Abstract
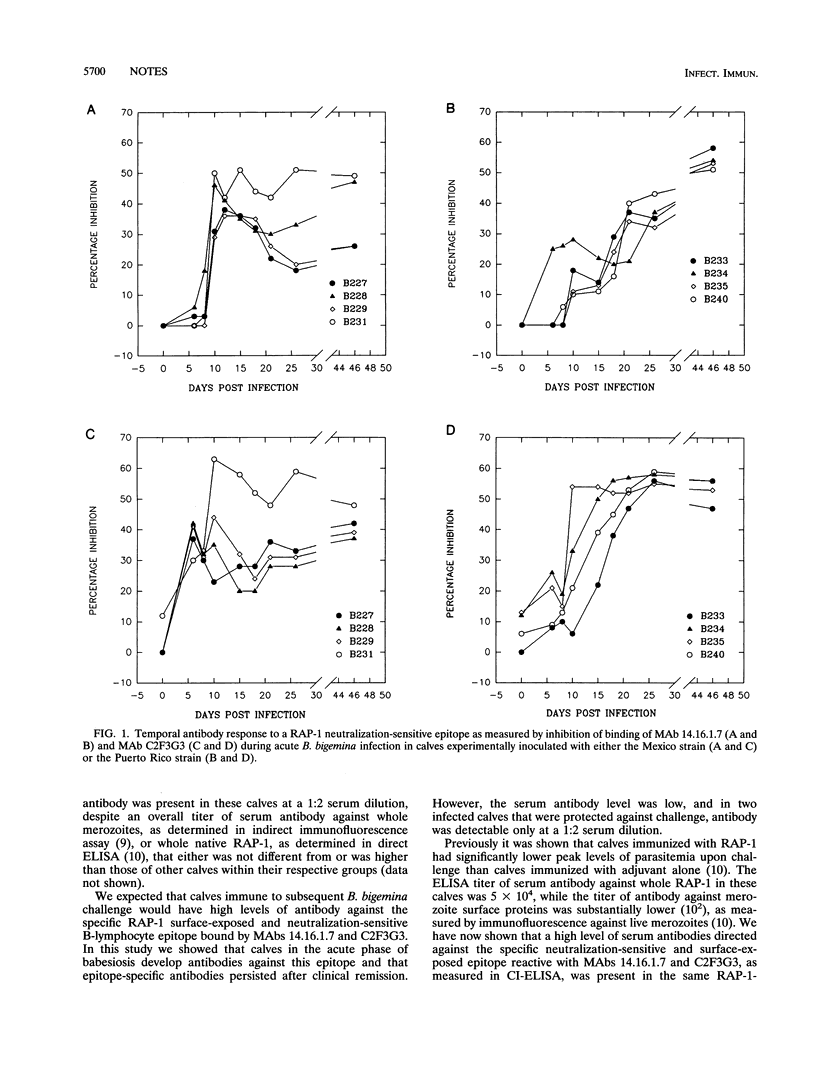
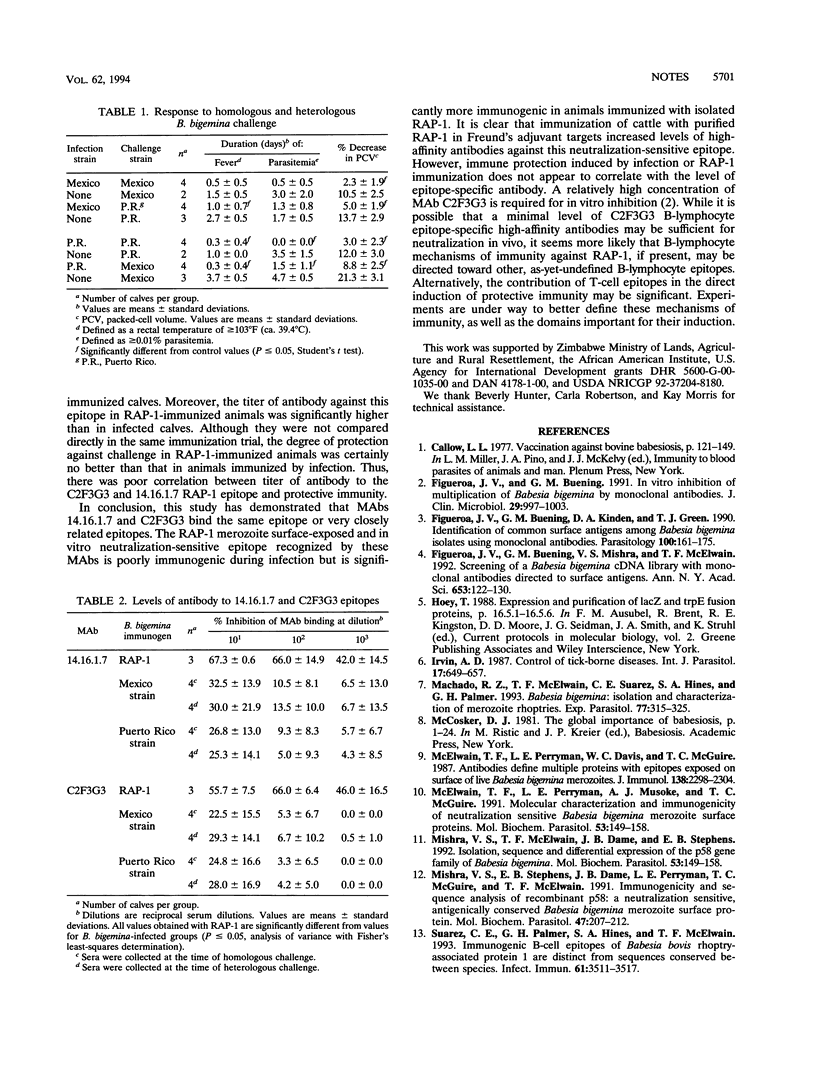
Protective immunity against Babesia bigemina is hypothesized to involve antibodies directed against merozoite surface-exposed epitopes. Levels of antibody against a rhoptry-associated protein 1 (RAP-1) B-lymphocyte epitope, defined by surface-reactive and inhibitory monoclonal antibodies, in immune cattle sera were determined. All cattle produced antibodies to the epitope; however, there was limited correlation between immune protection induced by infection or RAP-1 immunization and the level of antibody to the neutralization-sensitive B-lymphocyte epitope examined.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callow L. L. Vaccination against bovine babesiosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;93:121–149. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8855-9_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. V., Buening G. M. In vitro inhibition of multiplication of Babesia bigemina by using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):997–1003. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.997-1003.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. V., Buening G. M., Kinden D. A., Green T. J. Identification of common surface antigens among Babesia bigemina isolates by using monoclonal antibodies. Parasitology. 1990 Apr;100(Pt 2):161–175. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000061163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. V., Buening G. M., Mishra V., McElwain T. F. Screening of a Babesia bigemina cDNA library with monoclonal antibodies directed to surface antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Jun 16;653:122–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb19635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin A. D. Control of tick-borne diseases. Int J Parasitol. 1987 Feb;17(2):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(87)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machado R. Z., McElwain T. F., Suarez C. E., Hines S. A., Palmer G. H. Babesia bigemina: isolation and characterization of merozoite rhoptries. Exp Parasitol. 1993 Nov;77(3):315–325. doi: 10.1006/expr.1993.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwain T. F., Perryman L. E., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Antibodies define multiple proteins with epitopes exposed on the surface of live Babesia bigemina merozoites. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2298–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra V. S., McElwain T. F., Dame J. B., Stephens E. B. Isolation, sequence and differential expression of the p58 gene family of Babesia bigemina. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jul;53(1-2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90017-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra V. S., McElwain T. F., Dame J. B., Stephens E. B. Isolation, sequence and differential expression of the p58 gene family of Babesia bigemina. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jul;53(1-2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90017-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra V. S., Stephens E. B., Dame J. B., Perryman L. E., McGuire T. C., McElwain T. F. Immunogenicity and sequence analysis of recombinant p58: a neutralization-sensitive, antigenically conserved Babesia bigemina merozoite surface protein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Aug;47(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90180-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez C. E., Palmer G. H., Hines S. A., McElwain T. F. Immunogenic B-cell epitopes of Babesia bovis rhoptry-associated protein 1 are distinct from sequences conserved between species. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3511–3517. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3511-3517.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


