Abstract
Haloterrigena turkmenica (Zvyagintseva and Tarasov 1987) Ventosa et al. 1999, comb. nov. is the type species of the genus Haloterrigena in the euryarchaeal family Halobacteriaceae. It is of phylogenetic interest because of the yet unclear position of the genera Haloterrigena and Natrinema within the Halobacteriaceae, which created some taxonomic problems historically. H. turkmenica, was isolated from sulfate saline soil in Turkmenistan, is a relatively fast growing, chemoorganotrophic, carotenoid-containing, extreme halophile, requiring at least 2 M NaCl for growth. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence, and annotation. This is the first complete genome sequence of the genus Haloterrigena, but the eighth genome sequence from a member of the family Halobacteriaceae. The 5,440,782 bp genome (including six plasmids) with its 5,287 protein-coding and 63 RNA genes is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: extreme halophile, thermophile, free-living, aerobic, non-pathogenic, carotenoids-containing, Halobacteriaceae, GEBA
Introduction
Strain 4kT (= DSM 5511 = ATCC 51198 = VKM B-1734) is the type strain of the species Haloterrigena turkmenica, which is the type species of the genus Haloterrigena [1,2]. The strain was initially described in 1987 as Halococcus turkmenicus VKM B-1734 (basonym) by Zvyagintseva and Tarasov [3]. In 1999, Ventosa et al. proposed to transfer H. turkmenicus 4k as the type strain of the species H. turkmenica to the new genus Haloterrigena [1], whose name means salt, halos, (-requiring) and born from the earth, terrigena. Inconsistent data published on sequence similarity and DNA-DNA hybridization for some Haloterrigena and Natrinema strains created some confusion and taxonomic problems initially, but the problems were largely resolved in 2003 by Tindall [4], pointing to uncertainty about strain history. It has been suggested that the discrepancies may also be a result of 16S rDNA interoperon heterogeneity [5]. Published data appears to indicate that both strains GSL-11 and JCM 9743 (formally included in the species H. turkmenica by Ventosa et al. [1]) may be members of the genus Natrinema [4,6]. Those strains will not be considered further here.
There are no reliable reports of other strains of H. turkmenica having been isolated. 16S rRNA sequence identity with the other seven type strains in the genus, which were mainly isolated from salt lakes, range from 98.0% for H. salina [7] to 94.4% for H. longa [6]. The sequence similarity to the Natrinema type strains is somewhere in-between, 95.2-96.4% [8], underlining the taxonomic problems [4]. The sequence similarity to phylotypes in environmental metagenomic libraries was not above 87%, indicating a rather poor representation of closely related strains in the habitats analyzed (status January 2010). Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for H. turkmenica strain 4kT, together with the description of the complete genome sequencing and annotation.
Classification and features
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of H. turkmenica strain 4kT in a 16S rRNA based tree. The three 16S rRNA gene sequences in the genome differ from each other by up to two nucleotides, and differ by up to six nucleotides from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence (AB004878) generated from DSM 5511. The difference between the genome data and the previously reported 16S rRNA gene sequences is most likely due to sequencing errors in the previously reported sequence data. As expected, Haloterrigena and Natrinema strains appear as intermixed in the tree, indicating a paraphyletic status of Haloterrigena (within which Natronorubrum and Natrinema branch off) and of Natrinema (within which H. longa is placed) [18].
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of H. turkmenica strain 4kT relative to the other species within the genera Haloterrigena and Natrinema and the type strains of the other genera within the family Halobacteriaceae. The tree was inferred from 1,368 aligned characters [9,10] of the 16S rRNA sequence under the maximum likelihood criterion [11] and rooted with Natronomonas pharaonis [12]. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers above branches are support values from 800 bootstrap replicates [13] if larger than 60%. Strains with a genome sequencing project registered in GOLD [14] are printed in blue; published genomes in bold, e.g. the recently published GEBA genomes from Halogeometricum borinquense [15], Halorhabdus utahensis [16], and Halomicrobium mukohataei [17].
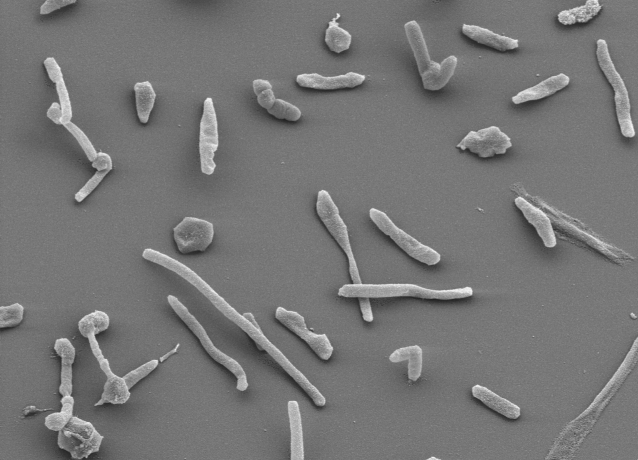
H. turkmenica cells occur mostly as single cells, rarely in pairs or tetrads [1]. They are described as Gram-negative, ovoid to coccoid, 1.5-2 μm in diameter [1], but can also be rod-shaped (Figure 2 and Table 1) [1]. Neither spores, nor flagella, nor lipid granules were reported. Colonies are pigmented red or light pink due of the presence of C5O-carotenoids [1]. Stain 4kT is chemoorganotrophic and aerobic, and requires at least 2 M NaCl [1]. Detailed physiological characteristics were described by Zvyagintseva and Tarasov [3]. The G+C content of DNA was reported to be 59.2-60-2 mol % (Thermal denaturation method [1]), which is significantly less than the 64.3% found in the genome. At optimal growth temperatures, H. turkmenica is the fastest growing member of the Halobacteriaceae, with only 1.5 hours generation time [26]. Besides the chemical characterization of siderophores [29], there are no published reports on the molecular biology of H. turkmenica.
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of H. turkmenica strain 4kT
Table 1. Classification and general features of H. turkmenica 4kT according to the MIGS recommendations [19].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Archaea | TAS [20] | |
| Phylum Euryarchaeota | TAS [21,22] | ||
| Class Halobacteria | TAS [23] | ||
| Order Halobacteriales | TAS [24] | ||
| Family Halobacteriacea | TAS [25] | ||
| Genus Haloterrigena | TAS [1] | ||
| Species Haloterrigena turkmenica | TAS [1] | ||
| Type strain 4k | TAS [3] | ||
| Gram stain | negative | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | rods | TAS [1] | |
| Motility | nonmotile | IDA | |
| Sporulation | non-sporulating | NAS | |
| Temperature range | 29-57°C | TAS [26] | |
| Optimum temperature | 51°C | TAS [26] | |
| Salinity | extreme halophile, requires at least 2% (w/v) NaCl |
TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | aerobic | TAS [1] |
| Carbon source | yeast extract | NAS | |
| Energy source | chemoorganotroph | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | soil | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | free living | NAS |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | none | NAS |
| Biosafety level | 1 | TAS [27] | |
| Isolation | sulfate saline soil | TAS [3] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Ashkhabad, Turkmenistan | TAS [3] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | about or before 1987 | TAS [3] |
| MIGS-4.1 MIGS-4.2 |
Latitude, Longitude | 37.950, 58.380 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | unknown | |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | unknown |
Evidence codes - IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay (first time in publication); TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from of the Gene Ontology project [28]. If the evidence code is IDA, then the property was directly observed by one of the authors or an expert mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Both diphytanyl moieties (C20, C20) and phytanyl-sesterterpanyl moieties (C20, C25) are present in polar lipids [1]. The presence of both phytanyl and esterterpanyl side chains implies the presence of three different prenyl transferases involved in lipid biosynthesis, which are probably chain length specific as well as stereospecific for the incorporation of the isoprenoid side chains into the glycerol backbone [30]. The presence of significant levels of both the diphytanyl moieties (C20, C20) and phytanyl-esterterpanyl moieties (C20, C25) is characteristic of all members examined of this evolutionary branch of the family Halobacteriaceae. Membrane polar lipids are glycerol-diether analogues of PG, PGP-Me and the disulfated digylcosyl diether lipid S2-DGD (mannose-2,6 disulfate 1→2 glucose-glycerol diether) [31], the characteristic glycolipid of Natrialba asiatica [32]. The presence of respiratory lipoquinones have not been reported, but it may be predicted that MK-8 and MK-8 (VIII-H2) should be present, since this is a feature of all members of the family Halobacteriaceae examined to date.
Genome sequencing and annotation information
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its phylogenetic position, and is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project [33]. The genome project is deposited in the Genomes OnLine Database [14] and the complete genome sequence in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI). A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Three genomic libraries: one Sanger 8 kb pMCL200 library, one 454 pyrosequence standard library and one Illumina standard library |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | ABI3730, 454 GS FLX, and Illumina GA |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 6.9× Sanger; 19.9× pyrosequence |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | Newbler version 1.1.03.24, phrap |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Prodigal 1.4, GenePRIMP |
| Genbank ID | CP001860 (chromosome) CP001861-CP001866 (plasmids) |
|
| Genbank Date of Release | January 19, 2010 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc01189 | |
| NCBI project ID | 30411 | |
| Database: IMG-GEBA | 2501939622 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 5511 |
| Project relevance | Tree of Life, GEBA |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
H. turkmenica 4kT, DSM 5511, was grown in DSMZ medium 372 (Halobacteria medium) [34] at 37°C. DNA was isolated from 1-1.5 g of cell paste using Qiagen Genomic 500 DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with lysis modification L according to Wu et al. [33].
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using a combination of Sanger and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing performed at the JGI can be found at the JGI website (http://www.jgi.doe.gov/). 454 Pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler version 1.1.03.24 (Roche). Large Newbler contigs were broken into 6,060 overlapping fragments of 1,000 bp and entered into assembly as pseudo-reads. The sequences were assigned quality scores based on Newbler consensus q-scores with modifications to account for overlap redundancy and adjust inflated q-scores. A hybrid 454/Sanger assembly was made using the parallel phrap assembler (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible misassemblies were corrected with Dupfinisher or transposon bombing of bridging clones [35]. A total of 1,183 Sanger finishing reads were produced to close gaps, to resolve repetitive regions, and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. Illumina reads were used to improve the final consensus quality using an in-house developed tool (the Polisher). The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. Together, the combination of the Sanger and 454 sequencing platforms provided 26.8× coverage of the genome. The final assembly contains 33,433 Sanger reads and 394,632 pyrosequencing reads.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using Prodigal [36] as part of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory genome annotation pipeline, followed by a round of manual curation using the JGI GenePRIMP pipeline [37]. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant database, UniProt, TIGR-Fam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. Additional gene prediction analysis and functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes - Expert Review (http://img.jgi.doe.gov/er) platform [38].
Genome properties
The genome is 5,440,782 bp long and comprises one main circular chromosome of 3,889,038 bp length and six circular plasmids of 15.8 to 698.5 kbp length, with an overall GC content of 64.3% (Table 3 and Figures 3 and 4). Of the 5,350 genes predicted, 5,287 were protein coding genes, and 63 RNAs; 174 pseudogenes were also identified. The majority of the protein-coding genes (60.1%) were assigned a putative function while those remaining were annotated as hypothetical proteins. The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 5,440,782 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 4,524,412 | 83.16% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 3,496,479 | 64.26% |
| Number of replicons | 7 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 6 | |
| Total genes | 5,350 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 63 | 1.18% |
| rRNA operons | 3 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 5,287 | 98.82% |
| Pseudo genes | 174 | 3.25% |
| Genes with function prediction | 3,213 | 60.06% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 1,706 | 31.89% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 3,259 | 60.92% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 3,208 | 59.96% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 625 | 11.68% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 1,140 | 21.31% |
| CRISPR repeats | 1 |
Figure 3.
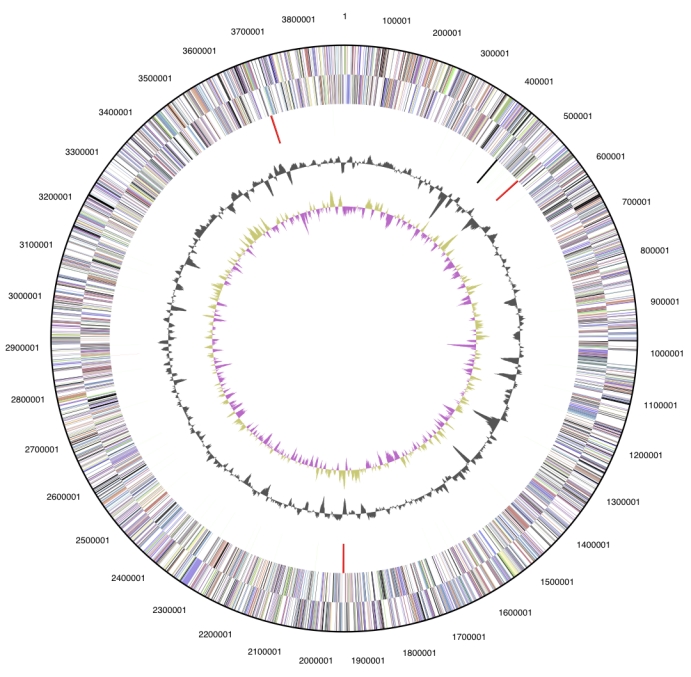
Graphical circular map of the chromosome. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
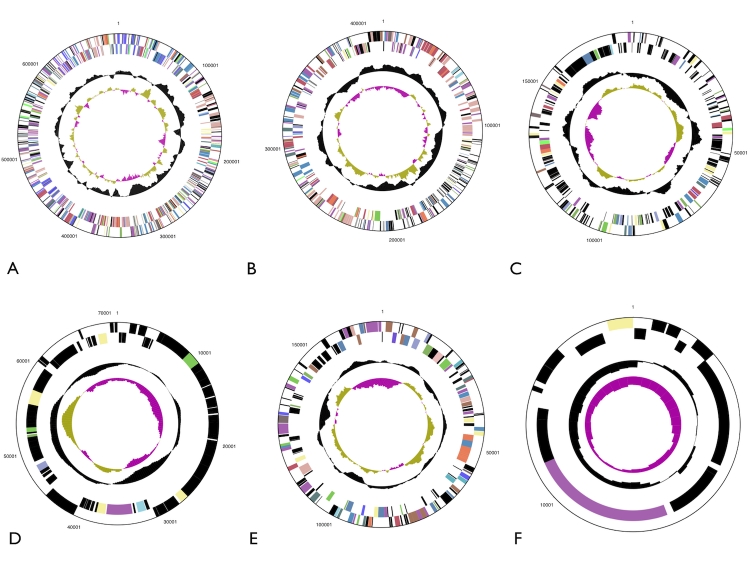
Figure 4.
Graphical circular map of the six plasmids: pHTUR01 (A), pHTUR02 (B), pHTUR03 (C), pHTUR04 (D), pHTUR05 (E), pHTUR06 (F). Plasmids not drawn to scale.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | Value | %age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 178 | 3.4 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | 1 | 0.0 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 190 | 3.6 | Transcription |
| L | 150 | 2.8 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 3 | 0.1 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 35 | 0.7 | Cell cycle control, mitosis and meiosis |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| V | 44 | 0.8 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 161 | 3.0 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 125 | 2.4 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 29 | 0.5 | Cell motility |
| Z | 0 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 0 | 0.0 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 26 | 0.5 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion |
| O | 141 | 2.7 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 258 | 4.9 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 221 | 4.2 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 349 | 6.6 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 78 | 1.5 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 189 | 3.6 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 176 | 3.3 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 224 | 4.2 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 87 | 1.6 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 630 | 11.9 | General function prediction only |
| S | 321 | 6.1 | Function unknown |
| - | 2,091 | 39.5 | Not in COGs |
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the help of Susanne Schneider (DSMZ) for DNA extraction and quality analysis. This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy's Office of Science, Biological and Environmental Research Program, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, and Los Alamos National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396, as well as German Research Foundation (DFG) INST 599/1-1.
References
- 1.Ventosa A, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Dyall-Smith ML. Proposal to transfer Halococcus turkmenicus, Halobacterium trapanicum JCM 9743 and strain GSL-11 to Haloterrigena turkmenica gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1999; 49:131-136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oren A, Arahal DR, Ventosa A. Emended descriptions of the genera of the family Halobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009; 59:637-642 10.1099/ijs.0.008904-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zvyagintseva IS, Tarasov AL. Extreme halophilic bacteria from saline soils. Mikrobiologiia 1987; 56:839-844 [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tindall BJ. Taxonomic problems arising in the genera Haloterrigena and Natrinema. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2003; 53:1697-1698 10.1099/ijs.0.02529-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Walsh DA, Bapteste E, Kamekura M, Doolittle WF. Evolution of the RNA polymerase B′ Subunit Gene (rpoB') in Halobacteriales: a complementary molecular marker to the SSU rRNA Gene. Mol Biol Evol 2004; 21:2340-2351 10.1093/molbev/msh248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cui HL, Tohty D, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ. Haloterrigena longa sp. nov. and Haloterrigena limicola sp. nov., extremely halophilic archaea isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006; 56:1837-1840 10.1099/ijs.0.64372-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Ventosa A. Haloterrigena salina sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2008; 58:2880-2884 10.1099/ijs.0.2008/001602-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW. EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2007; 57:2259-2261 10.1099/ijs.0.64915-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17:540-552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18:452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A Rapid Bootstrap Algorithm for the RAxML Web Servers. Syst Biol 2008; 57:758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Falb M, Pfeiffer F, Palm P, Rodewald K, Hickmann V, Tittor J, Oesterhelt D. Living with two extremes: conclusions from the genome sequence of Natronomonas pharaonis. Genome Res 2005; 15:1336-1343 10.1101/gr.3952905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pattengale ND, Alipour M, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Moret BME, Stamatakis A. How many bootstrap replicates are necessary? Lect Notes Comput Sci 2009; 5541:184-200 10.1007/978-3-642-02008-7_13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liolios K, Chen IM, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Hugenholtz P, Markowitz VM, Kyrpides NC. The Genomes On Line Database (GOLD) in 2009: status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38:D346-D354 10.1093/nar/gkp848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Malfatti S, Tindall BJ, Schneider S, Fähnrich R, Lapidus A, LaButtii K, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Nolan M, Chen F, et al. Complete genome sequence of Halogeometricum borinquense type strain (PR3T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:150-158 10.4056/sigs.23264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Anderson I, Tindall BJ, Pomrenke H, Göker M, Lapidus A, Nolan M, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Chen F, Tice H, et al. Complete genome sequence of Halorhabdus utahensis type strain (AX-2T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:218-225 10.4056/sigs.31864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tindall BJ, Schneider S, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Nolan M, Lucas S, Chen F, Tice H, Cheng JF, et al. Complete genome sequence of Halomicrobium mukohataei type strain (arg-2T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:270-277 10.4056/sigs.42644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Farris JS. Formal definitions of paraphyly and polyphyly. Syst Zool 1974; 23:548-554 10.2307/2412474 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thompson N, Allen MJ, Anguiuoli SV, et al. Towards a richer description of our complete collection of genomes and metagenomes: the “Minimum Information about a Genome Sequence” (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87:4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Garrity GM, Holt JG. Phylum AII. Euryarchaeota phy. nov. In: Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, vol. 1. 2nd ed. Edited by: Garrity, GM, Boone, DR and Castenholz, RW. Springer, New York; 2001:211-355. [Google Scholar]
- 22.List Editor Validation of publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSEM. Validation List no. 85. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2002; 52:685-690 10.1099/ijs.0.02358-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Garrity GM, Lilburn TG, Cole JR, Harrison SH, Euzeby J, Tindall BJ. “Part 1- The Archaea, Phyla Crenarchaeota and Euryarchaeota” Taxonomic Outline of the Bacteria and Archaea 2007. www.taxonomicoutline.org
- 24.Grant WD, Larsen H. Group III. Extremely halophilic archaeobacteria. Order Halobacteriales ord. nov. In: Staley JT, Bryant MP, Pfennig N & Holt JG(eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, First edition, Vol 3, The Williams & Watkins Co., Baltimore, 1989, pp 2216-2228. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gibbons NE. Family V. Halobacteriaceae fam. nov. In: Buchanan RE & Gibbons NE(eds) Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, eighth edition, The Williams & Watkins Co., Baltimore, 1974, pp 279. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Robinson JL, Pyzyna B, Atrasz RG, Handerson CA, Morrill KL, Burd AM, Desoucy E, Fogleman RE, III, Naylor JB, Steele SM, et al. Growth kinetics of extremely halophilic Archaea (family Halobacteriaceae) as revealed by Arrhenius plots. J Bacteriol 2005; 187:923-929 10.1128/JB.187.3.923-929.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Biological Agents. Technical rules for biological agents www.baua.de TRBA 466.
- 28.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dave BP, Anshuman K, Hajela P. Siderophores of halophilic Archaea and their chemical characterization. Indian J Exp Biol 2006; 44:340-344 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tachibana A. A novel prenyltransferase, farnesylgeranyl diphosphate synthase, from the haloalkaliphilic archaeon, Natronobacterium pharaonis. FEBS Lett 1994; 341:291-294 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80475-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kamekura M, Dyall-Smith ML, Upasani V, Ventosa A, Kates M. Diversity of alkaliphilic halobacteria: proposals for the transfer of Natronobacterium vacuolatum, Natronobacterium magadii, and Natronobacterium pharaonis to the genus Halorubrum, Natrialba, and Natronomonas gen. nov., respectively, as Halorubrum vacuolatum comb. nov., Natrialba magadii comb. nov., and Natronomonas pharaonis comb. nov., respectively. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1997; 47:853-857 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kamekura M, Dyall-Smith ML. Taxonomy of the family Halobacteriaceae and the description of two new genera Halorubrobacterium and Natrialba. J Gen Appl Microbiol 1995; 41:333-350 10.2323/jgam.41.333 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wu D, Hugenholtz P, Mavromatis K, Pukall R, Dalin E, Ivanova N, Kunin V, Goodwin L, Wu M, Tindall BJ. A phylogeny-driven genomic encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea. Nature 2009; 462:1056-1060 10.1038/nature08656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.List of growth media used at DSMZ: http://www.dsmz.de/microorganisms/ media_list.php
- 35.Sims D, Brettin T, Detter JC, Han C, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Nolan M, Chen F, Lucas S, et al. Complete genome of Kytococcus sedentarius type strain (541T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:12-20 10.4056/sigs.761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hyatt D, Chen GL, LoCascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Genomics (In press). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pati A, Ivanova N, Mikhailova N, Ovchinikova G, Hooper SD, Lykidis A, Kyrpides NC. GenePRIMP: A Gene Prediction Improvement Pipeline for microbial genomes. Nat Methods (In press); http://geneprimp.jgi-psf.org/ [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Markowitz VM, Ivanova NN, Chen IMA, Chu K, Kyrpides NC. IMG ER: a system for microbial genome annotation expert review and curation. Bioinformatics 2009; 25:2271-2278 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]