Abstract
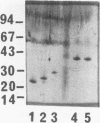
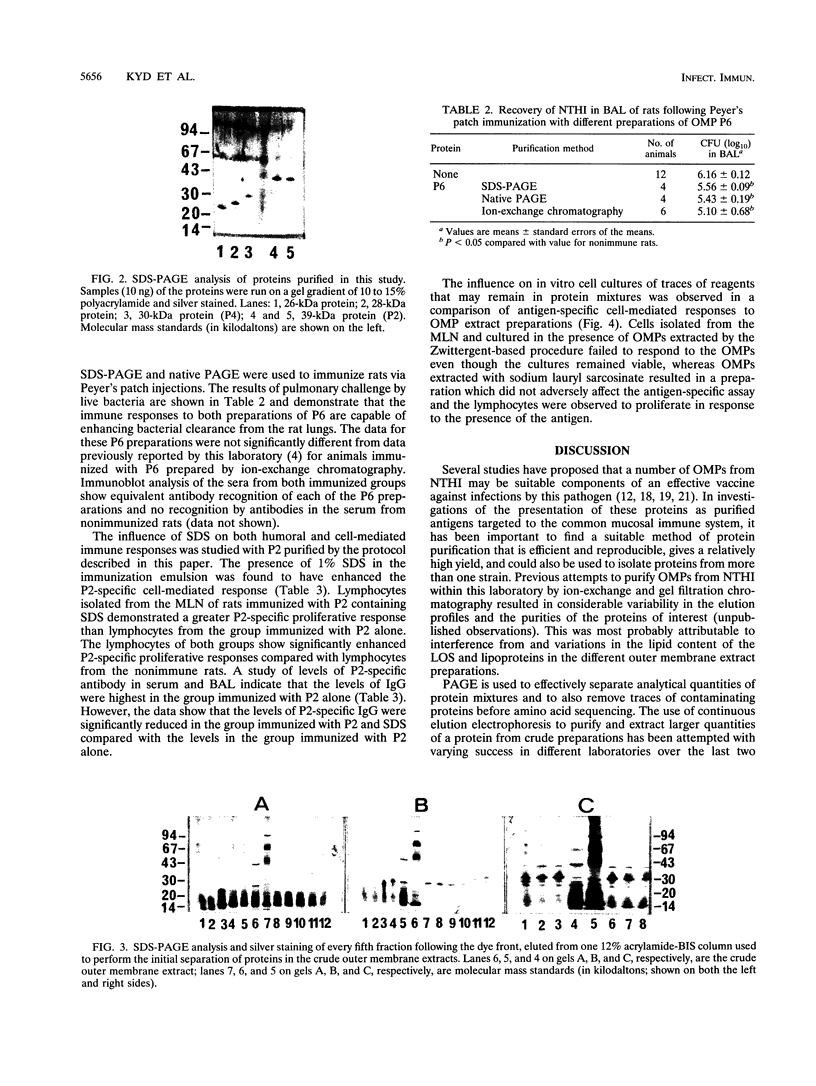
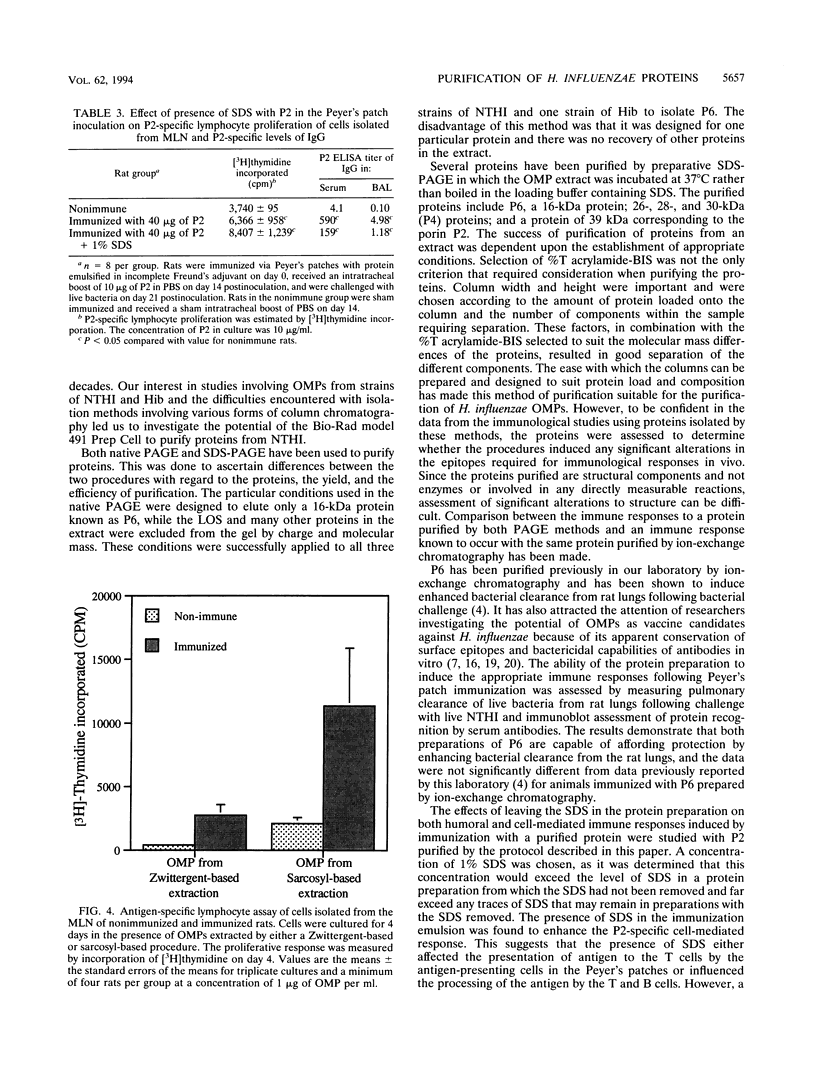
Outer membrane proteins P2, P4, and P6 and two with molecular masses of 26 and 28 kDa have been purified from a strain of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae by a preparative form of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Outer membrane protein P6, with a molecular mass of 16 kDa (determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS]-PAGE) was purified by both native PAGE and SDS-PAGE from three strains of nontypeable H. influenzae and one strain of type b H. influenzae. The same conditions were required for purification from each strain. The suitability of proteins isolated by these methods was assessed by studying the immune response of rats immunized with P6 in incomplete Freund's adjuvant into the Peyer's patches. P6 purified by either native PAGE or SDS-PAGE did not differ significantly from P6 purified by gel filtration and anion-exchange chromatography in the ability to enhance pulmonary clearance of live bacteria. This study also investigated the effects of SDS on P2 immunological responses in vivo and the effects of the reagents Zwittergent and sodium lauryl sarcosinate on outer membrane protein lymphocyte-proliferative responses in vitro. It was found that the presence of SDS in the immunization emulsion enhanced the antigen-specific cell-mediated response but suppressed the antigen-specific antibody responses. The presence of residual traces of Zwittergent in an outer membrane protein preparation inhibited antigen-specific cell-mediated proliferation, whereas extraction of outer membrane proteins with sodium lauryl sarcosinate did not inhibit antigen-specific proliferation. These results demonstrate that preparative PAGE is a suitable method for the purification of proteins from the outer membrane of H. influenzae required for investigation of their immunological significance as vaccine candidates and that traces of reagents used during protein purification may play an important role in determining the success of in vivo and in vitro studies.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Munson R. S., Jr Outer-membrane protein subtypes of Haemophilus influenzae type b and spread of disease in day-care centers. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):210–217. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps A. W., Taylor D. C., Wallace F. J., Clancy R. L. Respiratory immunity stimulated by intestinal immunization with purified nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae antigens. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 (Suppl 1):S199–S201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley M. L., Husband A. J. The induction and migration of antigen-specific helper cells for IgA responses in the intestine. Immunology. 1986 Mar;57(3):379–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Stephens D. S., Brachman P. S., Jr, Harvey R. C., Smith J. D., Wenger J. D. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease in adults. A prospective, population-based surveillance. CDC Meningitis Surveillance Group. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 15;116(10):806–812. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-10-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Quinn-Dey T., Zlotnick G. W. Biologic activities of antibody to a peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein of Haemophilus influenzae against multiple clinical isolates of H. influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2878–2883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2878-2883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingman K. L., Jansen E. M., Murphy T. F. Nearest neighbor analysis of outer membrane proteins of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3058–3063. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3058-3063.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Zachary A. L., Smith D. H. Isolation and partial characterization of outer and inner membranes from encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):596–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.596-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Brodeur B., Chong P., Grass S., Martin D., Proulx C. Outer membrane proteins P1 and P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b: structure and identification of surface-exposed epitopes. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 (Suppl 1):S86–S89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Antigenic characterization of the P6 protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.774-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. The P6 outer membrane protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a vaccine antigen. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 (Suppl 1):S203–S205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Munson R. S., Jr, Apicella M. A., Sikkema D. J., Molleston J. P., Murphy T. F. Molecular conservation of the P6 outer membrane protein among strains of Haemophilus influenzae: analysis of antigenic determinants, gene sequences, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2658–2663. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2658-2663.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Murphy T. F., van Keulen H., Rekosh D., Apicella M. A. Studies on P6, an important outer-membrane protein antigen of Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S331–S336. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proulx C., Munson R. S., Jr, Grass S., Hamel J., Martin D., Brodeur B. R. Identification of a surface-exposed immunodominant epitope on outer membrane protein P1 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):963–970. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.963-970.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Terada T. Removal of dodecyl sulfate from protein solution. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace F. J., Clancy R. L., Cripps A. W. An animal model demonstration of enhanced clearance of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae from the respiratory tract after antigen stimulation of gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):311–316. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]