Abstract
Methanocorpusculum labreanum is a methanogen belonging to the order Methanomicrobiales within the archaeal kingdom Euryarchaeota. The type strain Z was isolated from surface sediments of Tar Pit Lake in the La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles, California. M. labreanum is of phylogenetic interest because at the time the sequencing project began only one genome had previously been sequenced from the order Methanomicrobiales. We report here the complete genome sequence of M. labreanum type strain Z and its annotation. This is part of a 2006 Joint Genome Institute Community Sequencing Program project to sequence genomes of diverse Archaea.
Keywords: archaea, methanogen, Methanomicrobiales
Introduction
Methanocorpusculum labreanum is a methanogen belonging to the order Methanomicrobiales within the archaeal kingdom Euryarchaeota. Strain Z is the type strain of this species. It was isolated from surface sediments of Tar Pit Lake at the La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles [1]. Most of the other described members of this family have been isolated from anaerobic digesters or waste water [2]. The genus covers organisms with a wide temperature range. One psychrotolerant strain was isolated from a Russian pond polluted with paper mill waste water [3], while other strains were found in heated sediment at a hydrothermal vent site [4]. Methanocorpusculum species may be common in subsurface environments as they were the most prominent genus found in a coal bed in Indiana [5] and in shale in northern Michigan [6].
Methanogens have been divided into two groups known as Class I and Class II based on phylogeny [7]. Class I includes the orders Methanococcales, Methanobacteriales, and Methanopyrales, which use H2/CO2 or formate as substrates for methanogenesis, although some can also use alcohols as electron donors. Class II includes the orders Methanosarcinales and Methanomicrobiales. Some of the Methanosarcinales are capable of using various methyl compounds as substrates for methanogenesis including acetate, methylamines, and methanol, but Methanomicrobiales are restricted to the same substrates as the Class I methanogens [2]. Therefore, Methanomicrobiales are phylogenetically closer to Methanosarcinales but physiologically more similar to Class I methanogens, making them an interesting target for genome sequencing. In a 2006 Community Sequencing Program (CSP) project, we proposed sequencing two members of the order Methanomicrobiales: M. labreanum and Methanoculleus marisnigri. Previously only one genome was available from this order, that of Methanospirillum hungatei. Methanocorpusculum labreanum and Methanoculleus marisnigri are phylogenetically distant from each other and from Methanospirillum hungatei (Figure 1), and they represent the three families within the order Methanomicrobiales. We report here the sequence and annotation of M. labreanum type strain Z.
Figure 1.
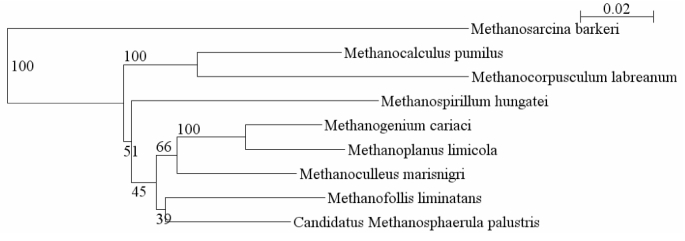
Phylogenetic tree of 16S rRNA of selected Methanomicrobiales showing the distance between the three organisms for which complete genomes are available – Methanospirillum hungatei, Methanocorpusculum labreanum, and Methanoculleus marisnigri. The tree uses sequences aligned within the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP), and the tree was constructed with the RDP Tree Builder [8]. Methanosarcina barkeri was used as the outgroup. The numbers indicate bootstrap values based on 100 replicates.
Organism information
Methanocorpusculum labreanum Z was isolated from surface sediments at the La Brea Tar Pits [1]. A polypropylene bottle was filled with half surface sediment and half lake water. In an anaerobic chamber the contents of the bottle were mixed to suspend the sediment, and 0.5 ml of the slurry was added to 5 ml enrichment medium. The enrichment medium contained sodium formate, trypticase peptone, and salts. The gas phase was H2-CO2 at a ratio of 4:1 and a pressure of 152 kPa. The physiological characteristics of M. labreanum were described as follows [1]. The cells were coccoid with a diameter of 0.4-2.0 μm. They were irregular in shape under some growth conditions, such as higher salt or with added acetate. Motility was not observed and no flagella were observed. Growth was observed on H2/CO2 or formate, but not with acetate, propionate, methanol, trimethylamine, or ethanol. Growth was observed in a narrow window of pH, from 6.5 to 7.5, with pH 7.0 as the optimal value. Growth was observed between 25 and 40°C, with an optimum at 37°C. M. labreanum can tolerate a wide range of salt concentration, from 0 to 30 g/L NaCl. Acetate was stimulatory at lower salt concentrations. Either trypticase peptone, yeast extract, or cysteine was required for growth. The features of M. labreanum Z are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Classification and general features of Methanocorpusculum labreanum Z in accordance with the Minimum Information about a Genome Sequence (MIGS) recommendations [9].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Archaea | ||
| Phylum Euryarchaeota | |||
| Class Methanomicrobia | |||
| Order Methanomicrobiales | |||
| Family Methanocorpusculaceae | |||
| Genus Methanocorpusculum | TAS [10] | ||
| Species Methanocorpusculum labreanum | TAS [1] | ||
| Gram stain | negative | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | irregular coccus | TAS [1] | |
| Motility | nonmotile | TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | nonsporulating | ||
| Temperature range | 25-40°C | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | 37°C | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-6.3 | Salinity | 0-30 g/L NaCl | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | anaerobe | TAS [1] |
| Carbon source | CO2, acetate | TAS [1] | |
| Energy source | H2/CO2, formate | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | sediment | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | free-living | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | none | |
| Biosafety level | 1 | ||
| Isolation | sediment | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Tar Pit Lake, La Brea Tar Pits | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-5 | Isolation time | 1989 | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-4.1 MIGS-4.2 | Latitude-longitude | 34.107811/-118.599658 | |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | 0-5 cm | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | not applicable |
Evidence codes - IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay (first time in publication); TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [10]. If the evidence code is IDA, then the property should have been directly observed, for the purpose of this specific publication, for a live isolate by one of the authors, or an expert or reputable institution mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Genome sequencing information
Genome project history
M. labreanum was selected for sequencing based upon its phylogenetic position relative to other methanogens of the order Methanomicrobiales. It is part of a 2006 Joint Genome Institute Community Sequencing Program project that included six diverse archaeal genomes. A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2. The complete genome sequence was finished in January, 2007. The GenBank accession number for the project is CP000559. The genome project is listed in the Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) [11] as project Gc00506. Sequencing was carried out at the Joint Genome Institute (JGI) Production Genomics Facility (PGF). Quality assurance was done by JGI-Stanford. Finishing was done at JGI-PGF. Annotation was done by JGI-Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and by JGI-PGF.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | 3kb, 6kb and 40kb (fosmid) |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platform | ABI3730, 454 |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 34x |
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| Sequencing quality | less than one error per 50kb | |
| MIGS-30 | Assembler | Newbler, Paracel |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | CRITICA, Glimmer |
| GenBank ID | CP000559 | |
| GenBank date of release | February 2, 2007 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc00506 | |
| NCBI project ID | 18109 | |
| IMG Taxon ID | 640069317 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 4855 |
| Project relevance | Tree of Life |
DNA isolation, genome sequencing and assembly
The methods for DNA isolation, genome sequencing and assembly for this genome have previously been published [12].
Genome annotation
Protein-coding genes were identified using a combination of CRITICA [13] and Glimmer [14] followed by a round of manual curation using the JGI GenePRIMP pipeline [15]. GenePRIMP points out cases where gene start sites may be incorrect based on alignment with homologous proteins. It also highlights genes that appear to be broken into two or more pieces, due to a premature stop codon or frameshift, and genes that are disrupted by transposable elements. All of these types of broken and interrupted genes are labeled as pseudogenes. Genes that may have been missed by the gene calling programs are also identified in intergenic regions. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant database, UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. Signal peptides were identified with SignalP [16], and transmembrane helices were determined with TMHMM [17]. CRISPR elements were identified with the CRISPR Recognition Tool (CRT) [18]. Paralogs are hits of a protein against another protein within the same genome with an e-value of 10-2 or lower. The tRNAScanSE tool [19] was used to find tRNA genes. Additional gene prediction analysis and manual functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes Expert Review (IMG-ER) platform [20].
Genome properties
The genome of M. labreanum Z consists of a single circular chromosome (Figure 2). The genome size of 1.80 Mbp is similar to those of Class I methanogens, but smaller than the genomes of Methanosarcina species and the other Methanomicrobiales, which range between 2.5 and 5.8 Mbp. The G+C percentage is 50.0%, higher than that of most other sequenced methanogens. There are 1,830 genes, of which 1,765 are protein-coding genes and the remaining 65 are RNA genes. There were only 26 pseudogenes identified, constituting 1.4% of the total genes. The properties and statistics of the genome are summarized in Table 3, and genes belonging to COG functional categories are listed in Table 4.
Figure 2.
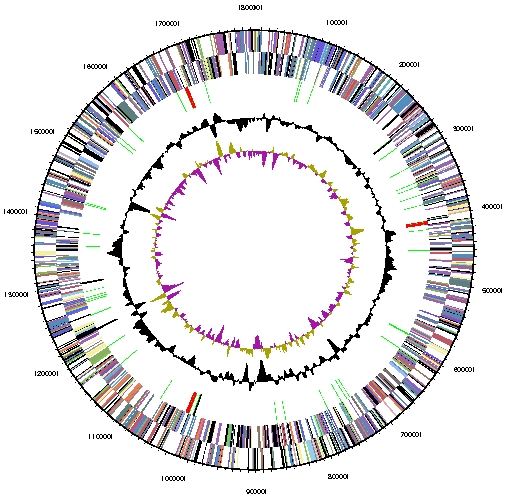
Graphical circular map of the chromosome of Methanocorpusculum labreanum Z. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (colored by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (colored by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
Table 3. Genome statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 1,804,962 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 1,600,673 | 88.68% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 902,600 | 50.01% |
| Number of replicons | 1 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 0 | |
| Total genes | 1830 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 65 | 3.55% |
| rRNA operons | 3 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 1765 | 96.45% |
| Pseudogenes | 26 | 1.42% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 745 | 42.21% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 1358 | 76.94% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 1335 | 75.64% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 406 | 23.00% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 368 | 20.85% |
| CRISPR repeats | 2 |
Table 4. Numbers of genes associated with the 25 general COG functional categories.
| Code | value | % of total | COG category |
|---|---|---|---|
| E | 130 | 7.4 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| G | 54 | 3.1 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| D | 10 | 0.6 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| N | 5 | 0.3 | Cell motility |
| M | 35 | 2.0 | Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis |
| B | 2 | 0.1 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| H | 129 | 7.3 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| Z | 0 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| V | 13 | 0.7 | Defense mechanisms |
| C | 134 | 7.6 | Energy production and conversion |
| W | 0 | 0.0 | Extracellular structures |
| S | 172 | 9.7 | Function unknown |
| R | 219 | 12.4 | General function prediction only |
| P | 95 | 5.4 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| U | 17 | 1.0 | Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport |
| I | 24 | 1.4 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| F | 49 | 2.8 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| O | 57 | 3.2 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| A | 0 | 0.0 | RNA processing and modification |
| L | 65 | 3.7 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| Q | 8 | 0.5 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| T | 30 | 1.7 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| K | 77 | 4.4 | Transcription |
| J | 147 | 8.3 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| - | 293 | 16.6 | Not in COGs |
Insights from the genome sequence
The genome sequence of M. labreanum Z shows some similarities to Class I methanogens and some to Methanosarcinales but also has some unique features. In common with Class I methanogens, M. labreanum uses a partial reductive TCA cycle to synthesize 2-oxoglutarate, and it has the Eha membrane-bound hydrogenase. Similar to Methanosarcinales, M. labreanum has the Ech membrane-bound hydrogenase. A unique feature of M. labreanum and the other Methanomicrobiales is the presence of anti- and anti-anti-sigma factors, which is surprising as Archaea do not use sigma factors. Phylogenetic analysis of methanogenesis and cofactor biosynthesis enzymes suggest that Methanomicrobiales form a group distinct from other methanogens, and therefore methanogens can be split in to three classes [12]. Surprisingly M. labreanum lacks the F420-nonreducing hydrogenase, which has been proposed to couple Coenzyme M-Coenzyme B heterodisulfide reduction and ferredoxin reduction for the first step of methanogenesis in the cytoplasm of Methanomicrobiales [21]. In place of this hydrogenase, M. labreanum may use the membrane-bound hydrogenase Mbh or energy-converting hydrogenase Ech to couple heterodisulfide reduction to a transmembrane ion gradient [12].
Acknowledgments
This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy’s Office of Science, Biological and Environmental Research Program, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, and Los Alamos National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396. L. H. and M. L. were supported by the Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-000R22725. M. S.-L., and W. B. W. were supported by DOE contract number DE-FG02-97ER20269.
References
- 1.Zhao Y, Boone DR, Mah RA, Boone JE, Xun L. Isolation and characterization of Methanocorpusculum labreanum sp. nov. from the LaBrea Tar Pits. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1989; 39:10-13 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garcia JL, Ollivier B, Whitman WB. The order Methanomicrobiales. Prokaryotes 2006; 3:208-230 10.1007/0-387-30743-5_10 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Simankova MV, Kotsyurbenko OR, Lueders T, Nozhevnikova AN, Wagner B, Conrad R, Friedrich MW. Isolation and characterization of new strains of methanogens from cold terrestrial habitats. Syst Appl Microbiol 2003; 26:312-318 10.1078/072320203322346173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dhillon A, Lever M, Lloyd KG, Albert DB, Sogin ML, Teske A. Methanogen diversity evidenced by molecular characterization of methyl coenzyme M reductase A (mcrA) genes in hydrothermal sediments of the Guaymas Basin. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005; 71:4592-4601 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4592-4601.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Strąpoć D, Picardal FW, Turich C, Schaperdoth I, Macalady JL, Lipp JS, Lin YS, Ertefai TF, Schubotz F, Hinrichs KU, et al. Methane-producing microbial community in a coal bed of the Illinois basin. Appl Environ Microbiol 2008; 74:2424-2432 10.1128/AEM.02341-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Waldron PJ, Petsch ST, Martini AM, Nüsslein K. Salinity constraints on subsurface archaeal diversity and methanogenesis in sedimentary rock rich in organic matter. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007; 73:4171-4179 10.1128/AEM.02810-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bapteste É, Brochier C, Boucher Y. Higher-level classification of the Archaea: evolution of methanogenesis and methanogens. Archaea 2005; 1:353-363 10.1155/2005/859728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, et al. The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37:D141-D145 10.1093/nar/gkn879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xun L, Boone DR, Mah RA. Deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization study of Methanogenium and Methanocorpusculum species, emendation of the genus Methanocorpusculum, and transfer of Methanogenium aggregans to the genus Methanocorpusculum as Methanocorpusculum aggregans comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1989; 39:109-111 [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liolios K, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Kyrpides NC. The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) in 2007: status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36:D475-D479 10.1093/nar/gkm884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Anderson I, Ulrich LE, Lupa B, Susanti D, Porat I, Hooper SD, Lykidis A, Sieprawska-Lupa M, Dharmarajan L, Goltsman E, et al. Genomic characterization of Methanomicrobiales reveals three classes of methanogens. PLoS ONE 2009; 4:e5797 10.1371/journal.pone.0005797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Badger JH, Olsen GJ. CRITICA: coding region identification tool invoking comparative analysis. Mol Biol Evol 1999; 16:512-524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL. Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res 1999; 27:4636-4641 10.1093/nar/27.23.4636 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pati A. GenePRIMP: A Gene Prediction Improvement Pipeline for microbial genomes. (Submitted). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 16.Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2007; 2:953-971 10.1038/nprot.2007.131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 2001; 305:567-580 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bland C, Ramsey TL, Sabree F, Lowe M, Brown K, Kyrpides NC, Hugenholtz P. CRISPR recognition tool (CRT): a tool for automatic detection of clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats. BMC Bioinformatics 2007; 8:209 10.1186/1471-2105-8-209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 1997; 25:955-964 10.1093/nar/25.5.955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Markowitz VM, Mavromatis K, Ivanova NN, Chen IMA, Chu K, Kyrpides NC. IMG ER: a system for microbial genome annotation expert review and curation. Bioinformatics 2009; 25:2271-2278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Thauer RK, Kaster AK, Seedorf H, Buckel W, Hedderich R. Methanogenic archaea: ecologically relevant differences in energy conservation. Nat Rev Microbiol 2008; 6:579-591 10.1038/nrmicro1931 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


