Abstract
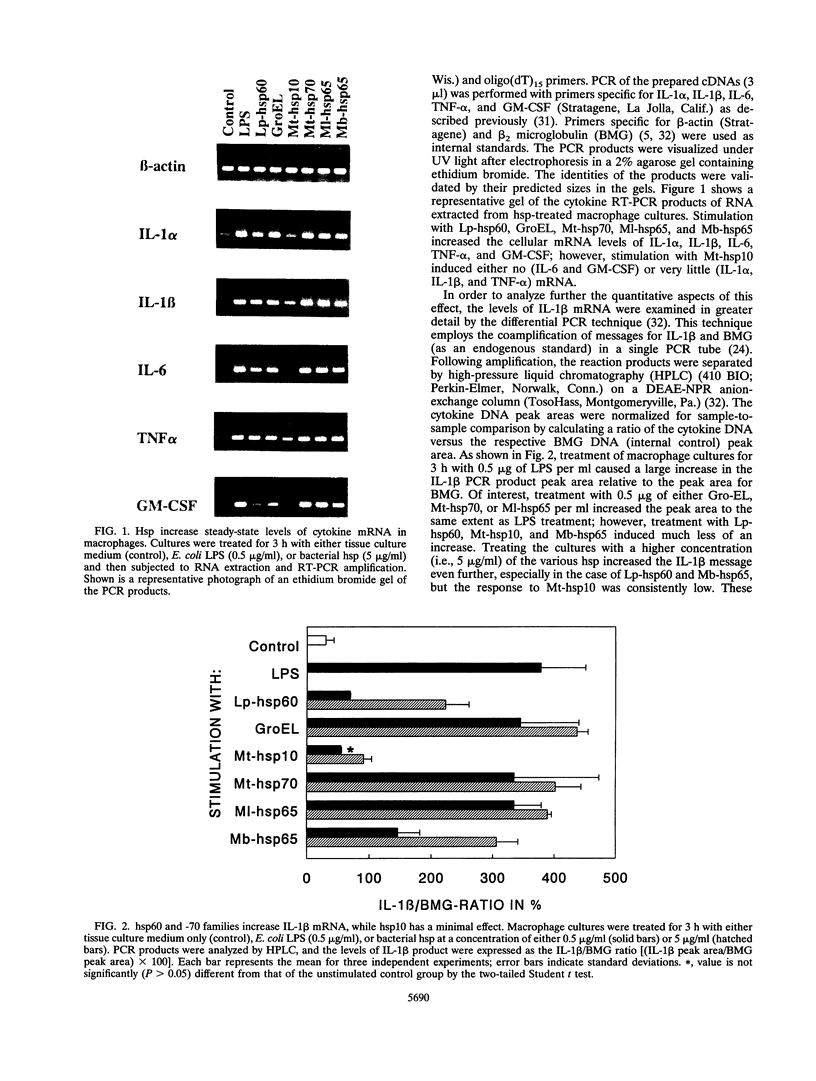
Bacterial heat shock proteins (hsp) have been shown to be important immunogens stimulating both T cells and B cells. However, little is known concerning the direct interactions between hsp and macrophages. In this study, we demonstrated that treatment of macrophage cultures with purified bacterial hsp, including Legionella pneumophila hsp60, Escherichia coli GroEL, Mycobacterium tuberculosis hsp70, Mycobacterium leprae hsp65, and Mycobacterium bovis BCG hsp65, increased the steady-state levels of cytokine mRNA for interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), IL-1 beta, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as well as supernatant IL-1 secretion. This effect was shown not to be due to contamination of the hsp preparations with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. However, not all hsp induced cytokines; M. tuberculosis hsp10 showed minimal activity in our study. These results suggest that bacterial hsp might modulate immunity by rapidly and directly increasing cytokine production in macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blander S. J., Horwitz M. A. Major cytoplasmic membrane protein of Legionella pneumophila, a genus common antigen and member of the hsp 60 family of heat shock proteins, induces protective immunity in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):717–723. doi: 10.1172/JCI116253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Young D. B. Autoimmunity, microbial immunity and the immunological homunculus. Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Gambill B. D., Nelson R. J. Heat shock proteins: molecular chaperones of protein biogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):402–414. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.402-414.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Mielke M. E., Blankenstein T., Hahn H. Kinetic analysis of cytokine gene expression in the livers of naive and immune mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. The immediate early phase in innate resistance and acquired immunity. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3016–3022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensgraber M., Loos M. A 66-kilodalton heat shock protein of Salmonella typhimurium is responsible for binding of the bacterium to intestinal mucus. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3072–3078. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3072-3078.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Engstrand L., Graham D. Y. Urease-associated heat shock protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2125–2127. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2125-2127.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C. The groES and groEL heat shock gene products of Escherichia coli are essential for bacterial growth at all temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1379-1385.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J. S., Shattock R., Remick D. G., Griffin G. E. Mycobacterial 65-kD heat shock protein induces release of proinflammatory cytokines from human monocytic cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):58–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Bangsborg J. M., Fjordvang H., Pedersen N. S., Hindersson P. Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2047-2053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Knudsen J. D., Axelsen N. H. Cloning and expression of treponema pallidum common antigen (Tp-4) in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):587–596. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Houston L., Butler C. A. Legionella pneumophila htpAB heat shock operon: nucleotide sequence and expression of the 60-kilodalton antigen in L. pneumophila-infected HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3380–3387. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3380-3387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E. D., Dong M. W. Rapid analysis and purification of polymerase chain reaction products by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biotechniques. 1990 May;8(5):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Schoel B., van Embden J. D., Koga T., Wand-Württenberger A., Munk M. E., Steinhoff U. Heat-shock protein 60: implications for pathogenesis of and protection against bacterial infections. Immunol Rev. 1991 Jun;121:67–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein T. W., Yamamoto Y., Wilson S., Newton C., Friedman H. Legionella pneumophila infection and cytokine production. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;319:97–104. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3434-1_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Wand-Württenberger A., DeBruyn J., Munk M. E., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. T cells against a bacterial heat shock protein recognize stressed macrophages. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.2788923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Bajardi A. C., Grisso C. L., Sieling P. A., Alland D., Convit J., Fan X. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A major T cell antigen of Mycobacterium leprae is a 10-kD heat-shock cognate protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):275–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noonan K. E., Roninson I. B. mRNA phenotyping by enzymatic amplification of randomly primed cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10366–10366. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. B., Carlone G. M., Pau C. P., Wilkinson H. W. Purified 60-kilodalton Legionella protein antigen with Legionella-specific and nonspecific epitopes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2080–2084. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2080-2084.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. L., Lowrie D. B. A single mycobacterial protein (hsp 65) expressed by a transgenic antigen-presenting cell vaccinates mice against tuberculosis. Immunology. 1994 Jun;82(2):244–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widen R. H., Klein T. W., Newton C. A., Friedman H. Induction of interleukin 1 by Legionella pneumophila in murine peritoneal macrophage cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Jul;191(3):304–308. doi: 10.3181/00379727-191-42925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Klein T. W., Newton C. A., Widen R., Friedman H. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages from A/J mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):370–375. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.370-375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Okubo S., Klein T. W., Onozaki K., Saito T., Friedman H. Binding of Legionella pneumophila to macrophages increases cellular cytokine mRNA. Infect Immun. 1994 Sep;62(9):3947–3956. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.9.3947-3956.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Doerfler M., Lee T. C., Guillemin B., Rom W. N. Mechanisms of stimulation of interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by Mycobacterium tuberculosis components. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2076–2083. doi: 10.1172/JCI116430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]