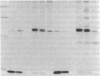
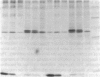
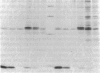
Abstract
Familial dysautonomia is a hereditary disorder that affects autonomic and sensory neurons. Nerve growth factor (NGF) is required for the normal development of sympathetic and sensory neurons and it has been postulated that an abnormality involving NGF may be responsible for familial dysautonomia. Previous studies have shown that the beta-NGF gene is not linked to the disease. However, NGF appears to be abnormal by immunochemical assays; the putative altered form of NGF could result from a disturbance in the processing pathway. To study the processing of the 35-kD glycosylated NGF precursor and the secretion of NGF in familial dysautonomia, we have employed a recombinant vaccinia virus vector to express high levels of NGF mRNA in primary fibroblast cultures from patients with the disorder; the processing pathway was then studied directly. Cells from several unrelated patients all produce the same 35-kD NGF precursor, process this normally to NGF within the cell, and release NGF into the medium. There are no differences in the ability of cells from patients and from unaffected relatives to process and secrete NGF. The use of similar recombinant vaccinia virus vectors to express proteins at high level in primary cell lines should facilitate the detection of posttranslational processing defects in a variety of human disorders.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breakefield X. O., Orloff G., Castiglione C., Coussens L., Axelrod F. B., Ullrich A. Structural gene for beta-nerve growth factor not defective in familial dysautonomia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4213–4216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunt P. W., McKusick V. A. Familial dysautonomia. A report of genetic and clinical studies, with a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1970 Sep;49(5):343–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Selby M. J., Garcia P. D., Rutter W. J. Processing of the native nerve growth factor precursor to form biologically active nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6810–6815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. Differential RNA splicing predicts two distinct nerve growth factor precursors. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):784–787. doi: 10.1038/319784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Purification and characterization of enkephalin convertase, an enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10950–10955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C., Gitlow S. E., Alton H. Decreased noradrenaline (norepinephrine) synthesis in familial dysautonomia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2734–2740. doi: 10.1172/JCI106774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin P. D., Johnson E. M. Experimental autoimmune model of nerve growth factor deprivation: effects on developing peripheral sympathetic and sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5382–5386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M., Varon S. Enzymatic activities of mouse nerve growth factor and its subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1383–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Bradshaw R. A. The alpha-subunit of mouse 7 S nerve growth factor is an inactive serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5380–5383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. Trafficking of lysosomal enzymes in normal and disease states. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI112262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. DESTRUCTION OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA IN MAMMALS BY AN ANTISERUM TO A NERVE-GROWTH PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):384–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Landis S. C., Bernanke J., Siminoski K. Absence of the alpha and gamma subunits of 7S nerve growth factor in denervated rodent iris: immunocytochemical studies. Dev Biol. 1986 Apr;114(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. C., Brennan S. O., Lewis J. H., Carrell R. W. Mutation of antitrypsin to antithrombin. alpha 1-antitrypsin Pittsburgh (358 Met leads to Arg), a fatal bleeding disorder. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 22;309(12):694–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309223091203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis N. J. Nerve growth factor synthesized by mouse fibroblast cells in culture: absence of alpha and gamma subunits. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4264–4271. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Pytel B. A., Grover-Johnson N., Axelrod F., Dancis J. Quantitative studies of dorsal root ganglia and neuropathologic observations on spinal cords in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Jan;35(1):77–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Pytel B. A. Quantitative studies of sympathetic ganglia and spinal cord intermedio-lateral gray columns in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Pytel B. Quantitative studies of ciliary and sphenopalatine ganglia in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Franke C. A., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Expression of Sindbis virus structural proteins via recombinant vaccinia virus: synthesis, processing, and incorporation into mature Sindbis virions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):227–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.227-239.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos M. J., Ojeda J. M., Garrido J., Leighton F. Peroxisomal organization in normal and cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6556–6560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Breakefield X. O. Altered nerve growth factor in fibroblasts from patients with familial dysautonomia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggers D. C., Rogers J. G., Boyer S. H., Margolet L., Dorkin H., Banerjee S. P., Shooter E. M. Increased nerve-growth-factor beta-chain cross-reacting material in familial dysautonomia. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 16;295(12):629–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609162951201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Nonpolarized expression of a secreted murine leukemia virus glycoprotein in polarized epithelial cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Physiology of nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1284–1335. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Herbert E., Hruby D. E. Expression and cell type--specific processing of human preproenkephalin with a vaccinia recombinant. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1641–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.3754979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Normura J., Shooter E. M. Reversible dissociation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein into different subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1296–1303. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]