Abstract
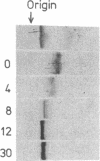
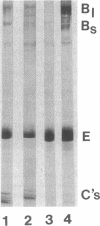
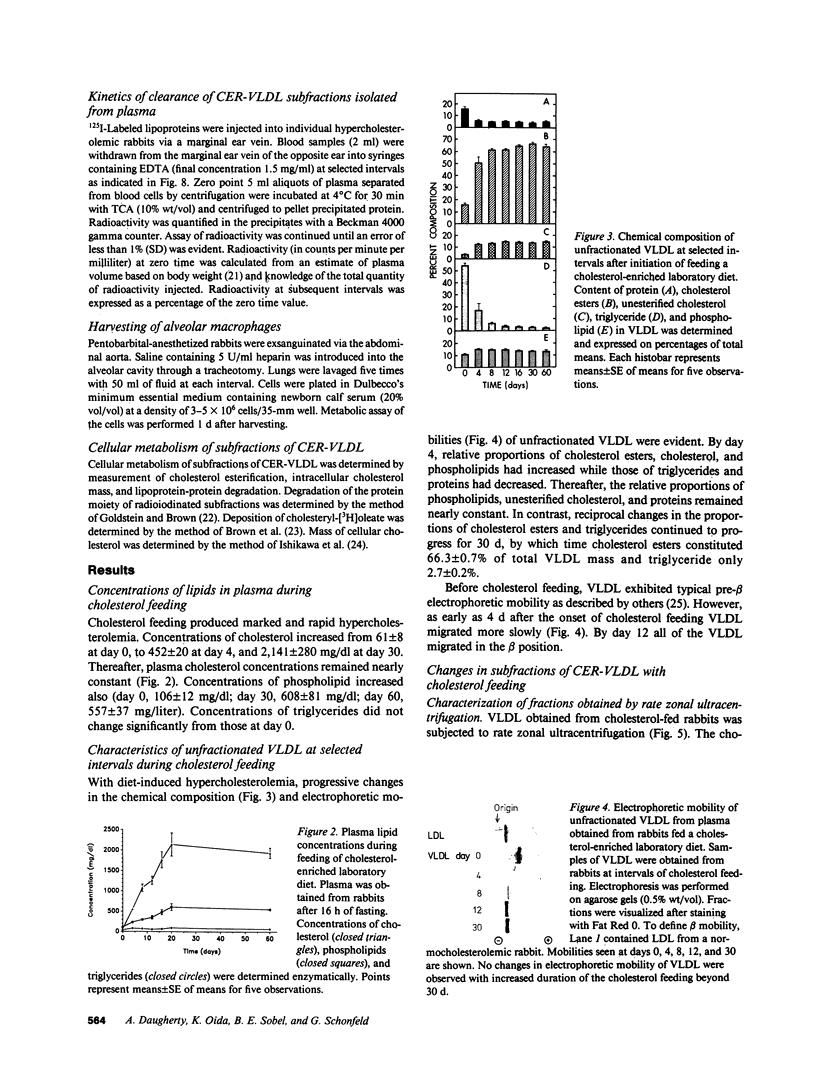
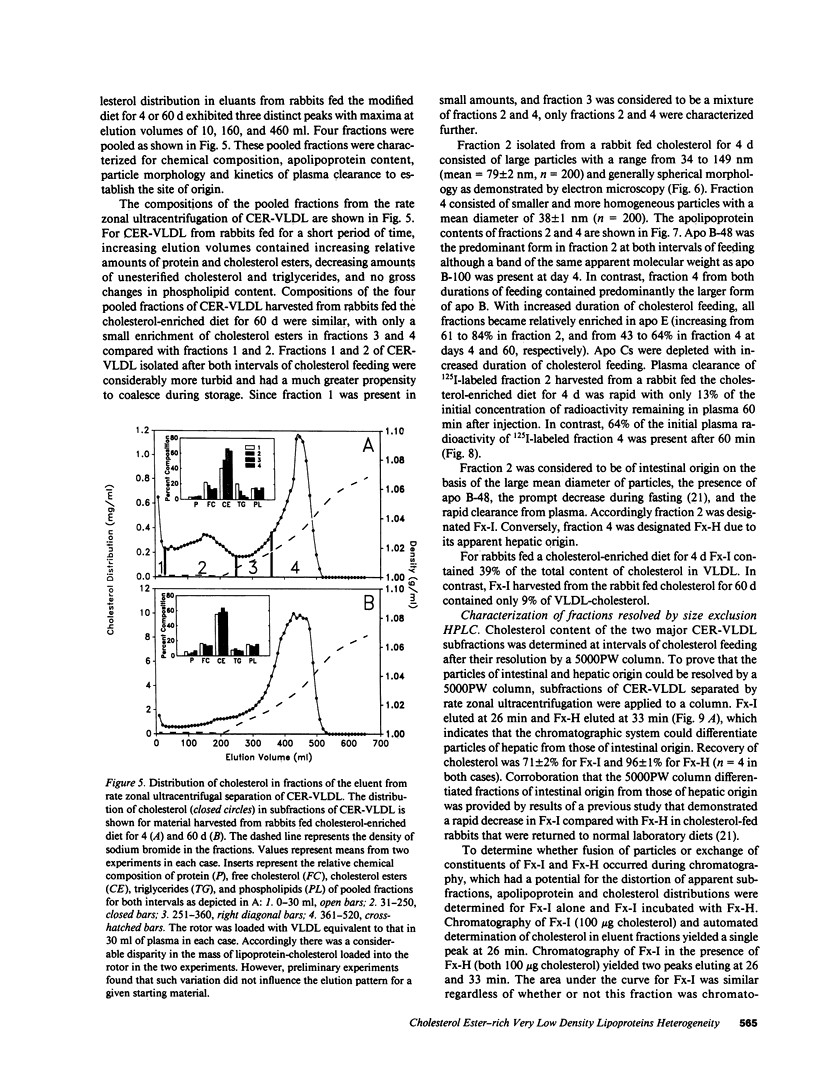
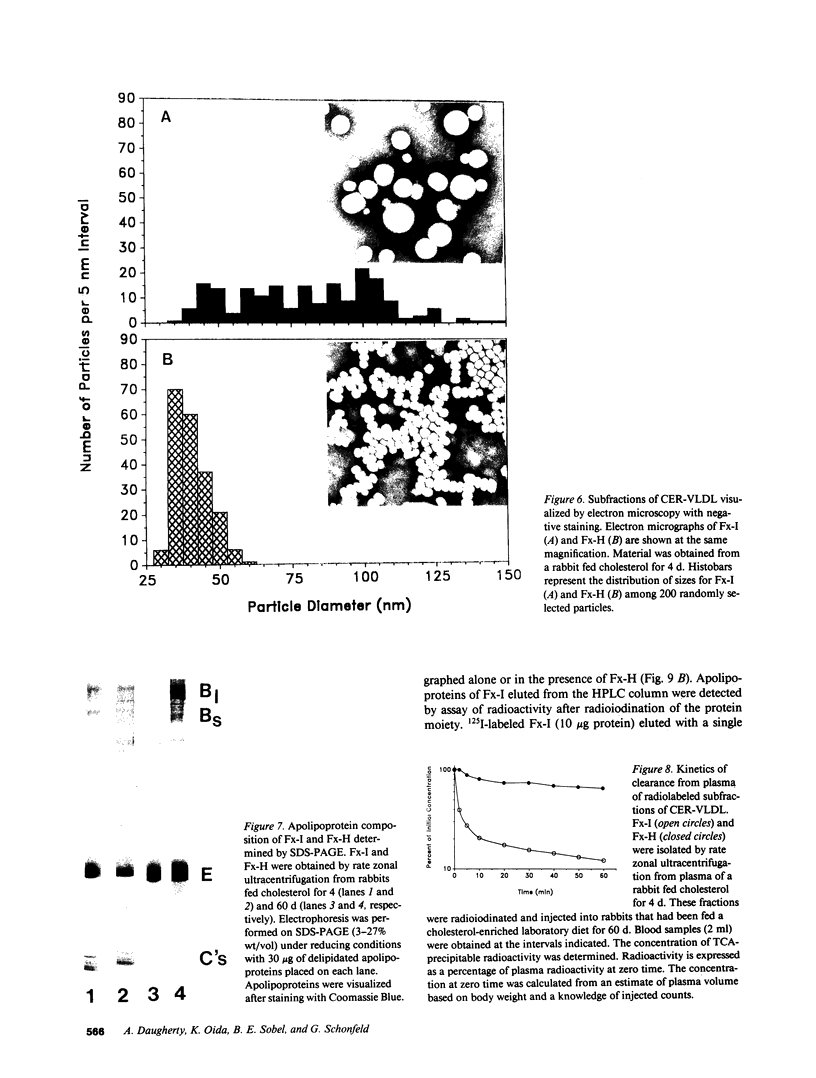
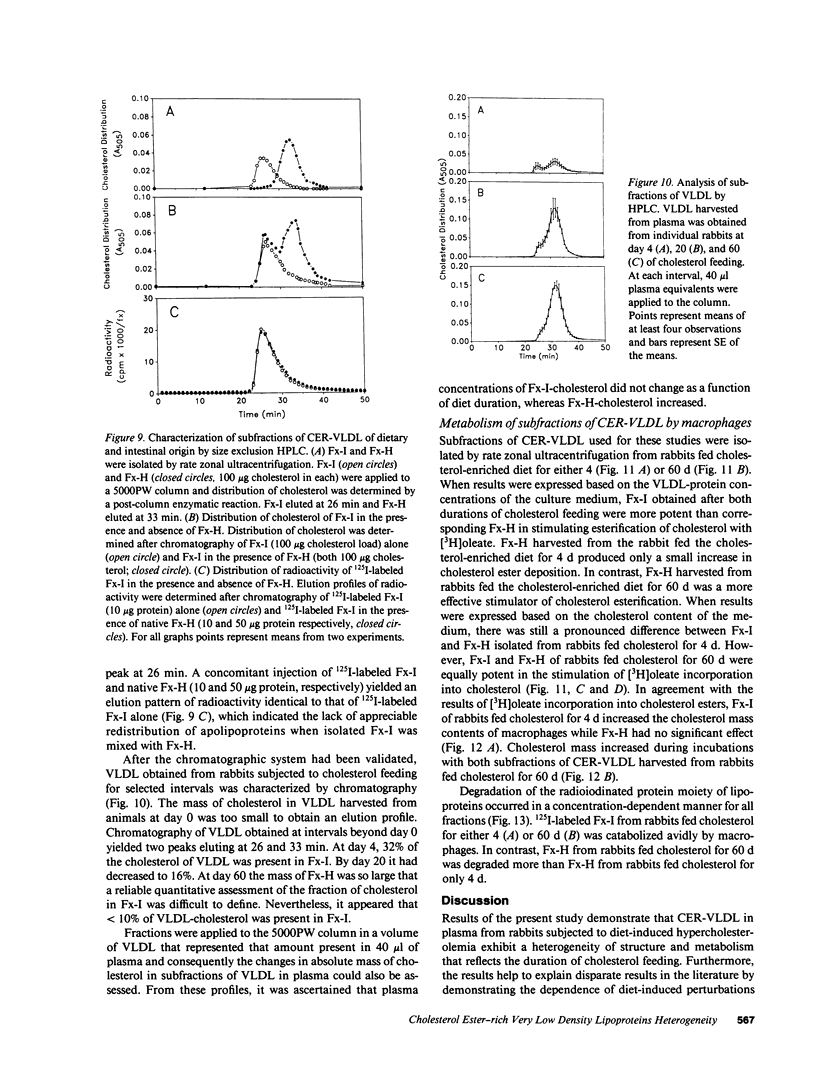
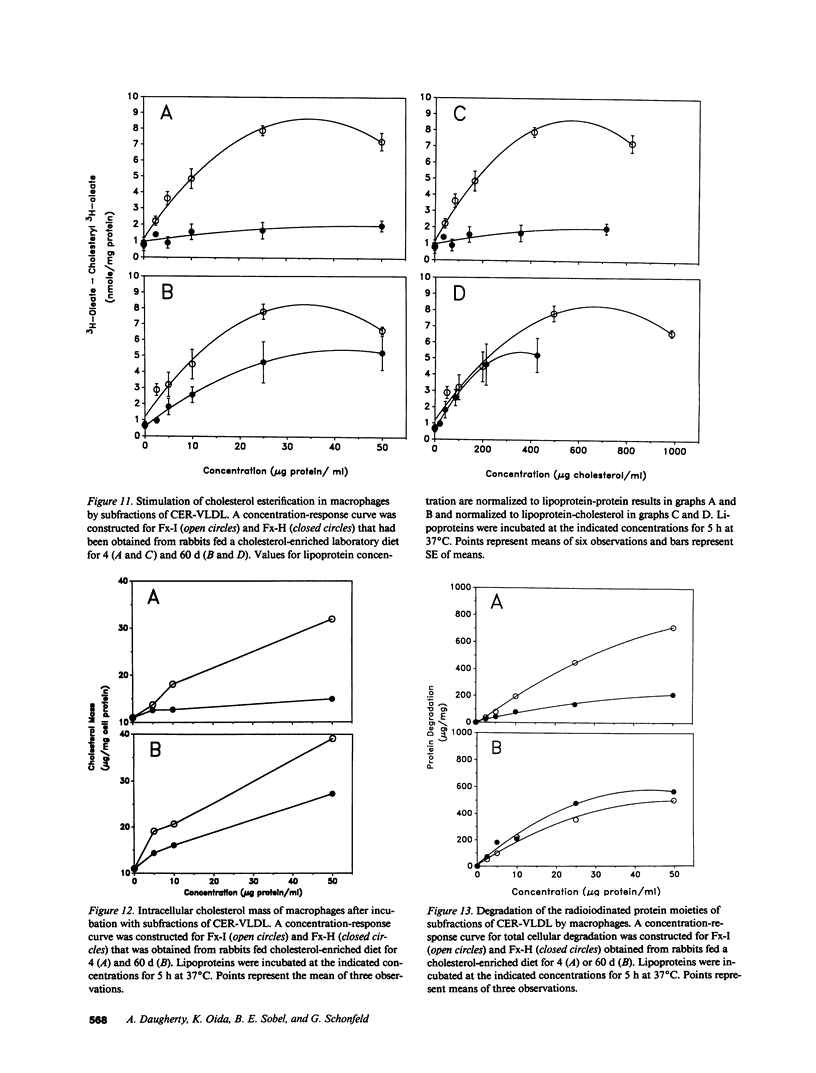
Cholesterol ester-rich (CER) VLDL accumulate rapidly in the plasma of rabbits fed cholesterol-enriched diets. However, the major loci of enhanced synthesis of subfractions of CER-VLDL, their interaction with macrophages, and their relative contribution to atherogenesis have not yet been elucidated. To determine whether anabolism is hepatic or intestinal, subfractions of CER-VLDL were characterized at selected intervals from day 0 to 60 of cholesterol feeding. Rate zonal ultracentrifugation of CER-VLDL from rabbits fed cholesterol for 4 and 60 d demonstrated an early increase of the proportion of cholesterol carried in the intestinally-derived fraction (designated as Fx-I) of VLDL compared with that in hepatically-derived particles (Fx-H). Quantification by size exclusion HPLC also demonstrated that Fx-I was a prominent CER-VLDL component at day 4, while Fx-H particles became increasingly prominent with further cholesterol feeding. At both 4 and 60 d Fx-I stimulated cholesterol esterification and intracellular cholesterol content in macrophages more than the corresponding Fx-H did. In fact, Fx-H harvested at 4 d produced no cholesterol ester deposition. In contrast, Fx-H harvested at 60 d markedly stimulated cholesterol esterification and intracellular cholesterol content. Thus, both compositional and metabolic characteristics of CER-VLDL changed as a function of the duration cholesterol feeding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bersot T. P., Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Fat feeding in humans induces lipoproteins of density less than 1.006 that are enriched in apolipoprotein [a] and that cause lipid accumulation in macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):622–630. doi: 10.1172/JCI112345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):150–154. doi: 10.1126/science.174194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The cholesteryl ester cycle in macrophage foam cells. Continual hydrolysis and re-esterification of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9344–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Bosch V., Arreaza C., Mendez H. C. Early changes in plasma lipoprotein structure and biosynthesis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jan;14(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Bosch V., López A. The very low density lipoproteins of cholesterol-fed rabbits. A study of their structure and in vivo changes in plasma. Atherosclerosis. 1974 Jan-Feb;19(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(74)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. M., Rudel L. L. Lipoprotein separation and low density lipoprotein molecular weight determination using high performance gel-filtration chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J. Animal lipoproteins: chemistry, structure, and comparative aspects. J Lipid Res. 1980 Sep;21(7):789–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corraze G., Lacombe C., Nibbelink M. Effect of dietary restriction on the plasma apolipoprotein pattern in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Lipids. 1985 Nov;20(11):751–756. doi: 10.1007/BF02534398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Schonfeld G., Sobel B. E., Lange L. G. Metabolism of very low density lipoproteins after cessation of cholesterol feeding in rabbits. A factor potentially contributing to the slow regression of atheromatous plaques. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1108–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI112409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Innerarity T. L. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed dogs and from humans with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):702–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Nordhausen R. W. Electron microscopy of negatively stained lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:442–457. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara I., Okazaki M. High-performance liquid chromatography of serum lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;129:57–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)29062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Arnold K. S., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E is the determinant that mediates the receptor uptake of beta-very low density lipoproteins by mouse macrophages. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):114–122. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T. T., MacGee J., Morrison J. A., Glueck C. J. Quantitative analysis of cholesterol in 5 to 20 microliter of plasma. J Lipid Res. 1974 May;15(3):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Hardman D. A., Paulus H. E. Heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B: isolation of a new species from human chylomicrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Watanabe Y., Hornick C. A., Havel R. J. Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants in WHHL rabbits: a mechanism genetically distinct from the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Wernette-Hammond M. E., Innerarity T. L. Uptake of canine beta-very low density lipoproteins by mouse peritoneal macrophages is mediated by a low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11194–11201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon P. A., Thompson G. M., Chao Y. S. Beta-very low density lipoproteins in cholesterol-fed rabbits are of hepatic origin. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Sep;56(3):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk L., Chung J., Scanu A. M. Properties and metabolic fate of two very low density lipoprotein subfractions from rhesus monkey serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 15;710(2):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon A. M., Savage J., Gibson R. A., Barter P. J. Secretion of cholesteryl ester-enriched very low density lipoproteins by the liver of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Feb;54(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Holcombe K. S. Alterations of the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins following cholesterol feeding in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. Canine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. II. Characterization of the plasma lipoproteins associated with atherogenic and nonatherogenic hyperlipidemia. Circ Res. 1974 Nov;35(5):722–733. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.5.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P., Tada N., Billington T., Huff M., Fidge N. Changes in very low density lipoproteins with cholesterol loading in man. Metabolism. 1982 Apr;31(4):398–405. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. L., Catapano A., Ghiselli G. C., Sirtori C. R. Very low density lipoproteins in normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits: lipid and protein composition and metabolism. Part 2. Metabolism of very low density lipoproteins in rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Jan-Feb;23(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. L., Ghiselli G. C., Torreggiani D., Sirtori C. R. Very low density lipoproteins in normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits: lipid and protein composition and metabolism. Part 1. Chemical composition of very low density lipoproteins in rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Jan-Feb;23(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. C., Zilversmit D. B. Chylomicron remnant cholesteryl esters as the major constituent of very low density lipoproteins in plasma of cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. I., Gaubatz J. W., Gotto A. M., Jr, Patsch J. R. Effect of cholesterol feeding on the distribution of plasma lipoproteins and on the metabolism of apolipoprotein E in the rabbit. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Marsh J. B. Metabolic heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. H., Zilversmit D. B. Plasma very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) in cholesterol-fed rabbits: chylomicron remnants or liver lipoproteins? J Nutr. 1983 Oct;113(10):2002–2010. doi: 10.1093/jn/113.10.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang-Iverson P., Ginsberg H. N., Peteanu L. A., Le N. A., Brown W. V. Apo E-mediated uptake and degradation of normal very low density lipoproteins by human monocyte/macrophages: a saturable pathway distinct from the LDL receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):578–586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90645-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]