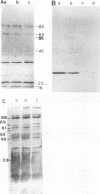
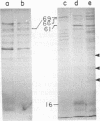
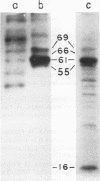
Abstract
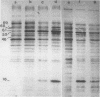
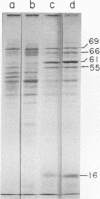
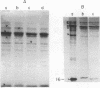
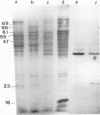
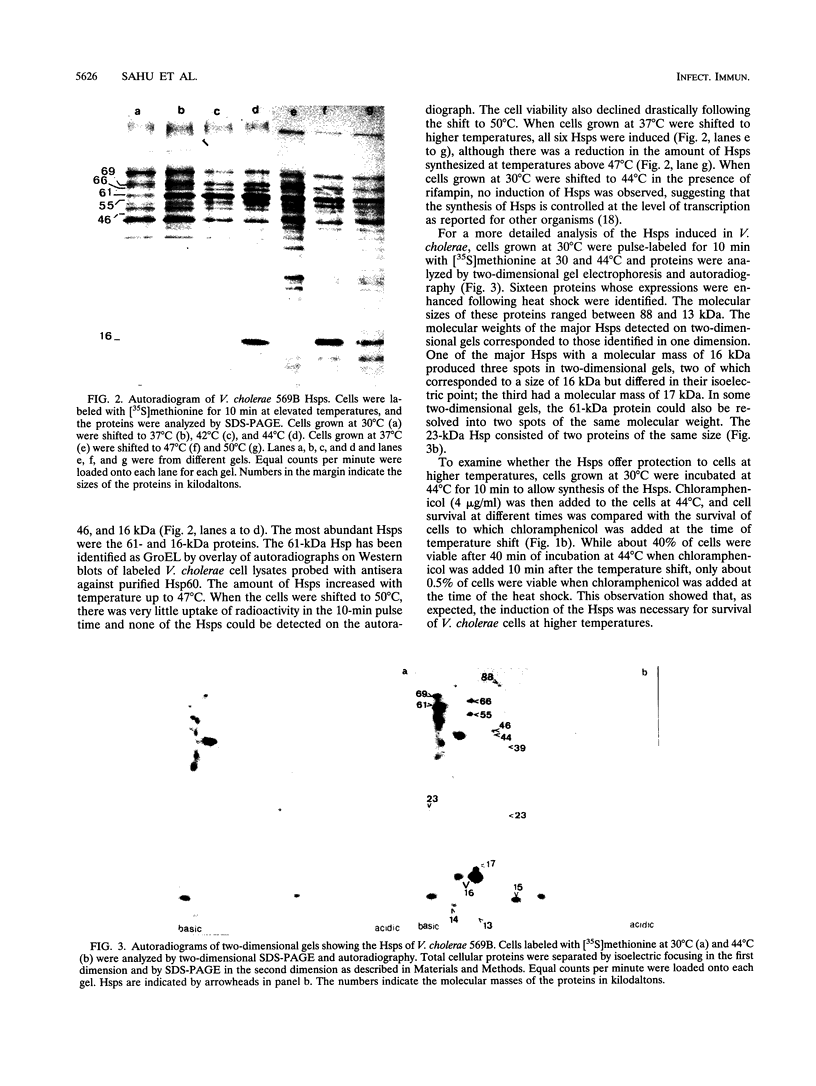
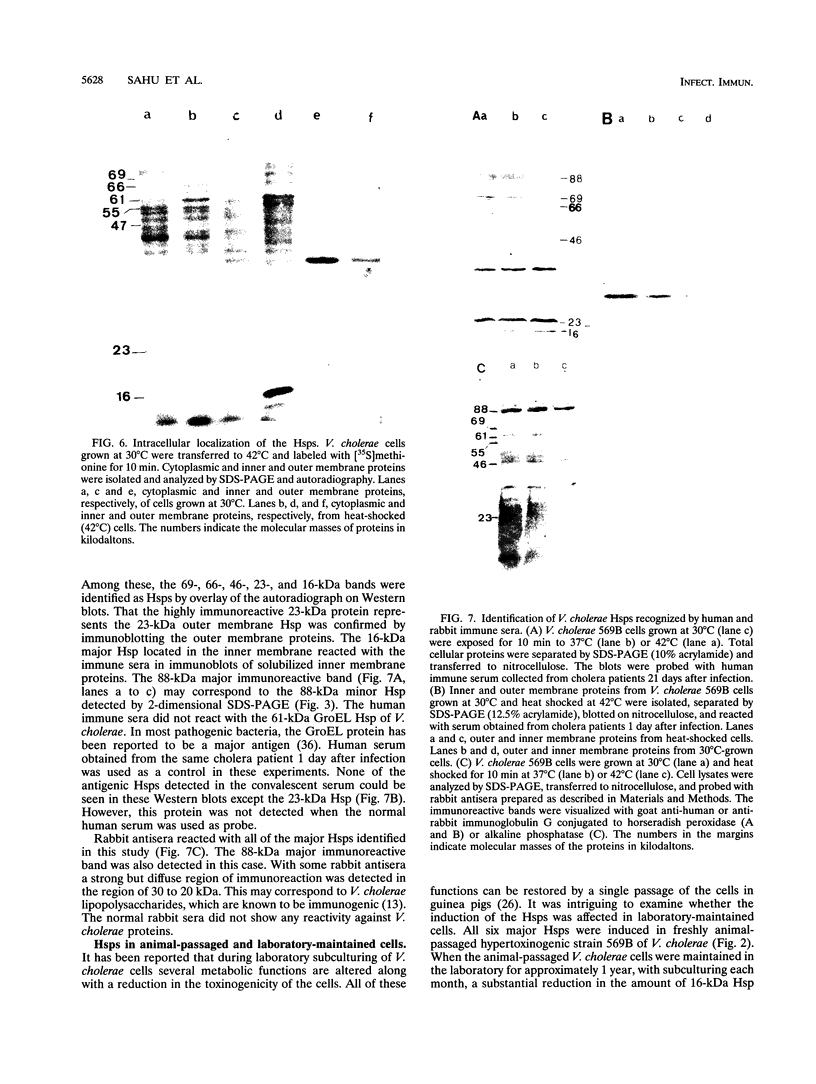
Sixteen heat shock proteins (Hsps) have been identified in the hypertoxinogenic strain 569B of Vibrio cholerae which are synthesized in response to small and large elevations of temperature. The induction of the Hsps is necessary for the cells to survive the deleterious effects of heat. There is no difference in the pattern of induction of the Hsps in V. cholerae strains varying in levels of toxinogenicity. One of the major low-molecular-mass Hsps, a 16-kDa protein, is preferentially degraded following shift down of temperature. This protein is induced at a much lower level at high temperatures in cells maintained in the laboratory for a prolonged period. The only Hsp located in the outer membrane of V. cholerae cells is a 23-kDa protein. Western immunoblot analysis with human immune sera collected from convalescent cholera patients revealed that this protein is markedly immunogenic. The human immune serum also reacted with the 69- and 16-kDa major Hsps and the 88-, 66-, and 46-kDa Hsps but not with the 61-kDa major Hsp identified as the groEL gene product. All major Hsps reacted with rabbit anti-V. cholerae sera. Ethanol stress leads to the induction of four of the major Hsps and three additional proteins.
Full text
PDF
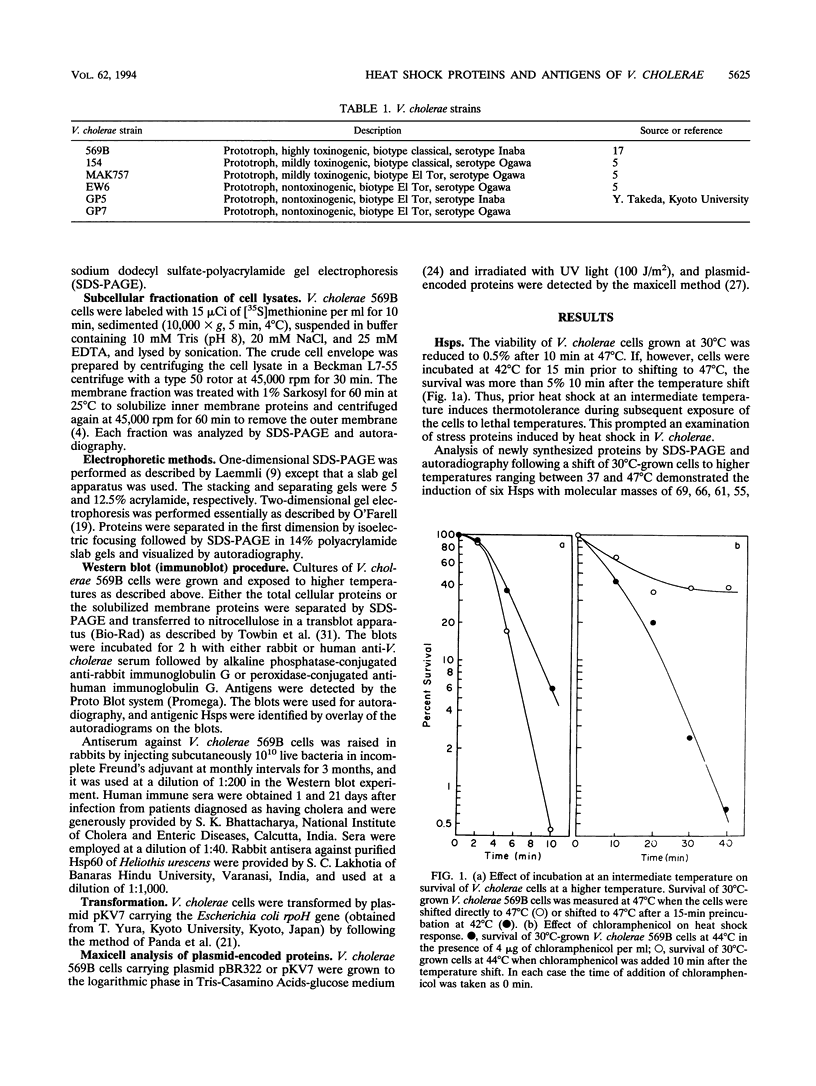




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreiro M. M., Laux D. C., Nelson D. R. Characterization of the heat shock response and identification of heat shock protein antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2186–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2186-2191.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. Identification of the sigma E subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a second alternate sigma factor involved in high-temperature gene expression. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1462–1471. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Charles I., Dougan G., Pickard D., O'Gaora P., Costa G., Ali T., Miller I., Hormaeche C. The role of a stress-response protein in Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaux P. G., Herendeen S. L., Bloch P. L., Neidhardt F. C. Transient rates of synthesis of individual polypeptides in E. coli following temperature shifts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Werb Z. Correlation between synthesis of heat shock proteins and development of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohia A., Majumdar S., Chatterjee A. N., Das J. Effect of changes in the osmolarity of the growth medium on Vibrio cholerae cells. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1158–1166. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1158-1166.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A. Involvement of cell envelope components in the pathogenesis of Vibrio cholerae: targets for cholera vaccine development. Vaccine. 1987 Jun;5(2):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Heat shock proteins and thermal resistance in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):819–824. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Environmental signals controlling expression of virulence determinants in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.1-7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek K. H., Walker G. C. Defect in expression of heat-shock proteins at high temperature in xthA mutants. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.763-770.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panda D. K., Dasgupta U., Das J. Transformation of Vibrio cholerae by plasmid DNA. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90520-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Mekalanos J. J. Expression of ToxR, the transcriptional activator of the virulence factors in Vibrio cholerae, is modulated by the heat shock response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9898–9902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina S., Georgopoulos C. A new Escherichia coli heat shock gene, htrC, whose product is essential for viability only at high temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3417–3426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3417-3426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Sengupta A., Das J. Phosphate repression of phage protein synthesis during infection by choleraphage phi 149. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):110–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron E. Z., Davis B. D. Growth rate of Escherichia coli at elevated temperatures: limitation by methionine. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):391–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.391-396.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy N. K., Das G., Balganesh T. S., Dey S. N., Ghosh R. K., Das J. Enterotoxin production, DNA repair and alkaline phosphatase of Vibrio cholerae before and after animal passage. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):1927–1932. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T., Watanabe S., Sasaki S. Enhancement of enterotoxin production by carbon dioxide in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):455–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.455-456.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. J., Yaffe M. P. Uncoupling thermotolerance from the induction of heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11091–11094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovic Z., Fuchs A., Goebel W. Synthesis of species-specific stress proteins by virulent strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3582–3587. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3582-3587.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Acton M. A., Neidhardt F. C. Induction of the heat shock regulon does not produce thermotolerance in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):525–531. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. A heat shock operon in Coxiella burnetti produces a major antigen homologous to a protein in both mycobacteria and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1227-1234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Yura T. Transient regulation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli upon shift-up of growth temperature. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1133-1140.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Electron microscopic study of Vibrio cholerae O1 adherence to the mucus coat and villus surface in the human small intestine. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2753–2759. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2753-2759.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lathigra R., Hendrix R., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Stress proteins are immune targets in leprosy and tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4267–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. N., Kusukawa N., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A., Yura T. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants that lack the heat shock sigma factor sigma 32. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3640–3649. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3640-3649.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]