Abstract
Thermobispora bispora (Henssen 1957) Wang et al. 1996 is the type species of the genus Thermobispora. This genus is of great interest because it is strictly thermophilic and because it has been shown for several of its members that the genome contains substantially distinct (6.4% sequence difference) and transcriptionally active 16S rRNA genes. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. This is the second completed genome sequence of a member from the suborder Streptosporangineae and the first genome sequence of a member of the genus Thermobispora. The 4,189,976 bp long genome with its 3,596 protein-coding and 63 RNA genes is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: Two distinct 16S rRNA genes, strictly thermophilic, non-pathogenic, Streptosporangineae, GEBA
Introduction
Strain R51T (= DSM 43833 = ATCC 19993 = JCM 10125) is the type strain of the species Thermobispora bispora, which is the type species of the genus Thermobispora [1]. The generic name of the genus derives from the Greek words ‘thermos’, ‘bis’, and ‘spora’, to indicate high temperature two-spored organisms [1]. Strain R51T was isolated from decaying manure in Berlin (Germany) in 1954 [2]. Other strains were isolated during the same research project from other types of manure in other cities in Germany and in Finland [2]. As deduced from 16S gene sequences, T. bispora was also found in compost in Sweden [3]. Historically, strain R51T was originally classified in 1957 as Thermopolyspora bispora [2]. At the same time, a morphologically similar genus, Microbispora, was described [4], which has priority and T. bispora was subsequently transferred to the genus Microbispora [5,6]. However, based on thermal preferences [2,7], chemotaxonomic features [7], and the two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis patterns of the ribosomal protein AT-L30 [8], Microbispora bispora was subsequently removed from the genus Microbispora to be the type species of the new genus Thermobispora [1]. T. bispora is currently the only species in the genus Thermobispora [1]. In 1997 T. bispora gained interest, as it was described as the first organism to have two distinct (6.4% of total nucleotides) types of transcriptionally active 16S rRNA genes (GenBank accessions U83909 and U83912) [9]. Based on the two copies of the 16S rRNA genes that match best to sequence U83909 the closest related type strain (9% sequence difference [10]) is Micromonospora pattaloongensis [11] of the family Micromonosporaceae; based on the two copies of the 16S rRNA genes that match best to sequence U83912 the closest related type strain (8% sequence difference [10]) is Planotetraspora silvatica [12] of the family Streptosporangiaceae. Neither fit to the taxonomic position as shown in the List of Procaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature that shows the genus Thermobispora as a member of the family Pseudonocardiaceae, reflecting the current uncertainty of the taxonomic position of T. bispora [13]. In their recent review of Actinobacteria taxonomy, Zhi et al. [14] suggested to place Thermobispora in the suborder Streptosporangineae without assignment to a family, which is in accordance with our SSU rRNA tree (Figure 1). 16S rRNA sequences from environmental samples and metagenomic surveys with both 16S rRNA sequences detected phylotypes with approximately 89-92% 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity to both (U83909 and U83912) reference sequences only in a compost metagenome [21], indicating a very rare occurrence of Thermobispora-spp. in the environment (status March 2010). Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for T. bispora R51T, together with the description of the complete genomic sequencing and annotation.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of T. bispora R51T relative to the type strains of the other genera within the suborder Streptosporangineae (except for Actinoallomurus, which was published after the analysis was completed). The tree was inferred from 1,371 aligned characters [15,16] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood criterion [17] and rooted in accordance with the current taxonomy [18]. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers above branches are support values from 1,000 bootstrap replicates if larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [19] are shown in blue, published genomes in bold, e.g. the recently published GEBA genome from Streptosporangium roseum [20].
Classification and features
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of for T. bispora R51T in a 16S rRNA based tree. The sequences of the four 16S rRNA gene copies in the genome differ from each other by up to 94 nucleotides, and differ by up to 95 nucleotides from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence generated from ATCC 19993 (U58523).
T. bispora cells form substrate mycelia whose hyphae are 0.5 to 0.8 µm in diameter [1] (Figure 2). The aerial mycelia branch monopodally and bear longitudinal pairs of spores [1] (not visible in Figure 2). The spore diameters are usually 1.2 to 2.0 µm, but in liquid media spores with a diameter of 3 µm may occur [1]. The aerial mycelia are white, and the substrate mycelia are yellow or yellowish brown on the media used in the respective study (International Streptomyces Project medium 4 agar and IF0328 agar; Institute for Fermentation) [1]. No soluble pigment is produced [1]. T. bispora is an obligately thermophilic organism (Table 1) [1]. Starch is not hydrolyzed; inositol and rhamnose are utilized for growth, but arabinose and glycerol are not utilized [1]. Also, T. bispora is negative for iodinin production and nitrate reduction [1].
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of T. bispora R51T
Table 1. Classification and general features of T. bispora R51T according to the MIGS recommendations [22].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [23] | |
| Phylum ‘Actinobacteria’ | TAS [13] | ||
| Class Actinobacteria | TAS [24] | ||
| Subclass Actinobacteridae | TAS [14,24] | ||
| Order Actinomycetales | TAS [14] | ||
| Suborder Streptosporangineae | TAS [14] | ||
| Family Incertae sedis | TAS [14] | ||
| Genus Thermobispora | TAS [1] | ||
| Species Thermobispora bispora | TAS [2] | ||
| Type strain R51 | TAS [5] | ||
| Gram stain | positive | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | mycelia with hyphae | TAS [2] | |
| Motility | non-motile | TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | sporulating | TAS [1] | |
| Temperature range | thermophile, 50°C - 65°C | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | not determined | TAS [1] | |
| Salinity | not determined | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | aerobic | TAS [1,2] |
| Carbon source | inositol and rhamnose | TAS [1] | |
| Energy source | sugars | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | compost and other decaying material | TAS [2,3] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | unknown | |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | not reported | |
| Biosafety level | 1 | TAS [25] | |
| Isolation | decaying mixed manure | TAS [2] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Berlin, Germany | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | September 30, 1954 | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-4.1 MIGS-4.2 |
Latitude Longitude |
52.52 14.42 |
NAS |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | not reported |
Evidence codes - IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay (first time in publication); TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from of the Gene Ontology project [26]. If the evidence code is IDA, then the property was directly observed for a live isolate by one of the authors or an expert mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Chemotaxonomy
The cell wall of strain R51T contains predominantly the menaquinone MK-9(H0) (75%) and only small amounts of MK-9(H2) and MK-9(H4) [7]. Strain R51T has a type PIV phospholipid pattern, and contains phosphatidylethanolamine but not phosphatidylglycerol and trace amounts of glucosamine-containing phospholipids [7]. The cell wall contains a major amount of meso-diaminopimelic acid, and the whole-cell hydrolysate contains madurose and galactose [1]. The fatty acid composition of strain R51T is dominated by saturated acids, with iso-C16:0 (55%) being the most frequent acid, followed by anteiso-C17:0 (8%), the unsaturated C18:1 (8%), iso-C18:0 (6%) and C16:0 [7]. Also, strain R51T contains minor amounts of 10-methyl-branched chain fatty acids [7].
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its phylogenetic position [27], and is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project [28]. The genome project is deposited in the Genome OnLine Database [19] and the complete genome sequence is deposited in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI). A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Three genomic libraries: two Sanger libraries – 8 kb pMCL200 and fosmid pcc1FOS and one 454 pyrosequece standard library |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | ABI3730, 454 GS FLX |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 7.1× Sanger; 1.1× pyrosequence pseudo-reads |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | Newbler version 1.1.02.15, phrap |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Prodigal, GenePRIMP |
| INSDC ID | CP001874 | |
| Genbank Date of Release | May 17, 2010 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc01281 | |
| NCBI project ID | 469371 | |
| Database: IMG-GEBA | 2501651196 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 43833 |
| Project relevance | Tree of Life, GEBA |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
T. bispora strain R51T, DSM 43833, was grown in DSMZ medium 84 (Rolled oats mineral medium) [29] at 55°C. DNA was isolated from 1-1.5 g of cell paste using Qiagen Genomic 500 DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with lysis modification st/FT according to Wu et al. [28].
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome of T. bispora was sequenced using a combination of Sanger and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing can be found at http://www.jgi.doe.gov/. 454 pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler version 1.1.02.15 (Roche). Large Newbler contigs were broken into 4,798 overlapping fragments of 1,000 bp and entered into assembly as pseudo-reads. The sequences were assigned quality scores based on Newbler consensus q-scores with modifications to account for overlap redundancy and to adjust inflated q-scores. A hybrid 454/Sanger assembly was made using the parallel phrap assembler (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with Dupfinisher or transposon bombing of bridging clones [30]. Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, custom primer walk or PCR amplification. A total of 1,181 Sanger finishing reads were produced to close gaps, to resolve repetitive regions, and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. The final assembly consists of 40,290 Sanger and 1.1× pyrosequence based pseudo-reads. Together Sanger reads and pseudo-reads provided 8.19× coverage of the genome.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using Prodigal [31] as part of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory genome an-notation pipeline, followed by a round of manual curation using the JGI GenePRIMP pipeline [32]. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant database, UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. Additional gene prediction analysis and manual functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes Expert Review (IMG-ER) platform [33].
Genome properties
The genome is 4,189,976 bp long and comprises one main circular chromosome with an overall GC content of 72.4% (Table 3 and Figure 3). Of the 3,659 genes predicted, 3,596 were protein-coding genes, and 63 RNAs; fifty pseudogenes were also identified. The majority of the protein-coding genes (71.9%) were assigned with a putative function while the remaining ones were annotated as hypothetical proteins. The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 4,189,976 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 3,548,135 | 84.68% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 3,034,765 | 72.43% |
| Number of replicons | 1 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 0 | |
| Total genes | 3,659 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 63 | 1.72% |
| rRNA operons | 3 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 3,596 | 98.28% |
| Pseudo genes | 50 | 1.37% |
| Genes with function prediction | 2,632 | 71.93% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 491 | 13.42% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 2,610 | 71.33% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 2,844 | 77.73% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 795 | 21.73% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 864 | 23.61% |
| CRISPR repeats | 6 |
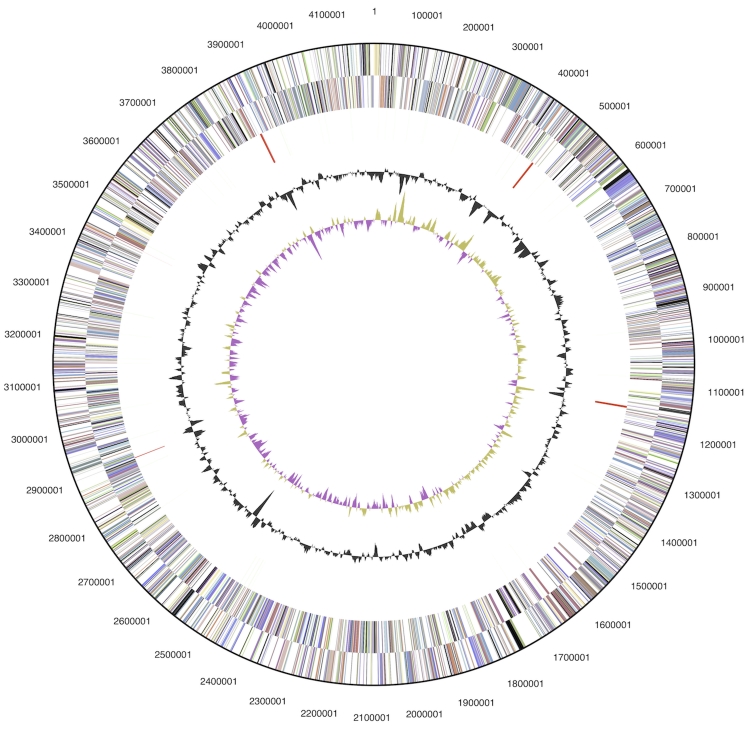
Figure 3.
Graphical circular map of the genome. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | value | %age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 149 | 5.0 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | 1 | 0.0 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 304 | 10.3 | Transcription |
| L | 141 | 4.8 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 1 | 0.0 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 21 | 1.0 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| V | 48 | 1.6 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 192 | 6.5 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 140 | 4.7 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 3 | 0.1 | Cell motility |
| Z | 0 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 0 | 0.0 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 29 | 1.0 | Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport |
| O | 98 | 3.3 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 204 | 6.9 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 221 | 7.5 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 279 | 9.4 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 82 | 2.8 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 146 | 4.9 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 133 | 4.5 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 138 | 4.7 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 85 | 2.9 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 351 | 11.9 | General function prediction only |
| S | 191 | 6.5 | Function unknown |
| - | 1,049 | 28.7 | Not in COGs |
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the help of Susanne Schneider (DSMZ) for DNA extraction and quality analysis. This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy Office of Science, Biological and Environmental Research Program, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, Los Alamos National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725, as well as German Research Foundation (DFG) INST 599/1-1 and SI 1352/1-2.
References
- 1.Wang Y, Zhang Z, Ruan J. A proposal to transfer Microbispora bispora (Lechevalier 1965) to a new genus, Thermobispora gen. nov., as Thermobispora bispora comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1996; 46:933-938 10.1099/00207713-46-4-933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Henssen A. Beiträge zur Morphologie und Systematik der thermophilen Actinomyceten. Arch Microbiol 1957; 26:373-414 10.1007/BF00407588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Steger K, Jarvis A, Vasara T, Romantschuk M, Sundh I. Effects of differing temperature management on development of Actinobacteria populations during composting. Res Microbiol 2007; 158:617-624 10.1016/j.resmic.2007.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nonomura H, Ohara I. On a new actinomycete, Microbispora, isolated from soil. Abstract 98, pages 31 and 32, Abstracts of papers presented at the annual meeting of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan. Tokyo University, April 9th to llth, 1957. Published by the Agricultural Chemical Society (in Japanese). 1957. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Henssen A, Schnepf E. Zur Kenntnis thermophiler Actinomyceten. Arch Microbiol 1967; 57:214-231 10.1007/BF00405948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lechevalier HA. Priority of the generic name Microbispora over Waksmania and Thermopolyspora. Int Bull Bacteriol Nomencl Taxon 1965; 15:139-142 10.1099/00207713-15-3-139 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Miyadoh S, Amano S, Tohyama H, Shomura T. A taxonomic review of the genus Microbispora and a proposal to transfer two species to the genus Actinomadura and to combine ten species into Microbispora rosea. J Gen Microbiol 1990; 136:1905-1913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ochi K, Haraguchi K, Miyadoh S. A taxonomic review of the genus Microbispora by analysis of ribosomal protein AT-L30. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1993; 43:58-62 10.1099/00207713-43-1-58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang Y, Zhang Z, Ramanan N. The actinomycete Thermobispora bispora contains two distinct types of transcriptionally active 16S rRNA genes. J Bacteriol 1997; 179:3270-3276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW. EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2007; 57:2259-2261 10.1099/ijs.0.64915-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Thawai C, Tanasupawat S, Kudo T. Micromonospora pattaloongensis sp. nov., isolated from Thai mangrove forest. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2008; 58:1516-1521 10.1099/ijs.0.65410-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tamura T, Sakane T. Planotetraspora silvatica sp. nov.,and emended description of the genus Planotetraspora. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2004; 54:2053-2056 10.1099/ijs.0.02981-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Garrity GM, Holt JG. The Road Map to the Manual. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 1, Springer, New York, 2001, p. 119-169. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhi XY, Li WJ, Stackebrandt E. An update of the structure and 16S rRNA gene sequence-based definition of higher ranks of the class Actinobacteria, with the proposal of two new suborders and four new families and emended descriptions of the existing higher taxa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009; 59:589-608 10.1099/ijs.0.65780-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17:540-552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18:452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst Biol 2008; 57:758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yarza P, Richter M, Peplies J, Euzeby JP, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO, Rossello-Mora R. The All-Species Living Tree project: A 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 2008; 31:241-250 10.1016/j.syapm.2008.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liolios K, Chen IM, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Hugenholtz P, Markowitz VM, Kyrpides NC. The Genomes On Line Database (GOLD) in 2009: status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38:D346-D354 10.1093/nar/gkp848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nolan M, Sikorski J, Jando M, Lucas S, Lapidus A, Glavina Del Rio T, Chen F, Tice H, Pitlick S, Cheng JF, et al. Complete genome sequence of Streptosporangium roseum type strain (NI 9100T). Stand Genomic Sci 2010; 2:29-37 10.4056/sigs.631049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Allgaier M, Reddy A, Park JI, Ivanova N, D'haeseleer P, Lowry S, Sapra R, Hazen TC, Simmons BA, VanderGheynst JS. et al. Targeted discovery of glycoside hydrolases from a switchgrass-adapted compost community. PLoS ONE 2010; 5:e8812 10.1371/journal.pone.0008812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87:4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey NL. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1997; 47:479-491 10.1099/00207713-47-2-479 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Classification of bacteria and archaea in risk groups. www.baua.de TRBA 466.
- 26.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Klenk HP, Göker M. En route to a genome-based classification of Archaea and Bacteria? Syst Appl Microbiol 2010; 33:175-182 10.1016/j.syapm.2010.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu D, Hugenholtz P, Mavromatis K, Pukall R, Dalin E, Ivanova NN, Kunin V, Goodwin L, Wu M, Tindall BJ, et al. A phylogeny-driven genomic encyclopaedia of Bacteria and Archaea. Nature 2009; 462:1056-1060 10.1038/nature08656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.List of growth media used at DSMZ: http://www.dsmz.de/microorganisms/media_list.php
- 30.Sims D, Brettin T, Detter J, Han C, Lapidus A, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Nolan M, Chen F, Lucas S, et al. Complete genome sequence of Kytococcus sedentarius type strain (541T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:12-20 10.4056/sigs.761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hyatt D, Chen GL, LoCascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. Bioinformatics 2010; 11:119 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pati A, Ivanova N, Mikhailova N, Ovchinikova G, Hooper SD, Lykidis A, Kyrpides NC. GenePRIMP: A gene prediction improvement ipeline for microbial genomes. Nat Methods 2010; 7:455-457 10.1038/nmeth.1457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Markowitz VM, Ivanova NN, Chen IMA, Chu K, Kyrpides NC. IMG ER: a system for microbial genome annotation expert review and curation. Bioinformatics 2009; 25:2271-2278 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]