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3291-3296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony L. S., Ghadirian E., Nestel F. P., Kongshavn P. A. The requirement for gamma interferon in resistance of mice to experimental tularemia. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony L. S., Kongshavn P. A. Experimental murine tularemia caused by Francisella tularensis, live vaccine strain: a model of acquired cellular resistance. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jan;2(1):3–14. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S. Immunization against tularemia: analysis of the effectiveness of live Francisella tularensis vaccine in prevention of laboratory-acquired tularemia. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):55–60. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., North R. J. Early pathogenesis of infection in the liver with the facultative intracellular bacteria Listeria monocytogenes, Francisella tularensis, and Salmonella typhimurium involves lysis of infected hepatocytes by leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5164–5171. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5164-5171.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Effects of purified anti-Lyt-2 mAb treatment on murine listeriosis: comparative roles of Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ cells in resistance to primary and secondary infection, delayed-type hypersensitivity and adoptive transfer of resistance. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):107–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. L., North R. J. Early gamma interferon production by natural killer cells is important in defense against murine listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2892–2900. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2892-2900.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. L., North R. J. Resolution of primary murine listeriosis and acquired resistance to lethal secondary infection can be mediated predominantly by Thy-1+ CD4- CD8- cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):869–877. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGELSBACH H. T., DOWNS C. M. Prophylactic effectiveness of live and killed tularemia vaccines. I. Production of vaccine and evaluation in the white mouse and guinea pig. J Immunol. 1961 Oct;87:415–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigelsbach H. T., Hunter D. H., Janssen W. A., Dangerfield H. G., Rabinowitz S. G. Murine model for study of cell-mediated immunity: protection against death from fully virulent Francisella tularensis infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.999-1005.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins K. L., Rhinehart-Jones T., Nacy C. A., Winegar R. K., Fortier A. H. T-cell-independent resistance to infection and generation of immunity to Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):823–829. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.823-829.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Hof H. Cell-mediated resistance to infection with Listeria monocytogenes in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):382–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.382-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier A. H., Polsinelli T., Green S. J., Nacy C. A. Activation of macrophages for destruction of Francisella tularensis: identification of cytokines, effector cells, and effector molecules. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):817–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.817-825.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier A. H., Slayter M. V., Ziemba R., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Live vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis: infection and immunity in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2922–2928. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2922-2928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. L., VanderVegt F. P., Havell E. A. Gamma interferon-dependent temporary resistance to acute Toxoplasma gondii infection independent of CD4+ or CD8+ lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5174–5180. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5174-5180.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiby D. A., Fortier A. H., Crawford R. M., Schreiber R. D., Nacy C. A. In vivo modulation of the murine immune response to Francisella tularensis LVS by administration of anticytokine antibodies. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.84-89.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke M. E., Ehlers S., Hahn H. T-cell subsets in delayed-type hypersensitivity, protection, and granuloma formation in primary and secondary Listeria infection in mice: superior role of Lyt-2+ cells in acquired immunity. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1920–1925. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1920-1925.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newborg M. F., North R. J. On the mechanism of T cell-independent anti-Listeria resistance in nude mice. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Anomalous high native resistance to athymic mice to bacterial pathogens. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):636–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.636-645.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Battye F., Scollay R. Expression of Thy-1 antigen is not limited to T cells in cultures of mouse hemopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4161–4165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity in mice to a 17-kilodalton lipoprotein of Francisella tularensis expressed by Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2855-2862.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A. Nature of protective immunity to Francisella tularensis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M. Natural killer cells and interferon. Crit Rev Immunol. 1984;5(1):55–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



