Abstract
Kytococcus sedentarius (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Stackebrandt et al. 1995 is the type strain of the species, and is of phylogenetic interest because of its location in the Dermacoccaceae, a poorly studied family within the actinobacterial suborder Micrococcineae. Kytococcus sedentarius is known for the production of oligoketide antibiotics as well as for its role as an opportunistic pathogen causing valve endocarditis, hemorrhagic pneumonia, and pitted keratolysis. It is strictly aerobic and can only grow when several amino acids are provided in the medium. The strain described in this report is a free-living, nonmotile, Gram-positive bacterium, originally isolated from a marine environment. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence, and annotation. This is the first complete genome sequence of a member of the family Dermacoccaceae and the 2,785,024 bp long single replicon genome with its 2639 protein-coding and 64 RNA genes is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: mesophile, free-living, marine, aerobic, opportunistic pathogenic, Dermacoccaceae
Introduction
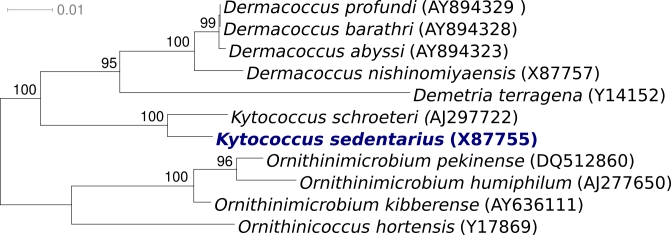
Strain 541T (DSM 20547 = ATCC 14392 = JCM 11482 = CCM 314 and other culture collections) is the type strain of the species Kytococcus sedentarius, which is the type species of the genus Kytococcus [1]. Strain 541T was first described as Micrococcus sedentarius (ZoBell and Upham 1944) [2] and later emended as Kytococcus sedentarius in a taxonomic dissection of the genus Micrococcus [1]. The organism is of interest for its biotechnological potential as source of natural antibiotics (oligoketides), for its role as an opportunistic pathogen, and for its position in the tree of life, where it represents the scarcely populated genus Kytococcus (2 species) within in the actinobacterial family Dermacoccaceae [1] (Figure 1). Kytococcus sedentarius 541T was first isolated around 1944 from a marine environment [2], but strains of the species were also frequently isolated from human skin [7]. More recently, closely related strains were also isolated from culture-dependant environmental screenings of a non-saline alkaline groundwater environment in Cabeco de Vide in southern Portugal [8], screening for pelagic bacteria in South Korea [9], tropical marine sediments from the intertidal zone off the coast of the Republic Palau [10], from the ciliate Collinia sp.), an endoparasite of euphausiids from the Gulf of California (unpublished literature, GenBank record EU090136), and in a culture-independent analysis of the microbial burden and diversity in commercial airline cabins [11]. Screening of environmental genomic samples and surveys reported at the NCBI BLAST server indicated no closely related phylotypes that can be linked to the species or genus. Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T (Table 1), together with the description of the complete genomic sequencing and annotation.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T with all type strains of the family Dermacoccaceae, inferred from 1,456 aligned 16S rRNA characters [3] under the maximum likelihood criterion [4,5]. The tree was rooted with four members of the neighboring family Intrasporangiaceae. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers above branches are support values from 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Strains with a genome-sequencing project registered in GOLD [6] are printed in blue; published genomes in bold.
Table 1. Classification and general features of Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T based on MIGS recommendations [12].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria | ||
| Phylum Actinobacteria | |||
| Class Actinobacteria | TAS [13] | ||
| Order Actinomycetales | TAS [14] | ||
| Suborder Micrococcineae | TAS [13] | ||
| Family Dermacoccaceae | TAS [15] | ||
| Genus Kytococcus | TAS [1] | ||
| Species Kytococcus sedentarius | TAS [1] | ||
| Type strain 541 | |||
| Gram stain | positive | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | spherical, predominantly in tetrads | TAS [1] | |
| Motility | nonmotile | TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | non-sporulating | TAS [1] | |
| Temperature range | mesophilic | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | 28-36°C | TAS [1] | |
| Salinity | nonhalophilic, but growth in media up to 10% (w/v) NaCl |
TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | mandatory aerobe | TAS [1] |
| Carbon source | not reported | ||
| Energy source | unknown, not starch | NAS | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | marine | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | free-living | NAS |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | in rare cases | TAS [16,17] |
| Biosafety level | 1 | TAS [18] | |
| Isolation | slide submerged in sea water | TAS [2] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | probably San Diego | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | about or before 1944 | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-4.1 MIGS-4.2 | Latitude – Longitude | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | not reported |
Evidence codes - IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay (first time in publication); TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [19]. If the evidence code is IDA, then the property was directly observed, for a live isolate by one of the authors, or another expert mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Classification and features
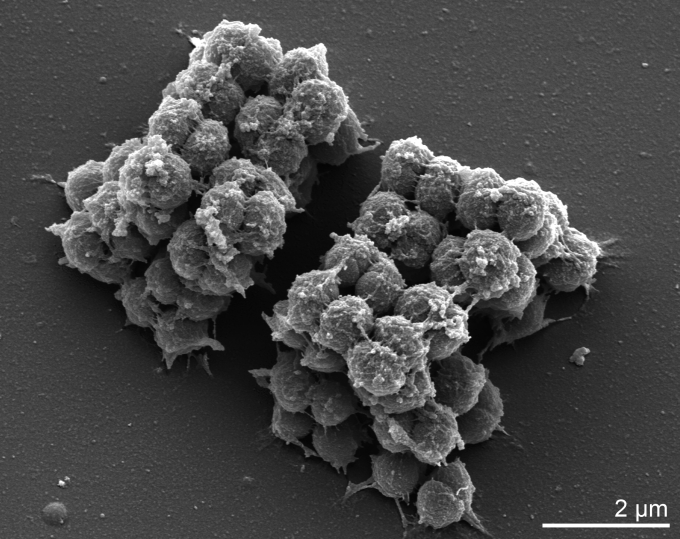
Kytococcus sedentarius cells are spherical/coccoid and occur predominantly in tetrads which can be arranged in cubical packets [1] (Figure 2). Cells are described as Gram-positive, nonmotile, non-encapsulated, and not endospore-forming [1]. Kytococcus sedentarius 541T is strictly aerobic and chemoorganotrophic, requires methionine and other amino acids for growth, and grows well in NaCl at concentrations up to 10% (w/v) [1].
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T (Manfred Rohde, Helmholtz Centre for Infection Biology, Braunschweig)
Kytococcus sedentarius (strain NK0508) is capable of degrading diphenylarsenic acid [20], but not starch [1], and does not produce acids from most carbohydrates and alcohols [1]. Its optimal growth temperature is 28-36°C. Nitrate is reduced to nitrite by some Kytococcus sedentarius strains [1]. Kytococcus sedentarius is not only described as the source of the oligoketide antibiotics monensin A and B [21], but has also been associated with pitted keratolysis [16], opportunistic infections, and fatal hemorrhagic pneumonia [17].
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T in a 16S rRNA based tree. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene copies in the genome of strain 541T differed by one nucleotide from each other, and by up to two nucleotides from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence generated from DSM 20547 (X87755).
Chemotaxonomy
The murein of Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T contains L-Lys-Glu2, a variation of cell wall type A4α [1]. Mycolic acids and teichonic acids were not reported [1]. Strain 541T contains only completely unsaturated menaquinones with 8-11 isoprene subunits (MK8 to MK11), with MK8 dominating [1]. The major cellular fatty acids are methyl-branched chain iso-C17:1 and anteiso-C17:0, as well as the straight chain saturated C15:0 and C17:0 [1]. Phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, and phosphatidylinositol were identified as dominating polar lipids [1]. Reported cytochromes include aa3, c626, c550, b557, b561, and b564 [1].
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its phylogenetic position, and is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project. The genome project is deposited in the Genome OnLine Database [6] and is deposited in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI). A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Two genomic Sanger libraries: 8kb pMCL200 and fosmid pcc1Fos libraries. |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | ABI3730 |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 17.3 x Sanger |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | phrap |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Genemark 4.6b, tRNAScan-SE-1.23, infernal 0.81 |
| Genbank ID | ABUD00000000 | |
| Genbank Date of Release | N/A | |
| NCBI project ID | 21067 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc01042 | |
| Database: IMG-GEBA | 2500901761 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 20547 |
| Project relevance | Tree of Life, GEBA |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T, DSM20547, was grown in DSMZ medium 92 (3% trypticase soy broth, 0.3% yeast extract) at 30°C. DNA was isolated from 1-1.5 g of cell paste using Qiagen Genomic 500 DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with a modified protocol for cell lysis in first freezing for 20 min. (-70°C), then heating 5 min. (98°C), and cooling 15 min to 37°C; adding 1.5 ml lysozyme (standard: 0.3 ml, only), 1.0 ml achromopeptidase, 0.12 ml lysostaphine, 0.12 ml mutanolysine, 1.5 ml proteinase K (standard: 0.5 ml, only), followed by overnight incubation at 35°C.
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using a combination of 8 kb and fosmid DNA libraries. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing performed at the JGI website. Draft assemblies were based on 60,742 total reads. The Phred/Phrap-/Consed software package was used for sequence assembly and quality assessment [22-24]. After the shotgun stage, reads were assembled with parallel phrap (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with Dupfinisher [25] or transposon bombing of bridging clones (Epicentre Biotechnologies, Madison, WI). Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, custom priming, or PCR amplification (Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN). A total of 1,255 additional reactions were necessary to close gaps and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. The completed genome sequence of Kytococcus sedentarius 541T contains 61,582 reads. The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. Together all libraries provided > 17x coverage of the genome.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using GeneMark [26] as part of the genome annotation pipeline in the Integrated Microbial Genomes Expert Review (IMG-ER) system [27], followed by a round of manual curation using JGI’s GenePRIMP pipeline. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant database, UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. The tRNAScanSE tool [28] was used to find tRNA genes, whereas ribosomal RNAs were found by using the tool RNAmmer [29]. Other non-coding RNAs were identified by searching the genome for the Rfam profiles using INFERNAL (v0.81) [30]. Additional gene prediction analysis and manual functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes (IMG) platform [31].
Metabolic network analysis
The metabolic Pathway/Genome Database (PGDB) was computationally generated using Pathway Tools software version 12.5 [32] and MetaCyc version 12.5 [33], based on annotated EC numbers and a customized enzyme name mapping file. It has undergone no subsequent manual curation and may contain errors, similar to a Tier 3 BioCyc PGDB [34].
Genome properties
The genome is 2,785,024 bp long and comprises one main circular chromosome with a 71.6% GC content (Table 3 and Figure 3). Of the 2,703 genes predicted, 2,639 were protein-coding genes, 64 encoded RNAs. Eighty-four pseudogenes were also identified. In addition, 72.1% of the genes were assigned with a putative function while the remaining ones were annotated as hypothetical proteins.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 2,785,024 | |
| DNA Coding region (bp) | 2,558,989 | 91.88% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 1,994,844 | 71.63% |
| Number of replicons | 1 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 0 | |
| Total genes | 2703 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 64 | 2.37% |
| rRNA operons | 2 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 2639 | 97.63% |
| Pseudo genes | 84 | 3.11% |
| Genes with function prediction | 1948 | 72.07% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 288 | 10.65% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 1851 | 68.48% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 1908 | 70.59% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 539 | 19.94% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 595 | 22.01% |
| CRISPR repeats | 0 | 0 |
Figure 3.
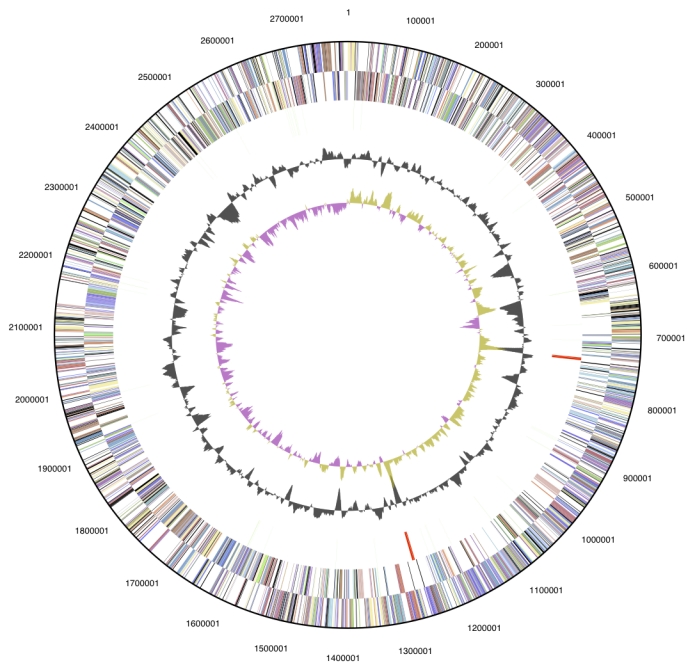
Graphical circular map of the genome. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
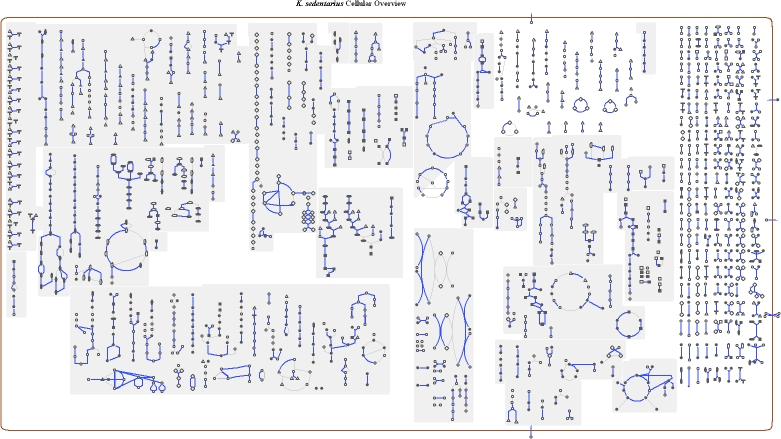
The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4, and a cellular overview diagram is presented in Figure 4, followed by a summary of metabolic network statistics shown in Table 5.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the 21 general COG functional categories.
| Code | Value | %age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 151 | 5.7 | Translation |
| A | 1 | 0.0 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 143 | 5.4 | Transcription |
| L | 160 | 6.1 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 2 | 0.1 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 22 | 0.8 | Cell cycle control, mitosis and meiosis |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| V | 56 | 2.1 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 73 | 2.8 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 111 | 4.2 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 2 | 0.1 | Cell motility |
| Z | 1 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 0 | 0.0 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 27 | 1.0 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion |
| O | 64 | 2.4 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 99 | 3.8 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 116 | 4.4 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 185 | 7.0 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 75 | 2.8 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 101 | 3.8 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 86 | 3.3 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 117 | 4.4 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 46 | 1.7 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 229 | 8.7 | General function prediction only |
| S | 160 | 6.1 | Function unknown |
| - | 788 | 29.9 | Not in COGs |
Figure 4.
Schematic cellular overview of all pathways of the Kytococcus sedentarius strain 541T metabolism. Nodes represent metabolites, with shape indicating class of metabolite. Lines represent reactions.
Table 5. Metabolic Network Statistics.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Total genes | 2703 |
| Enzymes | 531 |
| Enzymatic reactions | 922 |
| Metabolic pathways | 185 |
| Metabolites | 662 |
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the help of Katja Steenblock (DSMZ) for growing Kytococcus sedentarius 541T cultures. This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy Office of Science, Biological and Environmental Research Program, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, and Los Alamos National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396, as well as German Research Foundation (DFG)INST 599/1-1.
References
- 1.Stackebrandt E, Koch C, Gvozdiak O, Schumann P. Taxonomic dissection of the genus Micrococcus: Kocuria gen. nov., Nesterenkonia gen. nov., Kytococcus gen. nov., Dermacoccus gen. nov., and Micrococcus Cohn 1872 gen. emend. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1995; 45:682-692 10.1099/00207713-45-4-682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.ZoBell CE Upham HC. A list of marine bacteria including descriptions of sixty new species. Bull Scripps Inst Oceanogr Calif 1944; 5:239-292 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18:452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 1981; 17:368-376 10.1007/BF01734359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. [doi:10.1080/10635150802429642]. [pmid:18853362] Syst Biol 2008; 57:758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Liolios K, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Kyrpides NC. The Genomes On Line Database (GOLD) in 2007: status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36:D475-D479 10.1093/nar/gkm884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kloss WE, Tornabebe TG, Schleifer KH. Isolation and characterization of Micrococci from human skin, including two species: Micrococcus lylae and Micrococcus kristinae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1974; 24:79-101 10.1099/00207713-24-1-79 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tiago I, Chung AP, Verissimo A. Bacterial diversity in a nonsaline alkaline environment: heterotrophic aerobic populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004; 70:7378-7387 10.1128/AEM.70.12.7378-7387.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bhattarai HD, Lee YK, Cho KH, Lee HK, Shin HE. The study of antagonistic interactions among pelagic bacteria: a promising way to coin environmental friendly antifouling compounds. Hydrobiologica 2006; 568:417-423 10.1007/s10750-006-0220-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gontang EA, Fenical W, Jensen PR. Phylogenetic diversity of gram-positive bacteria cultured from marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007; 73:3272-3282 10.1128/AEM.02811-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Osman S, La Duc MT, Dekas A, Newcombe D, Venkateswaran K. Microbial burden and diversity of commercial airline cabin air during short and long durations of travel. ISME J 2008; 2:482-497 10.1038/ismej.2008.11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stackebrandt E, Rainey F, Ward-Rainey N. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1997; 47:479-491 10.1099/00207713-47-2-479 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Buchanan RE. Studies in the Nomenclature and Classification of the Bacteria: VIII. The Subgroups and Genera of the Actinomycetales. J Bacteriol 1918; 3:403-406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stackebrandt E, Schumann P. Description of Bogoriellaceae fam. nov., Dermacoccaceae fam. nov., Rarobacteraceae fam. nov. and Sanguibacteraceae fam. nov. and emendation of some families of the suborder Micrococcineae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2000; 50:1279-1285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Longshaw CM, Wright JD, Farrell AM, Holland KT. Kytococcus sedentarius, the organism associated with pitted keratolysis, produces two keratin-degrading enzymes. J Appl Microbiol 2002; 93:810-816 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2002.01742.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Levenga H, Donnelly P, Blijlevens N, Verweij P, Shirango H, de Pauw B. Fatal hemorrhagic pneumonia caused by infection due to Kytococcus sedentarius--a pathogen or passenger? Ann Hematol 2004; 83:447-449 10.1007/s00277-003-0831-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Anonymous. Biological Agents: Technical rules for biological agents. www.baua.de
- 19.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nakamiya K, Nakayama T, Ito H, Edmonds JS, Shibata Y, Morita M. Degradation of arylarsenic compounds by microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2007; 274:184-188 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00835.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pospísil S, Benada O, Kofronova O, Petricek M, Janda L, Havlicek V. Kytococcus sedentarius (formerly Micrococcus sedentarius) and Dermacoccus nishinomiyaensis (formerly Micrococcus nishinomiyaensis) produce monensins, typical Streptomyces cinnamonensis metabolites. Can J Microbiol 1998; 44:1007-1011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ewing B, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 1998; 8:186-194 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 1998; 8:175-185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P. Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res 1998; 8:195-202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Han CS, Chain P. Finishing repeat regions automatically with Dupfinisher. In: Arabnia AR, Valafar H, Editors. Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Bioinformatics & Computational Biology; 2006 June 26-29. CSREA Press. p 141-146. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M. GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29:2607-2618 10.1093/nar/29.12.2607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Markowitz V, Mavromatis K, Ivanova N, Chen I-M, Chu K, Palaniappan K, Szeto E, Anderson I, Lykidis A, Kyrpides N. Expert Review of Functional Annotations for Microbial Genomes. (Submited 2009).
- 28.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 1997; 25:955-964 10.1093/nar/25.5.955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rodland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35:3100-3108 10.1093/nar/gkm160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Griffiths-Jones S, Moxon S, Marshall M, Khanna A, Eddy SR, Bateman A. Rfam: annotating non-coding RNAs in complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33:D121-D124 10.1093/nar/gki081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Markowitz VM, Szeto E, Palaniappan K, Grechkin Y, Chu K, Chen IM, Dubchak I, Anderson I, Lykidis A, Mavromatis K, et al. The integrated microbial genomes (IMG) system in 2007: data content and analysis tool extensions. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36:D528-D533 10.1093/nar/gkm846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Karp PD, Paley S, Romero P. The pathway tools software. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Caspi R, Foerster H, Fulcher CA, Kaipa P, Krummenacker M, Latendresse M, Paley S, Rhee SY, Shearer AG, Tissier C, et al. The MetaCyc Database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36:D623-D631 10.1093/nar/gkm900 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Karp PD, Ouzounis CA, Moore-Kochlacs C, Goldovsky L, Kaipa P, Ahren D, Tsoka S, Darzentas N, Kunin V, Lopez-Bigas N. Expansion of the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases to 160 genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33:6083-6089 10.1093/nar/gki892 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]