Fis1 and Bap31 bridge the mitochondria–ER interface to establish a platform for apoptosis induction
The Fis1–Bap31 complex (ARCosome) recruits and activates the initiator procaspase-8 at the interface between the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum.
Keywords: calcium, caspase-8, cell death, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria
Abstract
The mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are two organelles that critically contribute to apoptosis induction. While it is established that they communicate, how cell death signals are transmitted from the mitochondria to the ER is unknown. Here, we show that the mitochondrial fission protein Fission 1 homologue (Fis1) conveys an apoptosis signal from the mitochondria to the ER by interacting with Bap31 at the ER and facilitating its cleavage into the pro-apoptotic p20Bap31. Exogenous apoptosis inducers likewise use this signalling route and induce the procession of Bap31. Moreover, we show that the recruitment of procaspase-8 to the Fis1–Bap31 platform is an early event during apoptosis induction. The association of procaspase-8 with the Fis1–Bap31 complex is dependent on the variant of death effector domain (vDED) in Bap31 and is required for the activation of procaspase-8. This signalling pathway establishes a feedback loop by releasing Ca2+ from the ER that activates the mitochondria for apoptosis. Hence, the Fis1–Bap31 complex (ARCosome) that spans the mitochondria–ER interface serves as a platform to activate the initiator procaspase-8, and thereby bridges two critical organelles for apoptosis signalling.
Introduction
Caspase activation complexes are acknowledged to have a critical role in the apoptosis process. At these protein aggregates, the final decision to activate these destructive enzymes is taken to dismantle the cells. The best-known caspase-activating complexes are the DISC and the apoptosome, both of which reside in the cytosol and are activated by the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways for apoptosis, respectively. With the PIDDosome (Tinel and Tschopp, 2004), the Hip-1–Hippi complex (Gervais et al, 2002), and unligated integrins (Stupack et al, 2001), additional protein aggregates have recently been determined to initiate the caspase cleavage cascade. Initiator caspases are the apical apoptosis proteases that comprise protein–protein interaction motifs in their N-terminal prodomains that allow them to aggregate through adaptor proteins such as FADD via homotypic DED–DED (death effector domain) or CARD–CARD (caspase recruiting domain) domain interactions within the caspase-activating complexes. This induced proximity initiates the mutual cleavage of procaspases and fully activates them. Caspase-8 is one of the most prominent initiator caspases, as it is activated in the DISC complex of the Fas or the TNF receptor (Schneider and Tschopp, 2000).
The mitochondria and the ER harbour diverse regulators and signalling pathways for apoptosis (Ferri and Kroemer, 2001). While it was long established that these two organelles interact physically (Vance, 1990; Rizzuto et al, 1998), only recently factors such as Mitofusin 2 and Mmm1/Mdm10, 12, 34 were discovered that facilitate the physical association between them (de Brito and Scorrano, 2008; Kornmann et al, 2009). Several proteins are known to mediate inter-organelle signalling, and PACS-2 and BIK have shown to transmit signals for apoptosis from the ER to the mitochondria (Germain et al, 2005; Simmen et al, 2005). However, how cell death signals are communicated in the reverse direction, from the mitochondria to the ER, is unknown.
One of the mitochondrial regulators of cell death that recently came to prominence are the fission factors. During apoptosis, the mitochondria undergo controlled fission and their network disintegrates (Detmer and Chan, 2007). This process is evolutionarily conserved (Jagasia et al, 2005) and universally associated with cell death (Suen et al, 2008). Hence, it was proposed that mitochondrial fission factors constitute essential components of apoptosis signalling pathways (Youle and Karbowski, 2005). This was supported by the downregulation of Fission 1 homologue (Fis1) and Dynamin-related protein (Drp1), which led to reduced apoptosis (Lee et al, 2004). While various models could account for this (Suen et al, 2008), emerging evidence suggests that fission factors can signal for apoptosis independently of their role in mitochondrial fission (James et al, 2003; Lee et al, 2004; Alirol et al, 2006; Cassidy-Stone et al, 2008; Sheridan et al, 2008). In an attempt to uncover the signalling pathways emanating from fission factors, it was recently reported that Fis1 requires the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) gateway for apoptosis signalling (Alirol et al, 2006), but the exact molecular target remained undefined.
Bap31 is a 28 kDa integral membrane protein expressed ubiquitously and highly enriched at the outer ER membrane. Its cytosolic C-terminal domain has been shown to associate with and promote the vesicular trafficking of cellubrevin (Annaert et al, 1997), major histocompatibility complex class I molecules (Spiliotis et al, 2000; Paquet et al, 2004), tetraspanins (Stojanovic et al, 2005), CD11b/CD18 (Zen et al, 2004), and the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (Wang et al, 2008). Furthermore, Bap31 constitutes a protein aggregate at the ER, comprising several apoptosis regulators such as Bcl-2/Bcl-XL and the specific isoform of procaspase-8L (Ng et al, 1997; Breckenridge et al, 2002). During apoptosis, two sites in Bap31 are targeted by caspases and one of the cleavage products, p20Bap31, which remains anchored to the ER via a transmembrane domain, further transmits the apoptosis signal (Breckenridge et al, 2002).
Our study describes a tripartite protein complex among procaspase-8, Bap31, and the fission factor Fis1. We show that Fis1 physically interacts with Bap31 to bridge the mitochondria and the ER. Both proteins constitute a platform for the recruitment and activation of procaspase-8. As this signalling pathway can be initiated by Fis1, the Fis1–Bap31 complex serves to transmit an apoptosis signal from the mitochondria to the ER and is, besides the DISC complex (Muzio et al, 1996) and the Hip-1–Hippi complex (Gervais et al, 2002), the third platform for procaspase-8 activation.
Results
Fis1-induced apoptosis requires Bap31 and induces its cleavage
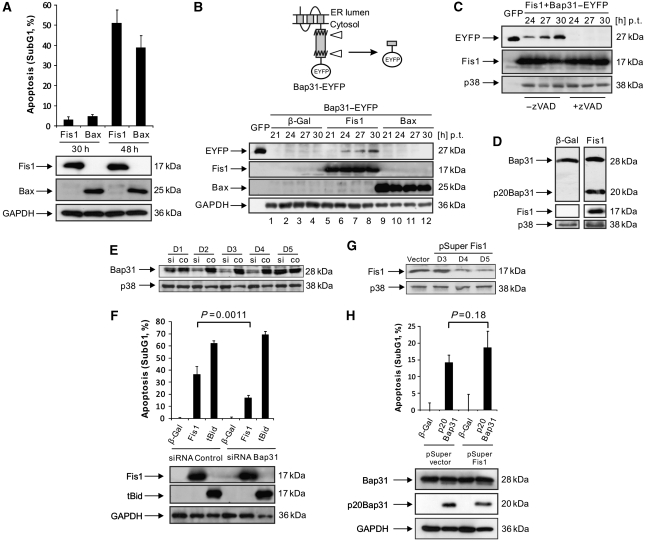
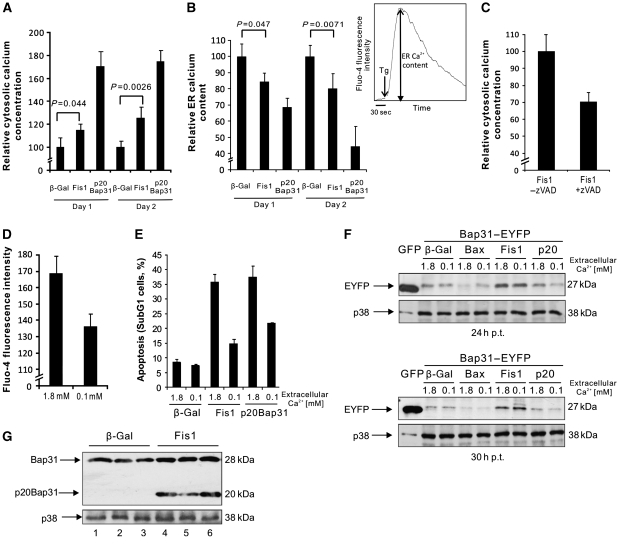
We found the mitochondrial fission factor Fis1 in a genetic screen (Albayrak et al, 2003) for pro-apoptotic factors (data unpublished). To study a potential functional interaction between Fis1 and Bap31 during the early phase of apoptosis, we transfected HeLa cells with a mammalian expression vector coding for Fis1 and determined apoptosis as the percentage of the cell population with subG1 DNA content. While we detected only minor indications of apoptosis with Fis1 30 h post transfection, after 48 h we observed DNA degradation, indicative of robust apoptosis (Figure 1A), as well as the activation of caspase-3 and poly-ADP-ribosomal polymerase (PARP) cleavage (Supplementary Figure S1A and B). Hence, the 30- and 48-h time points allowed for ordering the signalling events for apoptosis caused by Fis1. We then used Bap31, C-terminally tagged with the enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (Bap31–EYFP), which produces the GFP variant coupled to eight additional amino acids when the most C-terminal caspase recognition site in Bap31 is cleaved (Figure 1B, top). On co-expression of Fis1 with Bap31–EYFP, immunoblotting revealed cleavage of this fusion construct starting at 24 h after transfection and increasing over time (Figure 1B, bottom, lanes 5–8), even though the cells displayed insignificant DNA fragmentation at 30 h (Figure 1A). Similar results were obtained in HEK293T cells (data not shown). In contrast, when Bax, a known potent apoptosis inducer, was co-transfected with Bap31–EYFP under conditions that caused apoptosis with comparable efficiency and kinetics as Fis1 (Figure 1A), no procession of this fusion protein was observed (Figure 1B, bottom, lanes 9–12). Application of the pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk completely abrogated the cleavage of Bap31–EYFP induced by Fis1 (Figure 1C). We then sought to determine whether Fis1 can also provoke the cleavage of the endogenous Bap31. Immunoblotting at 27 h after Fis1 transfection also revealed cleavage of the endogenous Bap31 and the generation of the pro-apoptotic p20Bap31 fragment, thus recapitulating the procession of the Bap31–EYFP protein at this time point (Figure 1D). Overall, these data indicate that the cleavage of Bap31 is caused by a specific and early caspase-like protease activity during Fis1-induced apoptosis to produce the pro-apoptotic p20Bap31 fragment. To further investigate the functional relationship between Bap31 and Fis1, Bap31 was downregulated by short interfering RNA (siRNA; Figure 1E). Densitometric analysis revealed that the Bap31 protein level was reduced by ∼70% on day 2 and day 3, and by ∼50% on day 4 compared with the endogenous level (data not shown). On day 3, Fis1 was transfected into these cells and apoptosis measured by the percentage of the subG1 cell population 48 h post transfection. Figure 1F shows that apoptosis induced by Fis1 was significantly reduced (53% reduction) in cells transfected with Bap31 siRNA (17.0±2.1%) compared with control siRNA-transfected cells (36.4±6.7%). To assess the specificity of this effect, an expression vector for truncated Bid (tBid), which induces apoptosis by direct signalling to the mitochondria (Li et al, 1998), was transfected and its apoptosis was found not to be affected by the downregulation of Bap31 (Figure 1F). To assess whether this signalling pathway progresses in a unidirectional manner from Fis1 to Bap31, endogenous Fis1 was downregulated by shRNA (Figure 1G). Pro-apoptotic p20Bap31 was then introduced into these cells on day 4 post-shRNA transfection and apoptosis measured on day 5. No statistically significant change in the subG1 cell population was detected on Fis1 downregulation (Figure 1H).
Figure 1.
Fis1-induced apoptosis requires Bap31, but activated Bap31 does not depend on Fis1. (A) The percentage of apoptosis induced by Fis1 or Bax (as a control) was measured at different time points with propidium iodide staining of the cells by FACS. For Bax transfections, the amount of plasmid was 1/5 of Fis1 to match the percentage of apoptosis. (B) EYFP was fused to the C-terminus of human Bap31 to generate Bap31–EYFP. Its cleavage (indicated by triangles) can be determined by the production of EYFP plus an eight amino-acid extension (top panel). Cells were transfected and harvested at the indicated time periods (bottom panel). For Bax transfections, the amount of plasmid used was as in A. Bap31–EYFP cleavage was revealed by immunoblotting. Cell lysates from GFP-transfected cells were used as a size indicator. p.t.: post transfection. (C) Cells were co-transfected with Fis1 and Bap31–EYFP with or without zVAD-fmk (50 μM) and harvested at the indicated time points p.t. The cleavage of Bap31–EYFP was determined by immunoblotting as in B. (D) Cells were transfected either with β-gal or Fis1 and harvested 27 h p.t. and the cleavage of the endogenous Bap31 was revealed by immunoblotting. Note that the blots shown were from the same membrane with the same exposure time. (E) Cells were transfected with Bap31 siRNA (si) or control siRNA (co) and harvested on days 1 to 5. Downregulation of Bap31 was analysed by western blot. (F) Cells were transfected with the indicated genes on day 3 after siRNA transfection targeting Bap31 (or a control) and the percentage of subG1 population was quantified on day 5. (G) Cells were transfected with shRNA against Fis1 (pSuper Fis1) or an empty pSuper vector and harvested at the indicated time points. The vector-transfected cells were collected on day 5. Fis1 downregulation was determined by western blot. (H) Cells were transfected either with pSuper Fis1 or pSuper vector. On day 4 after shRNA transfection, cells were transfected with β-gal or p20Bap31 and the percentage of the subG1 cell population measured on day 5. All the histograms are presented as means±s.d.
Fis1 and Bap31 interact and form a platform for procaspase-8 recruitment
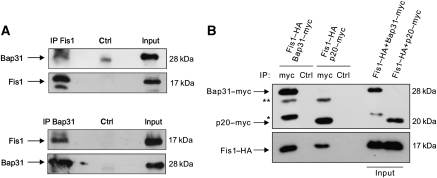
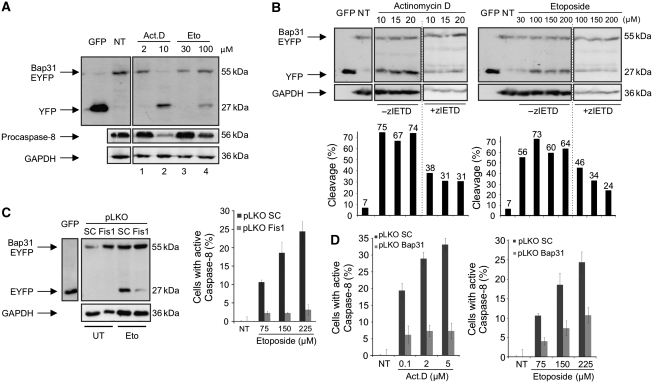
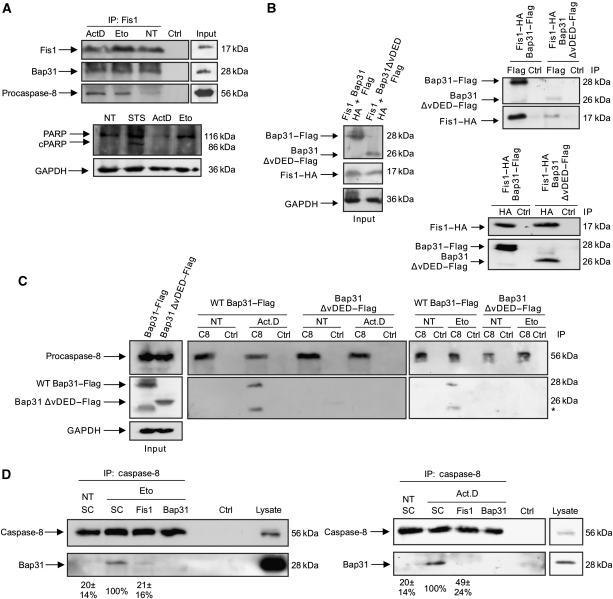
Having shown the functional relation between Fis1 and Bap31, we sought to examine their physical interaction. Using co-immunoprecipitations, we found that Fis1 and Bap31 associated endogenously (Figure 2A) and on overexpression (Figure 2B). We also found that the cleavage product of Bap31, p20Bap31, can still interact with Fis1 (Figure 2B). Furthermore, immunostaining revealed that Fis1 and Bap31 localized to the mitochondria and the ER, respectively, as previously described (Ng et al, 1997; James et al, 2003; Supplementary Figure S2A and B). Importantly, merging signals from Fis1 and Bap31 demonstrated a punctual overlap in line with the juxtaposition of these organelles within the cell (Supplementary Figure S2C). Collectively, these data indicate a close physical and functional connection between Fis1 and Bap31. We then tested two apoptosis signals, actinomycin D and etoposide, and observed that both led to Bap31 cleavage and to a concomitant reduction of the uncleaved procaspase-8 (Figure 3A, lanes 2 and 4). This led us to test zIETD-fmk, a specific inhibitor of caspase-8 that reduced the cleavage of Bap31 by both chemicals (Figure 3B). The procession of the Bap31–EYFP fusion protein was also reduced in cells with stable downregulation of Fis1 by lentiviral shRNA (Supplementary Figure S3) when treated with etoposide (Figure 3C, left panels). The basal apoptosis level (2.8%±0.68) in the control cells was slightly increased (5.5%±4.2) when Fis1 was downregulated. Moreover, the activation of caspase-8 was significantly reduced when Fis1 was knocked down (Figure 3C, right panel). The activation of this protease and the contribution of Bap31 were further supported by the specific caspase-8 assay, which revealed a prominent activation of the enzyme by both chemicals and a significant reduction of this effect when Bap31 was stably downregulated (Figure 3D and Supplementary Figure S3). We also confirmed that this reduction in caspase-8 activation was not due to an alteration in the ER stress response in these cells (Supplementary Figure S4). Immunoprecipitation of the endogenous Fis1 protein revealed that its interaction with Bap31 remained constant on application of the chemicals, whereas procaspase-8 was only recruited to this complex on apoptosis induction by actinomycin D or etoposide (Figure 4A, upper panels). This occurred even before any appreciable cleavage of PARP was detectable (Figure 4A, lower panels). Procaspase-8 is recruited to its activation complexes such as the DISC complex through DED–DED domain interactions. Bap31 was reported to display a variant DED (vDED) domain that deviates from the generic DED domains in its sequence (Reed et al, 2004). Using co-immunoprecipitations we tested the interaction of procaspase-8 with full-length Bap31 (WT Bap31) and with a Bap31 deletion mutant that lacks the vDED domain (Bap31–ΔvDED). Figure 4B shows that this deletion construct retained its ability to interact with Fis1. However, it was rendered unable to facilitate the recruitment of procaspase-8 to Bap31 when cells were treated with actinomycin D or etoposide (Figure 4C). We then sought to determine the requirement of Fis1 in the recruitment of caspase-8 to the Fis1–Bap31 complex. Figure 4D shows that the interaction between endogenous caspase-8 and Bap31 was diminished in the absence of Fis1 on etoposide (21±16% of control cells, left panel) and actinomycin D (49±24% of control cells, right panel) treatment. On the basis of its ability to bridge two critical organelles for apoptosis regulation, we have named this complex ARCosome.
Figure 2.
Fis1 and Bap31 interact. (A) Total cell lysates were prepared from HeLa cells and the endogenous Fis1 (top) or Bap31 (bottom) were immunoprecipitated (‘IP Fis1' and ‘IP Bap31'). The association of Bap31 or Fis1 proteins was then detected in a western blot. (B) Fis1–HA was co-expressed either with full-length Bap31–myc or p20Bap31–myc at a 1:1 plasmid ratio in HEK293T cells. Total cell lysates were then subjected to immunoprecipitation with an α-myc antibody and the immunoprecipitates were analysed by western blot using α-myc (top) and α-HA (bottom) antibodies. ** IgG light chain; * unspecific band. Note that input loadings were from cell lysates before immunoprecipitation.
Figure 3.
Caspase-8 activation is dependent on Fis1 and Bap31 (A) Cells were transfected with the Bap31–EYFP fusion construct. Following the expression of the fusion protein, cells were treated with actinomycin D (Act.D, 2 or 10 μM) for 4 h or etoposide (Eto, 30 or 100 μM) for 30 h. Procession of Bap31–EYFP and procaspase-8 was analysed on immunoblot. Cell lysates from GFP-transfected cells were used as size indicators. NT, lysates from non-treated cells. (B) Cells were transfected with Bap31–EYFP and treated either with actinomycin D (6 h) or with etoposide (30 h) with the indicated concentrations. Cells were also cultivated in the presence or absence of the caspase-8 inhibitor zIETD-fmk during the treatment. Cell lysates from GFP-transfected cells were used as size indicators. NT, lysates from non-treated cells (top). The percentages of the cleavage of Bap31–EYFP were calculated by the intensity of the cleaved product (EYFP band) divided by the sum of intensities of the uncleaved (Bap31–EYFP band) and the cleaved (EYFP band) bands obtained from densitometry analysis using the ImageJ programme (bottom). (C) The cleavage of Bap31–EYFP was assessed in a western blot using a stable Fis1 knockdown cell line (Fis1) or a control cell line (SC) with etoposide treatment (100 μM, 30 h, left panels). Cell lysates from GFP-transfected cells were used as size indicators. The activation of caspase-8 was determined using the stable Fis1 knockdown cell line (pLKO Fis1) with etoposide treatment of the cells (30 h, right panel). pLKO SC is a control cell line for pLKO Fis1. (D) HeLa cells with stably downregulated Bap31 (pLKO Bap31) or control cells (pLKO SC) were treated with actinomycin D (23 h, left panel) or etoposide (30 h, right panel) and the activation of caspase-8 was measured.
Figure 4.
Procaspase-8 is recruited to the Fis1–Bap31 platform on apoptosis induction. (A) Cells were treated with actinomycin D (2 μM) for 4 h or with etoposide (100 μM) for 28 h, and cell lysates subjected to immunoprecipitation with an antibody against endogenous Fis1. Immunoprecipitates were separated on a SDS–PAGE and subsequently probed for endogenous Fis1, Bap31, and procaspase-8 (top). The procession of poly-ADP-ribosomal polymerase (PARP) was determined in parallel using the same cell lysates before immunoprecipitation (bottom). Staurosporine (STS) was used as a positive control. cPARP, cleaved PARP. (B) Fis1–HA was co-transfected either with full-length Bap31–Flag or Bap31ΔvDED–Flag in HEK293T cells (left, input). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with α-Flag (right, top panels) or α-HA antibody (right bottom panels) and the immunoprecipitates were analysed for the indicated proteins by western blot using α-Flag or α-HA antibodies. (C) Full-length Bap31–Flag or Bap31ΔvDED–Flag were expressed in HEK293T cells (left, input) and cell lysates immunoprecipitated for endogenous procaspase-8 (C8) on treatment with actinomycin D (Act.D, 0.2 μM, 23 h) or with etoposide (Eto, 100 μM, 30 h). The immunoprecipitates were probed with α-caspase-8 and α-Flag antibodies (middle and right panels). NT, no treatment; * unspecific band (D) The association of caspase-8 with endogenous Bap31 was determined by co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous caspase-8 in cell lines depleted of Fis1 or Bap31 (as a control) on etoposide (Eto, 100 μM, 30 h) or actinomycin D (Act.D, 0.5 μM, 23 h) treatment. NT, no treatment. Numbers below show the percentage association between caspase-8 and Bap31 with respect to scramble-treated cells (SC), as revealed by densitometry analysis using the ImageJ programme. Figures are means±s.d. of three independent experiments.
Fis1 causes Ca2+ release from the ER for apoptosis induction
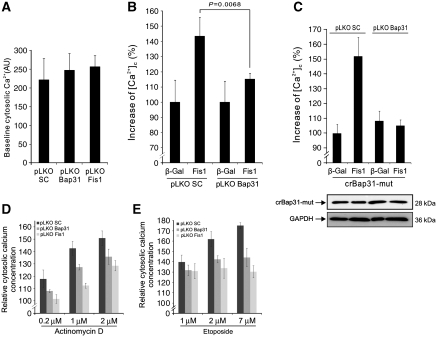
We wanted to explore the downstream signals and sought to address (i) how the ER reacts to the apoptosis signals from the ARCosome and (ii) as the mitochondria are regarded as the executioner organelle of apoptosis, how this signal is transferred back to the mitochondria. As chemical apoptosis inducers such as actinomycin D and etoposide can have pleiotropic consequences, which could obscure the downstream signals of the Fis1–Bap31 complex, Fis1 upregulation was used for the following experiments. We asked whether Fis1 expression results in an increased cytosolic calcium concentration, as expression of Bap31, when processed by caspase-8 (p20Bap31), produces an increase in the concentration of this ion (Ng et al, 1997; Breckenridge et al, 2003). As observed, on p20Bap31 transfection (which, similar to Bap31–EYFP, localized to the ER, Supplementary Figure S5A and B), Fis1 expression led to a significant increase of the calcium concentration in the cytosol on day 1 (27 h post transfection) and more prominently on day 2 (48 h post transfection; Figure 5A), although, as expected, the effect was less pronounced than with p20Bap31, as our data had placed Fis1 upstream of this factor. To determine the source of the increased cytosolic calcium, the ER calcium content was measured. After baseline Fluo-4/AM fluorescence determination, thapsigargin, a SERCA inhibitor, was added to empty the ER calcium store. The difference between the baseline calcium measurement and the peak fluorescence intensity after addition of thapsigargin indicated the ER calcium capacity (Figure 5B, right panel). Our data revealed that the calcium content of this organelle decreased on day 1 and day 2 after Fis1 expression, mirroring the increase in cytosolic calcium over the same time period and suggesting that this was due to calcium release from the ER (Figure 5B). The p20Bap31 control yielded a similar effect. We then asked whether the cleavage of Bap31 is responsible for the calcium release. The data showed that application of zVAD-fmk, which inhibits Bap31 cleavage (Figure 1C), reduced the early increase of cytosolic calcium on Fis1 expression (Figure 5C). This observation led us to ask whether the observed cytosolic calcium increase was critical for the induction of apoptosis. We incubated cells in medium with two calcium concentrations, 1.8 mM (corresponding to normal medium) or 0.1 mM (18-fold reduction), which led to a concomitant reduction of cytosolic calcium (Figure 5D). On incubation in the two different medium formulations, cells were transfected with expression vectors for Fis1 or p20Bap31. Both, the transfection efficiency (71.0±3.1% in normal DMEM and 70.0±0.54% in reduced calcium medium) and the background apoptosis (8.5±1.2% in normal DMEM and 7.4±0.6% in reduced calcium) were unaffected by this treatment. However, apoptosis induced by Fis1 and p20Bap31 was significantly diminished in medium with reduced calcium (Figure 5E). Hence, the increase of the cytosolic calcium concentration is required for apoptosis by both Fis1 and its downstream signalling factor p20Bap31. To determine at which stage, relative to the activation of Bap31, calcium is required for Fis1-induced apoptosis, the cleavage of Bap31 was assayed as before (Figure 1B). Figure 5F and G shows that the cleavage of the Bap31–EFYP fusion protein, both at 24 and 30 h after Fis1 transfection, and the procession of the endogenous Bap31 were unchanged in medium with reduced calcium and also when the intracellular calcium was chelated by BAPTA (Figure 5G; compare lanes 2 and 5, and lanes 3 and 6). This indicated that the release of Ca2+ from the ER is positioned downstream of the Fis1-induced cleavage and activation of Bap31. To further assess the role of the Bap31–Fis1 platform for the calcium release, we used the stable downregulation of Bap31 or Fis1 by lentiviral shRNAs (Supplementary Figure S3). While these knockdown cells did not display an altered baseline calcium levels (Figure 6A), Fis1 transfection in Bap31 knockdown cells revealed a significant decrease in cytosolic calcium when compared with the control cells (Figure 6B). We then investigated whether the cytosolic calcium increase induced by Fis1 is mediated by p20Bap31. A site-directed mutagenesis was performed on the mammalian expression vector coding for a caspase cleavage-resistant Bap31 (crBap31; Nguyen et al, 2000), which harbours two mutations, D164A and D238A, in order to introduce six silent mutations (crBap31-mut) so that the lentiviral shRNAs expressed in pLKO Bap31 cells were unable to target this construct (Supplementary Figure S6). The expression of this vector was confirmed in both, pLKO SC and pLKO Bap31, cell lines (Figure 6C, bottom). We then co-transfected cells with crBap31-mut and Fis1, and determined the level of the cytosolic calcium concentration. As Figure 6C shows, control cells expressing both endogenous Bap31 and crBap31-mut showed robust cytosolic calcium increase with Fis1 co-transfection, whereas Bap31 knockdown cells expressing only crBap31-mut failed to reveal any cytosolic calcium increase. This indicates that the increase of cytosolic calcium mediated by Fis1 (Figure 5A) is solely mediated by the production of pro-apoptotic p20Bap31. Moreover, both Fis1 and Bap31 downregulation showed a markedly reduced accumulation of cytosolic calcium on treatment with actinomycin D or etoposide (Figure 6D and E).
Figure 5.
Fis1 expression leads to increased cytosolic calcium. (A) Cells were transfected and the cytosolic calcium concentration was measured after 27 h (Day 1) and 48 h (Day 2) after transfection by FACS using the Fluo-4/AM dye. The mean Fluo-4/AM fluorescent intensities of the β-gal-transfected cells were set to 100% in both Day 1 and Day 2, and the relative cytosolic calcium increase was calculated for Fis1- and p20Bap31-transfected cells. (B) The ER calcium content was measured in the same samples as A at Day 1 and Day 2 after transfection as the Ca2+ released from the ER into the cytosol by thapsigargin. The ER calcium content was measured as the difference between the peak after addition of 10 μM thapsigargin (Tg) and the baseline fluorescence measured for 30 s (right panel). Similar to A, the mean ER calcium content measured by β-gal transfections was set to 100% on each day. (C) Cells were transfected with Fis1, with or without addition of zVAD-fmk. Cytosolic calcium was measured 27 h after transfection using the Fluo4/AM dye. The data are presented as the percentage reduction of cytosolic calcium in Fis1-transfected cells (without zVAD-fmk addition). (D) Baseline cytosolic calcium concentration of cells incubated either in DMEM containing 1.8 or 0.1 mM calcium were analysed. (E) Cells were transfected with the indicated genes, either in a medium containing 1.8 or 0.1 mM calcium. The percentage of subG1 population was analysed at 48 h p.t. (F) Cells were transfected with the indicated genes in two medium formulations, and the cleavage of Bap31–EYFP was determined after 24 h (top) and 30 h (bottom). (G) Cells were transfected either with β-gal or Fis1 in DMEM with 1.8 mM (lanes 1 and 4), 0.1 mM calcium (lanes 2 and 5), or 1.8 mM calcium with 5 μM BAPTA-AM (lanes 3 and 6). Cells were harvested at 27 h p.t. and the endogenous Bap31 cleavage was analysed by immunoblotting.
Figure 6.
Bap31 and Fis1 mediate cytosolic calcium release and the effects of apoptosis-inducing drugs. (A) Baseline cytosolic calcium concentrations of three virally transduced stable cell lines were measured: pLKO SC (control cell line), pLKO Bap31 (Bap31 knockdown cells), and pLKO Fis1 (Fis1 knockdown cells). AU, arbitrary unit (B) Stable Bap31 knockdown cells were transfected either with β-gal or Fis1. The cytosolic calcium concentration was measured 48 h after transfection with Fluo-4/AM dye using FACS. The mean Fluo-4/AM fluorescent intensity of the β-gal-transfected cells were set to 100% as before. (C) Stable Bap31-downregulated cells (pLKO Bap31) were co-transfected with crBap31-mut and Fis1. The cytosolic calcium level was determined using Fluo-4/AM staining and FACS analysis. The mean calcium level of pLKO SC β-gal-transfected cells were set to 100%. (D, E) pLKO SC control cells and knockdown cells for Bap31 or Fis1 were treated with actinomycin D (C) or etoposide (D) at the indicated concentrations for 6 and 20 h, respectively, and the relative cytosolic calcium levels were measured using Fluo-4/AM dye and FACS analysis.
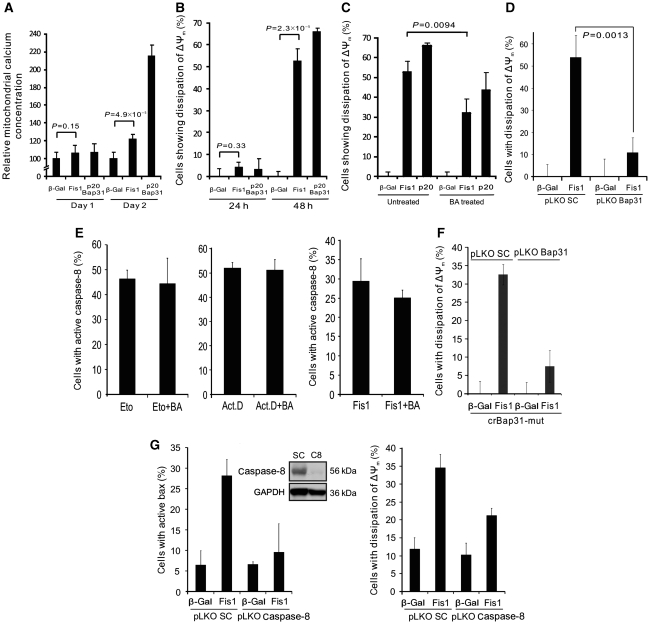
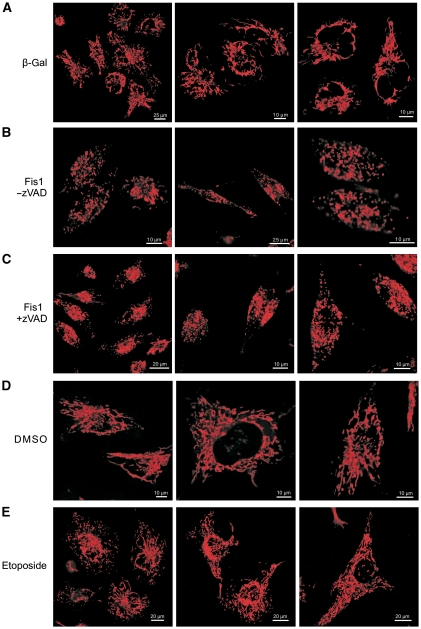
The mitochondria contain sensors for Ca2+ that eventually activate these organelles for apoptosis induction (Orrenius et al, 2003). Hence, we studied whether and how the signal induced by Fis1 feeds back to the mitochondria for cell death induction. As calcium released from the ER can be taken up by the juxtaposed mitochondria, we determined the mitochondrial calcium concentration. Figure 7A shows that this calcium concentration was significantly increased in the mitochondria by both Fis1 and p20Bap31 on day 2, but not on day 1 post transfection, suggesting that the increased cytosolic calcium observed in Figure 5A is absorbed by the mitochondria. To investigate whether this mitochondrial calcium increase has an effect on apoptosis, we measured the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), as its dissipation is linked to outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization for cell death induction. As Figure 7B shows, the majority of cells underwent membrane depolarization at 48 h, but not 24 h, post Fis1- or p20Bap31 transfection, a time point that also corresponds to the observed mitochondrial calcium increase (Figure 7A). This collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential was reduced when bongkrekic acid, the inhibitor of the permeability transition pore complex, was added, indicating that this protein aggregate is finally activated by the apoptosis signalling induced by Fis1 (Figure 7C). Finally, the dissipation of ΔΨm was significantly reduced when Fis1 was expressed in Bap31 knockdown cells, in comparison with control cells (Figure 7D). We used our insights to further support the ordering of the signalling from the ARCosome to caspase-8 activation, calcium release and mitochondrial activation for apoptosis. Bongkrekic acid was unable to reduce the activation of caspase-8 on treatment of the cells with etoposide or actinomycin D or on transfection of Fis1 (Figure 7E). Also, the expression of crBap31-mut in Bap31 knockdown cells failed to induce the loss of ΔΨm (Figure 7F). Furthermore, when we knocked down caspase-8, we reduced the number of cells with active Bax and loss of ΔΨm on transfection of Fis1 (Figure 7G). We then sought to determine the interrelation between caspase activation and mitochondrial fission. We recorded the consequences of Fis1 expression on the fission of mitochondria when caspases were inhibited. Whereas control-transfected cells retained their normal mitochondrial structure, the upregulation of Fis1 led to a striking disintegration of the mitochondrial network, which persisted even on the application of pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk (Figure 8A–C). The experimental settings were also validated by observing an increase of the mitochondrial network when Fis1 was downregulated (Supplementary Figure S7). As the above data (Figure 8A–C) were still compatible with fission being upstream of the ARCosome, we treated the cells with etoposide and assayed for fission at a time point when Bap31 cleavage was detectable (Figure 3A). As Figure 8E shows, the mitochondrial network was not changed, indicating that mitochondrial fission is not required for the cleavage of Bap31.
Figure 7.
Fis1 expression leads to increased mitochondrial calcium accumulation and to outer mitochondrial membrane depolarization. (A) Cells were transfected and the mitochondrial calcium concentration was determined 27 h (Day 1) and 48 h (Day 2) after transfection by FACS using the Rhod-2/AM dye. Measurements of β-gal (control) were set as 100%. (B) Cells were transfected and the mitochondrial outer membrane depolarization was quantified at 24 and 48 h p.t. using DiOC6. The percentage of DiOC6-negative population is shown. (C) Cells were transfected in the presence or absence of bongkrekic acid (75 μM), an inhibitor of the PT pore. At 48 h after transfection, mitochondrial outer membrane depolarization was measured as in B. (D) pLKO SC or pLKO Bap31 cells were transfected either with β-gal or Fis1, and the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential was measured with DiOC6 at 48 h after transfection. (E) HeLa cells were treated with etoposide (225 μM, 30 h, left panel) or with actinomycin D (5 μM, 23 h, middle panel), or transfected with Fis1 (right panel), either in the presence or absence of bongkrekic acid (BA). Cells were subsequently analysed for caspase-8 activation. (F) An expression vector for crBap31-mut was co-expressed with Fis1 in Bap31 knockdown (pLKO Bap31) or control (pLKO SC) cells. The loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential ΔΨm was measured 48 h after transfection with DiOC6 staining and analysed with FACS. (G) A cell line with stable knockdown of caspase-8 was created with lentiviral shRNA. The inset panel shows the western blot of control (SC) and caspase-8-downregulated (C8) cell lysates. Using this stable cell line (pLKO Casp.8), Fis1 was expressed and the activation of Bax (left panel) and the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential ΔΨm (right panel) were measured 48 h after transfection. All the histograms are presented as means±s.d.
Figure 8.
Mitochondrial fission is not required for Fis1-induced apoptosis. (A–C) HeLa cells were transfected with β-gal (A) or Fis1 (B, C). The pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk was added to one of the Fis1-transfected wells (C). Mitochondrial morphology was analysed 24 h after transfection. (D, E) HeLa cells were treated with etoposide (100 μM, 30 h) or control treated with DMSO. Mitochondria were stained with TMRE and analysed using confocal microscopy. Three representative panels are shown.
Discussion
Our study demonstrates that the association between the fission factor Fis1 and Bap31 is responsible for the transfer of an apoptosis signal from the mitochondria to the ER. The Fis1–Bap31 interaction is already detectable in normal, non-apoptotic cells (Figure 4A), indicating that it constitutes a preformed scaffold complex along which the cell death signal can be quickly transferred. The cleavage and the activation of Bap31 suggest that it is a genuine signalling complex, and not only a structural component in the cell that tethers the mitochondria to the ER. We have named this protein complex ARCosome to indicate that it spans two organelles critical for cell death induction.
Our data show that the generic procaspase-8 isoform is recruited to the ARCosome when various signals, such as chemical cell death inducers, are applied (Figure 4). The association of Bap31 with the specific isoform of procaspase-8L that comprises 59 additional N-terminal amino acids has previously been shown for apoptosis induced by the viral E1A protein (Breckenridge et al, 2002). Hence, besides the DISC complex (Muzio et al, 1996), the Hip-1–Hippi complex (Gervais et al, 2002) and unligated integrins (Stupack et al, 2001), the Fis1–Bap31 complex (ARCosome) represents another platform for procaspase-8 activation. Homotypic DED–DED domain interactions are responsible for the recruitment of procaspase-8 molecules. While, in the DISC complex, procaspase-8 associates with the DED domain protein FADD, Hip-1 and Hippi have only a weak consensus DED domain, and integrins lack such a domain all together. Fis1 is also devoid of a DED domain, but Bap31 contains a vDED domain (Reed et al, 2004). On the basis of the sequence, this DED domain represents a member of a sub-cluster of the DED domain family. We have presented here evidence for the essential role of this sequence by showing that the recruitment of procaspase-8 is abolished when it is deleted in Bap31 (Figure 4C).
It is currently being discussed in the apoptosis field whether mitochondrial fission is required for apoptosis induction or whether it constitutes a cellular feature that merely accompanies the cell death process (Sheridan et al, 2008; Tanaka and Youle, 2008). The procession of Bap31 makes the signalling pathway of the ARCosome to be dependent on caspases, while the fission of mitochondria is not (Sheridan et al, 2008; Figure 8). Hence, the signalling circuit for apoptosis, as outlined in this study, is not required for fission of mitochondria and this further separates the process of mitochondrial fission from apoptosis signalling, while, nevertheless, both are mediated by components of the fission factors. Our failure to observe any change in fission when caspases—and in extension, the activation of caspase-8 in the ARCosome—were inhibited (Figure 8A–C) suggests that the signalling pathway described here is independent of mitochondrial fission. It is known that the Fis1 signal for apoptosis can be repressed by Bcl-XL, without compromising its effect on fission (James et al, 2003). This is also supported by our finding on the kinetics of mitochondrial fission (Figure 8D and E), compared with Bap31 cleavage (Figure 3A). Hence, it seems that fission factors such as Fis1 have a role in both apoptosis signalling and fission that are separable, a notion that is also supported by several other studies (James et al, 2003; Lee et al, 2004; Alirol et al, 2006; Cassidy-Stone et al, 2008; Sheridan et al, 2008).
Our data allow for ordering the temporal succession of the apoptosis signalling events initiated by Fis1, and reveal how the signal that is transmitted from the mitochondria to the ER by the ARCosome is ferried back to the organelle of its origin. On day 1, we could observe only two features of this pathway: Bap31 cleavage (Figure 1B) and Ca2+ release from the ER (Figure 5A). On the second day, we detected more downstream processes such as uptake of calcium into the mitochondria (Figure 7A), the dissipation of the mitochondrial membrane potential (Figure 7B), and the cleavage of procaspase-3 and PARP (Supplementary Figure S1). Frieden et al (2004) observed a similar change in Ca2+ homeostasis. This supports that the cleavage of Bap31 is a very early event in the apoptosis signalling caused by Fis1. Thus, Fis1 can activate a signalling pathway that, rather than directly impacting on the mitochondria and initiating mitochondrial fission for apoptosis, progresses from the mitochondria to the ER through the interaction of Fis1 with Bap31, its cleavage, and finally the release of Ca2+, which then feeds back to the mitochondria. The integration of the ER with its numerous apoptosis regulators and calcium-binding proteins (Orrenius et al, 2003; Groenendyk et al, 2004) into this signalling circuit could allow for incorporating additional layers of signal regulation. This scenario would ensure that input from both organelles, the mitochondria and the ER, are processed and converge on the executioners for apoptosis. While activated Bap31 in the form of p20Bap31 does not rely on Fis1 for apoptosis signalling (Figure 1H), we cannot exclude that, in some cases, the ARCosome also functions to convey signals from the ER to the mitochondria.
Our study reveals a crucial role of Ca2+ released from the ER in the downstream signalling of the ARCosome. This Ca2+ could function as an amplifier of cell death in this signalling circuit that is able to reach many mitochondria in close proximity to the ER to engage them in apoptosis induction. In fact, high-resolution imaging of the mitochondrial network estimated that 5–20% of all mitochondria are in close contact with the ER (Rizzuto et al, 1998) and a recent report even suggested that all mitochondria are associated with the ER (Csordas et al, 2010), thus facilitating the efficient uptake of calcium in the microdomains of high calcium levels. Ca2+ release from the ER is a general mediator in many cell death scenarios (Orrenius et al, 2003), including those initiated by caspase-8 (Wozniak et al, 2006). Hence, as our data indicate that its cytosolic increase is a direct consequence of the activation of mitochondrial fission factors, the activation of Bap31 could tie in two generally observed features of apoptosis. The amplification of the apoptosis signal by Ca2+ could constitute an important aspect of ARCosome activation, as only a minority of the Bap31 and Fis1 proteins in the cell are engaged in this complex, as we detected them in co-immunoprecipitations but not in whole cell lysates (Figure 4A and B).
In summary, our data collectively suggest the existence of a novel protein complex that bridges the mitochondria and the ER and signals for apoptosis. The locale between two crucial organelles involved in apoptosis and the participation of fission factors make this protein aggregate especially intriguing and suggest that it establishes an additional level of cell death regulation.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and reagents
HeLa and HEK293T cells were cultivated in DMEM (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% FCS (Sigma), 2 mM L-glutamine (Invitrogen), 2 mM sodium pyruvate (Invitrogen), penicillin (100 U/ml), and streptomycin (100 μg/ml). Etoposide, actinomycin D, staurosporine, bongkrekic acid, and BAPTA were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. zIETD-fmk were from Merck Biosciences. zVAD-fmk was purchased from MP Biomedicals. Calcium-free DMEM was obtained from PAA Laboratories GmbH.
Plasmid vectors and transfections
All the plasmid vectors were cloned into the pcDNA3Δ (Invitrogen) vector unless otherwise stated. Fis1 was isolated in a genetic screen for apoptosis inducers (Albayrak et al, 2003), Bap31–myc, tBid, Bap31–EYFP, crBap31–myc, and Bax were previously described (Mund et al, 2003; Schoenfeld et al, 2004). p20Bap31 was subcloned using Phusion™ DNA polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with the following primers: 5′-AAAAGGAAAAGCGGCCGCCGTCAACAGCAGCTCCCTTC-3′ (forward) and 5′-CCGGAATTCAGGATGAGTCTGCAGTGG-3′ (reverse). Bap31ΔvDED mutant and crBap31-mut were produced using QuickChange II site-directed mutagenesis kit (Agilent Technologies) with the following primers: 5′-GTCGGGAATGCTGAGCACGCAAAGCTGCAG-3′ (forward) and 5′-CTGCAGCTTTGCGTGCTCAGCATTCCCGAC-3′ (reverse) for Bap31ΔvDED mutant and 5′-TCCTTGCTGCTGTCCTTCCTGCTTCGCAGATTAGTGACTCTCATTTCGCAGCAGGC-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCCTGCTGCGAAATGAGAGTCACTAATCTGCGAAGCAGGAAGGACAGCAGCAAGGA-3′ (reverse) for crBap31-mut. Production of WT Bap31–Flag and Bap31ΔvDED–Flag was constructed using StrataClone mammalian expression vector system (Agilent Technologies) with the following primers: 5′-GGGCCGCCATGAGTCTGCAGTGGA-3′ (forward) and 5′-CTCTTCCTTCTTGTCCAT-3′ (reverse). shRNA against Fis1 was cloned into the pSuper vector (OligoEngine) with the following target sequence 5′-GAGCACGCAGTTTGAGTAC-3′. Effectene or SuperFect (QIAGEN) was used to transfect plasmid DNA into HeLa or HEK293T cells, respectively. siRNA transfections for Bap31 (Szczesna-Skorupa and Kemper, 2006) were performed using Oligofectamine (Invitrogen).
Quantification of apoptosis
To measure the percentage cells with subG1 DNA content, cells were harvested and lysed in hypotonic lysis buffer (0.1% sodium citrate and 0.1% Triton X-100 in ddH2O) in the presence of propidium iodide (Sigma-Aldrich, 20 μg/ml) and analysed immediately. The mitochondrial depolarization was quantified using DiOC6 (Sigma-Aldrich, 40 nM) and counter stained with propidium iodide (6 μg/ml) in PBS. Cells were incubated for 90 min before analysis. Sample data were acquired using flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analysed with the FlowJo programme (TreeStar Inc.).
Caspase-8 and Bax activity assay
Caspase-8 assay was performed using CaspaTag™ caspase-8 assay kit (Millipore) according to the manufacturer's instructions. An antibody that specifically recognizes the activated form of Bax was used to measure its activity. Briefly, cells were incubated with the mouse α-Bax antibody (BD Pharmingen, clone 6A7) for 1 h in PBS with 3% BSA. Following washing, cells were incubated with an α-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 antibody (Invitrogen, Molecular Probes) for 1 h. Sample data were acquired using flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analysed with the FlowJo programme (TreeStar Inc.).
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting
Cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% SDS, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 1% IGEPAL) containing protease inhibitors (Fermentas), centrifuged, and the supernatant was pre-cleared with PureProteome™ protein G magnetic beads (Millipore). After pre-clearing, lysates were subjected to incubation with the respective antibody overnight with rotation at 4°C. The antibody–protein complexes were then immunoprecipitated with protein G magnetic beads and incubated for 1 h at 4°C. The beads were washed in RIPA buffer, resuspended in gel-loading dye (Fermentas), and were subjected to SDS–PAGE. Total cell lysates were prepared in RIPA buffer, likewise separated by SDS–PAGE, and the standard immunoblotting procedure was used. Antibodies used were mouse α-Bax, mouse α-GAPDH, GFP–HRP, mouse α-myc, and rabbit α-p38 from Santa-Cruz Biotechnologies; rabbit α-Bid and rabbit α-PARP from Cell Signalling; rabbit α-HA and rabbit α-Flag from Sigma-Aldrich; rabbit α-caspase-8 from Enzo Life Sciences; rabbit α-Bap31 from Proteintech; and rabbit α-Fis1 produced in our laboratory. Densitometry analysis was performed using ImageJ software.
Cytosolic and mitochondrial calcium measurement
Cells were harvested and resuspended in PBS (without CaCl2 supplement) containing either 2 μM of Fluo-4/AM or 1.0 μg/ml of Rhod-2/AM (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen) for 45 min in the incubator with frequent agitation. Cells were then washed and resuspended in PBS for FACS acquisition (BD Biosciences). To quantify the ER calcium content, 10 μM of thapsigargin (Merck Chemicals) was added to the tube after 30 s baseline calcium measurement.
Viral production and stable cell lines
The pLKO.1-TRC cloning vector (Moffat et al, 2006) was purchased from AddGene. The shRNA target sequence was cloned into the AgeI and EcoRI sites of the vector. The primers used were as follows: 5′-CCGGCAAGAGCACGCAGTTTGAGTACTCGAGTACTCAAACTGCGTGCTCTTGTTTTTG-3′ (forward) and 5′-AATTCAAAAACAAGAGCACGCAGTTTGAGTACTCGAGTACTCGAGTACTCAAACTGCGTGCTCTTG-3′ (reverse) for Fis1 shRNA and 5′-CCGGGACGCCTGGTGACTCTCATTTCTCGAGAAATGAGAGTCACCAGGCGTCTTTTTG-3′ (forward) and 5′-AATTCAAAAAGACGCCTGGTGACTCTCATTTCTCGAGAAATGAGAGTCACCAGGCGTC-3′ (reverse) for Bap31 shRNA. The plasmid encoding lentiviral shRNA against caspase-8 was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (TRCN0000003576). Viral particles were produced in HEK293T cells using the following protocol. Plasmids encoding for pVSV-G (5.4 μg, Invitrogen), pRev (3.8 μg, Invitrogen), pGag.Pol (7.8 μg, Invitrogen), pAdVantage (9 μg, Promega), and pLKO vector (20 μg) were mixed, replenished to 437.5 μl with water, and 62.5 μl of 2 M CaCl2 was added. After 5 min, DNA–calcium mix was transferred to 2 × HBS (500 μl) and added to cells dropwise for each 10 cm2 dish. Following overnight incubation, the medium was replaced with DMEM containing 1 mM sodium butyrate (Sigma-Aldrich). The supernatant was collected 48 h post transfection, centrifuged, and filtered (0.45 μm pore size). HeLa cells were transduced for 6 h in the presence of polybrene (6 μg/ml, Sigma). Cells were selected with puromycin (5 μg/ml) 3 days after transduction and cultured for further 3 days. Following the selection, cells were kept in the presence of 1 μg/ml puromycin.
Mitochondrial immunofluorescence
Cells were seeded on a glass-bottomed 24-well plate (Greiner Bio-One) and transfected. Cells were stained with tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (Invitrogen) diluted in DMEM for 15 min. Cells were washed twice with DMEM, 250 μl of DMEM was added, and were observed under a Leica TCS SP5 confocal laser-scanning microscope.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the unpaired student's t-test.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
RI was supported by the Deputy Rector's award and the Student Opportunity Fund from Imperial College, A-LM-M by a postdoc award from Breast Cancer Campaign, CD by a PhD studentship from Breast Cancer Campaign, and EP by a PhD studentship from CRUK. We thank Dr N Hajji for comments and Dr Remy Sadoul (Inserm U836, Grenoble, France) for expression vectors for DsRed-ER and YFP-mito.
Footnotes
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Albayrak T, Scherhammer V, Schoenfeld N, Braziulis E, Mund T, Bauer MK, Scheffler IE, Grimm S (2003) The tumor suppressor cybL, a component of the respiratory chain, mediates apoptosis induction. Mol Biol Cell 14: 3082–3096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alirol E, James D, Huber D, Marchetto A, Vergani L, Martinou JC, Scorrano L (2006) The mitochondrial fission protein hFis1 requires the endoplasmic reticulum gateway to induce apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 17: 4593–4605 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annaert WG, Becker B, Kistner U, Reth M, Jahn R (1997) Export of cellubrevin from the endoplasmic reticulum is controlled by BAP31. J Cell Biol 139: 1397–1410 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge DG, Nguyen M, Kuppig S, Reth M, Shore GC (2002) The procaspase-8 isoform, procaspase-8L, recruited to the BAP31 complex at the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 4331–4336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge DG, Stojanovic M, Marcellus RC, Shore GC (2003) Caspase cleavage product of BAP31 induces mitochondrial fission through endoplasmic reticulum calcium signals, enhancing cytochrome c release to the cytosol. J Cell Biol 160: 1115–1127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy-Stone A, Chipuk JE, Ingerman E, Song C, Yoo C, Kuwana T, Kurth MJ, Shaw JT, Hinshaw JE, Green DR, Nunnari J (2008) Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Dev Cell 14: 193–204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordas G, Varnai P, Golenar T, Roy S, Purkins G, Schneider TG, Balla T, Hajnoczky G (2010) Imaging interorganelle contacts and local calcium dynamics at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Mol Cell 39: 121–132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Brito OM, Scorrano L (2008) Mitofusin 2 tethers endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Nature 456: 605–610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmer SA, Chan DC (2007) Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 870–879 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri KF, Kroemer G (2001) Organelle-specific initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol 3: E255–E263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden M, James D, Castelbou C, Danckaert A, Martinou JC, Demaurex N (2004) Ca(2+) homeostasis during mitochondrial fragmentation and perinuclear clustering induced by hFis1. J Biol Chem 279: 22704–22714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain M, Mathai JP, McBride HM, Shore GC (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum BIK initiates DRP1-regulated remodelling of mitochondrial cristae during apoptosis. EMBO J 24: 1546–1556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais FG, Singaraja R, Xanthoudakis S, Gutekunst CA, Leavitt BR, Metzler M, Hackam AS, Tam J, Vaillancourt JP, Houtzager V, Rasper DM, Roy S, Hayden MR, Nicholson DW (2002) Recruitment and activation of caspase-8 by the Huntingtin-interacting protein Hip-1 and a novel partner Hippi. Nat Cell Biol 4: 95–105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenendyk J, Lynch J, Michalak M (2004) Calreticulin, Ca2+, and calcineurin—signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cells 17: 383–389 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagasia R, Grote P, Westermann B, Conradt B (2005) DRP-1-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation during EGL-1-induced cell death in C. elegans. Nature 433: 754–760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James DI, Parone PA, Mattenberger Y, Martinou JC (2003) hFis1, a novel component of the mammalian mitochondrial fission machinery. J Biol Chem 278: 36373–36379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornmann B, Currie E, Collins SR, Schuldiner M, Nunnari J, Weissman JS, Walter P (2009) An ER-mitochondria tethering complex revealed by a synthetic biology screen. Science 325: 477–481 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee YJ, Jeong SY, Karbowski M, Smith CL, Youle RJ (2004) Roles of the mammalian mitochondrial fission and fusion mediators Fis1, Drp1, and Opa1 in apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 15: 5001–5011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94: 491–501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, Kim SY, Kloepfer AM, Hinkle G, Piqani B, Eisenhaure TM, Luo B, Grenier JK, Carpenter AE, Foo SY, Stewart SA, Stockwell BR, Hacohen N, Hahn WC, Lander ES, Sabatini DM, Root DE (2006) A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell 124: 1283–1298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mund T, Gewies A, Schoenfeld N, Bauer MK, Grimm S (2003) Spike, a novel BH3-only protein, regulates apoptosis at the endoplasmic reticulum. FASEB J 17: 696–698 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, O'Rourke K, Shevchenko A, Ni J, Scaffidi C, Bretz JD, Zhang M, Gentz R, Mann M, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Dixit VM (1996) FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death--inducing signaling complex. Cell 85: 817–827 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng FW, Nguyen M, Kwan T, Branton PE, Nicholson DW, Cromlish JA, Shore GC (1997) p28 Bap31, a Bcl-2/Bcl-XL- and procaspase-8-associated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol 139: 327–338 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen M, Breckenridge DG, Ducret A, Shore GC (2000) Caspase-resistant BAP31 inhibits fas-mediated apoptotic membrane fragmentation and release of cytochrome c from mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol 20: 6731–6740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P (2003) Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 552–565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquet ME, Cohen-Doyle M, Shore GC, Williams DB (2004) Bap29/31 influences the intracellular traffic of MHC class I molecules. J Immunol 172: 7548–7555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed JC, Doctor KS, Godzik A (2004) The domains of apoptosis: a genomics perspective. Sci STKE 2004: re9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R, Pinton P, Carrington W, Fay FS, Fogarty KE, Lifshitz LM, Tuft RA, Pozzan T (1998) Close contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+ responses. Science 280: 1763–1766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P, Tschopp J (2000) Apoptosis induced by death receptors. Pharm Acta Helv 74: 281–286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld N, Bauer MK, Grimm S (2004) The metastasis suppressor gene C33/CD82/KAI1 induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen intermediates. FASEB J 18: 158–160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan C, Delivani P, Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2008) Bax- or Bak-induced mitochondrial fission can be uncoupled from cytochrome C release. Mol Cell 31: 570–585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen T, Aslan JE, Blagoveshchenskaya AD, Thomas L, Wan L, Xiang Y, Feliciangeli SF, Hung CH, Crump CM, Thomas G (2005) PACS-2 controls endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria communication and Bid-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J 24: 717–729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiliotis ET, Manley H, Osorio M, Zuniga MC, Edidin M (2000) Selective export of MHC class I molecules from the ER after their dissociation from TAP. Immunity 13: 841–851 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojanovic M, Germain M, Nguyen M, Shore GC (2005) BAP31 and its caspase cleavage product regulate cell surface expression of tetraspanins and integrin-mediated cell survival. J Biol Chem 280: 30018–30024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stupack DG, Puente XS, Boutsaboualoy S, Storgard CM, Cheresh DA (2001) Apoptosis of adherent cells by recruitment of caspase-8 to unligated integrins. J Cell Biol 155: 459–470 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suen DF, Norris KL, Youle RJ (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev 22: 1577–1590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczesna-Skorupa E, Kemper B (2006) BAP31 is involved in the retention of cytochrome P450 2C2 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 281: 4142–4148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A, Youle RJ (2008) A chemical inhibitor of DRP1 uncouples mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. Mol Cell 29: 409–410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinel A, Tschopp J (2004) The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress. Science 304: 843–846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance JE (1990) Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J Biol Chem 265: 7248–7256 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Heath-Engel H, Zhang D, Nguyen N, Thomas DY, Hanrahan JW, Shore GC (2008) BAP31 interacts with Sec61 translocons and promotes retrotranslocation of CFTRDeltaF508 via the derlin-1 complex. Cell 133: 1080–1092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak AL, Wang X, Stieren ES, Scarbrough SG, Elferink CJ, Boehning D (2006) Requirement of biphasic calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum for Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Cell Biol 175: 709–714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle RJ, Karbowski M (2005) Mitochondrial fission in apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 657–663 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen K, Utech M, Liu Y, Soto I, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2004) Association of BAP31 with CD11b/CD18. Potential role in intracellular trafficking of CD11b/CD18 in neutrophils. J Biol Chem 279: 44924–44930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.