Abstract
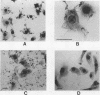
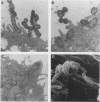
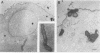
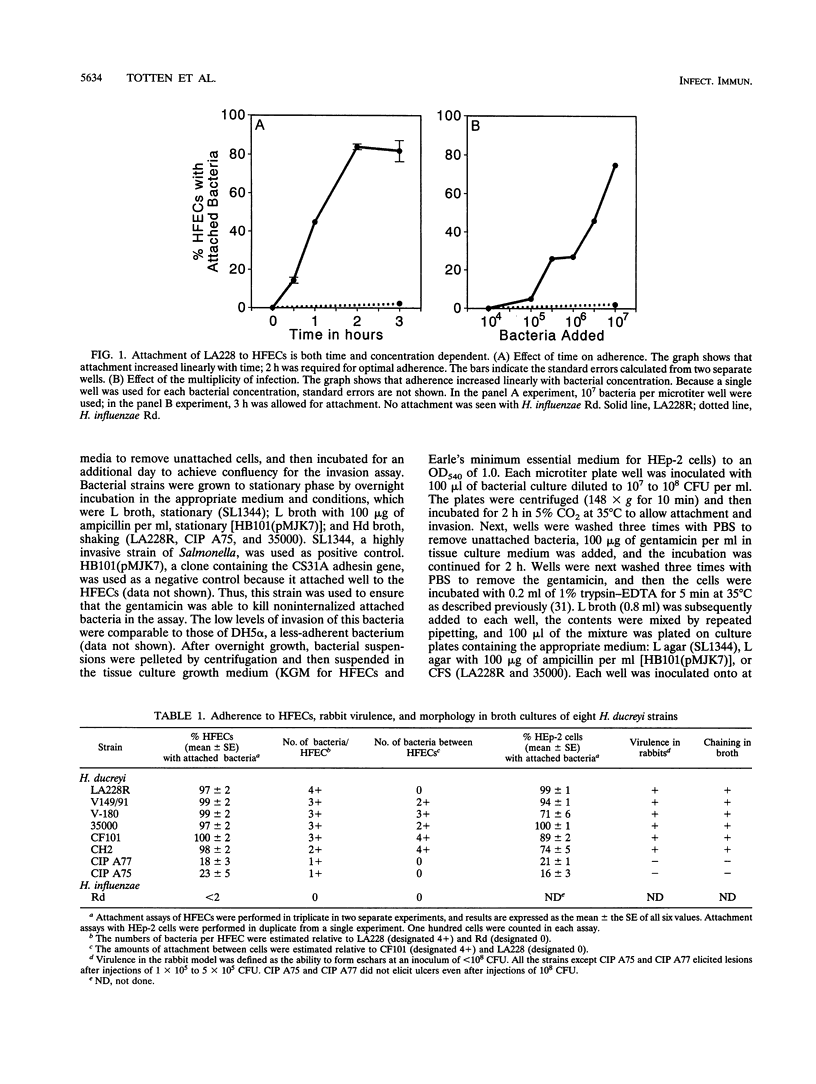
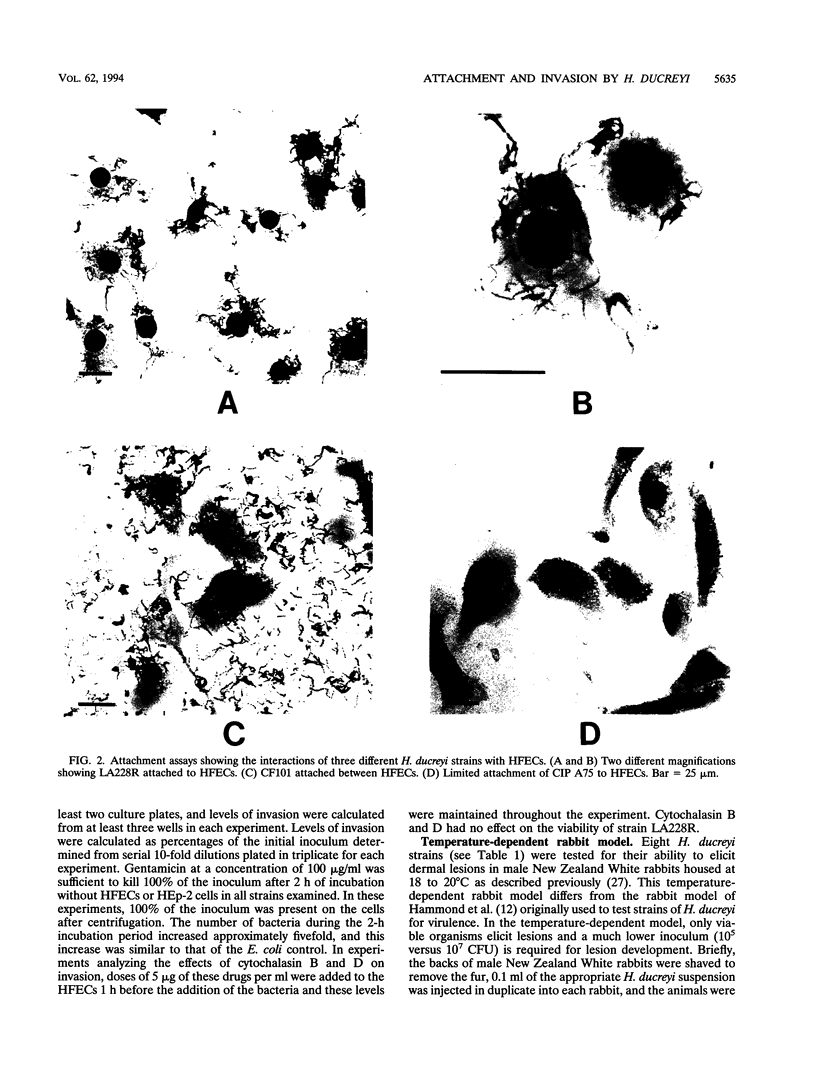
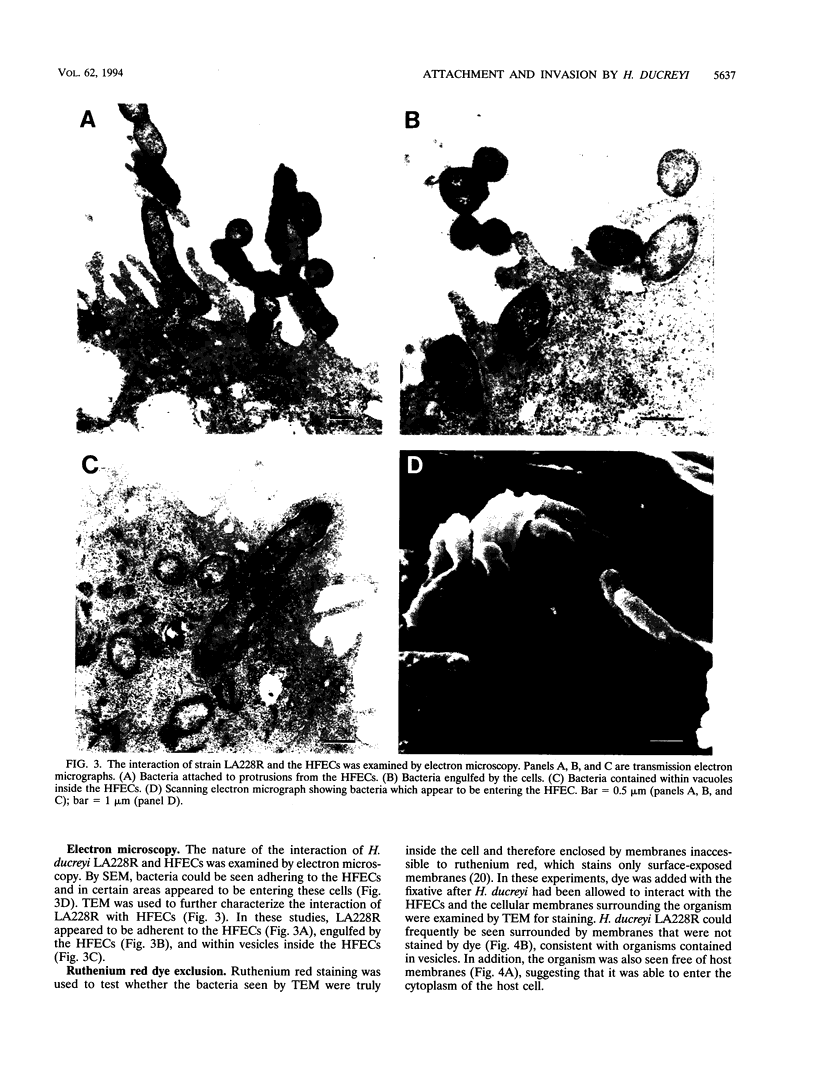
Haemophilus ducreyi is a sexually transmitted pathogen that causes genital ulcers and inguinal adenopathy. Because chancroidal ulcers are most commonly located on the foreskins of uncircumcised males, we utilized human foreskin epithelial cells (HFECs) to investigate the initial interaction of H. ducreyi with its host. The eight different strains of H. ducreyi that were studied varied in their abilities to attach to these epithelial cells, with six strains consistently attaching to > or = 90% of HFECs and two strains attaching to < 25% of HFECs. The strains with low levels of adherence also failed to exhibit chaining in broth culture and were avirulent in the rabbit model, suggesting that virulence in this model and attachment may be linked. The most adherent strain, LA228R, was further evaluated for its ability to invade HFECs and HEp-2 cells. Scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy of HFECs after interaction with LA228R produced images consistent with attachment, ingestion into vesicles, and escape from the vesicles into the cytoplasm. In addition, the gentamicin protection assay and inhibition of invasion by cytochalasin B and D indicated that LA228R was able to invade both HFECs and HEp-2 cells. Further examination of the mechanisms involved in the adherence and invasion of H. ducreyi into epithelial cells and their correlation with virulence will provide a better understanding of the pathogenesis of the disease caused by this important pathogen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeck D., Johnson A. P. Pathophysiological concept of Haemophilus ducreyi infection (chancroid) Int J STD AIDS. 1992 Sep-Oct;3(5):319–323. doi: 10.1177/095646249200300503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton W. L. Biology of Haemophilus ducreyi. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.377-389.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfa M. J. Cytopathic effect of Haemophilus ducreyi for human foreskin cell culture. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jul;37(1):43–50. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfa M. J., Degagne P., Hollyer T. Haemophilus ducreyi adheres to but does not invade cultured human foreskin cells. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1735–1742. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1735-1742.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton R. A., Kupper T. S., McDougall J. K., Dower S. Regulation of interleukin 1 and its receptor in human keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1273–1277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens R. J., Spinola S. M., Campagnari A. A. Haemophilus ducreyi adheres to human keratinocytes. Microb Pathog. 1994 Mar;16(3):243–247. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1994.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnari A. A., Wild L. M., Griffiths G. E., Karalus R. J., Wirth M. A., Spinola S. M. Role of lipooligosaccharides in experimental dermal lesions caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2601–2608. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2601-2608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzo A., Shero M., Apicella M. A., Spinola S. M. Expression of pili by Haemophilus ducreyi. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 (Suppl 1):S198–S199. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Lian C. J., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus ducreyi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):608–612. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Abraham S., Caparon M., Falk P., St Geme J. W., 3rd, Normark S. Pilus and nonpilus bacterial adhesins: assembly and function in cell recognition. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):887–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90269-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessamine P. G., Ronald A. R. Chancroid and the role of genital ulcer disease in the spread of human retroviruses. Med Clin North Am. 1990 Nov;74(6):1417–1431. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth M. J., Lara J. C., Moseley S. L. Epithelial cell invasion by bovine septicemic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.41-47.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth M. J., Schneider R. A., Moseley S. L. An F41-K88-related genetic determinant of bovine septicemic Escherichia coli mediates expression of CS31A fimbriae and adherence to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2333–2340. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2333-2340.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupsch E. M., Knepper B., Kuroki T., Heuer I., Meyer T. F. Variable opacity (Opa) outer membrane proteins account for the cell tropisms displayed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae for human leukocytes and epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):641–650. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammel C. J., Dekker N. P., Palefsky J., Brooks G. F. In vitro model of Haemophilus ducreyi adherence to and entry into eukaryotic cells of genital origin. J Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;167(3):642–650. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. Chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):137–157. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Wiseman G. M., Ronald A. R. Relationship between lipopolysaccharide composition and virulence of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):155–162. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Wiseman G. M., Ronald A. R. Role of lipopolysaccharide and complement in susceptibility of Haemophilus ducreyi to human serum. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):495–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.495-499.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons L. M., Waring A. L., Shayegani M. Molecular analysis of the Haemophilus ducreyi groE heat shock operon. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4111–4118. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4111-4118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer F. A., Simonsen J. N., Cameron D. W., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Kreiss J. K., Gakinya M. N., Waiyaki P., Cheang M., Piot P., Ronald A. R. Cofactors in male-female sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):233–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell B. K., Richardson J. A., Radolf J. D., Hansen E. J. A temperature-dependent rabbit model for production of dermal lesions by Haemophilus ducreyi. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):359–367. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvén M., Lagergård T. Haemophilus ducreyi, a cytotoxin-producing bacterium. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1156–1162. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1156-1162.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Stull T. L., Smith A. L. Comparative virulence of Haemophilus influenzae with a type b or type d capsule. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.518-524.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Haemophilus influenzae adheres to and enters cultured human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4036–4044. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4036-4044.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Stamm W. E. Clear broth and plate media for culture of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Aug;32(8):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.8.2019-2023.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserheit J. N. Epidemiological synergy. Interrelationships between human immunodeficiency virus infection and other sexually transmitted diseases. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Mar-Apr;19(2):61–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]