Abstract
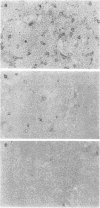
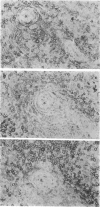
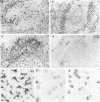
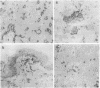
Previous investigations of p150,95 (CD11c), the third member of the CD18 membrane glycoprotein family that includes CR3 (Mac-1 or CD11b) and LFA-1 (CD11a), had demonstrated that solubilized p150,95 bound to iC3b-agarose in a manner similar to isolated CR3. The current study showed that membrane surface p150,95 also expressed iC3b-receptor activity and was probably the same as the neutrophil receptor for iC3b- or C3dg-coated erythrocytes (EC3bi or EC3dg) that had been previously designated CR4. Normal neutrophil and macrophage CR4-dependent EC3bi rosettes were inhibited by monoclonal anti-p150,95, and cells from a patient with CD18 deficiency did not form CR4-dependent EC3bi rosettes. With neutrophils that bore large amounts of CR1 and CR3 and little p150,95, EC3bi were found primarily via CR1 and CR3, and demonstration of p150,95-dependent rosettes required large amounts of fixed iC3b, low-ionic strength buffer, and antibody blockade of CR1 and CR3. By contrast, culture-derived macrophages expressed eight times more p150,95 than did monocytes and EC3bi were bound to both p150,95 and CR3 when EC3bi bore small amounts of fixed iC3b and assays were carried out in isotonic buffer. Comparison of the amounts of CR1, CR3, and CR4 in various tissues by immunoperoxidase staining revealed that CR4 was the most abundant C3 receptor molecule on tissue macrophages, and suggested that CR4 might be involved in clearance of C3-opsonized particles or immune complexes.
Full text
PDF

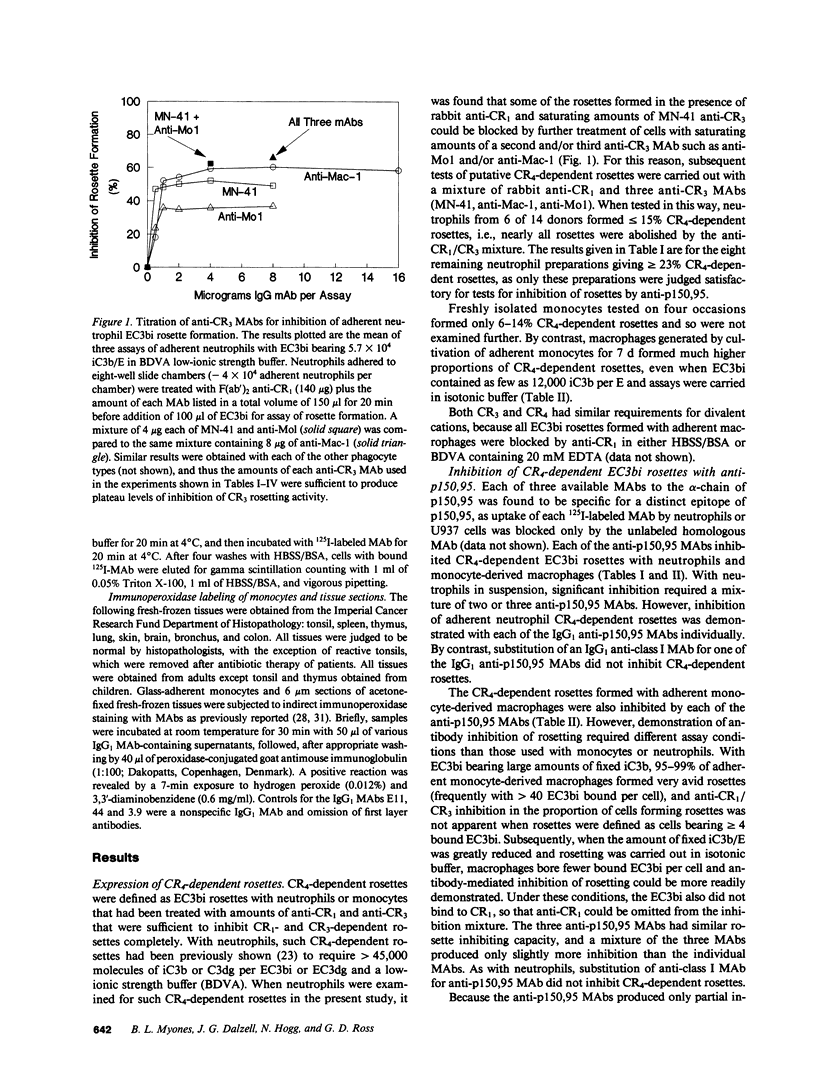
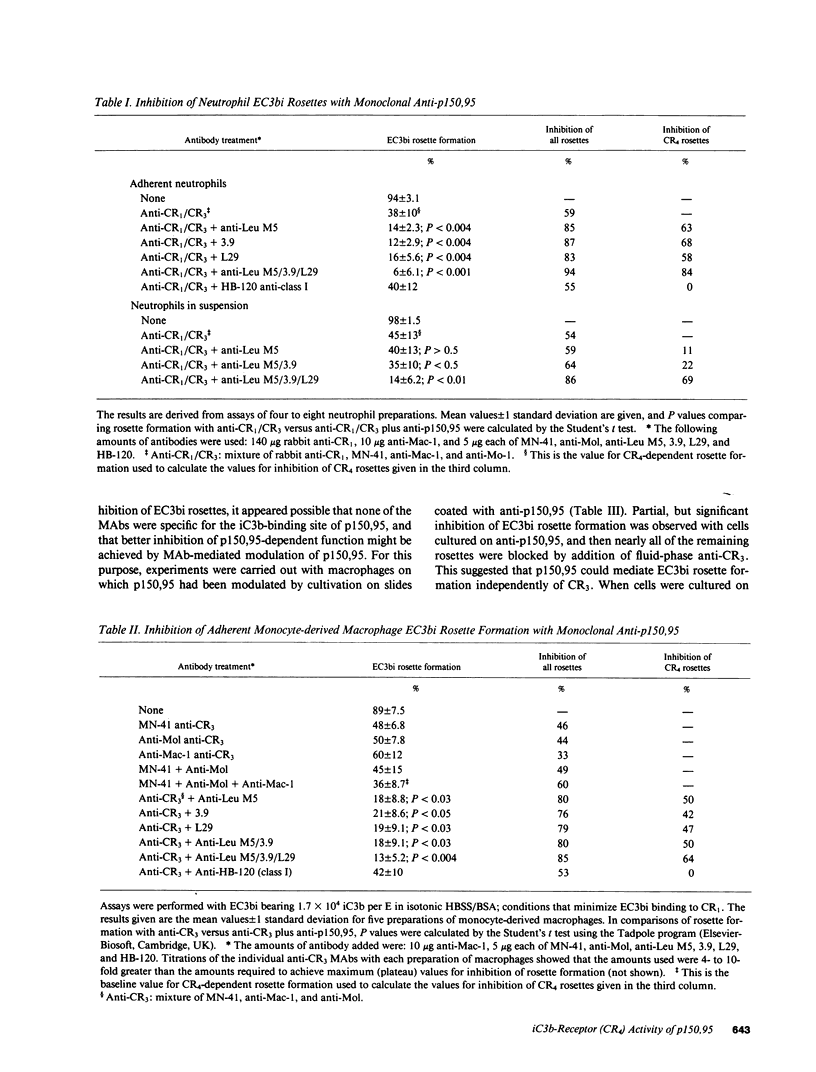
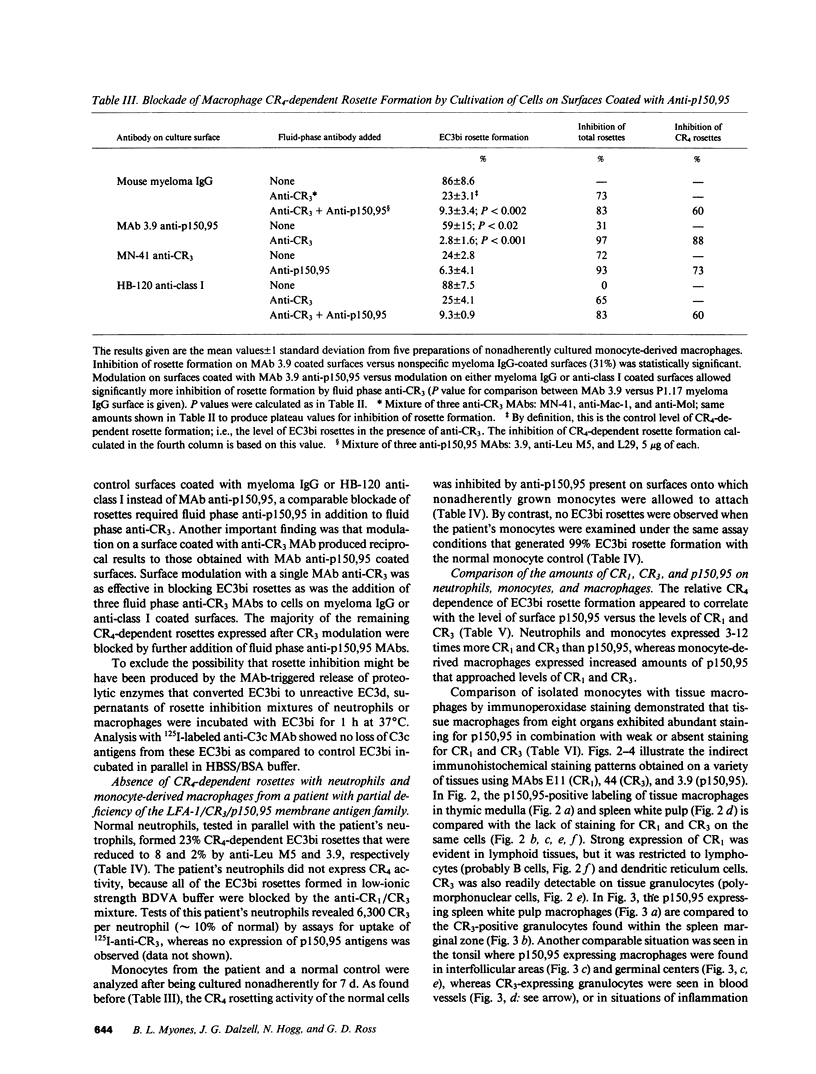
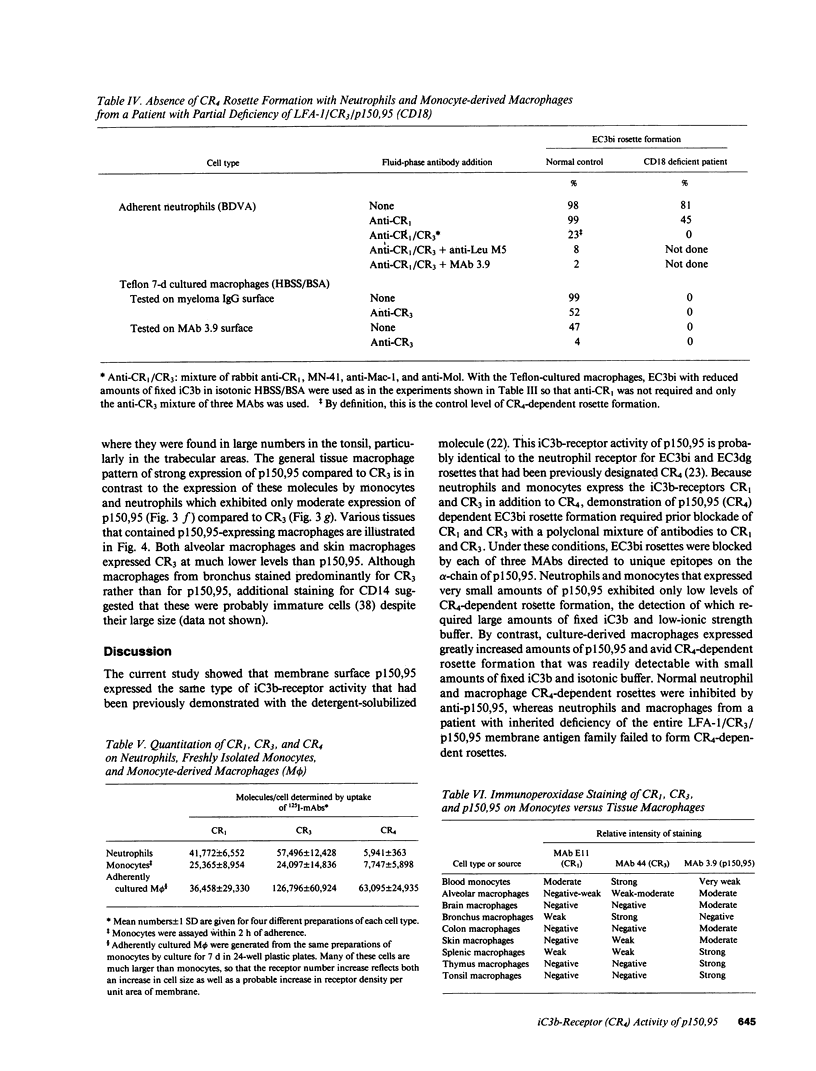


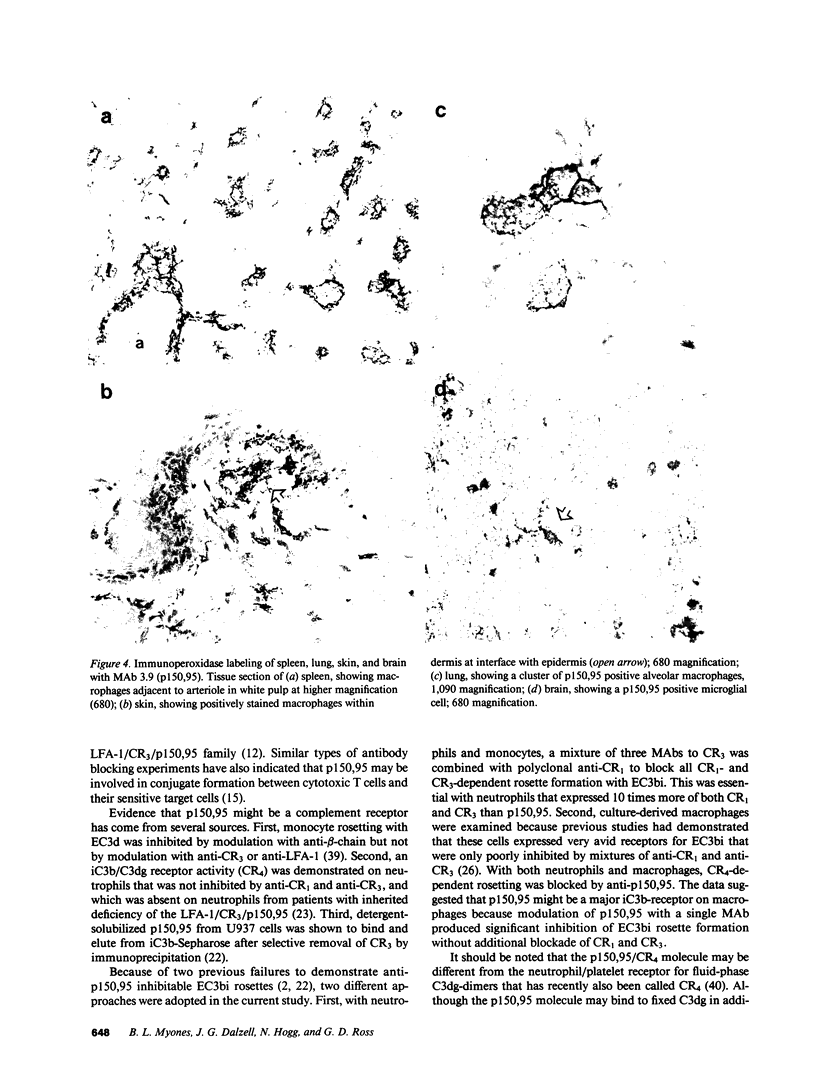



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Miller L. J., Schmalstieg F. C., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence-dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., Springer T. A. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: an inherited defect in the Mac-1, LFA-1, and p150,95 glycoproteins. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:175–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A., Todd R. F., 3rd, Dana N., Melamed J., Schlossman S. F., Colten H. R. Inhibition of phagocytosis of complement C3- or immunoglobulin G-coated particles and of C3bi binding by monoclonal antibodies to a monocyte-granulocyte membrane glycoprotein (Mol). J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):171–179. doi: 10.1172/JCI110955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Springer T. A., Schreiber R. D. Anti-Mac-1 selectively inhibits the mouse and human type three complement receptor. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1000–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P. Monomorphic anti-HLA-A,B,C monoclonal antibodies detecting molecular subunits and combinatorial determinants. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornacoff J. B., Hebert L. A., Smead W. L., VanAman M. E., Birmingham D. J., Waxman F. J. Primate erythrocyte-immune complex-clearing mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):236–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI110764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson N. J., Lambris J. D., Ross G. D. Characteristics of isolated erythrocyte complement receptor type one (CR1, C4b-C3b receptor) and CR1-specific antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):693–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A., Newman S. L., Cosio F., LeBien T., Michael A. The distribution of the CR3 receptor on human cells and tissue as revealed by a monoclonal antibody. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Jun;31(3):371–389. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Myones B. L., Barel M., Krikorian L., Charriaut C., Ross G. D. gp140, a C3b-binding membrane component of lymphocytes, is the B cell C3dg/C3d receptor (CR2) and is distinct from the neutrophil C3dg receptor (CR4). Eur J Immunol. 1985 Dec;15(12):1192–1197. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Ross G. D., Jones D. B., Slusarenko M., Walport M. J., Lachmann P. J. Identification of an anti-monocyte monoclonal antibody that is specific for membrane complement receptor type one (CR1). Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):236–243. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Takacs L., Palmer D. G., Selvendran Y., Allen C. The p150,95 molecule is a marker of human mononuclear phagocytes: comparison with expression of class II molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Mar;16(3):240–248. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer G. D., Borst J., Visser W., Schwarting R., de Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. Membrane glycoprotein p150,95 of human cytotoxic T cell clone is involved in conjugate formation with target cells. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3130–3136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Connor K., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Cloning of the beta subunit of the leukocyte adhesion proteins: homology to an extracellular matrix receptor defines a novel supergene family. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Arnaout M. A., Schwarting R., Warner N. L., Ross G. D. p150/95, Third member of the LFA-1/CR3 polypeptide family identified by anti-Leu M5 monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):713–718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Gagnon J., Hildreth J. E., Wells C. E., Willis A. C., Wong A. J. The primary structure of the beta-subunit of the cell surface adhesion glycoproteins LFA-1, CR3 and p150,95 and its relationship to the fibronectin receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):915–919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Hogg N., Sim R. B. Ligand binding by the p150,95 antigen of U937 monocytic cells: properties in common with complement receptor type 3 (CR3). Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1117–1123. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklem K. J., Sim R. B. Isolation of complement-fragment-iC3b-binding proteins by affinity chromatography. The identification of p150,95 as an iC3b-binding protein. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2310233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. J., Bainton D. F., Borregaard N., Springer T. A. Stimulated mobilization of monocyte Mac-1 and p150,95 adhesion proteins from an intracellular vesicular compartment to the cell surface. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):535–544. doi: 10.1172/JCI113102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. J., Schwarting R., Springer T. A. Regulated expression of the Mac-1, LFA-1, p150,95 glycoprotein family during leukocyte differentiation. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2891–2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Devery-Pocius J. E., Ross G. D., Henson P. M. Phagocytosis by human monocyte-derived macrophages. Independent function of receptors for C3b (CR1) and iC3b (CR3). Complement. 1984;1(4):213–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Musson R. A., Henson P. M. Development of functional complement receptors during in vitro maturation of human monocytes into macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2236–2244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. G., Hogg N., Revell P. A. Lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, macrophages and platelets in synovium involved by rheumatoid arthritis. A study with monoclonal antibodies. Pathology. 1986 Oct;18(4):431–437. doi: 10.3109/00313028609087564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Lanier L. L. Correlation of biophysical properties and cell surface antigenic profile of Percoll gradient-separated human natural killer cells. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1983;3(2):73–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Stanness K. A., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. An endothelial cell surface factor(s) induced in vitro by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases neutrophil adherence by a CDw18-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4548–4553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabellino E. M., Nachman R. L., Williams N., Winchester R. J., Ross G. D. Human megakaryocytes. I. Characterization of the membrane and cytoplasmic components of isolated marrow megakaryocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1273–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Membrane complement receptor type three (CR3) has lectin-like properties analogous to bovine conglutinin as functions as a receptor for zymosan and rabbit erythrocytes as well as a receptor for iC3b. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3307–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D. Clinical and laboratory features of patients with an inherited deficiency of neutrophil membrane complement receptor type 3 (CR3) and the related membrane antigens LFA-1 and p150,95. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;6(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00918742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Lambris J. D. Identification of a C3bi-specific membrane complement receptor that is expressed on lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):96–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Newman S. L., Lambris J. D., Devery-Pocius J. E., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Generation of three different fragments of bound C3 with purified factor I or serum. II. Location of binding sites in the C3 fragments for factors B and H, complement receptors, and bovine conglutinin. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):334–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Thompson R. A., Walport M. J., Springer T. A., Watson J. V., Ward R. H., Lida J., Newman S. L., Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. Characterization of patients with an increased susceptibility to bacterial infections and a genetic deficiency of leukocyte membrane complement receptor type 3 and the related membrane antigen LFA-1. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):882–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Nagy J. A., Robbins E., Simon P., Springer T. A. A human leukocyte differentiation antigen family with distinct alpha-subunits and a common beta-subunit: the lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1), the C3bi complement receptor (OKM1/Mac-1), and the p150,95 molecule. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1785–1803. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Frank M. M. Role of antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes. I. In vivo effects of IgG and IgM complement-fixing sites. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):575–582. doi: 10.1172/JCI106846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Stein H., Wang C. Y. The monoclonal antibodies alpha S-HCL 1 (alpha Leu-14) and alpha S-HCL 3 (alpha Leu-M5) allow the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):974–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Miller L. J., Anderson D. C. p150,95, the third member of the Mac-1, LFA-1 human leukocyte adhesion glycoprotein family. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Rothlein R., Anderson D. C., Burakoff S. J., Krensky A. M. The function of LFA-1 in cell-mediated killing and adhesion: studies on heritable LFA-1, Mac-1 deficiency and on lymphoid cell self-aggregation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;184:311–322. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8326-0_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., 3rd, Freyer D. R. The CD11/CD18 leukocyte glycoprotein deficiency. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;2(1):13–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik D. P., Fearon D. T. Cellular distribution of complement receptor type 4 (CR4): expression on human platelets. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik D. P., Fearon D. T. Neutrophils express a receptor for iC3b, C3dg, and C3d that is distinct from CR1, CR2, and CR3. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2571–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Jong M. T. Adhesion-promoting receptors on human macrophages recognize Escherichia coli by binding to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1876–1888. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. Methods for the study of receptor-mediated phagocytosis. Methods Enzymol. 1986;132:204–221. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)32009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Reddy P. A., Jong M. T., Erickson B. W. C3bi receptor (complement receptor type 3) recognizes a region of complement protein C3 containing the sequence Arg-Gly-Asp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1965–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]