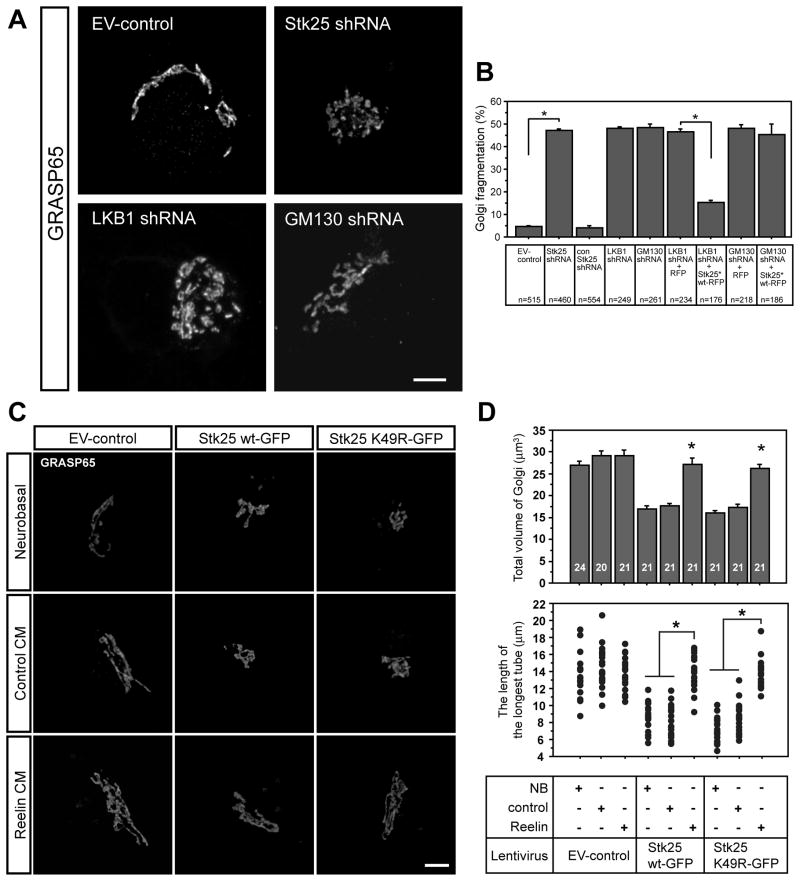
Figure 4. Golgi apparatus morphology is regulated by Stk25, LKB1 and GM130 expression and Reelin signaling.
A Stage III neurons that were infected with the EV-control virus had typical cis-Golgi ribbons (GRASP65, movie S3). In contrast, the cis-Golgi in Stk25 shRNA-, LKB1 shRNA- or GM130 shRNA-expressing neurons was fragmented (movie S5). GFP signal was omitted for clarity. B Significantly more Stk25 knockdown neurons had fragmented Golgi complexes compared to the EV-control and the control shRNA (n, as indicated). LKB1 and GM130 knockdown also caused significant Golgi fragmentation as compared to EV-control infected neurons. Stk25*-RFP expression rescued Golgi fragmentation in LKB1 shRNA but not GM130 shRNA-expressing neurons. C Neurons overexpressing either Stk25 wt-GFP or Stk25 K49R-GFP had condensed cis-Golgi (GRASP65 signal) compared to EV-controls when grown in either neurobasal or control-CM. Growth in Reelin-CM partially rescued the Golgi appearance in Stk25-overexpressing cells. GM130 and GRASP65 colocalized under all conditions (not shown). D Golgi volume (upper panel) and the length of the longest Golgi ribbon (lower panel) were determined (* p< 0.0001, Student’s t-test, n indicated in bars). Bars 5 μm. See also Fig. S3.