Abstract
Streptobacillus moniliformis Levaditi et al. 1925 is the type and sole species of the genus Streptobacillus, and is of phylogenetic interest because of its isolated location in the sparsely populated and neither taxonomically nor genomically much accessed family 'Leptotrichiaceae' within the phylum Fusobacteria. The 'Leptotrichiaceae' have not been well characterized, genomically or taxonomically. S. moniliformis,is a Gram-negative, non-motile, pleomorphic bacterium and is the etiologic agent of rat bite fever and Haverhill fever. Strain 9901T, the type strain of the species, was isolated from a patient with rat bite fever. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. This is only the second completed genome sequence of the order Fusobacteriales and no more than the third sequence from the phylum Fusobacteria. The 1,662,578 bp long chromosome and the 10,702 bp plasmid with a total of 1511 protein-coding and 55 RNA genes are part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: Fusobacteria, 'Leptotrichiaceae', Gram-negative, rods in chains, L-form, zoonotic disease, non-motile, non-sporulating, facultative anaerobic, Tree of Life
Introduction
Strain 9901T (= DSM 12112 = ATCC 14647 = NCTC 10651) is the type strain of Streptobacillus moniliformis, which also represents the type species of the genus first described in 1925 by Levaditi et al. [1,2] The taxonomic history of S. moniliformis; affiliated several genera such as 'Haverhillia [1]' and was only placed recently in the family “Leptotrichiaceae” (unpublished). It has also been suggested that S. moniliformis be placed within the Mycoplasmatales due to its similarity to some members based on the low G+C content of 24-26%, the fastidious requirements for growth and the production of L-form organisms [3]. S. moniliformis is commonly found in the nasopharynx of feral rats as well as in laboratory or pet rats. Between 50 and 100% of wild rats carry the commensal and secrete it with their urine [4]. The organism has been associated with rat bite fever and Haverhill fever in humans, following a bite or contamination of food by rat urine, respectively. Before it could be demonstrated that both diseases are caused by the same organism, the etiologic agent for Haverhill fever was called 'Haverhillia multiformis' [5]. Both are systemic illnesses characterized by fever, rigors and migratory polyarthralgias and nearly 75% of patients develop a rash. Untreated, rat bite fever has a mortality rate of approximately 10%, with most deaths occurring due to endocarditis [6].
S. moniliformis is only the second species from the phylum Fusobacteria for which a complete genome sequence is described. Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for S. moniliformis strain 9901T (Table 1), together with the description of the complete genomic sequencing and annotation.
Table 1. Classification and general features of S. moniliformis 9901T in accordance to the MIGS recommendations [7].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [8] | |
| Phylum Fusobacteria | TAS [9] | ||
| Class Fusobacteria | TAS [9] | ||
| Order Fusobacteriales | TAS [9] | ||
| Family 'Leptotrichiaceae' | NAS | ||
| Genus Streptobacillus | TAS [1] | ||
| Species Streptobacillus moniliformis | TAS [1] | ||
| Type strain 9901 | TAS [1] | ||
| Gram stain | negative | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | long rods | TAS [1] | |
| Motility | nonmotile | TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | non-sporulating | TAS [1] | |
| Temperature range | mesophile | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | 37°C | TAS [1] | |
| Salinity | normal | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | facultative anaerobic | TAS [1] |
| Carbon source | monosaccharides, starch | TAS [10] | |
| Energy source | carbohydrates | TAS [10] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | nasopharynx of rats | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | free living | NAS |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | pathogenic for humans | TAS [1] |
| Biosafety level | 2 | TAS [11] | |
| Isolation | patient with rat-bite fever | NAS | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | France | NAS |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | unknown | |
| MIGS-4.1 MIGS-4.2 | Latitude , Longitude | unknown | |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | not reported |
Evidence codes - IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay (first time in publication); TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [12]. If the evidence code is IDA, then the property was observed for a living isolate by one of the authors or an expert mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Classification and features
Isolate H2730, from a clinical case of fatal rat bite fever in the US [13] perfectly matches the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the genome of strain 9901T described in this report; other recently described strains (TSD4, IKB1, IKC1, and IKC5) isolated from feral rats in Japan differ in just 1-4 nucleotides [14]. No phylotypes from environmental screening or genomic surveys could be linked with more than 90% 16S rRNA sequence similarity to S. moniliformis (status May 2009), indicating that the strain is rarely found in the environment outside of its natural hosts.
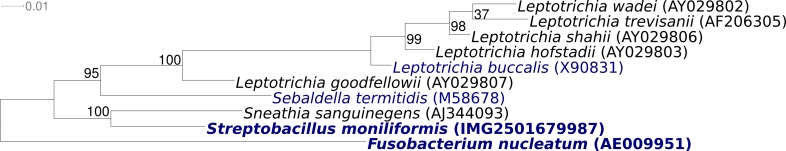
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of S. moniliformis strain 9901T in a 16S rRNA based tree. The sequences of the five 16S rRNA gene copies in the genome of S. moniliformis 9901T do not differ from each other, and differ by six nucleotides from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence generated from ATCC 14647 (Z35305). The difference between the genome data and the reported 16S rRNA gene sequence is most likely due to sequencing errors in the previously reported sequence data.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of S. moniliformis 9901T relative to the other type strains of the family ‘Leptotrichiaceae’. The tree was inferred from 1399 aligned characters [15,16] of the 16S rRNA sequence under the maximum likelihood criterion [17] and rooted with the type strain of the family 'Fusobacteriaceae' The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers above branches are support values from 1,000 bootstrap replicates if larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [18] are shown in blue, published genomes in bold, e.g. the GEBA type strain Leptotrichia buccalis [19].
S. moniliformis is a Gram-negative, non-motile, fastidious, slow-growing and facultatively anaerobic organism that grows as elongated rods (0.3-0.7 µm by 1-5 µm in length) which tend to form chains or filaments with occasional bulbar swellings leading to a necklace-like appearance ("moniliformis" means necklace-shaped) (Figure 2). The organism exists in two variants: the bacillary form and a cell wall-deficient L-form, which is considered nonpathogenic [20]. The primary habitat of S. moniliformis is small rodents, including rats (dominant reservoir) and more rarely gerbils, squirrels and mice. Rat-eating carnivores such as dogs, cats, ferrets and pigs can also become hosts and thus transfer the pathogen to humans. However, the organism is not directly transmitted from person to person and thus presents a typical zoonotic agent. A large number of case reports of S. moniliformis infections have been published (references in [4]). For cultivation, complex media containing blood, serum or ascitis fluid are necessary and increased CO2 concentration enhances growth. The organism is extremely sensitive to sodium polyanethol sulfonate ("Liquoid"), an anticoagulant used in commercial blood culture bottles, which can lead to problems during primary isolation [21]. S. moniliformis is catalase and oxidase negative and is biochemically rather inert. The metabolism is fermentative. Acid but no gas is produced from glucose, fructose, maltose and starch; H2S is produced. Arginine dihydrolase is synthesized [22,23]. S. moniliformis is susceptible to all β-lactam antibiotics, no β-lactamase activity could be demonstrated thus far [10].
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of S. moniliformis 9901T
Chemotaxonomy
No data are available about the murein composition of strain 9901T. The fatty acid pattern of S. moniliformis can be used for its rapid identification and comprises a mixture of saturated and unsaturated straight-chain acids: C16:0, C18:0, C18:1 and C18:2. The type of menaquinones and polar lipids used by S. moniliformis has not been described yet.
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its phylogenetic position, and is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project. The genome project is deposited in the Genomes OnLine Database [18] and the complete genome sequence in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI). A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Two genomic libraries: 8kb pMCL200 and fosmid pcc1Fos Sanger libraries. One 454 pyrosequence standard library |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | ABI3730, 454 GS FLX |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 11.5× Sanger; 24.9x pyrosequence |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | Newbler version 1.1.02.15, phrap |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Prodigal 1.4, GenePRIMP |
| INSDC / Genbank ID | CP001779 | |
| Genbank Date of Release | November 19, 2009 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc01145 | |
| NCBI project ID | 29309 | |
| Database: IMG-GEBA | 2501651197 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 12112 |
| Project relevance | Tree of Life, GEBA, Medical |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
S. moniliformis strain 9901T, DSM 12112, was grown aerobically with high humidity and increased CO2 concentration on DSMZ medium 429 (Columbia Blood Agar [24] at 37°C. DNA was isolated from 0.4 g of cell paste using Qiagen Genomic 500 DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer's instructions, but with cell lysis modification ‘L’ solution according to Wu et al [25].
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using a combination of Sanger and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing performed at the JGI can be found at the JGI website (http://www.jgi.doe.gov). 454 Pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler version 1.1.02.15 (Roche). Large Newbler contigs were broken into 1,459 overlapping fragments of 1,000 bp and entered into assembly as pseudo-reads. The sequences were assigned quality scores based on Newbler consensus q-scores with modifications to account for overlap redundancy and to adjust inflated q-scores. A hybrid 454/Sanger assembly was made using the phrap assembler (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with Dupfinisher or transposon bombing of bridging clones [26]. Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, custom primer walk or PCR amplification. 1,081 Sanger finishing reads were produced to close gaps and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. The final assembly consists of 22,979 Sanger and 326,576 pyrosequence reads. Together all sequence types provided 36.4× coverage of the genome.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using Prodigal [27] as part of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory genome annotation pipeline, followed by a round of manual curation using the JGI GenePRIMP pipeline (http://geneprimp.jgi-psf.org) [28]. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant database, UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. Additional gene prediction analysis and functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes - Expert Review (IMG-ER) platform (http://img.jgi.doe.ogv/er) [29].
Genome properties
The genome is 1,673,280 bp long and comprises one circular chromosome and one plasmid with a 26.3% GC content (Table 3 and Figure 3). Of the 1,566 genes predicted, 1,511 were protein coding genes, and 55 RNAs. A total of 69 pseudogenes were also identified. The majority of the protein-coding genes (67.3%) genes were assigned with a putative function, while the remaining ones were annotated as hypothetical proteins. The properties and the statistics of the genome are summarized in Table 3. The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 1,673,280 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 1,556,870 | 93.04% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 439,733 | 26.28% |
| Number of replicons | 2 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 1 | |
| Total genes | 1,566 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 55 | 3.51% |
| rRNA operons | 5 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 1,511 | 96.49% |
| Pseudo genes | 69 | 4.41% |
| Genes with function prediction | 1,054 | 67.31% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 321 | 20.50% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 1,018 | 65.01% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 1,067 | 68.18% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 262 | 16.73% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 343 | 21.90% |
| CRISPR repeats | 1 |
Figure 3.
Graphical circular map of the genome. Lower-right part: plasmid, not drawn to scale. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | value | % age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 134 | 8.9 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | 2 | 0.1 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 66 | 4.4 | Transcription |
| L | 88 | 5.8 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 0 | 0.0 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 18 | 1.2 | Cell cycle control, mitosis and meiosis |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| V | 32 | 2.1 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 25 | 1.7 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 57 | 3.8 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 11 | 0.7 | Cell motility |
| Z | 0 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 2 | 0.1 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 36 | 2.4 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion |
| O | 45 | 3.0 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 39 | 2.6 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 119 | 7.9 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 75 | 5.0 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 50 | 3.3 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 21 | 1.4 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 25 | 1.7 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 56 | 3.7 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 4 | 0.3 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 114 | 7.5 | General function prediction only |
| S | 72 | 4.8 | Function unknown |
| - | 493 | 32.6 | Not in COGs |
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the help of Sabine Welnitz for growing S. moniliformis cultures and Susanne Schneider for DNA extraction and quality analysis (both at DSMZ). This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy Office of Science, Biological and Environmental Research Program, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, and Los Alamos National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396, as well as German Research Foundation (DFG) INST 599/1-1.
References
- 1.Levaditi C, Nicolau S, Poincloux P. Sur le role étiologique de Streptobacillus moniliformis (nov. spec.) dans l’érythéme polymorphe aigu septicémique. Compte Rendu Hebdomadaire des Séances de l’Académie des Scienes (Paris) 1925; 180: 1188-1190 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA. Approved list of bacterial names. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1980; 30: 225-230 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Savage N. Genus Streptobacillus Levaditi, Nicolau and Poincloux 1925. N.R. Krieg and J.G. Holt (ed.) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, USA. 1984, Vol. 1:598-600. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Elliott SP. Rat bite fever and Streptobacillus moniliformis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2007; 20: 13-22; . 10.1128/CMR.00016-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Parker F, Hudson NP. The etiology of Haverhill fever (erythema arthriticum epidemicum). Am J Pathol 1926; 2: 357-379 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rupp ME. Streptobacillus moniliformis endocarditis: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 14: 769-772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. Towards a richer description of our complete collection of genomes and metagenomes: the “Minimum Information about a Genome Sequence” (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garrity GM, Holt JG. Taxonomic Outline of the Archaea and Bacteria In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Springer, New York, 2001, p. 155-166 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Edwards R, Finch RG. Characterisation and antibiotic susceptibilities of Streptobacillus moniliformis. J Med Microbiol 1986; 21: 39-42 10.1099/00222615-21-1-39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Anonymous. Biological Agents: Technical rules for biological agents www.baua.de TRBA 466.
- 12.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 2000; 25: 25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Fatal rat-bite fever--Florida and Washington, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2005; 53: 198-202 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kimura M, Tanikawa T, Suzuki M, Koizumi N, Kamiyama T, et al. Detection of Streptobacillus spp. in feral rats by specific polymerase strain reactions. Microbiol Immunol 2008; 52: 9-15 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2008.00005.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18: 452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17: 540-552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web-servers. Syst Biol 2008; 57: 758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liolios K, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Kyrpides NC. The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) in 2007: status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: D475-D479 10.1093/nar/gkm884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ivanova N, Gronow S, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Nolan M, Lucas S, Chen F, Tice H, Feng C, et al. Complete genome sequence of Leptotrichia bucchalis type strain (C-1013bT). Standard Genomic Sci 2009; 1: 126-132 10.4056/sigs.1854 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Freundt EA. Experimental investigations into the pathogenicity of the L-phase variant of Streptobacillus moniliformis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 1956; 38: 246-258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shanson DC, Pratt J, Greene P. Comparison of media with and without "Panmede" for the isolation of Streptobacillus moniliformis from blood cultures and observations on the inhibitory effect of sodium polyanethol sulphonate. J Med Microbiol 1985; 19: 181-186 10.1099/00222615-19-2-181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aluotto BB, Wittler RG, Williams CD, Faber JE. Standardized bacteriologic techniques for characterization of Mycoplasma species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1970; 20: 35-58 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cohen RL, Wittler RG, Faber JE. Modified biochemical tests for characterization of L-phase variants of bacteria. Appl Microbiol 1968; 16: 1655-1662 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.List of growth media used at DSMZ: http://www.dsmz.de/microorganisms/media_list.php
- 25.Wu M, Hugenholtz P, Mavromatis K, Pukall R, Dalin E, Ivanova N, Kunin V, Goodwin L, Wu M, Tindall BJ, et al. A phylogeny-driven genomic encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea. Nature 2009; 462: 1056-1060 10.1038/nature08656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sims D, Brettin T, Detter JC, Han C, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Nolan M, Chen F, Lucas S, et al. Complete genome sequence of Kytococcus sedentarius type strain (541T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1: 12-20 10.4056/sigs.761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Anonymous. Prodigal Prokaryotic Dynamic Programming Genefinding Algorithm. Oak Ridge National Laboratory and University of Tennessee 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pati A, Ivanova N, Mikhailova N, Ovchinikova G, Hooper SD, Lykidis A, Kyrpides NC. GenePRIMP: A Gene Prediction Improvement Pipeline for microbial genomes. (Submitted) 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Markowitz VM, Mavromatis K, Ivanova NN, Chen IMA, Kyrpides NC. Expert IMG ER: A system for microbial genome annotation expert review and curation. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2271-2278 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]