Abstract
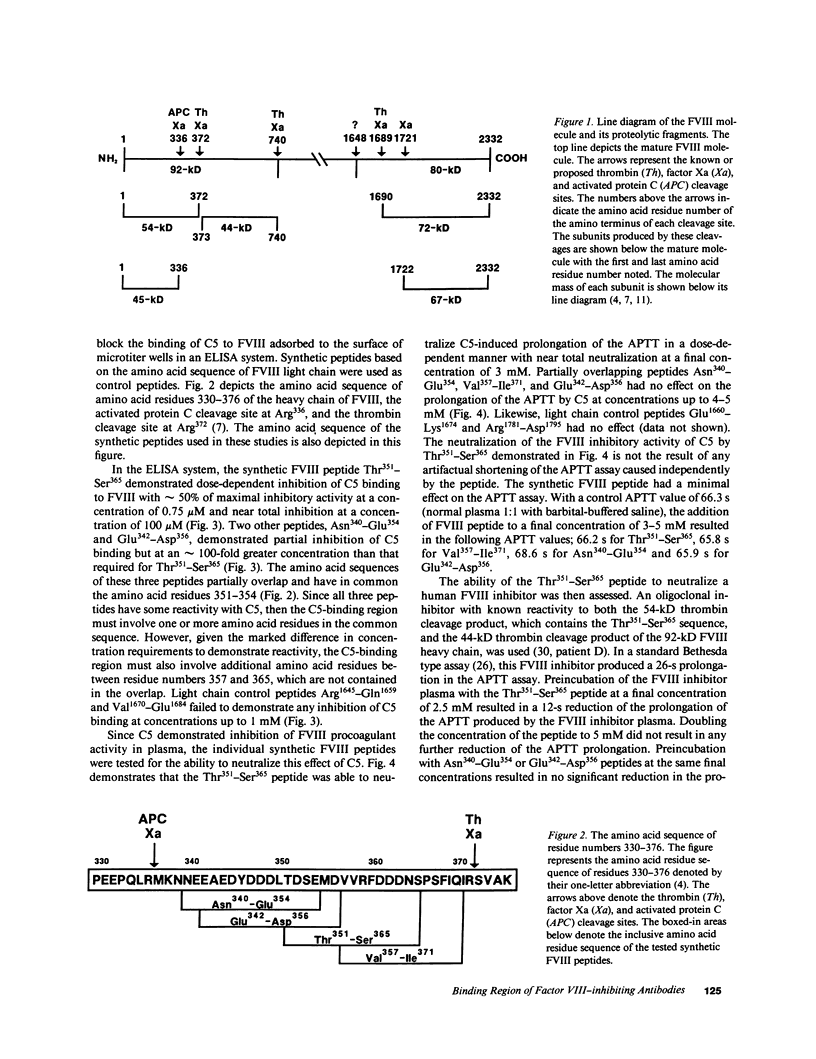
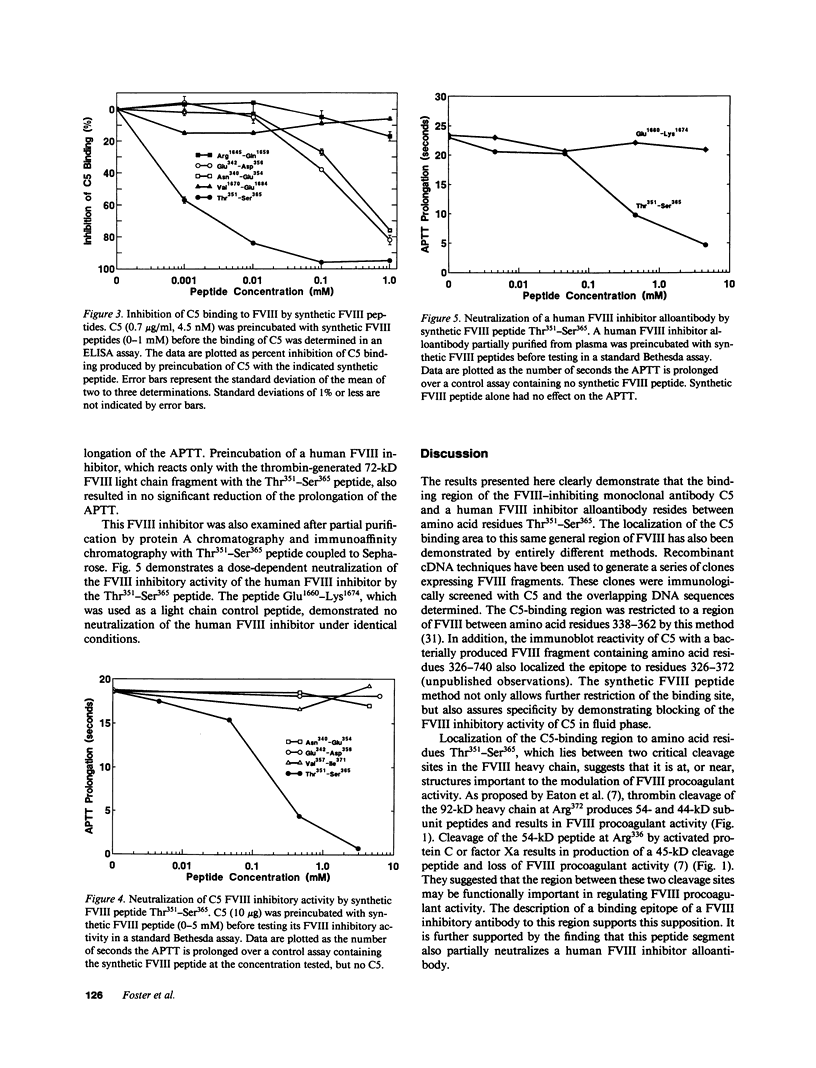
We have localized the binding region of a previously described monoclonal anti-factor VIII (FVIII) inhibitory antibody (C5) to amino acid residues Thr351-Ser365 of the thrombin-generated 54-kD fragment of the heavy chain of FVIII. Synthetic FVIII peptides were examined for the ability to competitively inhibit the binding of C5 to FVIII in an ELISA system. The synthetic FVIII peptide Thr351-Ser365 blocked C5 binding to FVIII in a dose-dependent manner in this system. Two other synthetic FVIII peptides, Asn340-Glu354 and Glu342-Asp356, which partially overlapped Thr351-Ser365, also blocked C5 binding to FVIII. Blocking of C5 binding with these peptides, however, required much greater concentrations (greater than 100 times stronger) than that required for Thr351-Ser365. The Thr351-Ser365 peptide also neutralized the FVIII inhibitory activity of C5 in plasma. A human FVIII inhibitor (anti-FVIII heavy chain alloantibody) was also partially neutralized by Thr351-Ser365. Thr351-Ser365 lies between a thrombin cleavage site (Arg372) and an activated protein C cleavage site (Arg336) and may be at or near a region of functional importance in the expression of FVIII procoagulant activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Hass P. E., Riddle L., Mather J., Wiebe M., Gregory T., Vehar G. A. Characterization of recombinant human factor VIII. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3285–3290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Vehar G. A. Factor VIII structure and proteolytic processing. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1986;8:47–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D., Rodriguez H., Vehar G. A. Proteolytic processing of human factor VIII. Correlation of specific cleavages by thrombin, factor Xa, and activated protein C with activation and inactivation of factor VIII coagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):505–512. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass D. N., Knutson G. J., Katzmann J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to porcine factor VIII coagulant and their use in the isolation of active coagulant protein. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Anderson M. T., Chavin S. I., Marder V. J. The size of human factor VIII heterodimers and the effects produced by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 23;871(3):268–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Houghten R. A., Zimmerman T. S. An immunogenic region within residues Val1670-Glu1684 of the factor VIII light chain induces antibodies which inhibit binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5230–5234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Gardiner J. E., Griffin J. H., Zimmerman T. S. Proteolytic inactivation of human factor VIII procoagulant protein by activated human protein C and its analogy with factor V. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):486–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Holland L. Z., Zimmerman T. S. Human factor VIII procoagulant protein. Monoclonal antibodies define precursor-product relationships and functional epitopes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI111933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Zimmerman T. S. Thrombin proteolysis of purified factor viii procoagulant protein: correlation of activation with generation of a specific polypeptide. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Roberts J. R., Kasper C. K., Zimmerman T. S. Localization of human factor FVIII inhibitor epitopes to two polypeptide fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7728–7732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Zimmerman T. S. FVIII inhibitor IgG subclass and FVIII polypeptide specificity determined by immunoblotting. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1475–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Zimmerman T. S. FVIII inhibitor IgG subclass and FVIII polypeptide specificity determined by immunoblotting. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1475–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Goralka T. M., Wion K. L., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Vehar G. A., Capon D. J., Lawn R. M. Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):326–330. doi: 10.1038/312326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Nemerson Y. Activation of factor X by factors IXa and VIII; a specific assay for factor IXa in the presence of thrombin-activated factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):928–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Ashby M. A., Lazarchick J. J., Sens D. A. Mechanism of factor VIII inactivation by human antibodies. IV. Antibody binding prevents factor VIII proteolysis by thrombin. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1986 Nov-Dec;16(6):497–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: A more uniform measurement of factor VIII inhibitors. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):869–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordfang O., Ezban M., Dinesen B. Reactivity of factor VIII inhibitors in a micro ELISA for factor VIII: CAg and in solid phase immunoisolation of VIII: CAg. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Jun 24;53(3):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordfang O., Ezban M., Favaloro J. M., Dahl H. H., Hansen J. J. Specificity of monoclonal antibodies to factor VIII:C. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):586–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotblat F., O'Brien D. P., O'Brien F. J., Goodall A. H., Tuddenham E. G. Purification of human factor VIII:C and its characterization by Western blotting using monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4294–4300. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Knopf J. L., Wozney J. M., Sultzman L. A., Buecker J. L., Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J., Brown E., Shoemaker C., Orr E. C. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human antihaemophilic factor. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):342–347. doi: 10.1038/312342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Pittman D., Murtha P., Wasley L. C., Wang J., Amphlett G., Hewick R., Foster W. B., Kamen R., Kaufman R. J. Exploration of structure-function relationships in human factor VIII by site-directed mutagenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):543–549. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Keyt B., Eaton D., Rodriguez H., O'Brien D. P., Rotblat F., Oppermann H., Keck R., Wood W. I., Harkins R. N. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):337–342. doi: 10.1038/312337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Capon D. J., Simonsen C. C., Eaton D. L., Gitschier J., Keyt B., Seeburg P. H., Smith D. H., Hollingshead P., Wion K. L. Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):330–337. doi: 10.1038/312330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


